Latarjet两种术式治疗肩关节复发性前脱位伴重度骨缺损3~5年随访的比较研究
2014-07-05向明杨国勇陈杭胡晓川唐浩琛
向明 杨国勇 陈杭 胡晓川 唐浩琛
Latarjet两种术式治疗肩关节复发性前脱位伴重度骨缺损3~5年随访的比较研究
向明 杨国勇 陈杭 胡晓川 唐浩琛
目的研究Latarjet手术治疗肩关节复发性前脱位伴重度骨缺损患者的疗效。方法结合三维CT扫描和肩关节镜对肩关节复发性前脱位的肩盂前缘骨缺损和肱骨头后外侧的Hill-Sachs损伤的范围和程度进行评估,如肩盂呈倒梨形(骨缺损大于肩盂宽度的25%)合并或伴有Engaging Hill-Sachs损伤,即通过三角肌胸大肌入路运用Latarjet技术进行重建,治疗伴有重度骨缺损的肩关节复发性前脱位37例。其中2006年4月至2007年12月采用喙突内旋90°转位术式,随访资料完整的共16例;2008年1月至2009年10月采用喙突平行转位术式,随访资料完整的共21例。男性23例,女性14例,平均年龄26.5岁(17~46岁)。术前Apprehension sign均为阳性,平均脱位次数13.5次(8~28次),随访时采用美国肩与肘协会评分系统(ASES)评分、Constant-Murley评分以及视觉模拟评分法(VAS)不稳定评分进行功能评估。结果平均随访时间为48.3个月(37~61个月),术后患肩制动2周后即在医师指导下按计划进行肩关节功能康复及力量恢复训练,术后6个月三维CT显示喙突平行转位组骨块均与肩胛颈愈合,而喙突内旋90°转位组有3例骨块未与肩胛颈愈合,两组喙突骨块愈合率相比,差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.258,P<0.05)。喙突平行转位组手术前对终末次随访比较,前屈上举(152.5±22.6)°与(168.0±7.8)°比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.028,P <0.05),平均体侧外旋(52.6±18.4)°与(44.9±15.0)°比较,差异无统计学意义(t=1.486,P >0.05),ASES评分80.7±16.7与92.2±6.4比较,差异有统计学意义(t=2.947,P <0.05),Constant-Murley评分78.6±10.1与91.6±13.2比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.584,P <0.05),VAS不稳定评分平均6.0±1.4与4.3±1.6比较,差异有统计学意义(t=3.664,P <0.05);而喙突内旋90°转位组前屈上举(148.5±19.2)°与(170.0±10.5)°比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.930,P <0.05);平均体侧外旋(55.8±16.9)°与(40.6±13.6)°比较,差异有统计学意义(t=2.803,P <0.05);ASES评分81.4±14.7与92.4±7.0比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-2.702,P <0.05),Constant-Murley评分80.2±12.6与92.8±5.1比较,差异有统计学意义(t=3.708,P <0.05),VAS不稳定评分平均6.4±1.5与4.2±2.1比较,差异有统计学意义(t=3.410,P<0.05);至末次随访喙突平行转位组与喙突内旋90°转位组相比,无论前屈上举、平均体侧外旋、ASES评分、Constant-Murley评分或VAS不稳定评分,P值均>0.05,差异无统计学意义。终末复查时X线片6例出现骨关节炎表现,其中喙突平行转位组有1例,喙突内旋90°转位5例,两者相比差异有统计学意义。结论对于重度骨缺损的肩关节复发性前脱位,肩关节镜下或开放铆钉重建修复Bankart损伤脱位复发率较高,风险大,微创治疗难以彻底治愈,多采用Latarjet手术治疗,目前有喙突平行转位和喙突内旋90°转位两种术式,均能为该种类型的肩关节复发性前脱位提供更好的静力稳定性,从而有效减少脱位的再发率;而喙突平行转位较喙突内旋90°转位固定强度相对较高、接触面积更大,愈合率相对较高,并且发生骨关节炎改变的几率相对较低。
