DNA-PKcs协同自身免疫调节因子调控小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞Toll样受体的表达及其意义
2012-12-06付海英张英林孙际童
吴 静,付海英,张英林,孙际童,杨 巍
(1.吉林大学白求恩医学院免疫学系,吉林 长春130021;2.吉林大学第一医院转化医学研究院,吉林 长春130021)
DNA-PKcs协同自身免疫调节因子调控小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞Toll样受体的表达及其意义
吴 静1,2,付海英1,张英林1,孙际童1,杨 巍1
(1.吉林大学白求恩医学院免疫学系,吉林 长春130021;2.吉林大学第一医院转化医学研究院,吉林 长春130021)
目的:探讨小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞内DNA-PKcs协同自身免疫调节因子调控Toll样受体(TLRs)的表达水平,阐明外周免疫系统中自身免疫调节因子的调控作用及其意义。方法:小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞分为pEGFPC1/m Aire转染组、p EGFPC1/m Aire与negative control siRNA共转染组、p EGFPC1/m Aire与DNA-PKcs siRNA共转染组、p EGFPC1转染组、p EGFPC1与negative control siRNA共转染组和pEGFPC1与DNA-PKcs siRNA共转染组,采用RT-PCR方法检测各组小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞内TLR1~9的表达水平;采用脂质体转染重组质粒p EGFPC1/m Aire和空载质粒p EGFPC1至小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞,采用RT-qPCR方法检测2组细胞TLR1~9的表达水平;采用RT-qPCR方法检测2组转染细胞沉默DNA-PKcs前后TLRs的表达水平。结果:小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞能表达TLR1~9;与转染pEGFPC1/m Aire组细胞比较,转染自身免疫调节因子后巨噬细胞TLR1、3和8的表达水平增加(P<0.05),其他组TLRs表达水平无明显变化(P>0.05);DNA-PKcs沉默后,转染pEGFPC1/m Aire组细胞TLR1、3和8的表达水平较未沉默组明显下降(P<0.05),而在转染p EGFPC1的细胞内DNA-PKcs沉默前后TLR1-9表达水平均无明显变化(P>0.05)。结论:在小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞内,自身免疫调节因子能够调控TLR1、3和8的表达,其机制可能与DNA-PKcs协同作用有关。
自身免疫调节因子;巨噬细胞;Toll样受体;协同分子
自身免疫调节因子(autoimmune regulator,Aire)作为一个重要的转录激活子,主要表达于胸腺髓质上皮细胞(medullar thymic epithelial cells,m TECs),调节许多外周组织自身抗原(peripheral tissue self-antigen,PTA)的 表 达[1],从而诱导中枢耐受。此外,在外周组织中也存在自身免疫调节因子的表达,包括外周淋巴器官、胎儿的肝 脏、 睾 丸 和 卵 巢[2-3]。Suzuki等[4]研 究 显 示:在外周血CD14+树突状细胞(dentritic cell,DC)、巨噬细胞、粒细胞和B细胞中可检测到自身免疫调节因子基因的表达。目前,虽然自身免疫调节因子在胸腺中的功能较为明确,但其在外周的意义尚不清楚。本课题组前期研究[5]结果显示:在稳定转染自身免疫调节因子的小鼠巨噬样细胞系RAW264.7细胞内,自身免疫调节因子能够上调Toll样受体(Toll like receptor,TLR)1、TLR3和TLR8的表达,但是自身免疫调节因子在正常细胞内是否具有相同的作用以及其影响TLR1、3、8表达的机制尚不清楚。许多研究[6]表明:自身免疫调节因子不是一个经典的转录因子[1],其需与其他蛋白相互协作进而调控目的基因的表达[1,7-8],如DNA 依 赖 的 蛋 白 酶(DNA-dependent protein kinase,DNA-PK)是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,属于磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)家族成员,以一种全酶的形式存在,包括2个调节亚单位Ku70,Ku80和1个大的催化亚单位—正DNA-蛋白激酶(catalytic sunbunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase,DNA-PKcs)。DNA-PKcs能够正向或负向调节转录[9-10]。本研究旨在探讨在小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞内DNA-PKcs是否能够与自身免疫调节因子相互作用促进TLRs的表达,为研究自身免疫调节因子在外周的功能提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物及主要试剂 BALB/c小鼠购自吉林大学实验动物中心,6~8周龄,体质量18~22 g,合格证号:SCXK吉2003-001。主要试剂:RPMI 1640培养基(Invitrogen公司,USA),胎牛血清(杭州四季清公司),胰酶(北京鼎国生物技术有限责任公司),琼脂糖(厦门百维信生物科技有限公司),逆转录酶(Takara公司,日本),TransFast Taq聚合酶、DNA Marker(北京全式金生物技术有限公司),2.5 mmol·L-1d NTP、Oligod T(天根生物试剂有限公司),PCR引物(上海生工生物技术有限公司合成)。
