3D Model Retrieval Method Based on Affinity Propagation Clustering
2013-09-16LinLinXiaoLongXieFangYuChen
Lin Lin,Xiao-Long Xie,Fang-Yu Chen
(School of Mechatronics Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150001,China)
1 Introduction
With the development and wide application of CAD/CAM technology,the number of 3D models grows greatly.How to retrieve the desired 3D model from the mass model base efficiently and to use them for redesign becomes an urgent demand.When designing 3D model for a new product,the designers often need to retrieve similar models and revise them and this will improve the design efficiency.If the number of 3D model is small,it is easy to find the suitable 3D model,but if the number of 3D models is large,it is difficult to find the desired model only by the designer’s memory in a short time.So the computer is required to speed up the design process.In addition,in other areas which need to process a large number of 3D geometry information,3D retrieval technology also has the wide application.
Feature extraction of 3D model is the most important part of retrieval technology.Feature extraction is extracting the characteristic descriptors from the 3D model and forming a feature vector,which can be utilized to distinguish 3D models.The similarity between two models can be calculated based on the feature vectors,and then the most similar 3D model is retrieved from the model bases.The algorithms of 3D model feature extraction can be divided into the following categories[1-3]:the algorithms based on the geometric information,the algorithms based on the sum moment of the spatial and frequency domain and the algorithms based on topological relationships.The raybased method[4]belonging to the geometry information method has been widely used and many feature extraction algorithms are derived from it.However,due to the low efficiency of the algorithm and its application limitations on the some issues,it should be improved in practice.In order to improve the efficiency of ray-based method,the projection ray-based method is proposed in this paper,which reduces the intersection calculation of triangular facets and rays.
The process of 3D model retrieval is calculating and comparing the similarity between the feature vectors of 3D models.Supposing there are a feature vector space F∈Rnand two feature vectors X=(x1,x2,…,xn)and Y=(y1,y2,…,yn),the similarity can be calculated by using the following methods:
(1)χ2statistical distance:
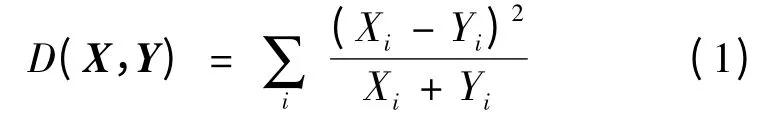
(2)Minkowski-form distance(Lp):

If n=1,the absolute distance is

If n=2,the Euclidean distance is

According to the above expressions,the largescale model base and high dimension of feature vector will lead to a high computational complexity of 3D retrieval.In order to limit the retrieval scope and improve the efficiency,the cluster algorithm is applied in the paper to find the representative models from the model base and they are used to classify the query model into the correct cluster.Then the retrieval is executed only in cluster,so it can improve the efficiency.
K-means clustering[5-6]is the most widely applied method,and it can deal with large-scale data with fast iteration speed.But K-means algorithm is sensitive to initial cluster centers and easy to fall into the local minimum.Therefore it is required to run many times with the different initialization to find the best clustering results.However,this strategy is effective only with a small number of clusters and the better initialization.
Support vector machine technology[7](SVM)has wide application in the field of data classification and it overcomes the problems of high dimension and local minimum.However,SVM is a supervised learning algorithm and a large-scale quadratic programming.As to a multi-classification problem,although various solutions are proposed,the large computation is not solved.
The recent proposed affinity propagation clustering(AP)algorithm[8-11]and K-means algorithm both belong to the K centers clustering method.However,it overcomes the shortcomings of K-means and it does not need to select the initial cluster centers.AP continually searches for the right cluster center during the iterative process,and finally makes the fitness function(objective function)of clustering maximizes.It avoids the problems of selecting initial values and it has fast run speed on large-scale data.Therefore,it is very suitable for high dimensional and large-scale classification issue.
In this paper,AP is adopted to obtain the representative models from each model base,and then the query model is determined which the most possible model base it belongs to by comparing with the representative models.Then,the above similarity Eqs.(1)-(4)are used for the most similar model retrieval from the model base.It limits the retrieval scope and improves retrieval speed and accuracy.
2 Principle and Steps of Ray-Based Method
The basic idea of the ray-based method is that:the sampling rays are emitted to some directions from the center of 3D model.If the rays intersect the triangular facets which compose the model surface,the maximum distance from the intersections to the center is used as a feature of 3D model(as shown in Fig.1.)