Latarjet; 骨缺损; 肩关节复发性前脱位; 喙突
肩关节脱位占全身关节脱位的40%以上[1],其中绝大部分为前脱位,主要的病理机制是外伤引起前下方盂唇关节囊韧带复合体的功能缺失,即Bankart损伤,如未修复可致复发性前脱位,部分病例同时伴有肩盂的撕脱骨折或骨性缺损,甚至形成倒梨形肩盂,软组织性Bankart损伤和骨性缺损<25%时,切开或关节镜下Bankart重建术临床效果优良,再脱位率低[2];但如肩盂骨缺损25%~30%形成倒梨形,和(或)伴啮合型的肱骨头后外上方压缩骨折(Hill-Sach损伤),单纯的Bankart重建术再脱位率可达67%[3],Latarjet术式重建肩盂骨性结构则能明显减少再脱位率[4],在Latarjet手术中,喙突转位有平行转位和内旋90°转位两种[5]。2006年4月至2009年10月,我科对伴有重度骨缺损的肩关节复发性前脱位采用Latarjet手术治疗。其中2006年4月至2007年12月采用喙突内旋90°转位术式,随访资料完整的共16例;2008年1月至2009年10月采用喙突平行转位术式,随访资料完整的共21例。随访时间37~61个月。
临床资料
一、一般资料
患者37例,其中男性23例,女性14例;平均年龄26.5岁(17~46岁)。左肩10例,右肩27例;优势侧29例。初次肩关节前脱位的原因:运动损伤23例,日常活动12例,其他外伤2例。平均脱位次数13.5次(8~28次)。初次脱位至手术时间为9个月至21年,平均6.4年;末次脱位至手术时间为2~3.5个月,平均75d。术前体格检查:均有恐惧试验(Apprehension sign)阳性,33例为单一前向不稳定,其余4例伴下方不稳定。术前拍摄肩关节正位、肩胛骨侧位X线片,并对患侧肩关节行三维CT检查,通过对重建CT影像的处理,去掉肱骨头影像并使肩盂转向正对检查者形成所谓“en face view”[67],根据术中肩关节镜镜检,其中 Hill-Sachs损伤34例(91.9% ),根据 Calandra分型标准[8]:Ⅰ型8例、Ⅱ型16例、Ⅲ型10例;上盂唇前后位(superior labrum anterior and posterior,SLAP)损伤3例(8.1% ),根据Snyder等[9]的分型标准:Ⅰ型2例、Ⅲ型1例。
二、手术方法
患侧臂丛神经阻滞加全身麻醉下,取沙滩椅位,标记肩关节骨性标志。先行肩关节镜镜检,证实肩盂骨性缺损的程度;处理Hill-Sachs损伤,其中2例Hill-Sachs损伤因骨缺损>1/3,行取自体髂骨植骨;对I型SLAP损伤用刨刀给予清创;而1例Ⅲ型损伤因长头腱附丽点稳定,仅给予清创处理。然后,采用三角肌胸大肌间隙入路,保护头静脉拉向外侧,显露喙突及附着于其上的喙肩韧带、胸小肌腱和联合腱,切断胸小肌腱喙突止点,在肩峰处切断喙肩韧带,于喙锁韧带的锥状韧带前方截下喙突,约24~25mm,经肩胛下肌中下1/3水平劈开显露前关节囊并沿肩胛盂外侧纵向切开,暴露肩胛盂,清除撕脱的盂唇小骨片和瘢痕组织,尽量保留残留的盂唇、韧带和关节囊组织,去除肩胛颈前下方的骨皮质。喙突平行转位时,喙突下方去皮质后将其连同附于其上联合腱穿过肩胛下肌水平裂隙,使喙突外侧缘和关节面平整,用2枚3.5mm全螺纹皮质骨螺钉将其固定于肩胛盂前下方;喙突内旋90°转位时,喙突内侧(胸小肌腱附着侧)去皮质后将其连同附于其上联合腱穿过肩胛下肌水平裂隙,使喙突下缘和关节面平整,用2枚3.0mm中空螺钉将其固定于肩胛盂前下方。将肩关节置于外旋10°位仔细缝合喙突相连的喙肩韧带残端与关节囊,逐层关闭切口,放置引流管,体侧外旋中立位吊带制动。
三、术后处理
