抗血栓药物的研究进展
2014-09-07邢峻豪杨凌云李清周金培张惠斌
邢峻豪,杨凌云,李清,周金培,张惠斌
(中国药科大学新药研究中心,江苏南京 210009)
抗血栓药物的研究进展
邢峻豪,杨凌云,李清,周金培,张惠斌*
(中国药科大学新药研究中心,江苏南京 210009)
血栓栓塞性疾病是引起人类疾病死亡的主要原因之一,随着人们对其发病机制研究与认识的不断深入以及药物设计和筛选技术的日臻成熟,针对各种靶点的新型抗血栓药物不断涌现,如二磷酸腺苷受体阻滞剂、Ⅹa因子抑制剂、凝血酶抑制剂等,我国药学研究者也在这些靶向抗血栓药物研究领域取得一定进展。综述我国学者近些年在国内外学术期刊上发表的相关研究论文中所涉及的各类新型抗血小板药物、抗凝血药物和血栓溶解剂的结构、活性和构效关系。
抗血小板药物;抗凝血药物;血栓溶解剂;结构;活性;构效关系
血栓栓塞性疾病是目前引起人类疾病死亡的主要原因之一,随着人们对其发病机制研究与认识的不断深入以及药物设计和筛选技术的日臻成熟,近年来各类新型抗血栓药物相继涌现,如二磷酸腺苷(ADP)受体阻滞剂、Ⅹa因子(FXa)抑制剂、凝血酶抑制剂等,其中已开发上市的有利伐沙班、达比加群酯和阿哌沙班等。我国药学研究者也在针对这些新靶点的药物研究领域取得一定进展,本文通过对我国学者在近些年国内外学术期刊上发表的相关研究论文进行检索,并按照不同靶标分类,对其中发表的新化合物的结构、活性和构效关系作一综述。
1 抗血小板药物
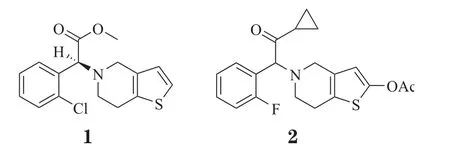
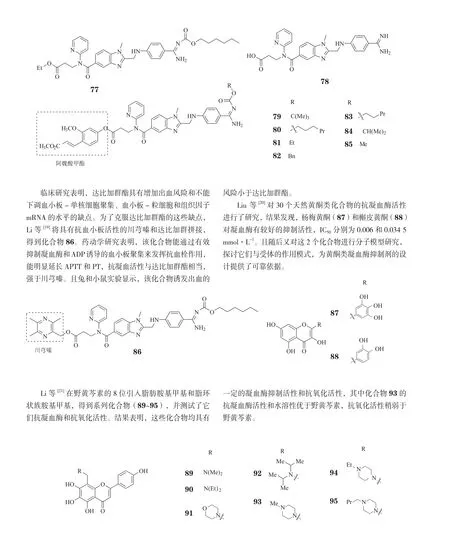
抗血小板药物即血小板聚集抑制剂,是一类重要的抗血栓药物,主要通过作用于ADP受体、抑制花生四烯酸(AA)代谢和增加血小板内环磷酸腺苷(cAMP)浓度等机制而抑制血小板的黏附、聚集和分泌功能。氯吡格雷(1)为ADP受体阻滞剂,可与血小板膜表面ADP受体结合,使纤维蛋白原无法与糖蛋白Ⅱb/Ⅲa(GP IIb/IIIa)受体结合,从而抑制血小板聚集。不过,氯吡格雷为前药,需在体内经氧化和水解才能转化成活性分子,而其氧化过程需要CPY2C19的参与,但3%~5%的白种人和15%~20%的亚洲人体内CPY2C19的活性较低,这些人群不能有效代谢活化氯吡格雷,可能无法获得该药的充分疗效,这种现象称为“氯吡格雷抵抗”。鉴于此,日本三共(Sankyo)制药公司和美国礼来(Eli Lilly)制药公司共同开发了前药普拉格雷(2),其在体内只需经2步水解即转化为活性分子,研究表明,该转化过程不存在种族差异性,此药给临床治疗带来很大便利。

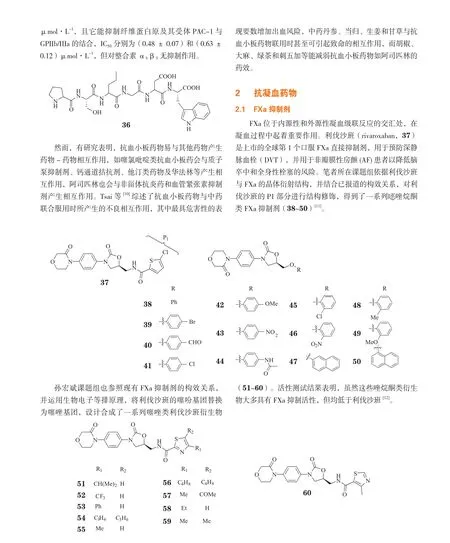
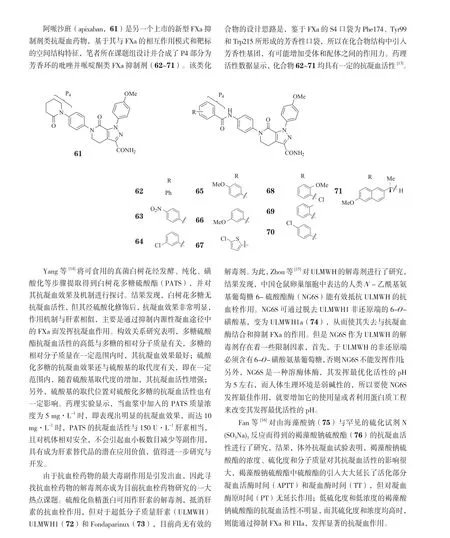
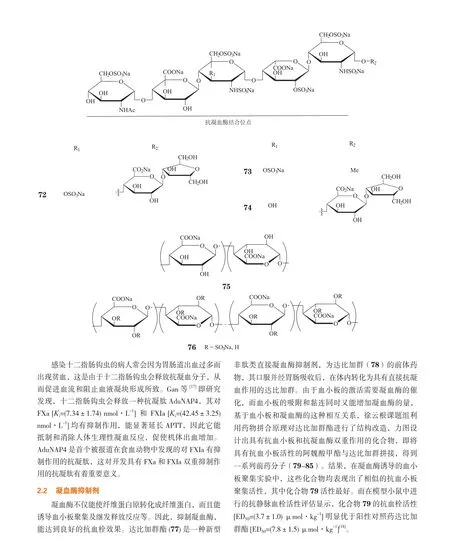

FIXa是内源性凝血途径中重要因子之一,能促进FX转化为FXa,对血液凝固的扩大和增固起重要作用。为了更加科学合理地设计FIXa抑制剂,了解配体分子与受体的作用模式,Hao等[27]应用三维定量构效关系(3D-QSAR)模型对84个苯并噻吩化合物进行了分析,首先利用对接方法取得这些化合物与FIXa结合的最优构象,然后用比较分子场方法(CoMFA)对所选取的最优构象进行有意义的统计学分析。这些分析数据为苯并噻吩类FIXa抑制剂的设计和新型FIXa抑制剂先导物的发现提供了定量构效关系依据。