Fig.1 Principle of ray-based method
The feature extraction process includes the following steps:
1)The pretreatment of the 3D model:the model’s center is moved to the origin,and then the model is scaled to the unit size,and all the models are put in the same direction;
2)Supposing the model is surrounded by the unit ball whose center is the origin,the rays are emitted around uniformly,and then the coordinates of the intersection point are calculated.
A series of sampling rays through the origin in spherical coordinates can be expressed as:


Fig.2 Diagram of spherical coordinates
The coordinates of a point on a triangular facet can be expressed as:
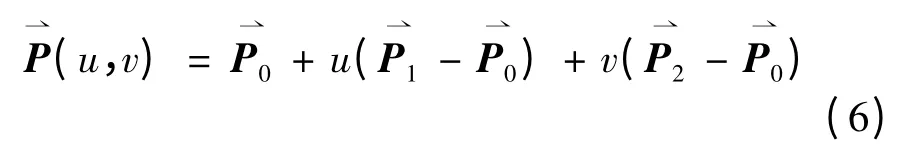

If 0≤u,v≤1,t>0,the corresponding parametersθ,φand t are saved.
3)Taking the maximum distance from the intersections to the origin as a feature of the model,and then extracting the all feature vectors from 3D model.
3 Project Ray-Based Method
3.1 Project Relationship Analysis of Ball-Section and Triangular Facets
The rays with a fixedφand variousθcompose a ball cross-section,and then the ball cross-section is projected to the section through the origin and perpendicular to the ball cross-section.The projection is a line whose equation is:

The locations of the ball cross-section and triangular facets are shown in Fig.3.

Fig.3 Relations of cross-section and triangular facets
Because the model is limited in the unit ball,the intersection of the ball cross-section and the triangular facets can be judged according to whether the project line of ball cross-section intersects the projections of the triangular facets.The relationship is shown in Fig.4.

Fig.4 Projection relationship of ball cross-section and triangular facets
Figs.3 and 4 describe the location relationship between the ball cross-section and the spatial triangle facets and the corresponding projection relationship.According to the above analysis,the location relationship between the line and the triangle in the same plane can be used to determine whether the triangle intersects the ball section.Then two judgment methods are:
1)The method based on distance.If at least one vertex of triangle is on the line or on the other side of the line,the triangle intersects the line.The distance equation from a point P(x,y)to a line through the origin is(ax+by)/,where the sign of ax+by can be used to determine the location relationship between the points and lines.Then by using the relationships between all the points of triangle and the line,whether the ball cross-section and intersect the triangular facet can be determined.For example,P1and P2are endpoints of a side L1of triangle;D1and D2are the distances from P1and P2to L2.If D1·D2≤0,L1intersects L2;otherwise,they do not intersect.The location relationship is shown in Fig.5.

Fig.5 Location relation between two lines
2)The method based on intersection angle.As to a triangle ΔABC,if one of the following Eq.(9)holds,it means that the line is through any side of the triangle,then the line and triangle intersect.The process is shown in Fig.6.

whereθAOCis the angle between the vectors OA and OC,which can be got by the cosine formula.

Fig.6 Diagram of angle relationship
3.2 Steps of Project Ray-Based Algorithm
An important way to improve the efficiency of raybased method is to reduce the number of unnecessary intersection.The idea is that:1)getting N planes with a fixedφ,differentθin the ball;2)using the method in Section 3.1 to record the triangular facets intersecting the planes.Because a plane(a ball crosssection)includes a series of rays,if triangular facets do not intersect the ball cross-section,it definitely does not intersect the rays in the ball cross-section.3)removing the rays which do not intersect the triangular facets.The steps of project ray-based method are as follows:
(1)The graticule variables l and w are initialized as 0.
(2)If l<lmax,the correspondingφis calculated,and the ball cross-section with angleφis determinate whether it intersects triangular facets.The intersected triangles facets are put into the collection s.l++.if l≥lmax,the algorithm is end.
(3)If w<wmax,the correspondingθis calculated.w++.if w≥wmax,it goes to step(2);
(4)If the index number k<smax(smaxis the maximum number of triangular facets),the corresponding variables u,v and t are calculated by using the method proposed in Section 2.k++.if k≥smax,k=0 and the algorithm returns to step(3).
(5)If the variables u,v and t do not meet the intersection conditions,t=0.Then{θ,φ,tmax}is a feature vector of 3D model.
The algorithm flow is shown in Fig.7.The variables l,w and k represent the index numbers of graticule and triangular facets while lmax,wmaxand smaxrepresent the maximum numbers of graticule and triangular facets.The variable t is the distance from the intersection to origin while tmaxis the maximum distance.