术后24h拔出引流管,制动2周后即开始在医师指导下行被动前屈和体侧外旋活动,6周后行肩关节主动前屈上举和外旋活动,8周开始内旋练习,并逐渐力量练习;所有患者术后定期拍摄肩关节正位、肩胛骨侧位X线片及术后6个月肩关节三维CT扫描检查。术后3周、6周、3个月、6个月、1年时门诊随访,此后每年随访1次。随访时采用ASES评分、Constant-Murley评分和视觉模拟评分法(VAS)不稳定评分进行功能评估。
四、统计学分析方法
采用SPSS 19.0统计软件包进行数据分析。对患者手术前与后的肩关节前屈上举、体侧外旋的活动度,ASES评分、Constant-Murley评分以及VAS不稳定评分比较比较采用t检验,数据以±s表示;两组喙突骨块愈合率比较采用软件中的χ2检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
患者术后平均随访时间为48.3个月(37~61个月),术后患肩制动2周后即在医师指导下按计划进行肩关节功能康复及力量恢复训练,术后6个月时三维CT显示喙突平行转位组骨块均与肩胛颈愈合,而喙突内旋90°转位组有3例骨块未与肩胛颈愈合,两组喙突骨块愈合率相比,差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.258,P <0.05)。喙突平行转位组手术前与末次随访比较结果详见表1,其中前屈上举(152.5±22.6)°与(168.0±7.8)°比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.028,P <0.05),平均体侧外旋(52.6±18.4)°与(44.9±15.0)°比较,差异无统计学意义(t =1.486,P >0.05),ASES评分80.7±16.7与92.2±6.4比较,差异有统计学意义(t=2.947,P <0.05),Constant-Murley评分78.6±10.1与91.6±13.2比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.584,P <0.05),VAS不稳定评分平均6.0±1.4与4.3±1.6比较,差异有统计学意义(t=3.664,P <0.05);而喙突内旋90°转位组(表2)前屈上举(148.5±19.2)°与(170.0±10.5)°比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.930,P <0.05);平均体侧外旋(55.8±16.9)°与(40.6±13.6)°比较,差异有统计学意义(t=2.803,P <0.05);ASES评分81.4±14.7与92.4±7.0比较,差异有统计学意义(t=-2.702,P <0.05),Constant-Murley评分80.2±12.6与92.8±5.1比较,差异有统计学意义(t=3.708,P <0.05),VAS不稳定评分平均6.4±1.5与4.2±2.1比较,差异有统计学意义(t=3.410,P <0.05);至末次随访喙突平行转位组与喙突内旋90°转位组相比,无论前屈上举、平均体侧外旋、ASES评分、Constant-Murley评分或VAS不稳定评分,P值均>0.05,差异无统计学意义。终末复查X线片,按照Samilson和Prieto骨关节炎的分型[10],6例出现轻至中度骨关节炎,其中喙突平行转位组有1例,喙突内旋90°转位5例,两者相比差异有统计学意义。喙突内旋90°转位组有1例术后残留Apprehension sign阳性,2例在最大外展、外旋时有轻度疼痛;喙突平行转位组有1例在最大外展、外旋时有轻度疼痛。
1.典型病例1:患者男性,37岁,26岁时发生初次脱位,后反复脱位28次。见图1。
2.典型病例2:患者男性,27岁,16岁时发生初次脱位,后反复脱位19次。见图2。
表1 喙突平行转位组患者术前与末次随访的各项检测结果(±s)
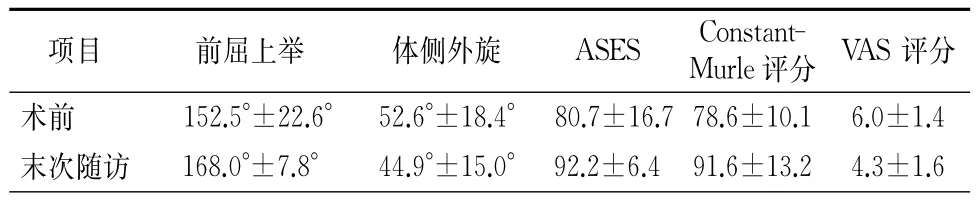
表1 喙突平行转位组患者术前与末次随访的各项检测结果(±s)
注:ASES为美国肩与肘协会评分系统;VAS为视觉模拟评分法
