炎症及营养指标对RICU下呼吸道感染患者临床转归预测分析
2014-07-25何烨颖
黄 蕾,陈 怡,何烨颖
炎症及营养指标对RICU下呼吸道感染患者临床转归预测分析
黄 蕾,陈 怡,何烨颖
目的 探讨炎症及营养指标对严重下呼吸道感染患者临床转归的预测价值。方法 运用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)计算曲线下面积(AUC),分析143例呼吸重症监护病区(RICU)下呼吸道感染患者入院时血清降钙素原(PCT)、超敏C反应蛋白(Hs-CRP),清蛋白(Alb)、前清蛋白(PA)、尿素氮(BUN)、肌酐(Cr)、总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、血红蛋白(Hb)水平和淋巴细胞计数(LY)等指标对于入院25 d死亡及实施机械通气的预测价值,进行炎症与营养指标的相关性分析。结果 ROC曲线对于25 d死亡预测分析中,PCT的AUC值最高(>0.70),其余指标AUC均>0.50。25 d死亡组与非死亡组间各指标比较,LY、PCT、Alb及PA的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。各指标预测实施机械通气 ROC曲线分析中,LY的AUC值最高,除PA和Cr外,各指标AUC均>0.50。实施机械通气与未实施机械通气组间比较,LY、PCT、Hb及HDL-C的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。患者PCT与Hb、PA、Alb、TC、HDL-C及LDL-C水平呈负相关(P<0.05或P<0.01),与BUN及Cr水平呈正相关(P<0.01);Hs-CRP与PA、Alb水平呈负相关(P<0.01)。结论 PCT、LY对于严重下呼吸道感染患者近期死亡及实施机械通气独立预测价值相对较高,且PCT水平与营养状况有密切关系。
下呼吸道感染;降钙素原;超敏C反应蛋白;营养指标;ROC曲线;相关性
严重下呼吸道感染病情危重,并发症发生率高,病死率较高,如何积极采取预防治疗措施,改善不良临床转归,提高救治水平是研究热点。目前,对于影响严重下呼吸道感染患者临床转归的相关因素研究较少,本研究将临床常见的营养及炎症指标作为临床转归的预测指标,通过受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC curve),分析比较其预测价值;通过相关性分析,探讨炎症与营养的关系,为提高救治效率、改善临床转归提供依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例资料 依据卫生部《医院感染诊断标准》中下呼吸道感染诊断标准,选择2011年10月~2012年10月收入我院呼吸重症监护病区(RICU)严重下呼吸道感染患者143例,年龄19~94岁。其中男性91例,平均(71.05±13.55)岁;女性52例,平均(69.23±15.41)岁。疾病包括:慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)急性加重期伴感染89例、社区获得性肺炎(CAP)45例、肺脓肿2例、支气管扩张合并感染5例以及支气管哮喘合并感染2例等。排除伴有严重肝肾功能损害、结核及恶性肿瘤等疾病患者。
1.2 主要设备和试剂 Bekman Au2700全自动生化仪,法国梅里埃Mini-VIDAS荧光免疫分析仪,SysmexF-800型血液分析仪;血清清蛋白(Alb)、前清蛋白(PA)、总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)等试剂盒由中生北控生物科技股份有限公司提供,降钙素原(PCT)试剂盒由梅里埃公司提供,超敏C反应蛋白(Hs-CRP)试剂盒由德国德灵公司提供,尿素氮(BUN)、肌酐(Cr)试剂盒由北京九强生物技术股份有限公司提供。
1.3 检测指标及分组 患者入院次日早晨空腹抽血,采用酶联荧光分析法测定血PCT水平,采用乳胶增强免疫比浊法测定Hs-CRP,光电比色法测定Alb、PA、TC、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C、;BUN水平,速率法测定Cr水平,采用血液分析仪测定血红蛋白(Hb)和淋巴细胞计数(LY);记录患者入院后死亡及实施机械通气情况。
1.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS 17.0统计软件录入数据,正态分布计量资料采用t检验;各指标对患者25 d死亡和机械通气预测效率采用ROC曲线分析,分别以各炎症及营养指标为检验变量,25 d死亡和实施机械通气结果为状态变量,计算曲线下面积(AUC),并采用Wilcoxon 秩和检验行组间比较;采用Spearman 法进行PCT和Hs-CRP与各营养指标相关性分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 各指标预测25 d死亡的ROC曲线参数 21例患者25 d内死亡;ROC曲线分析结果表明,PCT的AUC值最高>0.70,其后依次为LY、Hs-CRP、PA、Alb和BUN等,其AUC均>0.50。对各指标进行比较,25 d内死亡组与非死亡组的LY、PCT、Alb及PA间的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表1。