Fig.7 Flow of projection ray-based algorithm
Supposing the number of rays is M×M,the number of the triangular facets that compose the surface of a 3D model is K;the vertices number of triangles facets is P and the final number of the triangular facets needed to be calculated for the intersection is S.
Because the computation of removing the nointersection triangular is much smaller than intersection calculation between the rays and triangle facets,it can be ignored.The iteration times in ray-based method is M×M×K;the iteration times in the improved project ray-based method is M×M×S.Thus,the ratio of computing work is K/S.The larger K/S means that the method is more effective.The number of removed nointersection triangular facets is M×P by method based on distance and M×K by method based on intersection angle.The computation of method based on distance is M×M×(K-P),which is less than that of method based on intersection angle.From Eq.(9),it can be concluded that intersection judgment by method based on intersection angle is more complexity than that by method based on distance.Therefore,the method based on distance is better.
The above approach uses single-layer sphere to extract features.However,this approach ignores the inner information of the model,so it is only suitable for convex model.In order to use the inner information of models when the approach is utilized in dealing with models with other topological structures,multi-layer spheres approach is proposed.The steps are:(i)limiting the model in a ball;(ii)dividing the ball into N layers averagely;(iii)emitting the rays from center to sampling points on each sphere,and calculating the intersection points of rays and the model.If there is no sampling point between the(n-1)-th sphere and n-th sphere,then this sampling point is eliminated as the features of n-th layer,where n=1,2,…,N.
Now the examples are presented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.The singlelayer sphere is utilized firstly,and the project raybased algorithm is utilized to extract features.Then the Euclidean distance is utilized to compare the similarity between models,and the results are used to draw the Precision-Recall diagram to evaluate the precision of the retrieval.
The Precision and Recall represent the precision ratio and recall ratio respectively,and they can be utilized to evaluate the retrieval results.Precision ratio is the ratio of correct models in all retrieved models,and it is utilized to evaluate the precision of retrieved results.Precision ratio is calculated as the number of correct models divided by the number of retrieved models.Recall ratio is the ratio of correct retrieved models in all models,and it is utilized to evaluate the ability to retrieve the correct models.Recall ratio is calculated as the number of correct retrieved models divided by the number of all models.So in the Precision-Recall diagram,the curve which is closer to upper-right means the retrieved results are better.
The models of bottle and box are utilized as test data,and the number of rays is 1024.In the experiments,the results of different models are different,as shown in Fig.8.According to the results in Fig.8,the precise of box models is lower than that of bottle models,and the reason is that the topological structure of box models is more complicated than that of bottle models.There is plenty inner information in box models,so the single-layer sphere cannot describe these models accurately.
The results of box models are not very good when using single-layer sphere,so two-layer spheres are used,and the precision is improved.The results are shown in Fig.9.
According to the experiments,the multi-layer spheres project ray-based approach can extract the features of models with the complicated topological structure effectively.
The Gear models,Lflange models and Sflange models are also taken as testing models.In the experiments,the ray numbers are set as 1024,and then the numbers of spheres are increased from 1 to 3.The results show that retrieved precision of two-layer spheres method is much better than one-layer sphere method,while the retrieved precision of three-layer spheres method is only little better than one-layer sphere method.Thus,the number of spheres should be set a reasonable value.The experiment also evaluates the number of rays.The ray numbers are set as 64256 and 1024,and the results show that the precision increases as the increase of ray numbers,while the improvement is not very obvious.Thus,generally,the ray number is set as 1024,and the two-layer sphere method is utilized.In this way,the feature vector of 3D models contains more information.It uses finegrained features to describe 3D models,so it is more accurate and it can improve the retrieval precision.
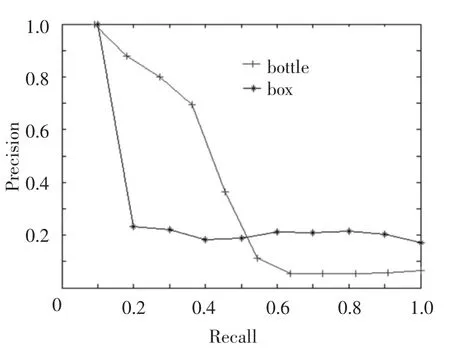
Fig.8 Results of bottle and box models
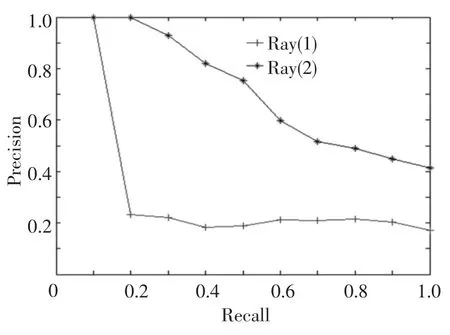
Fig.9 Results of box models
4 Affinity Propagation Clustering Method
Affinity propagation clustering(AP)is a new clustering algorithm and its run speed is fast even for multi-classification problem.Before the iteration process of AP,the similarity matrix S:S(i,j)=-‖xi-xj‖2consisting of the similarity between data points is fed as input.The algorithm first takes all the data points as the potential cluster centers and supposes that there are messages energy r(i,k)and α(i,k)between any two data points i and k.The r(i,k)is value message sent from point i to the candidate cluster center point k,which is used to evaluate whether the point k is of suitability as the cluster center for the point i;α(i,k)is the value message sent from candidate cluster centers k to point i,which is used to evaluate whether the point i is ready to select the point k as the cluster centers.The stronger the information energy r(i,k)andα(i,k)are,the more possible the point k is as the clustering center,while the point i is more possible to belong to the class with the center point k.The expressions of r(i,k)andα(i,k)are shown in the following equations:

