缬沙坦与氨氯地平联合用药治疗原发性高血压的疗效
2014-07-18周邠玮段佳佳刘新林赵季红
周邠玮,袁 毅,毕 莹,王 飞,段佳佳,刘新林,赵季红
缬沙坦与氨氯地平联合用药治疗原发性高血压的疗效
周邠玮,袁 毅,毕 莹,王 飞,段佳佳,刘新林,赵季红
目的探讨缬沙坦联合氨氯地平不同用药方式和服药时间,治疗原发性高血压的疗效。方法201例原发性高血压患者(男92例,女109例),接受缬沙坦(80 mg/d)联合氨氯地平(5 mg/d)治疗,随机分为四组,各组治疗方案如下:A组两种药物均于清晨服用,B组两种药物均于睡前服用,C组缬沙坦清晨服用、氨氯地平睡前服用,D组氨氯地平清晨服用、缬沙坦睡前服用。监测各组服药前及服药后12周的24 h动态血压值。结果服药12周后,各组血压指标均较治疗前下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。B组服药后各血压指标下降幅度明显低于其他三组,其中24 h SBP/DBP平均值分别为A组(123.0±13.2)mmHg/(73.1±6.7)mmHg、B组(113.6±11.0)mmHg/(67.1±8.3)mmHg、C组(124.4±13.7)mmHg/(73.6±9.0)mmHg、D组(119.8±13.0)mmHg/(70.6±7.2)mmHg,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。结论缬沙坦与氨氯地平睡前联合服用,治疗原发性高血压的效果最佳。
缬沙坦;氨氯地平;原发性高血压;联合用药
众所周知,原发性高血压可显著增加脑卒中、心肌梗死、心力衰竭及肾脏疾病发生的风险[1,2],且服用药物有效控制血压可显著减少恶性事件的发生,提高生活质量。单药降压治疗抑制了某种升压机制,必然会激活某种代偿机制[3],使得降压达标率有限;联合降压治疗采用不同降压机制的药物以合适的剂量进行不同组合,有可能满足临床不同类型高血压的治疗需要,同时也是现阶段提高降压达标率的重要途径[4]。例如,血管紧张素受体拮抗药(ARB)及钙通道阻滞药(CCB)已被证实是有效的单一降压药物。更多临床研究证实,ARB联合CCB降压治疗可发挥互补作用,较单一药物能更有效、更安全地控制血压[1,2],可使外周水肿的发生率较单一使用氨氯地平显著降低[5,6],有效提高患者的药物耐受性及依从性[7]。本研究旨在探讨ARB/CCB联合用药治疗原发性高血压对不同时间给药的降压效果。
1 对象与方法
1.1 对象 收集2013-08至2013-11我院确诊的原发性高血压患者201例,未经治疗且无并发症,男92例,女109例,年龄≥18岁,昼夜活动及睡眠习惯相对规律,服药前完成24 h动态血压监测。随机分为四组,四组患者性别、年龄、身高、体重、BMI等一般情况比较无统计学差异(表1)。
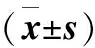
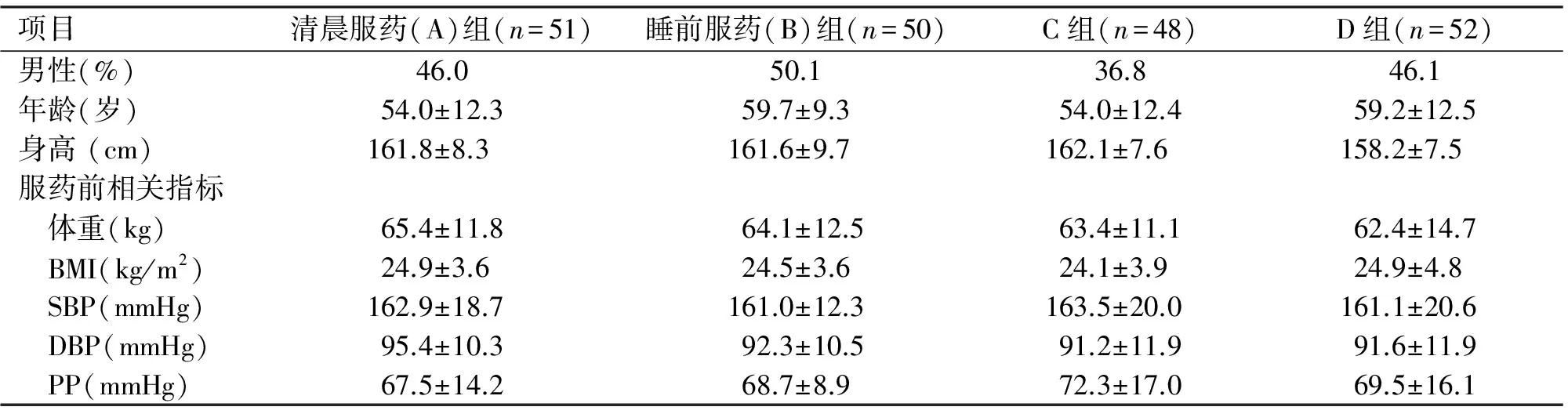