2.2 各指标预测机械通气的ROC曲线参数 56例实施机械通气,ROC曲线分析结果表明,LY的AUC值最高为0.682,其后依次为PCT、HDL-C、Hb等。对各指标进行比较,实施机械通气与未实施机械通气组间LY、PCT、Hb及HDL-C的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表2。

表1 各指标预测25 d死亡的ROC曲线参数
注:a为25 d死亡组与非死亡组间各指标Wilcoxon 秩和检验值

表2 各指标预测机械通气的ROC的曲线参数
注:b为实施机械通气与未实施机械通气组间各指标Wilcoxon秩和检验值
2.3 患者PCT及Hs-CRP水平与各营养指标相关性分析 患者PCT与Hb、PA、Alb、TC、 HDL-C及LDL-C水平呈负相关(P<0.05或P<0.01);与BUN及Cr水平呈正相关(P<0.01)。Hs-CRP与PA、Alb水平呈负相关(P<0.01)。见表3。
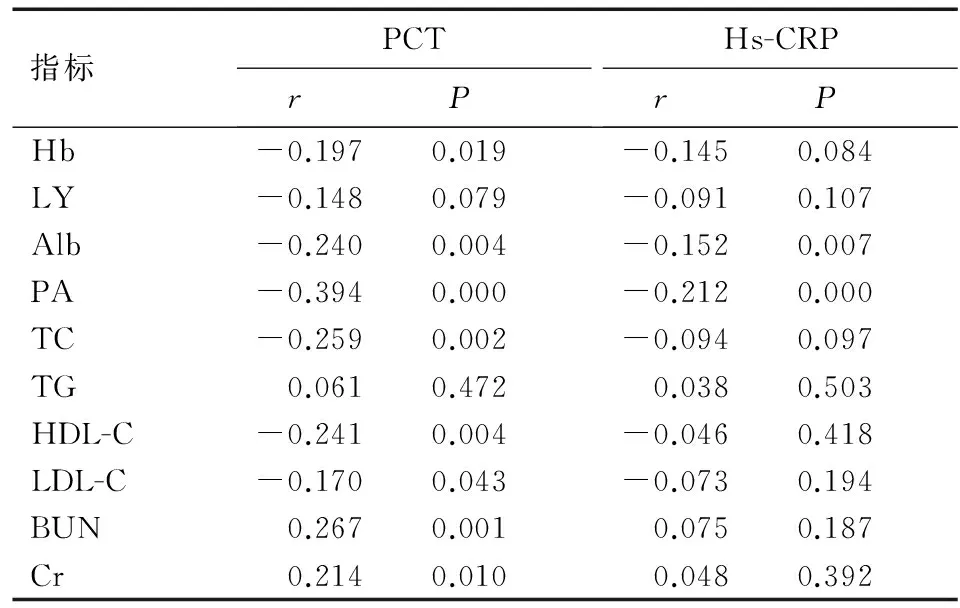
表3 PCT及Hs-CRP水平与各营养指标相关性分析
3 讨论
下呼吸道感染不仅局限于肺系的病理、生理过程,还表现为全身感染、氧化应激、炎症反应及营养状况的改变。严重的下呼吸道感染不良临床转归发生率较高,如实施机械通气可能增加医疗费用及相关并发症的发生率,从而影响临床转归。血清PCT及Hs-CRP水平反映了机体全身炎症负荷以及炎症因子的上调情况[1]。Hs-CRP是评价感染所致炎症反应的一种有效指标,但对感染缺乏特异性,文献报道其对临床转归的预测价值评价不一。PCT主要是在细菌毒素和炎性细胞因子的刺激下产生,而在非感染性炎症状态下血清PCT一般不升高。在系统炎症反应综合征(systemic inflammatory response syndrome,SIRS)中,PCT显著增高,其水平高低与感染的严重程度呈正相关,因而PCT可作为判断病情与预后以及疗效的指标[2-4],可作为呼吸道感染患者死亡预测的可靠指标[5-6]。LY指示机体的免疫功能,也是可靠的营养指标,在外科手术患者中的研究发现,低LY可延长住院时间,增加伤口感染率以及1年期病死率等[7-8]。BUN、Cr反映器官功能、肌肉和蛋白质代谢水平,高炎症反应导致机体高分解代谢,造成BUN及Cr水平升高。有文献报道,血清PA、Alb、LY、TC、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C等营养指标对临床转归也有一定的预测价值[9-11]。
本研究从ROC曲线分析结果上看,PCT、Hs-CRP、LY、PA及Alb水平是严重下呼吸道感染患者25 d内死亡的独立预测指标,其中PCT的AUC值>0.7,其他4项在0.60~0.70之间,提示PCT对于下呼吸道感染患者25 d死亡的独立预测价值最高。本研究还发现,LY、PCT、Hb及HDL-C水平是患者实施机械通气的独立预测指标,其中LY的AUC为0.682,预测价值最高。所有指标的AUC值与理想值1.0均有一定的距离,这是因为各指标AUC的计算均以治疗前的资料为基础,而患者的实际预后在很大程度上还受到治疗等诸多因素的影响,因而用入院指标预测结果必然与患者的实际临床转归存在一定的差异。感染导致的全身炎症反应致使机体蛋白质与脂质的消耗增加,使其水平快速下降。本研究对于下呼吸道感染患者血清PCT及Hs-CRP水平与各营养指标相关性分析结果表明,PCT与Hb、PA、Alb、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C BUN和Cr水平等具有显著相关性,Hs-CRP水平仅与PA和Alb水平存在相关性。在炎症指标中,较之Hs-CRP,PCT与各营养指标间具有更密切的相关关系,可能是PCT对严重下呼吸道感染患者25 d内死亡和机械通气预测价值更高的原因之一。
综合来看,PCT、LY是预测严重下呼吸道感染患者25 d内死亡、机械通气较好的指标,而且二者与患者营养有密切关系。
[1] Karadag F,Kirdar S,Karul AB,et al.The value of C-reactive protein as a marker of systemic inflammation in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary diseasfe[J].Eur J Intern Med,2008,19(2):104-108.