In order to avoid vibrations during the iteration process,the damping factorλis introduced in the algorithm,and the message energy in the iteration t is:
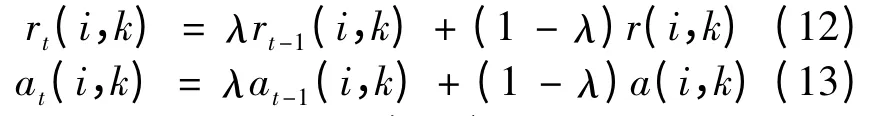
The diagonal values S(k,k)in S matrix are used as the evaluation criteria for a point k being a cluster center,which is called the bias parameter p(k).Generally,the median of all non-diagonal elements is adopted as the value of p(k).The parameter p(k)is used in Eq.(14).
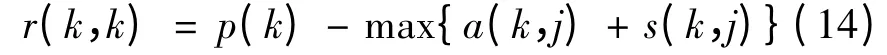
A larger p(k)leads to larger r(k,k)and a(i,k),which means the point k is more possible to be the final cluster center.When p(k)is larger,more points tend to be the final cluster centers.Therefore,enlarging p(k)or not can increase or decrease cluster numbers produced by AP.
The steps of AP algorithm are as follows:
(1)Initializing the elements of similarity matrix S,attraction matrix R and the attribution matrix A as 0,and the damping factorλ=0.5,the number of iterations t=1,the maintain number of cluster information count=0.Assigning the maximum iteration number tmaxand the maximum information maintain number countmaxand the medians of all S-diagonal elements to p(k);
(2)The new attraction r(i,j)and new attributions a(i,j),a(i,i)in iteration t are calculated by Eqs.(10)to(11);
(3)The final attraction r(i,j)and final attributions a(i,j),a(i,i)in iteration t are calculated by Eqs.(12)to(13);
(4)Finding the representative points by the equation ei
(5)Repeating steps(2)-(4)until the representative points keep consistent during many times iteration or t≥tmax.
According to AP algorithm,it assumes that all the clusters in feature space are compact.In AP,the energy function is the sum of similarities between samples and cluster centers,which is E(C)=.Supposing that the number of clusters is J,and AP minimizesThus,if the cluster structure is compact,it is easy to guarantee that each Ejis small,and thenEjis small,so AP can achieve good results in this condition.But if the cluster structure is loose,that is to say,the clusters are not very clear,AP algorithm tends to produce more clusters to make every Ejand minimizeEj,so AP would produce too many clusters,and the results are not accurate.