项目 前屈上举 体侧外旋 ASES Constant-Murle评分 VAS评分术 前 152.5°±22.6° 52.6°±18.4° 80.7±16.7 78.6±10.1 6.0±1.4末 次随 访 168.0°±7.8° 44.9°±15.0° 92.2±6.4 91.6±13.2 4.3±1.6
表2 喙突内旋90°转位组患者术前与末次随访的各项检测结果(±s)

表2 喙突内旋90°转位组患者术前与末次随访的各项检测结果(±s)
注:ASES为美国肩与肘协会评分系统;VAS为视觉模拟评分法
项目 前屈上举 体侧外旋 ASES Constant-Murle评分 VAS评分术 前 148.5°±19.2° 55.8°±16.9° 81.4±14.7 80.2±12.6 6.4±1.5末 次随 访 170.0°±10.5° 40.6°±13.6° 92.4±7.0 92.8±5.1 4.2±2.1
讨 论
盂肱关节的稳定性是肌肉、韧带和骨结构共同作用的结果,以维持肱骨头和肩盂始终处于同一的旋转中心。美国肩关节脱位的发生率为11.2/100 000,其中90%为前脱位[11];肩关节初次前脱位后常见病变有前下关节囊、盂唇和盂肱韧带等软组织从肩盂缘撕脱即Bankart损伤,同时有关节囊的变薄,或伴不同程度的骨性损伤,如骨性Bankart损伤和Hill-Sachs损伤,反复脱位所致的磨损会进一步改变盂肱关节的接触面积和静力稳定装置从而降低盂肱关节的稳定性[2]。通过对每例肩关节急性前脱位的患者进行MRI检查,Widjaja等发现初次脱位后73%有Bankart损伤,67%有Hill-Sachs损伤[12];Yiannakopoulos等发现肩关节反复前脱位后Bankart和前方盂唇韧带骨膜袖状撕脱(anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion,ALPSA)损伤高达97%而Hill-Sachs损伤高达93%,倒梨形肩盂占15%[13]。
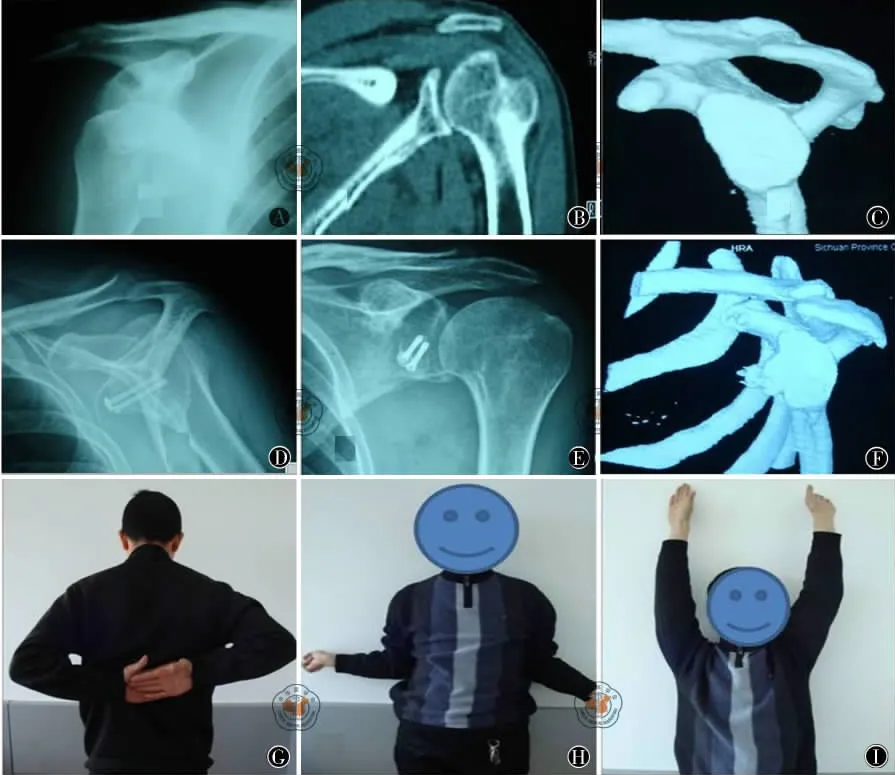
图1 喙突内旋90°转位Latarje术式 图A为术前X线正位片;图B为术前CT冠状位;图C为术前三维CT重建显示肩盂有骨缺损和Hill-sachs损伤;图D、E为喙突内旋90°转位两枚螺钉固定,术后6个月X线正侧位片;图F为术后6个月三维CT显示喙突骨块已与肩胛盂愈合,关节面平整,肩盂形状恢复良好;图G~I为术后3年半随访肩功能恢复良好,Apprehension sign阴性,从事较重体力劳动
Robinson等的一项前瞻性临床研究表明15~35岁的患者发生肩关节前脱位后经保守治疗平均13个月后,56%再次脱位,而20岁左右的男性高达72%~86%[14]。切开Bankart重建术以恢复前方肩盂的解剖结构,3%的复发率曾是金标准手术方式,随着关节镜技术和器械的发展,多数作者报道关节镜下Bankart重建术获得了优良的效果[15-16],甚至接近20%的肩盂骨缺损也能通过关节镜仅重建软组织获得满意的疗效[17-18]。然而,越来越多的研究表明肩盂骨性结构的完整性是手术修复是否能成功的一个最重要因素[19-21],Burkhart等[3]的研究证实,倒梨形肩盂仅行软组织Bankart重建术,失效率高达67%。因此,建议对倒梨形肩盂合并或伴有Engaging Hill-Sachs损伤的患者应行骨性重建术。
Latarjet和Helfet于1954和1958年分别报道采用喙突移位阻滞术治疗肩关节复发性前脱位,取得了较满意的疗效[11]。Latarjet手术的原理是移植局部的喙突骨块使之成为关节外的平台而达到关节面的延伸,其稳定肩关节的作用有三:(1)骨块增加了脱位前肱骨头在肩盂上移动的安全面积;(2)上臂外展外旋时,联合腱可发挥动力系带的作用阻挡肱骨头向前移动;(3)转位的喙突和联合腱跨过肩胛下肌中下1/3能起到肌腱固定的效应从而加固前下方关节囊的缺损[3]。本研究证实Latarjet手术对伴有重度骨缺损的肩关节复发性前脱位疗效确切,能明显增加肩关节的前方稳定性,患者的前屈上举等以及多种功能评分均明显增加。