白芷药材水提液指纹图谱的研究
2013-12-23吕洁丽牛秉轩
张 慧 ,吕洁丽,张 崇,牛秉轩
1新乡医学院药学院药理学教研室;2 新乡医学院药学院中药学教研室,新乡453003
Introduction
The dried root of Angelica dahurica var. formosana,a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)Baizhi,is an important herbal medicine documented in Chinese Pharmacopoeia. It has been widely used as an antipyretic and analgesic for cold,headache (especially for migraine)and toothache for thousands of years in Asia[1].This herb is grown and used all over China but the concentrations of its components vary significantly due to differences in geographic origin,climate conditions,environment and other factors.Normally,the therapeutic effects of TCM are usually caused by multiple constituents.Hence,merely targeting one or few components in A.dahurica is not adequate for efficient analysis and/or quality control[2,3]. Among various methods for the quality control of herbal medicine preparations,the chromatographic fingerprinting technique is regarded as the most meaningful tool for controlling the quality of herbal samples and/or their products. The fingerprinting technique emphasizes the systemic characterization of multiple compositions in given samples and focuses on identifying and assessing the stability and variability of the plants or their preparations.Nowadays,this technique has been accepted by WHO as a methodology for the assessment of TCM,and is also taken as a method for quality control of TCM in Chinese Pharmacopoeia[4].
In addition,different chromatographic methods were used for fingerprinting analysis,such as Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC),HPLC,X-ray,and Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)[2,5]. In this study,a HPLC method was developed to investigate the fingerprints of water extracts of A.dahurica considering the traditional use of A. dahurica is based on oral rehydration water decoction.The results provided a practical method for the investigation and quality control of Angelica dahurica var.formosana.
Materials and Methods
Samples and chemicals
The dried root of Angelica dahurica var.formosana were obtained from 12 different herbal markets in 7 provinces of China,including Sichuan,Jiangsu,Yunnan,Zhejiang,Anhui,Henan,and Hebei (Table 1). The species are all Angelica dahurica (Fisch. ex Hoffm.)Benth. et Hook. f. var. formosana (Boiss.)Shan et Yuan.All herbal samples were identified by Dr.Lv Jieli from the College of pharmacy,Xinxiang Medical University,according to Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (2005). The voucher specimen (No.090302)was deposited at the Herbarium Center of Xinxiang Medical University,Xinxiang 453003,China.The sample was cut into small pieces and further ground into powder that were passed through a 20-mesh(0.9 mm)sieve and stored at 4 ℃before using.Methanol was of chromatographic grade.Deionized water was obtained from a Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore,Bedford,MA,USA).

Table 1 Sources of A.dahurica
Sample preparation
Accurately weighed sample powder (20 g)was added into a 250 mL volumetric flask with 160 mL of water.The volumetric flask was then recirculated for 2 h.The suspended particles were removed by filtering through a 0.45 μm membrane filter.20 μL of the filtered sample solution was injected into a HPLC system and separated under the chromatographic conditions described behind.
HPLC-DAD analysis
An Agilent/HP 1100 series HPLC-DAD system,consisting of a vacuum degasser,a binary pump,an autosampler,a thermostated column compartment and a photodiode array detector (DAD)(Agilent,Palo Alto,CA,USA)was used to analyze the water extracts of A.dahurica.A Lichrospher-C18column (250 mm × 4.6 mm,5 μm)manufactured by Jiangsu Hanbang Science& Technology Co.,Ltd was applied for chromatographic separation.The mobile phase consisted of water (A)and methanol (B)with a gradient program of 5%-20% (B)in 0-5 min,20%-70%(B)in 5-20 min,70% (B)in 20-30 min,and 70%-90% (B)in 30-40 min.The flow rate was 1. 0 mL/min and the column temperature was maintained at 30 ℃.The DAD detection wavelength was set at 254 nm.
Method validation
All tests below were carried out on the sample extracts prepared as described. The precision was determined by replicating HPLC injections of the same sample solution five times per day.The repeatability was assessed by analyzing six separate extracts of one sample. The sample stability was determined with measurements from a single sample solution stored at room temperature for 0,4,8,12,18 and 24 hours.