1.2 siRNA的合成和转染 siRNA是由广州锐博生物(RiboBio公司,中国)设计合成。采用RT-qPCR方法检测到了最有效的一对siRNA(si-m-Prkdc-003)应用于后续实验的研究。si-m-Prkdc-003 的 序 列 如 下:Sense,5′-GGAUCGAGCUGUUCAGAAA d Td T-3′; Anti-sense,3′-d Td T CCUAGCUCGACAAGUCUUU-5′。先向12孔培养板中接种细胞,融合度达到40%~60%,24 h后采用Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂(Invitrogen公司,USA)进行转染,6 h后更换新的培养基。细胞培养48或72 h后,收集细胞,采用RT-qPCR方法检测DNA-PKcs的沉默效率。
1.3 小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞的分离和转染 BALB/c小鼠腹腔内注射1 m L 3%淀粉,第4天用8 m L PBS冲洗腹腔,收集腹腔液并离心后重悬于含10%胎牛血清的1640培养基中,并接种于12孔培养板内(4×105m L-1)。37°C培养3 h后,用培养液洗去未黏附的细胞,黏附的细胞即为巨噬细胞。采用Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂将p EGFPC1/m Aire或p EGFPC1质粒(由本室构建并保存)分别转染小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞,48 h后收集细胞进行检测。DNA-PKcs沉默时,将p EGFPC1/m Aire细胞分为p EGFPC1/m Aire转染组、p EGFPC1/m Aire与 negative control siRNA共转染组、p EGFPC1/m Aire与DNA-PKcs siRNA共转染组,将p EGFPC1细胞分为p EGFPC1转染组、p EGFPC1与negative control siRNA共转染组,p EGFPC1与 DNA-PKcs siRNA 共转染组,48 h后收集各组细胞进行检测。
1.4 RT-PCR 与 RT-qPCR 采 用 RNAisoTMPLUS(Takara公司,Japan)提取总 RNA。以1μg RNA进行逆转录,条件为30℃、10 min;42℃、60 min;70℃、15 min,4℃、10 min,1个循环。TLRs的引物序列见文献[5]。DNA-PKcs的引物序列:Sense,5′-ATTGCTGTATCAAGGCTCA-3′;Antisense,5′-ACACTTCCTCCAGTTCTGC-3′。PCR 反 应 条 件:95 ℃、2 min;95℃、30 s,58℃、30 s,72℃、1 min,72℃、10 min,共35个循环。qPCR的反应条件:95℃、10 min;95℃、15 s,60℃、1 min,共40个循环;95℃、15 s,60℃、1 min,95℃、15 s,1个循环。用ABI PRISM7300检测系统(Applied Biosystems公司,USA)进行检测。
1.5 流式细胞术(FCM)检测siRNA沉默效率 小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞转染青色素染料(Cy3)荧光标记的转染对照siRNA。细胞培养24 h后收细胞,PBS洗3遍,1000 r·min-1离心5 min,用4%的多聚甲醛重悬细胞以备上机检测,以未转染siRNA细胞做为对照,Cy3阳性细胞比率即为沉默效率。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 10.0统计软件进行数据分析,小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLRs和DNA-PKcs表达水平以±s表示,组间比较采用Student’s t检验。
2 结 果
2.1 小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLRs的表达水平 采用RT-PCR方法检测小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLR1~9的表达水平,小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞表达TLR1~9。见图1。
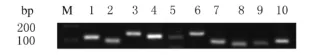
图1 小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞中TLR1~9表达电泳图Fig.1 Electrophoregram of expressions of TLR1-9 in peritoneal macrophages of mice
2.2 自身免疫调节因子作用后小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLRs表达水平 采用RT-qPCR方法检测瞬时转染自身免疫调节因子的小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLR1~9 mRNA 表 达 水 平。p EGFPC1/m Aire转 染 组TLR1、TLR3和TLR8的表达水平均较转染p EGFPC1组增加(P<0.05),而其他组TLRs的表达水平与转染p EGFPC1组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1
表1 自身免疫调节因子作用后小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞上TLR1~9的表达水平Tab.1 The expression levels of TLR1-9 in peritoneal macrophages in mice after treated with Aire (±s)

表1 自身免疫调节因子作用后小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞上TLR1~9的表达水平Tab.1 The expression levels of TLR1-9 in peritoneal macrophages in mice after treated with Aire (±s)
*P<0.05 vs p EGFPC1 group.