项目清晨服药(A)组(n=51)睡前服药(B)组(n=50)C组(n=48)D组(n=52)男性(%)46.050.136.846.1年龄(岁)54.0±12.359.7±9.354.0±12.459.2±12.5身高(cm)161.8±8.3161.6±9.7162.1±7.6158.2±7.5服药前相关指标 体重(kg)65.4±11.864.1±12.563.4±11.162.4±14.7 BMI(kg/m2)24.9±3.624.5±3.624.1±3.924.9±4.8 SBP(mmHg)162.9±18.7161.0±12.3163.5±20.0161.1±20.6 DBP(mmHg)95.4±10.392.3±10.591.2±11.991.6±11.9 PP(mmHg)67.5±14.268.7±8.972.3±17.069.5±16.1
注:C组为清晨服缬沙坦,睡前服氨氯地平;D组为清晨服氨氯地平,睡前服缬沙坦
1.2 研究方法 全部患者均接受缬沙坦(80 mg/d)联合氨氯地平(5 mg/d)治疗,各组治疗方案如下:A组两种药物均于清晨服用,B组两种药物均于睡前服用,C组缬沙坦清晨服用、氨氯地平睡前服用,D组氨氯地平清晨服用、缬沙坦睡前服用。分别于用药后第4周、第8周、第12周门诊随访,并统计各组服药前及服药后12周的体重指数(BMI)、24 h动态血压的平均值、晨起空腹SBP/DBP值、脉压(PP)、白昼SBP及DBP的平均值、夜间SBP及DBP的平均值、昼夜SBP及DBP下降幅度等指标。

2 结 果
服药12周后,各组血压指标均较治疗前下降,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。B组服药后各血压指标明显低于其他3组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01,表2)。
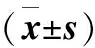
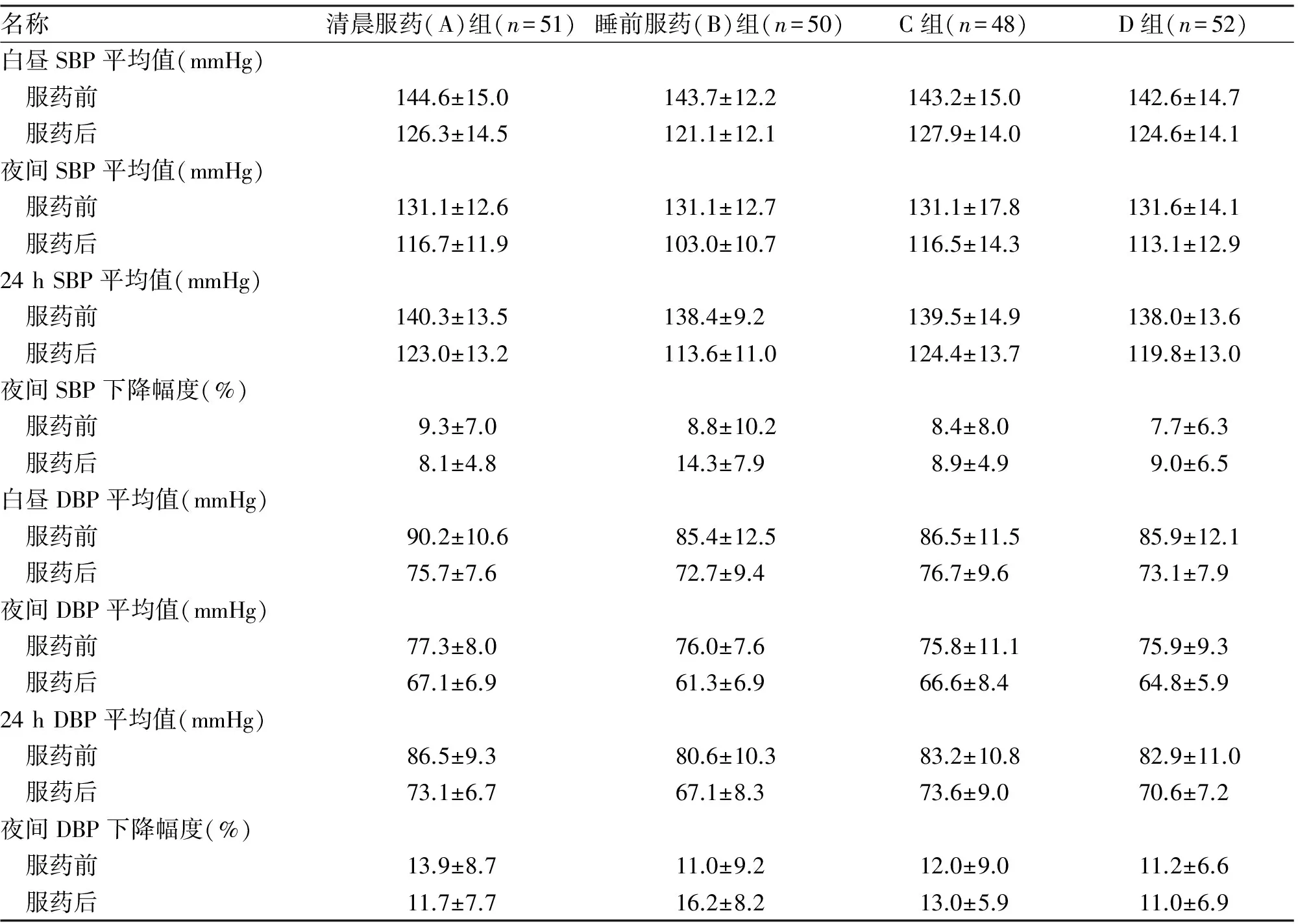
名称清晨服药(A)组(n=51)睡前服药(B)组(n=50)C组(n=48)D组(n=52)白昼SBP平均值(mmHg) 服药前144.6±15.0143.7±12.2143.2±15.0142.6±14.7 服药后126.3±14.5121.1±12.1127.9±14.0124.6±14.1夜间SBP平均值(mmHg) 服药前131.1±12.6131.1±12.7131.1±17.8131.6±14.1 服药后116.7±11.9103.0±10.7116.5±14.3113.1±12.924hSBP平均值(mmHg) 服药前140.3±13.5138.4±9.2139.5±14.9138.0±13.6 服药后123.0±13.2113.6±11.0124.4±13.7119.8±13.0夜间SBP下降幅度(%) 