尖吻蝮蛇毒抗凝血因子Ⅱ(ACFII)是FIX和FX结合蛋白(IX/X-bps)家族中唯一一个具有抗血栓和抗高血压双重作用的蛋白质[28]。聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳和表面等离子体共振试验证实,在Ca2+诱导下,ACFII通过与FIX结合而发挥对外源性凝血途径的抑制作用,且当Ca2+浓度为0.1 mmol·L-1时,ACFII对FIX的识别能力最强,而浓度高于0.1 mmol·L-1时,ACFII的识别能力下降[29]。
FXIa也是内源性凝血途径中重要因子之一,对血液的凝固起重要作用,而抑制FXIa,可有效抑制血栓形成。但FXIa的晶体结构鲜见报道,这主要是因为在FXIa的催化区域存在着2个潜在糖基化位点和一个游离的半胱氨酸,使得FXIa异质化。为了解决FXIa难以结晶的问题,Jiang等[30]通过移除其糖基化位点和游离的半胱氨酸,分别得到了2个易结晶的突变体hFXI370~607(N73Q-N113Q-C123S)和rhFXI370~607(N73Q-N113Q),并分析比对了它们与其他丝氨酸蛋白酶的结构差异,为设计活性强、选择性高的小分子FXIa抑制剂创造了基础条件。
3 血栓溶解剂
Wu等[31]从镰刀菌属CPCC 480097中提取得到具有溶解纤维蛋白作用的酶Fu-P,该酶是单一蛋白,相对分子质量为28 000,其 N端序列中的前15个氨基酸为Q-A-S–S-G-T-P-A-T- I-R-V-L-V-V,与其他已知的纤溶蛋白酶无同源性。在大鼠动静脉旁路血栓模型中进行的抗血栓形成实验显示,0.1 mg·kg-1剂量的Fu-P对血栓形成的抑制率为58.4%,而0.6 mg·kg-1剂量的肝素对血栓形成的抑制率为42.5%,表明Fu-P的抗血栓活性优于肝素。另有实验表明,Fu-P对凝血酶和FXa无抑制作用[32]。
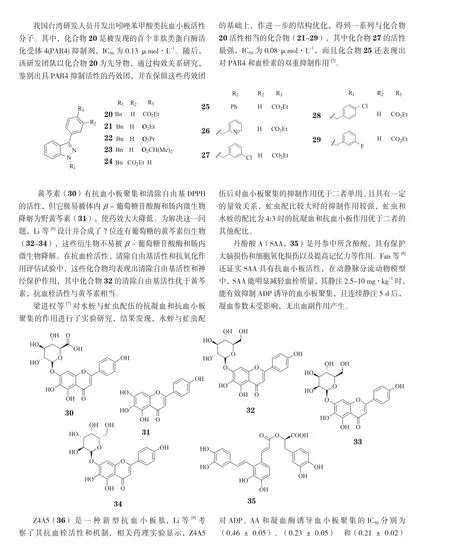
Song等[33]从浙江产蝮蛇毒中提取得到名为AHPM的金属蛋白,该蛋白是一种二聚糖蛋白,相对分子质量为110 000,在pH 7.9左右有多个等电点,分子内含有Zn2+和Ca2+,其中Zn2+对AHPM的蛋白水解活性起重要作用。研究表明,AHPM能迅速水解纤维蛋白原的Aα和Bβ链,但对γ链无水解作用;其对胶原蛋白和ADP诱导的血小板聚集的IC50分别为(200±8)和(280±10)nmol·L-1。AHPM是目前被发现的唯一一个同时具有血栓溶解作用和抗血小板作用的蛇毒液金属蛋白酶,有可能成为临床使用的血栓溶解剂类候选药物。
纤溶酶能通过直接作用于纤维蛋白而有效安全地溶解血栓,但不能静脉注射给药,因为它易被血浆中的抗纤溶酶中和,因此,开发能耐受抗纤溶酶的直接作用于纤维蛋白的抗血栓药物具重要意义。人们早已发现中华地鳖虫能安全有效地抑制血栓形成,Yang等[34]从中华地鳖虫中提取得到一种名为Eupolytin1的蛋白质,该蛋白能同时活化纤维蛋白(原)溶解酶和血纤溶酶原。在大鼠动静脉分流模型实验中,Eupolytin1表现出安全有效的抗血栓活性,且活性优于尿激酶。更重要的是,在兔子模型实验中,Eupolytin1的注射剂量达0.12 µmol·kg-1时,也未发生出血现象。随后,该研究小组又利用蛋白质组学和转录组学分析了从中华地鳖虫中获取的105种丝氨酸蛋白酶,发现它们分属于4个不同的蛋白家族。药理实验证明,这些蛋白酶中有5个(即Eupolytin 1-5)具有水解纤维蛋白(原)和活化血纤溶酶原的双重作用,能水解纤维蛋白原的α、β和γ链,而目前发现的纤维蛋白(原)酶只能水解α和β链[35]。