传统的Latarjet手术要切断肩胛下肌近端止点纤维,导致肩胛下肌肌力下降和限制肱骨头向前的作用降低,并且因重叠缝合肩胛下肌和内旋固定引起肩关节外旋功能丢失明显[22]。经典的Latarjet手术在胸小肌腱止点和喙锁韧带附着点之间截骨,向外平行移位于肩盂前下缘,喙突骨块的外缘与关节面平整;由de Beer改良的Latarjet手术喙突骨块沿其长轴内旋90°转位,使喙突下缘和关节面平整[5]。作者分期采用喙突内旋90°转位术式和采用喙突平行转位术式,均通过水平劈开肩胛下肌并纵行切开肩关节囊,以尽量降低手术操作对肩胛下肌肌力的削弱,术毕缝合关节囊时将肩关节置于外旋10°从而减少外旋的丢失。喙突骨块因其宽度大于厚度[1],平行转位时与肩盂有较大的接触面积,能用2枚3.5mm皮质骨螺丝钉进行固定,从而提供更高的强度;相反,内旋90°转位喙突骨块与肩盂之间接触面积相对较小,只能用2枚3.0mm中空螺丝钉进行固定。因此,喙突骨块平行转位时较内旋90°转位有更大的接触面积和生物力学强度,从而提高骨块愈合率。但内旋90°转位本身能提供更大的关节面安全范围,有利于肩盂骨缺损较大的患者。本研究内旋90°转位组3例不愈合均发生在该组的早期,骨块未愈合降低了Latarjet手术所提供的稳定机制,所以1例术后残留Apprehension sign阳性,2例在最大外展、外旋时有轻度疼痛。为了增加骨块的愈合率,作者取喙突基底的松质骨植骨于喙突骨块与肩盂接触面的内侧,之后的病例6个月CT显示骨块均已愈合。从终末随访来看,喙突平行转位组与喙突内旋90°转位组相比,无论前屈上举、平均体侧外旋、ASES评分、Constant-Murley评分或VAS不稳定评分差异均无统计学意义。内旋90°转位组患者外旋丢失程度大于平行转位组,原因可能在于患者和康复师早期担心骨块愈合,有一定的恐惧心理,不愿严格执行术后康复计划。
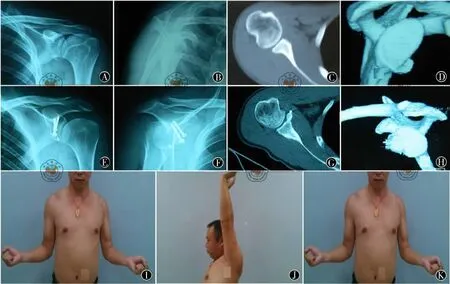
图2 喙突平行转位Latarje术式 图A、B为术前X线正、侧位片;图C、D为术前CT平扫及三维CT重建显示肩盂有骨缺损和Hill-sachs损伤;图E、F为喙突平行转位两枚螺钉固定,术后6个月X线正侧位片;图G、H为术后6个月横截面及三维CT显示喙突骨块已与肩胛盂愈合,关节面平整,肩盂形状恢复良好;图I~K为术后2年半随访肩功能恢复良好,Apprehension sign阴性,从事较重体力劳动
术中关节面的平整度对术后关节炎的发生密切相关[20],为此,作者在术中调整骨块的弧度与关节面的弧度一致和平整后,先用2枚1.0mm克氏针临时固定,再用螺丝钉最终固定,术后CT证实两组喙突骨块的弧度与关节面的弧度均较平滑,台阶小于3mm。终末随访时按照Samilson和Prieto骨关节炎的分型[10],本研究仅有6例患者终末复查时X线片出现骨关节炎表现,可能与术中精确对合喙突骨块有关,也可能与随访年限过短有关。喙突平行转位组与喙突内旋90°转位组相比,喙突平行转位组因其固定强度相对更高、接触面积更大,喙突骨块全部愈合,骨关节炎在喙突平行转位组仅发生1例,而喙突内旋90°转位组发生5例,其中3例不愈合病例均出现了轻至中度的骨关节炎表现。因此,喙突骨块不愈合会导致喙突骨块不稳定,使盂肱关节出现非同心运动也是导致骨关节炎的重要原因。
Latarjet手术虽能增加肩盂关节面的安全范围从而稳定肩关节,但改变了肩关节的自然解剖,降低了肩胛下肌肌力,导致其不同程度的挛缩,会不同程度降低肩关节外旋的范围以及后期可能出现骨关节炎[2]。因此,应严格掌握其适应证。尽管结果显示喙突平行转位较喙突内旋90°转位固定强度更高、接触面积更大、愈合率更高且骨关节炎发生率较低;但喙突内旋90°转位则能提供更大的关节面安全范围,通过在喙突骨块与肩盂接触面的内侧进行植骨则有利于骨愈合,从而减少并发症。由于本组资料样本量尚较小,且为非随机对照和回顾性的研究,这两种转位方式的选用原则尚需进一步的研究。
[1] 张伟滨,张治华,王蕾,等.喙突移位阻滞术治疗肩关节复发性前脱位[J].上海医学,2005,28(2):91-95.