Group TLR1 TLR2 TLR3 TLR4 TLR5 p EGFPC1 1.03±0.03 1.00±0.11 1.01±0.06 1.02±0.02 1.21±0.10 pEGFPC1/m Aire 1.77±0.05* 1.37±0.04 1.87±0.08* 1.03±0.03 1.00±0.09 Group TLR6 TLR7 TLR8 TLR9 pEGFPC1 1.01±0.13 1.07±0.05 1.00±0.10 1.09±0.05 p EGFPC1/m Aire 1.06±0.09 0.94±0.20 1.87±0.06*1.31±0.06
2.3 DNA-PKcs协同自身免疫调节因子作用后小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLRs的表达水平 siRNA的转染效率能够达到71%(图2)。采用RT-qPCR方法检测DNA-PKcs和TLR1~9 mRNA的表达水平,在瞬时转染p EGFPC1/m Aire和p EGFPC1的巨噬细胞中,DNA-PKcs沉默组较negative control组DNA-PKcs的表达水平明显下调。pEGFPC1/m Aire瞬时转染的细胞在DNA-PKcs沉默后,TLR1、TLR3和TLR8的mRNA表达水平明显下调,而在p EGFPC1瞬时转染的细胞中,TLR1、TLR3和TLR8的表达水平无明显变化。TLR2、TLR4、TLR5、TLR6、TLR7和 TLR9表达水平在2组细胞内均无明显变化。见表2~4。
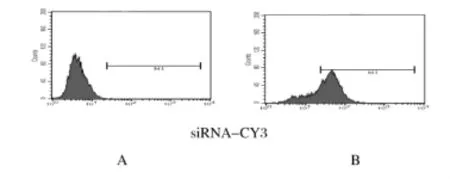
图2 流式细胞术检测siRNA转染效率Fig.2 The siRNA transfection efficiency detected by FCM
表2 DNA-PKcs沉默后p EGFPC1和p EGFPC/m Aire巨噬细胞中DNA-PKcs mRNA的表达水平Tab.2 The expression levels of DNA-PKcs mRNA in p EGFPC1 and p EGFPC1/m Aire macrophages after DNAPKcs silence (±s)

表2 DNA-PKcs沉默后p EGFPC1和p EGFPC/m Aire巨噬细胞中DNA-PKcs mRNA的表达水平Tab.2 The expression levels of DNA-PKcs mRNA in p EGFPC1 and p EGFPC1/m Aire macrophages after DNAPKcs silence (±s)
*P<0.01 vs negative control siRNA group.
Group pEGFPC1 pEGFPC1/m Aire Negative control siRNA 1.00±0.03 1.00±0.12 DNA-PKcs siRNA 0.52±0.12* 0.51±0.04*
表3 DNA-PKcs沉默后p EGFPC1/m Aire巨噬细胞TLR的表达水平Tab.3 The expression levels of TLR in pEGFPC/m Aire macrophages after DNA-PKcs silence (±s)
表3 DNA-PKcs沉默后p EGFPC1/m Aire巨噬细胞TLR的表达水平Tab.3 The expression levels of TLR in pEGFPC/m Aire macrophages after DNA-PKcs silence (±s)
*P<0.05,**P<0.01 vs negative control siRNA group.