服药前9.3±7.08.8±10.28.4±8.07.7±6.3 服药后8.1±4.814.3±7.98.9±4.99.0±6.5白昼DBP平均值(mmHg) 服药前90.2±10.685.4±12.586.5±11.585.9±12.1 服药后75.7±7.672.7±9.476.7±9.673.1±7.9夜间DBP平均值(mmHg) 服药前77.3±8.076.0±7.675.8±11.175.9±9.3 服药后67.1±6.961.3±6.966.6±8.464.8±5.924hDBP平均值(mmHg) 服药前86.5±9.380.6±10.383.2±10.882.9±11.0 服药后73.1±6.767.1±8.373.6±9.070.6±7.2夜间DBP下降幅度(%) 服药前13.9±8.711.0±9.212.0±9.011.2±6.6 服药后11.7±7.716.2±8.213.0±5.911.0±6.9
注:C组为清晨服缬沙坦,睡前服氨氯地平;D组为清晨服氨氯地平,睡前服缬沙坦
3 讨 论
临床研究表明,约2/3的高血压患者需要联合治疗才能达标[8]。大量研究证实,缬沙坦联合氨氯地平治疗原发性高血压的效果显著强于缬沙坦及氨氯地平单一用药的方案[9-12]。本研究通过动态血压监测,比较了缬沙坦联合氨氯地平不同用药方式和服药时间,对治疗原发性高血压的疗效。结果表明,两药于睡前联合使用治疗原发性高血压的疗效,较其他方案的疗效显著提高,且在随访过程中未出现低血压等不良事件。说明联合用药的降压效果不取决于各自单一用药方案的降压疗效,而与联合使用药物的方式及服药时间有关。相关研究表明,人体自身存在昼夜节律变化的特点,如胃肠道的蠕动、肝酶的活性、肾小球滤过率等[13,14],均可以引起降压药物在体内药代动力学的变化,或许与睡前服用复方制剂降压效果最佳有关。
据文献[15,16]报道,夜间血压控制欠佳可增加靶器官及心血管事件的发生,这意味着夜间血压的平均值较白昼血压平均值及24 h血压平均值能更有效地预测心血管事件的病死率。文献[17,18]表明,脉压升高可增加动脉的僵硬度,而动脉僵硬度是预测心肌梗死、心力衰竭、心源性猝死等心血管疾病风险的独立危险因子。本研究表明,四个治疗组降压效果的差异性主要体现在夜间收缩压及舒张压平均值,其中B组降压差值显著高于其他三组。另外,睡前服用缬沙坦联合氨氯地平可有效控制脉压。因此,推测该治疗方案可有效降低心血管事件的病死率,改善生活质量,从而有效提高生存率。
综上所述,缬沙坦与氨氯地平睡前联合服用治疗原发性高血压,可提高患者依从性,有效降低夜间收缩压及舒张压的平均值,更大幅度地降低脉压,疗效较好,值得临床推广应用。有关睡前联合用药的机制,仍需进一步探讨研究。
[1] Chobanian A V,Bakris G L,Black H R,etal. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention,detection,evaluation,and treatment of high blood pressure[J]. Hypertens,2003,42:1206-1252.