[2] Provencher MT,Bhatia S,Ghodadra NS,et al.Recurrent shoulder instability:current concepts for evaluation and management of glenoid bone loss[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2010,92Suppl 2:133-151.
[3] Burkhart SS,De Beer JF.Traumatic glenohumeral bone defects and their relationship to failure of arthroscopic Bankart repairs:significance of the inverted-pear glenoid and the humeral engaging Hill-Sachs lesion[J].Arthroscopy,2000,16(7):677-694.
[4] Schmid SL,Farshad M,Catanzaro S,et al.The Latarjet procedure for the treatment of recurrence of anterior instability of the shoulder after operative repair:a retrospective case series of forty-nine consecutive patients[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2012,94:e75.
[5] Giles JW,Puskas G,Welsh M,et al.Do the traditional and modified latarjet techniques produce equivalent reconstruction stability and strength[J]?Am J Sports Med,2012,40(12):2801-2807.
[6] Sugaya H,Moriishi J,Dohi M,et al.Glenoid rim morphology in recurrent anterior glenohumeral instability[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2003,85-A(5):878-884.
[7] Chuang TY,Adams CR,Burkhart SS.Use of preoperative three-dimensional computed tomography to quantify glenoid bone loss in shoulder instability[J].Arthroscopy,2008,24(4):376-382.
[8] Calandra JJ,Baker CL,Uribe J.The incidence of Hill-Sachs lesions in initial anterior shoulder dislocations [J].Arthroscopy,1989,5(4):254-257.
[9] Snyder SJ,Banas MP,Karzel RP.An analysis of 140injuries to the superior glenoid labrum[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1995,4(4):243-248.
[10] Samilson RL,Prieto V.Dislocation arthropathy of the shoulder[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1983,65(4):456-460.
[11] Anakwenze OA,Hsu JE,Abboud JA,et al.Recurrent anterior shoulder instability associated with bony defects [J].Orthopedics,2011,34(7):538-544;quiz 545-546.
[12] Widjaja AB,Tran A,Bailey M,et al.Correlation between Bankart and Hill-Sachs lesions in anterior shoulder dislocation[J].ANZ J Surg,2006,76(6):436-438.
[13] Yiannakopoulos CK,Mataragas E,Antonogiannakis E.A comparisonof the spectrum of intra-articular lesions in acute and chronic anterior shoulder instability[J].Arthroscopy,2007(23):985-990.
[14] Robinson CM,Howes J,Murdoch H,et al.Functional outcome and risk of recurrent instability after primary traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation in young patients[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2006,88(11):2326-2336.
[15] Kim SH,Ha KI,Cho YB,et al.Arthroscopic anterior stabilization of the shoulder:two to six-year follow-up[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2003,85-A(8):1511-1518.
[16] Cole BJ,Romeo AA.Arthroscopic shoulder stabilization with suture anchors:technique,technology,and pitfalls [J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2001,(390):17-30.
[17] Porcellini G,Campi F,Paladini P.Arthroscopic approach to acute bony Bankart lesion[J].Arthroscopy,2002,18(7):764-769.
[18] Piasecki DP,Verma NN,Romeo AA,et al.Glenoid bone deficiency in recurrent anterior shoulder instability:diagnosis and management[J].J Am Acad Orthop Surg,2009,17(8):482-493.
[19] Sugaya H,Moriishi J,Kanisawa I,et al.Arthroscopic osseous Bankart repair for chronic recurrent traumatic anterior glenohumeral instability.Surgical technique[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2006,88Suppl 1Pt 2:159-169.
[20] Neyton L,Young A,Dawidziak B,et al.Surgical treatment of anterior instability in Rugby union players:clinical and radiographic results of the Latarjet-Patte procedure with minimum 5-year follow-up[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2012,21(12):1721-1727.
[21] 檀臻炜,黄富国.肩盂骨性缺损致肩关节前方不稳定的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(03):296-298.
[22] Allain J,Goutallier D,Glorion C.Long-term results of the Latarjet procedure for the treatment of anterior instability of the shoulder[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1998,80(6):841-852.