微生物溶栓酶是一类具有良好应用前景的溶栓酶,不仅能大量生产,还能弥补传统溶栓剂的缺陷。Yuan等[36]从豆豉中分离出一株能产出具高纤溶活性的溶栓酶的菌株——枯草芽孢杆菌LD-8547,其经发酵、盐析、透析、浓缩等步骤,得到粗酶液,再通过Sephadex G-100凝胶分子筛柱纯化,最终获得豆豉溶栓酶(DFE)。实验研究显示,DFE具有一定的抗栓及溶栓作用,且口服安全性好,是一种潜在有效的抗血栓药物。
4 结语
近年来,针对传统抗血栓药物不能口服给药和易引起出血等副作用,我国药物科学家对新型抗血栓药物进行了广泛而深入的研究与开发,利用人工合成、生物发酵、蛋白质组学和基因工程等手段发现了一些更为安全有效的抗血栓药物。在诸多抗血栓靶标中,FXa、凝血酶、ADP和AA受体等已成为我国科学家关注的焦点,其中对凝血酶抑制剂和抗ADP及AA诱导的血小板聚集药物的研究颇为深入,而对FXa作为抗血栓靶标的研究相对较薄弱,与国外存在较大差距。另外,从中草药和海洋生物中发现抗血栓药物,一直以来都是国内研究的热点。可以相信,随着人们对抗血栓靶标及药物的深入研究和探索,必将会有更多新型抗血栓药物开发上市,使得抗血栓治疗变得更加安全、方便、有效。
[1]Shan J, Zhang B, Zhu Y, et al. Overcoming clopidogrel resistance: discovery of vicagrel as a highly potent and orally bioavailable antiplatelet agent[J]. J Med Chem, 2012, 55(7):3342-3352.
[2]Wu J, Ling J,Wang X,et al. Discovery of a potential anti-ischemic stroke agent: 3-pentylbenzo[c]thiophen-1(3H)-one[J]. J Med Chem, 2012, 55(16):7173-7181.
[3]Sun Y, Jiang J, Zhang Z, et al. Antioxidative and thrombolytic TMP nitrone for treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2008, 16(19):8868-8874.
[4]Sun Y, Zhang G, Zhang Z, et al. Novel multi-functional nitrones for treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2012, 20(12):3939-3945.
[5]Chen H S, Kuo S C, Teng C M, et al. Synthesis and antiplatelet activity of ethyl 4-(1-benzyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)benzoate (YD-3) derivatives[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2008, 16(3): 1262-1278.