[2] Mancia G,De Backer G,Dominiczak A,etal.2007 guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)[J]. Hypertension, 2007,25:1105-1187.
[3] 唐 哲,孙玉坤,李耀红,等. 氨氯地平对比索洛尔在大鼠体内药动学的影响[J]. 武警医学,2013,24(4):319-322.
[4] 贾德安,王志坚,杨士伟,等.缬沙坦/氨氯地平或氨氯地平单药治疗高危高血压患者[J].中华高血压杂志,2013,21(6):569-572.
[5] Allemann Y,Fraile B,Lambert M,etal. Efficacy of the combination of amlodipine and valsartan in patients with hypertension uncontrolled with previous monotherapy:the Exforge in Failure after Single Therapy (EX-FAST) study[J]. Clin Hypertens,2008,10:185-194.
[6] Brachmann J,Ansari A,Mahla G,etal. Effective and safe reduction of blood pressure with the combination of amlodipine 5 mg and valsartan 160 mg in hypertensive patients not controlled by calcium channel blocker monotherapy[J].Adv Ther,2008,25:399-411.
[7] Liebson P R. Calcium channel blockers in the spectrum of antihypertensive agents[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother,2003,7:2385-2401.
[8] Miura S,Saku K.Efficacy and safety of angiotensin Ⅱ type 1 receptor blocker/calcium channel blocker combination therapy for hypertension:focus on a single-pill fixed-dose combination of valsartan and amlodipine [J].J Int Med Res ,2012,40(1):1-9.