Comparison of two kinds of Latarjet procedures for recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder with severe glenoid bone defects:a 3-5year follow-up study
Xiang Ming,Yang Guoyong,Chen Hang,Hu Xiaochuan,Tang Haochen.Department of Upper Extremity,Sichuan Provincial Orthopadic Hospital,Chengdu 610041,China
Latarjet; Coracoid; Shoulder dislocation; Bony defect
Xiang Ming,Email:josceph_xm@sina.com
2013-06-23)
(本文编辑:史凤颖)
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2014.01.007
610041 成都,四川省骨科医院上肢科
向明,Email:josceph_xm@sina.com
【Abstract】ObjectiveShoulder dislocations,most of which are anterior dislocations,account for over 40%of joint dislocations.The main pathological mechanism is the dysfunction of the anteroinferior glenolabral articular ligamental complex,namely theBankart injury.Failure of the repair can cause the recurrent dislocation.Some cases are accompanied with the glenoidavulsion fracture or the bony defect,even with the inverted pear glenoid.Open or arthroscopic reconstruction can achieve excellent clinical results for the Bankart injury which bone defect is less than 25%.But if bony defect of glenoid is over 25%-30%or associtaed with Hill-Sachs injury,the re-dislocation rate is up to 67%after the simple Bankart reconstruction.The Latarjet procedure is able to reduce the recurrent dislocation significantly.This study is to retrospectively evaluate the three-to-five years'follow-up results of the Latarjet coracoid bone block procedure for the recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder associated with the severe bony defects.MethodsThirty-seven patients (23men and 14 women)underwent the Latarjet procedure for the anterior glenohumeral instability between April 2006 and October 2009.All the shoulders had the severe osseous deficiency of the anterior glenoid rim,which was more than 25%of the glenoid width according to 3-dimensional CT scan and arthroscopic findings.The patients were associtated with Engaging Hill-Sachs lesion.21patients were treated by the parallel coracoid transposition bone block from January 2008to October 2009,and 16patients were performed with the intorted coracoid transposition method from April 2006to December 2007.Apprenhension sign was positive in all of the 37patients before operation.And the mean time of their dislocations was 13.5 (ranged from 8to 28times).We evaluated the preoperative and postoperative pain,the daily living activities,the range of motion,stability of the shoulders,and function of the shoulder using the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons Assessment(ASES),the Constant-Murley Score and the VAS score.ResultsThe follow-up period ranged from 37to 61months (mean,48.3 months).All the patients got bony union in the coracoid parallel transposition group while three got a nonunion in the intorted group according to the 3dimensional CT scan taken at 6months'follow-up.For the parallel transposition group,most of the patients had a satisfactory pain relief and daily living activities postoperatively at the final follow-up.The forward elevation improved from (152.5±22.6)°preoperatively to (168.0±7.8)°postoperatively,the average external rotational limitation measured in the neutral position of the arm improved from (52.6±18.4)°to(44.9±15.0)°(t=1.486,P >0.05),the ASES scores increased from 80.7±16.7to 92.2±6.4(t =2.947,P <0.05),the Constant-Murley scores increased from 78.6±10.1to 91.6±13.2(t=-3.584,P <0.05),and the VAS scores increased from 6.0±1.4to 4.3±1.6(t =3.664,P <0.05).However,for the intorted transposition group,the forward elevation improved from (148.5±19.2)°to(170.0±10.5)°(t =3.930,P <0.05),the mean external rotation improved from (55.8±16.9)°to (40.6±13.6)°(t =2.803,P <0.05),the ASES score increased from 81.4±14.7to 92.4±7.0(t =-2.702,P <0.05),the Constant-Murley score increased from 80.2±12.6to 92.8±5.1(t=3.708,P <0.05),the VAS score increased from 6.4±1.5 to 4.2±2.1(t =3.410,P <0.05),and one patient had a residual positive Apprehension sign postoperatively,two had mild pain at the position of the maximal abduction or the external rotation.Only one got mild pain at this position in the parallel group.Secondary mild to moderate osteoarthritic changes of the glenohumeral joint were observed in six shoulders postoperatively in the final follow-up.Discussion Glenohumeral stability depends on the structure of the muscle,the ligament and the bone,which can maintain the rotation center of the humeral head and the glenoid.The incidence of shoulder dislocation in US is 11.2/10million,90%of which is areanterior dislocation.The recurrent dislocation will further change the glenohumeral joint contact area and the static stability,which reduces the stability of glenohumeral.Through the MRI examination for patients with the acute anterior shoulder dislocation,Widjaja and colleagues found that 73%of the initial dislocation were associated with Bankart injury and 67%with Hill-Sachs injury.Yiannakopoulos et al.demonstrated that the rates of Bankart and ALPSA injury were up to 97%after the repeated anterior dislocation,howerer,the rates of Hill-Sachsinjury and inverted pearglenoid were 93%and 15%,respectively.Robinson et al.reported a prospective clinical study of patients(aged from 15-35years old)after the conservative treatment forthe anterior shoulder dislocation,56%of which were re-dislocated.The instability rate of those 20-yearold males was as high as 72%-86% .The open Bankart reconstruction could restore the anterior glenoid anatomy,and had been considered as