[6]Li N G, Shen M Z, Wang Z J, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of glucose-containing scutellarein derivatives as neuroprotective agents based on metabolic mechanism of scutellarin in vivo[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2013, 23(1):102-106.
[7]梁进权, 宓穗卿, 王宁生. 水蛭、虻虫配伍的抗凝血和抗血小板聚集的作用[J]. 中药材, 2009, 32(9):1347-1350.
[8]Fan H Y, Fu F H, Yang M Y, et al. Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of salvianolic acid A[J]. Thromb Res, 2010, 126(1): e17-22.
[9]Li Y X, Sun Q, Zhang H, et al. A novel anti-platelet peptide (Z4A5) potential for glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibits platelet aggregation[J]. Thromb Res, 2012, 129(5): e217-222.
[10]Tsai H H, Lin H W, Lu Y H, et al. A review of potential harmful interactions between anticoagulant/antiplatelet agents and Chinese herbal medicines[J].PLoS One, 2013. 8(5): e64255.
[11]李慧, 杨凌云, 周金培, 等.唑烷酮醚类化合物的合成及其Xa因子抑制活性[J].中国药科大学学报, 2013, 44(5):385-389.
[12]高娜娜,孙宏斌. 利伐沙班衍生物的合成及Xa因子抑制活性[J].中国药科大学学报, 2011, 42(5):392-399.
[13]邢峻豪, 张媛, 胡晓雯, 等. 阿哌沙班衍生物的合成及FXa因子抑制活性[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2013, 44(4): 289-295.
[14]Yang X M, Fan C, Guo N, et al. Preparationof polyporus albicans teng sulfate and its anti-coagulation activity[J].Chem Res, 2010, 26(6): 948-954.
[15]Zhou X X, Li L Y, Linhardt R J, et al.Neutralizing the anticoagulant activity of ultra-low-molecular-weight heparins usingN-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase[J]. FEBS J, 2013, 280(10):2523-2532.