Data analysis
The correlation coefficients of entire chromatographic patterns among samples were calculated by using the Computer Aided Similarity Evaluation System (CASES),developed by the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing,China).The CASES was mainly applied in the similarity study of chromatographic and spectral patterns[2,3,6,7]..The similarities of the entire chromatographic profiles were analyzed among tested samples.The relative retention time and relative peak area of each characteristic peak to reference peak were also calculated[8,9].
Results and Discussion
Optimization of HPLC methods
The optimal DAD detection wavelength was selected in a full-scan experiment. The HPLC chromatogram at wavelength 254 nm showed richer component information and better separation than other wavelengths. In addition,as some components of the sample eluted quite late in isocratic elution mode,the gradient elution was used instead. Satisfactory separation results were obtained within 40 min for each sample.
HPLC fingerprint analysis
The relative retention time (RRT)and relative peak area (RPA)of each characteristic peak were calculated for the estimation of precision,stability and repeatability and all the results of the relative standard deviation (RSD)of RRT and RPA were found not to exceed 3.0%.Thus,all results indicated that the quality of the tested samples and the HPLC-DAD measurements were stable and under control.
The water extracts of 12 A.dahurica samples were prepared and analyzed. The chromatographic peaks that existed in all 12 samples were assigned as“common peaks”.According to the results of HPLC fingerprint,13“common peaks”were detected.The representative fingerprints of the 12 samples were shown in Fig.1.The correlation coefficients of similarity of the 12 batches were above 0.81.
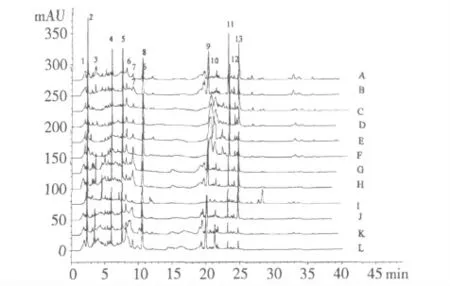
Fig.1 Typical HPLC chromatograms of 12 batches of A dahurica samples
The standardization of the fingerprint analysis was performed based on the relative retention time (the ratio of peak retention time to the reference peak retention time)and the relative peak area (the ratio of peak area to the reference peak area). Considering common peak 8 had a better separation than other peaks and eluted in the middle of the chromatogram,it was selected as the reference peak. The relative retention times and relative peak areas for all the other common peaks were then obtained and shown in Table 2 and 3.The ranges of relative retentions time and relative peak areas of the 13 common peaks of 12 batches’A.dahurica were tentatively assigned in Table 4. The position and proportion of characteristic peaks which were selected from the whole chromatogram constituted an unique chromatographic fingerprint.
Hierarchical clustering analysis
The hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA)of samples A-L was performed using SPSS 11.0 statistics software based on the relative peak areas of characteristic peaks. The furthest neighbor method was applied to generate the hierarchical clustering chart (Fig.2).