In order to improve the accuracy of AP algorithm and make the algorithm effective when the scale of model set changes or the complex degree of models changes,the semi-supervised AP clustering algorithm(S-AP)in Ref.[12]is utilized to cluster 3D models.
In S-AP algorithm,the clustering centers are also determined according to smaller Ej,but the objective function is not minimizingEj,while it uses validity index to supervise the clustering.The Silhouette index[13]is used as the validity index.
Supposing that a(t)is the average dissimilarity or distance between sample t in cluster Cjand all the other samples in this cluster,while d(t,Ci)is the average dissimilarity or distance between sample t and samples in another cluster Ci,and b(t)=min{d(t,Ci)},i=1,2,…,k,i≠j.Then the Silhouette index of sample t is
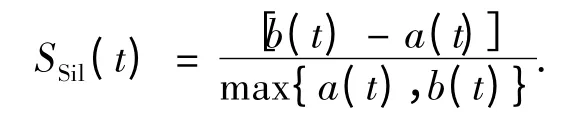
The average of SSilvalues of all the samples in data set can represent the quality of the clustering results.The larger average Silhouette index is,the better the quality of clustering is,so the cluster results of the maximum index is the best result of clustering.In AP,the number of clusters increases and decreases with the increase and decrease of the value of p.In S-AP,the initial value of p is the median of attraction degree pm,and its value decreases dynamically to obtain smaller number of clusters.Then the maximum SSilmaxand its clustering results are obtained.The increment of p is Δp=pmin/10,where pminis the minimum of attraction degree.The flow of S-AP algorithm is shown in Fig.10.
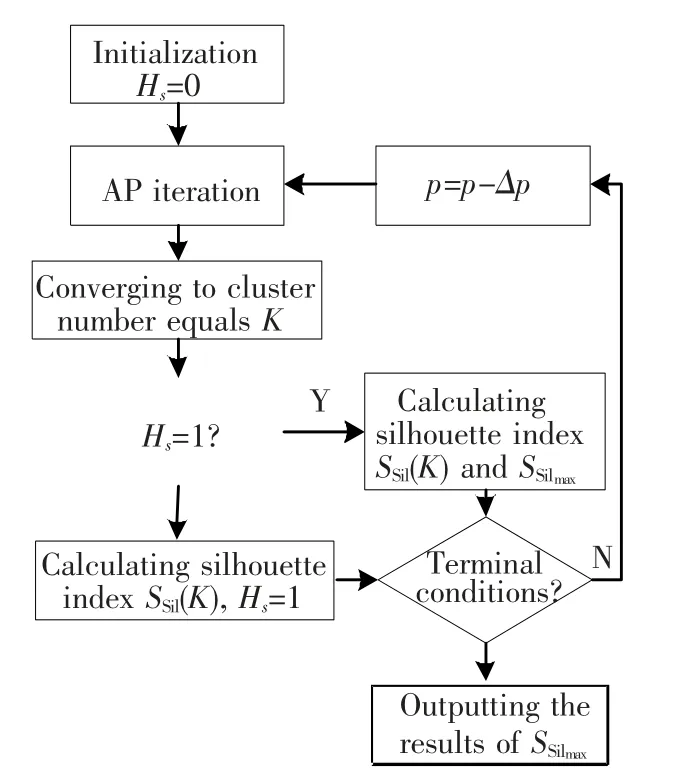
Fig.10 Flow of S-AP
AP algorithm is an unsupervised method,but searching representative models as cluster centers in 3D models is a classification problem which is a supervised problem.In order to enhance the effectiveness of AP algorithm,the similarity matrix S which is input into the algorithm is modified.