[2] Luyt CE,Guerin V,Combes A.Procalcitonin kinetics as a prognostic marker of ventilator associated pneumonia[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2005,171(1):48-53.
[3] Lacoma A,Prat C,Andreo F,et al.Value of procalcitonin,C-reactive protein,and neopterin in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J].Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis,2011,6:157-169.
[4] Snider RH Jr,Nylen ES,Beeker KI.Procalcitonin and its component peptides in systemic inflammation:immunochemical characterization[J].J Investing Med,1997,45(9):552.
[5] Kurata K,Kazuyori T,Shimizu K,et al.Usefulness of serum procal-citonin measurement in the diagnosis of respiratory infectious diseases[J].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi,2010,48(9):654-660.
[6] Rammaert B,Verdier N,Cavestri B,et al.Procalcitonin as a prognostic factor in severe acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseas[J].Respirology,2009,14(7):969-974.
[7] Nicholson JA,Dowrick AS,Liew SM,et al.Nutritional status and short-term outcome of hip arthroplasty[J].J Orthop Surg,2012,20(3):331-335.
[8] Pacheco-Haro LJ,Chavez-Cadena MA.Preoperative lymphocytes as a factor related with delayed healing in hip surgery[J].Acta Ortop Mex,2012,26(4):224-227.
[9] Bouillanne O,M orineau G,Dupont C.et al.Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index:a new index for evaluating at risk elderly medical patients[J].Am JC Iin Nutr,2005,82(4):777-783.
[10] Omran ML,Morley JE.Assessment of protein energym alnutrition in older persons,part Ⅱ:laboratory evaluation[J].Nutrition,2000,16(2):131-140.
[11] Walter O,Seiler MD.Clinical pictures of malnutrition in ill elderly subjects[J].Nutrition,2001,17(6):496-498.
Value of inflammation and nutrition indexes in the prediction of clinical turnover in patients with lower respiratory infection in RICU
Huang Lei1,Chen Yi1,He Yeying2
1.Department of Trophology;2.Department of Respiratory Diseases,General Hospital of Chengdu Military Command,Chengdu,Sichuan,610083,China
Objective To discuss the value of inflammation and nutrition indexes in the prediction of clinical turnover in patients with lower respiratory infection in RICU.Methods The receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC curve)was used to calculate the area under the curve(AUC)in order to analyze the value of the indexes below in the prediction of death within 25 days after the admission and the application of mechanical ventilation.The indexes included PCT,Hs-CRP,Alb,PA,Bun,Cr,TC,TG,HDL-C,LDL-C,Hb,and LY of the 143 patients with lower respiratory infection at the time of admission in RICU.The correlation between the inflammation and the nutritive indexes was analyzed.Results Based on ROC curve analysis of death within 25 d,the AUC of PCT was the highest(>0.70),and the AUCs of other indexes were all larger than 0.50.There were significant differences in LY,PCT,Alb,and PA between the death within 25 days group and non-death group(P<0.05).In the ROC curve of the prediction of mechanical ventilation application,the AUC of LY was the highest,and the AUCs of other indexes were all larger than 0.50 except PA and Cr.There were significant differences in the LY,PCT,Alb,and PA between the groups receiving and not receiving the mechanical ventilation(P<0.05).There was a negative correlation between the level of PCT and Hb,PA,Alb,TC,HDL-C,and LDL-C(P<0.05 orP<0.01)and a positive correlation between the level of Bun and Cr(P<0.01).There was a negative correlation between the level of Hs-CRP and PA and Alb(P<0.01).Conclusion PCT and LY have a great independent value in the prediction of the recent death and the application of mechanical ventilation in patients with severe lower respiratory infection,and the PCT level is closely related to the nutriture.
lower respiratory infection;PCT;Hs-CRP;nutritive index;ROC curve;correlation
610083 成都,成都军区总医院营养科(黄 蕾,陈 怡),呼吸科(何烨颖)
陈 怡, E-mail:hlei18@126.com
R 56
A
1004-0188(2014)01-0031-03
10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2014.01.012
2013-04-16)