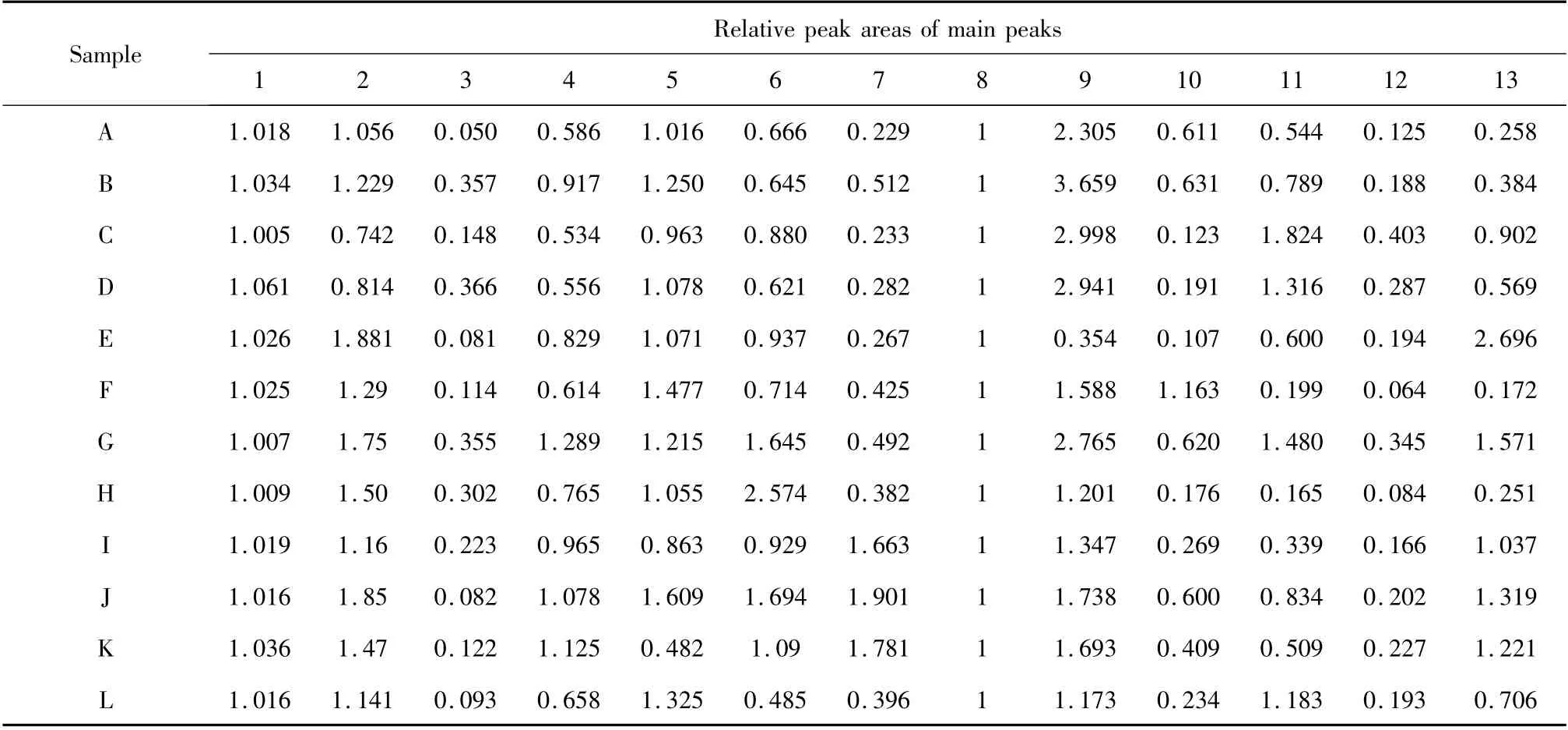
Table 2 Relative peak areas of the 13 common peaks
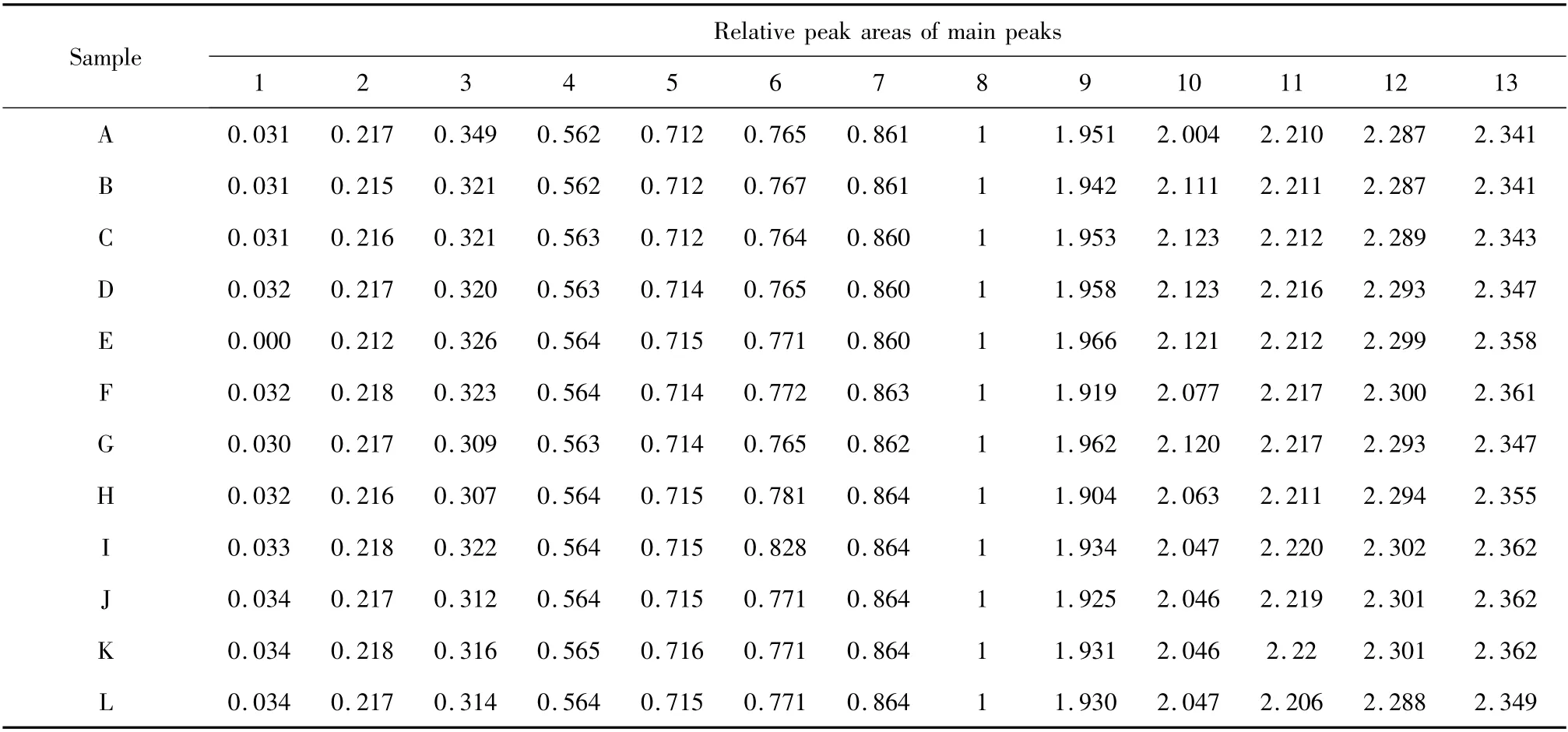
Table 3 Relative retention time of the 13 common peaks
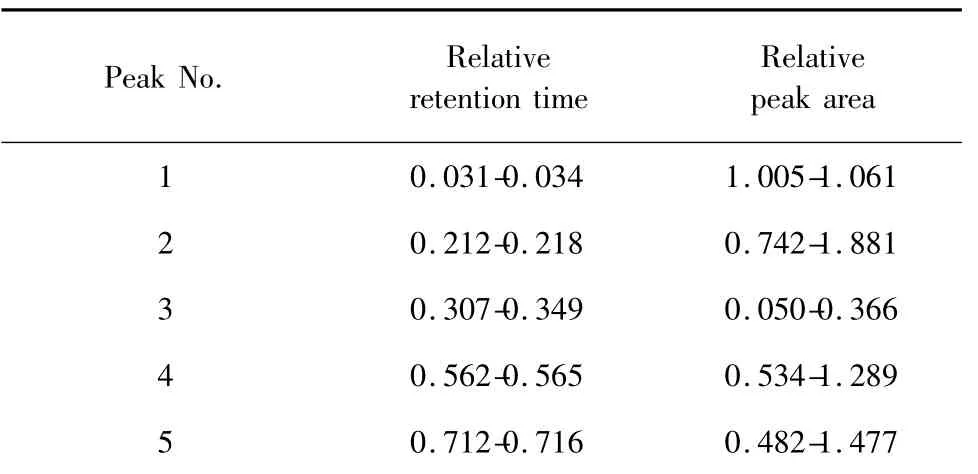
Table 4 The range of relative retention time and relative peak area of common peaks from fingerprints of 12 different samples
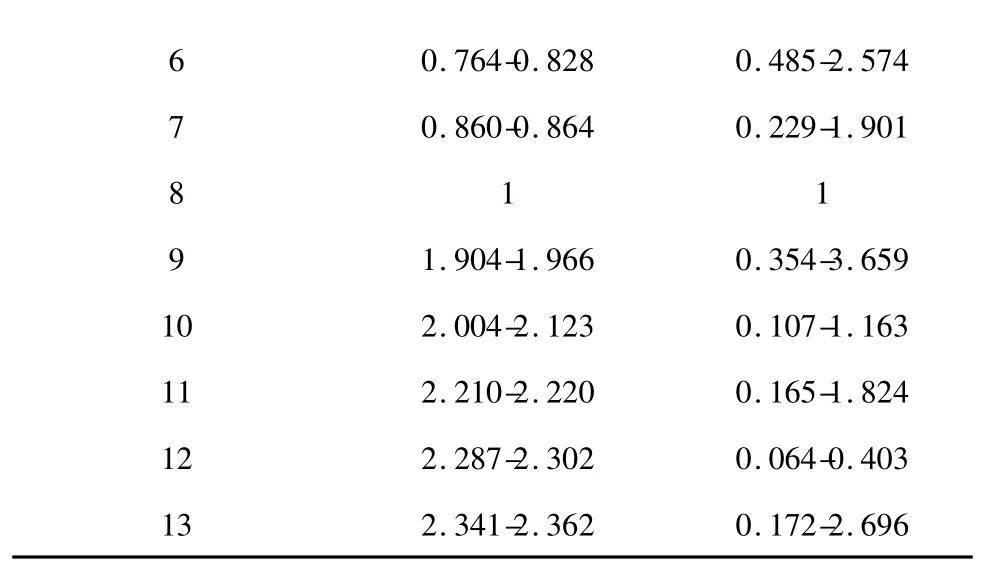
6 0.764-0.828 0.485-2.574 7 0.860-0.864 0.229-1.901 8 1 1 1.904-1.966 0.354-3.659 10 2.004-2.123 0.107-1.163 11 2.210-2.220 0.165-1.824 12 2.287-2.302 0.064-0.403 9 13 2.341-2.362 0.172-2.696
As indicated in Fig.2,the 12 samples can be divided into three clusters:samples D,I,L and E in cluster one,samle B G J and G in cluster two,and samples A,F,H and K in cluster three. A. dahurica samples from the same source showed smaller differences,e. g. A and F,H and K;the differences among samples from different sources were larger,e.g. A,F,H,K and D,L,I,E. The results suggested that the geographical source had an important influence on the quality of A.dahurica.
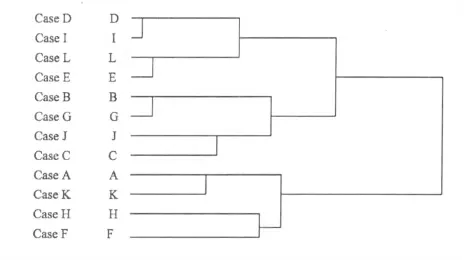
Fig.2 Hierarchical clustering analysis of 12 batches of A dahurica.samples.
Conclusion