In this study,the similarity between two samples in one cluster multiplies a weight to increase the information energy between samples in one cluster and decrease the information energy between samples in different clusters.This modification can make the cluster center model more representative because a sample model which is on the edge of two clusters is not likely to be a cluster center.Supposing that the set of cluster centers is,and the number of models in k-th cluster isThe computational complexity is,while the computational complexity of original approach is
5 Simulation and Result Analysis
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method proposed,6 types of 3D models are selected from the Princeton library[14].The projection ray-based method is used to get the 256 feature vectors(i,j,Dij)by emitting 16×16 rays,where i≤16,j≤16 are the index number of graticule and Dijis the maximum distance from the intersections to origin.The 3D models include bottle,flange,gear,gun,helicopter and human body model.The parts of the sample models are shown in Fig.11.

Fig.11 Parts of the sample models
First,AP algorithm is adopted to classify the 78 models in 6 model bases in order to find the center models of each base which are representative and distinctive.The test environment is Windows XP.MATLAB 7.1 software is used for simulation.The clustering error is calculated as follows:

The clustering results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Clustering results
The clustering errors of gun and helicopter models are larger.The reason is that the gun and helicopter models have a lot of detailed characteristic.As mentioned above,a ray may intersect several facets,but only the maximum distance from the intersections to origin is adopted as the feature vector.So the features extracted from gun and helicopter models cannot describe the models exactly.However,for the convex models,such as the human body,flange and bottle models,the clustering results are better.Therefore the ray-based methods are not suitable for the 3D models with more detail characteristics.The extraction method with higher precision can be used in this situation:such as wavelet moments[15],3D Zernik moments[16],Fourier analysis[17],and spherical harmonic analysis method[18-20]and other 3D model feature extraction methods.
(1)The analysis of computation complexity.First,the Euclidean distance between the retrieved model and the center models is utilized to judge which model base it may belong to.

Then,the retrieval algorithm searches in the corresponding model base for the most similar 3D model.The total computational complexity is

However,if retrieval from all of the model bases by the original method,the calculation isDue to,therefore,the calculation of the method is much smaller than that of original method.
(2)The analysis of precision.39 bottle,body and flange models are selected from 75 samples for testing.After clustering by Eq.(15),the clustering error is 0.This means that the all 39 models are classified to the correct model base.The most similar model and the entire similar models will be retrieved from the correct model base.Therefore the recall and precision rates are 100%.On the other hand,the 3D retrieval system developed by the paper is used to retrieve the similar model from all the model bases.With the 256 feature vectors extracted by the project ray-based method,the retrieval process of the 3 bottle,3 human body and 3 flange models are done(as shown in Figs.12-14).The retrieval results are listed in descending order of the similarity,and the first 10 retrieved models are taken to calculate the precision rate which is shown in Table 2.
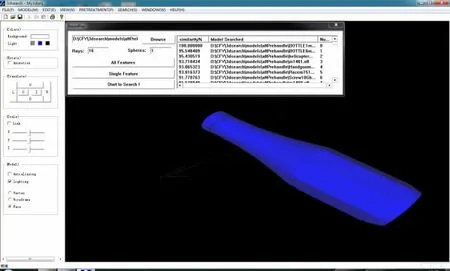
Fig.12 Interface of bottle retrieval

Fig.13 Interface of flange retrieval
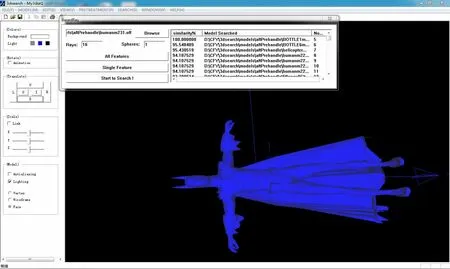
Fig.14 Interface of human body retrieval