[9] Flack J M,Calhoun D A,Satlin L,etal. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with amlodipine/valsartan compared with amlodipine monotherapy in black patients with stage 2 hypertension:the EX-STAND study[J].Hum Hypertens,2009,23:479-489.
[10] Philipp T,Smith T R,Glazer R,etal. Two multicenter,8-week,randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled,parallel-group studies evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of amlodipine and valsartan in combination and as monotherapy in adult patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension[J].Clin Ther,2007,29:563-580.
[11] Schunkert H,Glazer R D,Wernsing M,etal. Efficacy and tolerability of amlodipine/valsartan combination therapy in hypertensive patients not adequately controlled on amlodipine monotherapy[J].Curr Med Res Opin,2009,25:2655-2662.
[12] Sinkiewicz W,Glazer R D,Kavoliuniene A,etal. Efficacy and tolerability of amlodipine/valsartan combination therapy in hypertensive patients not adequately controlled on valsartan monotherapy[J].Curr Med Res Opin,2009,25:315-324.
[13] Koopman M G,Koomen G C,Krediet R T,etal. Circadian rhythm of glomerular filtration rate in normal individuals[J].Clin Sci (Lond),1989,77:105-111.
[14] Labrecque G,Beauchamp D.Rhythms and pharmacokinetics.In Redfern P (ed.).Chronotherapeutics.London:Pharmaceutical Press,2003:75-110.
[15] Boggia J,Li Y,Thijs L,etal. Prognostic accuracy of day versus night ambulatory blood pressure: a cohort study[J].Lancet,2007,370:1219-1229.
[16] Brotman D J,Davidson M B,Boumitri M,etal. Impaired diurnal blood pressure variation and all-cause mortality[J]. Hypertens,2008,21:92-97.
[17] Benetos A,Safar M,Rudnichi A,etal. Pulse pressure:a predictor of long-term cardiovascular mortality in a French male population.[J].Hypertension,1997,30:1410-1415.
[18] Verdecchia P,Schillaci G,Reboldi G,etal. Different prognostic impact of 24-hour mean blood pressure and pulse pressure on stroke and coronary artery disease in essential hypertension[J].Circulation,2001,103:2579-2584.
(2014-03-09收稿 2014-05-03修回)
(责任编辑 尤伟杰)
Clinicaleffectofvalsartan/amlodipinecombinationtherapyintreatmentofessentialhypertension
ZHOU Binwei,YUAN Yi,BI Ying,WANG Fei,DUAN Jiajia,LIU Xinlin,and ZHAO Jihong.
Department of Cardiology,Affiliated Hospital,Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces,Tianjin 300162,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the clinical efficacy of valsartan / amlodipine combination and different time of taking medicine in treatment of essential hypertension.Methods201 essential hypertensive subjects (92 men/109 women), were recruited randomized to receive valsartan(80 mg/day) and amlodipine (5 mg/day) in one of the following four therapeutic schemes: both medications on awakening, both at bedtime, either one administered on awakening and the other at bedtime. BP was measured by ambulatory monitoring for 24 consecutive hours before and after 12 wks of treatment.ResultsBP-lowering efficacy (quantified in terms of reduction of the 24-h mean of systolic/diastolic BP) was highest when both antihypertensive medicines were ingested at bedtime, as compared with any one of the three other tested therapeutic schemes[A(123.0±13.2)mmHg/(73.1±6.7)mmHg、B(113.6±11.0)mmHg/(67.1±8.3)mmHg、C(124.4±13.7)mmHg/(73.6±9.0)mmHg、D(119.8±13.0)mmHg/(70.6±7.2)mmHg,P<0.01].ConclusionsThe greater proportion of controlled patients, improved efficacy on lowering asleep BP mean, and increased sleep-time relative BP decline suggest that valsartan/amlodipine combination therapy should be preferably administered at bedtime.
valsartan ;amlodipine;essential hypertension;combination therapy
周邠玮,硕士,医师,E-mail:christian83@163.com
300162天津,武警后勤学院附属医院心脏医院
赵季红,E-mail:zjhwj@126.com
R972.4