In the present study,a HPLC method was developed for fingerprinting analysis of A. dahurica. The fingerprints of A.dahurica samples (12 batches)from different regions with 13“common peaks”were created using the developed HPLC-DAD method. The results indicated that this method was simple,reproducible and accurate for the quality control of water extracts of A.dahurica.
1 Jiangsu New Medical College. Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Shanghai:People’s Publisher of Shanghai,2000.Part I,11.
2 Li BY,Hu Y,Liang YZ,et al. Quality evaluation of fingerprints of herbal medicine with chromatographic data. Anal Chim Acta,2004,514:69.
3 Liang YZ,Xie PS,Chan K. Quality control of herbal medicines. J Chromatogr B:Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2004,812(1-2):53-70.
4 Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China.Beijing:China Medical Science Press,2005.117-118.
5 Chuang WC,Wu HK,Sheu SJ,et al.A comparative study on commercial samples of ginseng radix.Planta Med,1995,61:459-465.
6 Gong F,Liang YZ,Xie PS. Information theory applied to chromatographic fingerprint of herbal medicine for quality control.J Chromatogr A,2003,1002:25.
7 Gong F,Liang YZ,Fung YS. Correction of retention time shifts for chromatographic fingerprints of herbal medicines.J Chromatogr A,2004,1029:173.
8 Li YG,Wang ZT. Data processing and criteria selection of chromatographic fingerprint analysis of Chinese herbal medicines.Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharm,2005,1:15-19.
9 Xie PS. Traditional Chinese medicine colour spectrum and fingerprinting. Beijing:People’s Public Health Publishing Company,2005.117-119.