[16]Fan L H, Jiang L, Xu Y M, et al. Synthesis and anticoagulant activity of sodium alginate sulfates [J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2011, 83(4):1797-1803.
[17]Gan W, Deng L, Yang C, et al. An anticoagulant peptide from the human hookworm, Ancylostoma duodenale that inhibits coagulation factors Xa and XIa[J]. FEBS Lett, 2009, 583(12):1976-1980.
[18]Yang X Z, Diao X J, Yang W H, et al. Design, synthesis and antithrombotic evaluation of novel dabigatran prodrugs containing methyl ferulate[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2013, 23(7): 2089-2092.
[19]Li Y Z, Gong G Q, Yang W H, et al. Antithrombotic activity of HY023016, a novel dabigatran prodrug evaluated in animal thrombosis models[J]. Thromb Res, 2013, 131(5):425-435.
[20]Liu L, Ma H, Yang N, et al. A series of natural favonoids as thrombin inhibitors: structure-activity relationships[J]. Thromb Res, 2010, 126(5):e365-378.
[21]Li N G, Song S L, Shen M Z, et al. Mannich bases of scutellarein as thrombin-inhibitors: design, synthesis, biological activity and solubility[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2012, 20(24):6919-6923.
[22]Abdel Aziz M H, Sidhu P S, Liang A, et al. Designing allosteric regulators of thrombin. Monosulfated benzofuran dimers selectively interact with Arg173 of exosite 2 to induce inhibition[J]. J Med Chem, 2012, 55(15):6888-6897.
[23]Gandhi N S, Mancera R L. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins[J]. Chem Biol Drug Des, 2008, 72(6):455-482.
[24]Mao W, Li H, Li Y, et al. Chemical characteristic and anticoagulant activity of the sulfated polysaccharide isolated from Monostroma latissimum (Chlorophyta)[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2009, 44(1):70-74.
[25]张彬, 汪波, 龚元, 等. 几种水蛭抗凝血物质提取及活性分析[J].中山大学学报, 2012, 51(4):92-96.
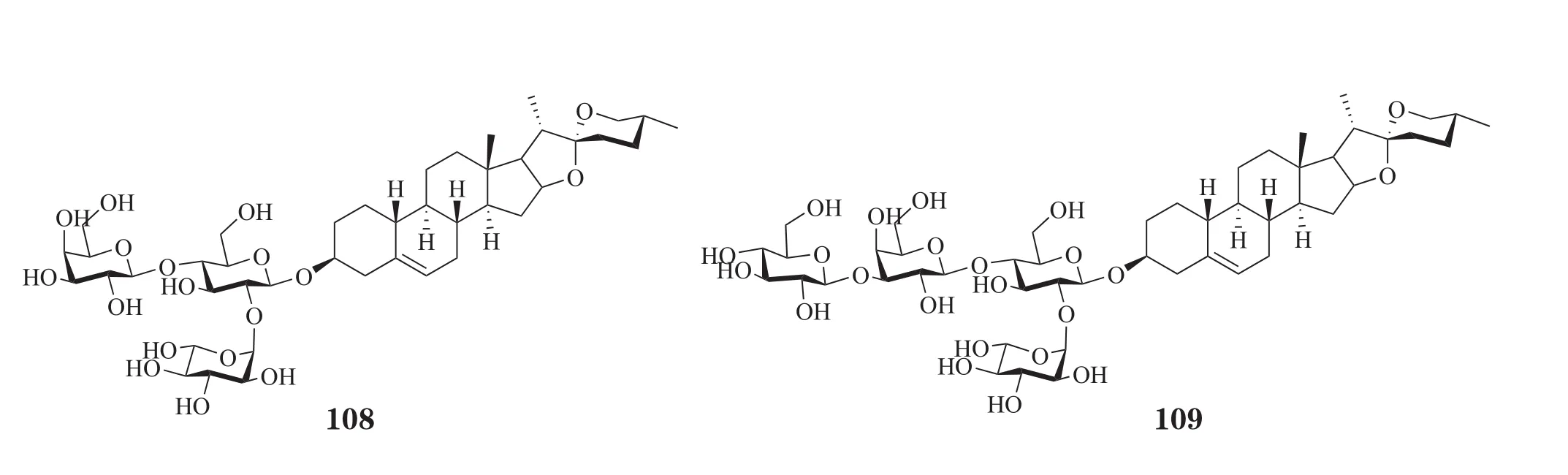
[26]Zhang R, Huang B, Du D, et al. Anti-thrombosis effect of diosgenyl saponins in vitro and in vivo[J]. Steroids, 2013, 78(11):1064-1070.