the gold standard with the 3%recurrence rate.With the development of the arthroscopic techniqueand instruments,many authors have reported the arthroscopic Bankart reconstruction with excellent results,even 20%of the patients with the glenoid bone defect had satisfactory outcomes for the reconstruction of the arthroscopic soft tissue.However,a growing number of researches show that the structural integrity of the glenoid bone is one of the key factors for the successful surgical repair.Burkhart et al.demonstrated the rate of the failure repair was as high as 67%in the soft tissue Bankart reconstruction for the obpyriform glenoid.Therefore,the bony reconstruction was recommended for the obpyriform glenoid associated with the Engaging Hill-Sachs injury.Latarjet and Helfet reported the treatment of the recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation with the coracoid process transposition had achieved satisfactory results in 1954and 1958,respectively.The principle of latarjet procedure is to make the coracoid fragment become a platform to attain the extra-articular extension of the articular surface.Its role in stabilizing the shoulder are:1the fragment increases the security area of glenoid before the humeral head is dislocated;2the conjoined tendon acts to prevent the huemral head to move forward while the external rotation of the arm;3the anteroinferior capsule can be reinforced by the translocated coracoid process and the conjoined tendon strided across the lower 1/3position of the subscapularis tendon.This study demonstrated that the Latarjet procedure had good results to treat recurrent anterior dislocation associated with severe bone defects,and significantly increased the anterior stability and the flexion of the shoulder as well as a variety of functional scores.The traditional Latarjet procedure needs to cut off the proximal subscapularis tendon,which declines the muscle strength of subscapularis and reduces the restriction of the humeral head moving forward.The overlapping suture of subscapularis and the shoulder immobilization in internal rotation cause a significant loss of the external rotation of shoulder.Osteotomy in the classic Latarjet surgery is between the origins of the pectoralis minor and the coracoclavicular ligaments.The coracoid fragment is shifted laterally to anteroinferior rim of glenoid,and its lateral edge is surfaced.In the latarjet procedure modified by de Beer,the coracoid fragment is pronated 90°along its long axis,so that the lower edge of the coracoid processis is surfaced.The width of the coracoid fragment is greater than its thickness,so the coracoid fragment has a larger contact area with the glenoidin classic transposition,and can be fixed with two 3.5mm cortical screws with more stability.On the contrary,the fragment has a smaller contact area with the glenoid in the modified transposition,and can be fixed with only two 3.0mm cannulated screws.Therefore,the classic transposition has a better biomechanical advantage and improves the union of bones.However,the modified transposition provides a greater articular surface,and are advised for the patients with the massive bone defect.In this study,the first three patients from the intorted coracoid transposition group suffered the nonunion which reduced the stabilization offered by Latarjet procedure,therefore,Apprehension sign of one case was positive,and the mild pain existed while the maximum of abduction and external rotation in the remaining two cases.In order to decrease the risk of the nonunion,we performed the autograft between the glenoid and the fragment with the cancellous bone obtained from the base of the corocoid process.There was no significant statistical differences between the parallel group and the intorted group on the forward elevation,the external rotation in the neutral position of the arm,the ASES scores,the Constant-Murley scores,and the VAS instability scores.The loss of the external rotation was obviously greater than that in intorted group,for the rehabilitation physicians were unwilling to strictly carry out the postoperative rehabilitation program due to their anxiety about the bone union.The roughness of the articualr surface is closely related with the occurrence of the postoperative arthritis.So we adjusted the curvature of the fragment to make it consistent with articular surface.The fragment was first fixed with two 1.0mm K-wires for the temporary fixation,and then screws were used for the fixation.Postoperative CT scans confirmed that the glenoid surface was relatively smooth and the step was less than 3mm.According to the Samilson and Prieto osteoarthritisclassification,6patients had OA in X-ray films in the final follow-up of this study,which might be related with the intraoperative fragment reduction and the short follow-up period.Compared with the modified transposition,the classic procedure had more stability of fixation,so the bone heeled in all cases and OA only appeared in one case.Conclusions The Latarjet coracoid bone block procedure has proved effective with a lower redislocation rate for most of the patients with the complex recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder accompanied by the severe glenoid bony defect.The parallel coracoid transposition group with more contact area and more stable fixation strength had a higher union rate compared with the coracoid intorted group.
向明,杨国勇,陈杭,等.Latarjet两种术式在治疗肩关节复发性前脱位伴重度骨缺损中3~5年随访的比较研究[J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2014,2(1):33-40.