Table 2 Results of model retrieval
From Table 2,the retrieval precisions of 3 types of models are low.The reasons are that less feature vectors are extracted,and moreover,the limitation of ray-based method itself.It is inaccurate that only the maximum distance is extracted as the feature vector for 3D model.However,even in the case of fewer features,the method proposed by the paper can achieve the higher retrieval precision,which shows that the method is of the practicability and effectiveness.
6 Conclusions
The project ray-based method which reduces the computational complexity and improves the extraction efficiency is proposed for feature extraction of 3D models in this paper.In feature extraction,multi-layer spheres method is proposed and the choice of ray number and sphere number are discussed.The twolayer spheres method is utilized and it can make the feature vector more accurate and improve retrieval precision.Semi-supervised Affinity Propagation(SAP)Clustering is utilized because it can be applied to different cluster structures.S-AP algorithm is adopted to cluster and find the center models which can represent the model library.The query model is firstly classified to corresponding model base,and then,the most similar model is retrieved in the model base.The S-AP clustering algorithm is efficient and its clustering results are more accurate.In feature extraction,the multi-layer spheres method can extract accurate features even for complicated 3D models,and in model retrieval,the application of S-AP improves the retrieval efficiency.
[1]Cui Chenyang,Shi Jiaoying.Analysis of feature extraction in 3D model retrieval.Journal of Computer-aided Design&Computer Graphics,2004,16(7):882-889.(In Chinese)
[2]Yang Yubin,Lin Hui,Zhu Qing.Content-based 3D model retrieval:a survey.Chinese Journal of Computers,2004,27(10):1297-1310.(In Chinese)
[3]Zheng Bochuan,Peng Wei.A survey on 3D model retrieval techniques.Journal of Computer-aided Design&Computer Graphics,2004,16(7):873-881.(in Chinese)
[4]Vranic D V,Saupe D.3D model retrieval.Proceedings of Spring Conference on Computer Graphics.Budmerice,Slovakia.2000.89-93.
[5]Chang Chihtang,Lai Jim Z C,Jeng Muder.A fuzzy Kmeans clustering lgorithm using cluster center displacement.Journal of Information Science and Engineering,2011,27(3):995-1009.
[6]Ahmad Amir,Dey Lipika.A K-means type clustering algorithm for subspace clustering of mixed numeric and categorical datasets.Pattern Recognition,2011,32(7):1062-1069.
[7]Cortes C,Vapnik V.Support-vector networks.Machine Learning,1995,20(3):273-297.
[8]Frey B J,Dueek D.Clustering by passing messages between data points.Science,2007,315(5814):972-976.
[9]Guan Renchu,Shi Xiaohu,Marchese Maurizio.Text clustering with seeds affinity propagation.IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2011,23(4):627-637.
[10]Guo Kun,Zhang Qishan.Affinity propagation clustering based on grey relational analysis.Journal of Grey System,2010,22(2):147-156.
[11]Kelly K.Affinity program slashes computing times.http://www.news.utoronto.ca/bin6/070215-2952.asp,2007-10-25.
[12]Wang Kaijun,Li Jian,Zhang Junying,et al.Semi-supervised affinity propagation clustering.Computer Engineering,2007,33(23):197-201.(in Chinese).
[13]Dudoit S,Fridlyand J.A prediction-based resampling method for estimating the number of clusters in a dataset.Genome Biology,2002,3(7):0036.1-0036.21.
[14]Dobkin D.Princeton shape retrieval and anlysis group.http://shape.cs.princeton.edu/search.html.2001-11.
[15]Cui Li.The theories of N-D generalized quasi-real wavelets&wavelet moments and their applications.Jilin:Jilin University.2004.33-86.
[16]Novitni M,Klein R.3D Zernik descriptors for content based shaped retrieval.Proceedings of ACM Symposium On Solid Modeling And Applications.Washington,D C.2003.216-225.
[17]Osada R,Funkhouser T,Chazelle B,et al.Shape distributions.ACM Transaction on Graphics,2002,21(4):807-823.
[18]Vranic D V,Saupe D.3D model retrieval with spherical harmonics and moments.Proceedings of the DAGM 2001.Munich.2001.392-397.
[19]Vranic D V,Saupe D,Richter J.Tools for 3D-object retrieval:Karhuner-Loeve transform and spherical harmonics.Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing.Cannes.2001.293-296.
[20]Vranic D V,Saupe D.An improvement of rotation invariant 3D-shape descriptor.Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing.Barcelona.2003.757-760.
杂志排行
Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology(New Series)的其它文章
- Slip Detection of Robotic Hand Based on Vibration Power of Pressure Center
- An Ant Colony Algorithm Based Congestion Elusion Routing Strategy for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
- Robust Audio Blind Watermarking Algorithm Based on Haar Transform
- Research of Multiagent Coordination and Cooperation Algorithm
- Impact of Online Community Structure on Information Propagation:Empirical Analysis and Modeling
- Prediction of Aircraft Engine Health Condition Parameters Based on Ensemble ELM