[27]Hao M, Li Y, Zhang S W, et al. Investigation on the binding mode of benzothiophene analogues as potent factor IXa (FIXa) inhibitors in thrombosis by CoMFA, docking and molecular dynamic studies[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem, 2011, 26(6):792-804.
[28]Shen D, Xu X, Zhang L, et al. Identifcation of a nitric oxide-dependent hypotensive effect of anticoagulation factor II from the venom of
[29]Agkistrodon acutus[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2010, 79(3):498-506. Shen D K, Xu X L, Zhang Y, et al. Ca2+-induced binding of anticoagulation factor II from the venom of Agkistrodon acutus with
[30]factor IX[J]. Biopolymers, 2012, 97(10):818-824. Jiang L G, Yuan C, Chen H W, et al. Preparation and structure of a new coagulation Factor XI catalytic domain for drug discovery[J]. 结构化学,
[31]2011, 30(7): 1021-1029. Wu B, Wu L, Chen D, et al. Purification and characterization of a novel fbrinolytic protease from Fusarium sp. CPCC 480097[J]. J Ind
[32]Microbiol Biotechnol, 2009, 36(3):451-459. Wu B, Xu J. Antithrombotic effect of a novel protein from Fusarium sp. CPCC 480097 in a rat model of artery-vein bypass thrombosis[J].
[33]Pharm Biol, 2012, 50(7):866-870. Song J, Xu X, Zhang Y, et al. Purification and characterization of AHPM, a novel non-hemorrhagic P-IIIc metalloproteinase with alphafibrinogenolytic and platelet aggregation-inhibition activities, from
[34]Agkistrodon halys Pallas venom[J]. Biochimie, 2013, 95(4):709-718. Yang H, Wang Y, Xiao Y, et al. A bi-functional anti-thrombosis protein containing both direct-acting fibrin(ogen)olytic and plasminogen-
[35]activating activities[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(3): e17519. Wang Y, Yan H, Wang Y, et al. Proteomics and transcriptome analysis coupled with pharmacological test reveals the diversity of antithrombosis proteins from the medicinal insect, Eupolyphaga sinensis[J].
[36]Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2012, 42(8):537-544. Yuan J, Yang J, Zhuang Z, et al. Thrombolytic effects of Douchi fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus subtilis LD-8547 in vitro and in vivo[J]. BMC Biotechnol, 2012, 12:36.
本文原载于《中国药学年鉴》2013卷,经作者和原刊授权,略有删改。
Advances in Antithrombotic Drugs
XING Junhao, YANG Lingyun, LI Qing, ZHOU Jinpei, ZHANG Huibin
(Center of Drug Discovery, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China)
Thromboembolic disease is one of leading causes of death caused by diseases in humans. As the research and understanding of the pathogenesis is getting deeper and the drug design and screening technology is becoming mature gradually, some new antithrombotic drugs against a variety of targets are constantly emerging, such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor blockers, factor Xa (FXa) inhibitors and thrombin inhibitors. Pharmaceutical researchers in our country have also made some progress in the research on antithrombotic drugs against these targets. The structures, activities and structure-activity relationships of different types of novel anti-platelet drugs, anticoagulants and thrombolytic agents, which have been reported by Chinese scholars in the related research papers in academic journals both at home and abroad in recent years, were reviewed.
anti-platelet drug; anticoagulant; thrombolytic agent; structure; activity; structure-activity relationship
R973.2
A
1001-5094(2014)03-0174-11
接受日期:2013-12-20
*通讯作者:张惠斌,教授;
研究方向:心血管药物和抗凝血药物的研发;
Tel:025-83271302; E-mail:zhanghb80@163.com