Group TLR1 TLR2 TLR3 TLR4 TLR5 Negative control siRNA 1.01±0.05 1.00±0.06 1.02±0.08 1.21±0.10 1.01±0.14 pEGFPC1/m Aire 1.00±0.08 0.98±0.03 1.00±0.10 1.19±0.07 1.00±0.14 DNA-PKcs siRNA 0.43±0.08** 0.83±0.15 0.49±0.05* 1.20±0.04 1.11±0.17 Group TLR6 TLR7 TLR8 TLR9 Negative control siRNA 1.01±0.14 1.01±0.13 1.03±0.08 1.00±0.06 p EGFPC1/m Aire 1.00±0.13 0.99±0.12 1.01±0.09 0.99±0.04 DNA-PKcs siRNA 0.97±0.09 1.00±0.12 0.53±0.10*1.09±0.14
表4 DNA-PKcs沉默后p EGFPC1巨噬细胞TLR的表达水平Tab.4 The expression levels of TLR in p EGFPC macrophages after DNA-PKcs silence (±s)

表4 DNA-PKcs沉默后p EGFPC1巨噬细胞TLR的表达水平Tab.4 The expression levels of TLR in p EGFPC macrophages after DNA-PKcs silence (±s)
Negative control siRNA 1.01±0.06 1.00±0.10 1.00±0.10 1.00±0.09 pEGFPC1 1.00±0.07 1.00±0.05 0.99±0.03 1.00±0.04 DNA-PKcs siRNA 0.98±0.02 1.10±0.08 0.91±0.03 0.98±0.07
3 讨 论
自身免疫调节因子的基因突变可导致自身免疫性多内分泌腺病-念珠菌病-外胚层营养不良(autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasesectodermal dystrophy,APECED),主要表现为慢性皮肤黏膜的念珠菌病、甲状旁腺功能减退和Addison’s病[11]。有研究[4,12]显示:许多蛋白能够协同自身免疫调节因子作用调控其内源性基因的表达。自身免疫调节因子的协同分子按功能大概分为4类:核转运、染色质结合、转录和pre-mRNA加工[1]。研 究[8,13]显 示: 一 组 蛋 白(DNA-PKcs、PARP-1、 TOP2a、 FACT、 Ku80、 Ku70 和H2AX)可能与自身免疫调节因子形成大的分子复合体,参与自身免疫调节因子介导的调控内源性基因的表达;另外一些蛋白与自身免疫调节因子相互作用参与pre-mRNA的剪接,即为自身免疫调节因子能够有效地加工许多PTA转录的原因。
DNA-PKcs能够被断裂的DNA双链激活,并且在其重组过程中发挥重要作用[9,14]。DNA-PKcs能够磷酸化许多参与转录过程中的蛋白,例如RNA聚合酶Ⅱ(Pol-Ⅱ)、Fos、Jun和TATA盒结合蛋白(TATA binding protein,TBP)等[14]。Liiv等[7]采用pull-down实验检测转染自身免疫调节因子的单核细胞发现:DNA-PKcs能够与自身免疫调节因子相互作用,并且进一步采用广泛的质谱分析证实了这一点。体外研究[7]也表明:DNAPKcs能够磷酸化自身免疫调节因子并且影响自身免疫调节因子的转录激活能力。本研究结果显示:在原代小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞内,自身免疫调节因子能够调控TLR1、3和8表达。DNA-PKcs沉默后,p EGFPC1/Aire瞬时转染的巨噬细胞内的TLR1、3和8表达水平下调,因此DNA-PKcs可能协同自身免疫调节因子调控小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞TLR1、3和8的表达,由此推测在巨噬细胞内DNA-PKcs可能通过磷酸化自身免疫调节因子进而促进TLR1、3和8的表达,但确切机制还需要进一步研究证实。
表达在外周淋巴器官的DC和单核/巨噬细胞上的TLR1、3和8不仅发挥着模式识别受体的作用,即识别和清除病原微生物,而且还通过特殊的机制发挥免疫耐受作用。有研究[15]显示:TLR3通过调节Ⅰ型干扰素、IL-10、IL-27、吲哚胺2和3-双加氧酶(indoleamine2,3-dioxygenase,IDO)的表达进而诱导调节性T细胞的产生和抑制Th17细胞以维持外周免疫耐受。本文作者推测:在巨噬细胞内,自身免疫调节因子可能通过调节TLR1、3和8的表达进而诱导调节性T细胞的产生以发挥维持外周免疫耐受的作用,在此过程中,DNA-PKcs作为一个协同分子发挥着十分重要的作用。此外,表达在DC和巨噬细胞上的TLR3作为模式识别受体,能够识别真菌,特别是白色念珠菌[15]。因此本文作者推测:自身免疫调节因子调节TLR3的表达可以起到抵抗真菌免疫的作用。
综上所述,自身免疫调节因子能够上调巨噬细胞内TLR1、3和8的表达,并且DNA-PKcs能够协同自身免疫调节因子发挥这一作用,提示DNA-PKcs与自身免疫调节因子相互作用调控巨噬细胞TLRs的表达,这一作用对介导其识别病源微生物和维持外周免疫耐受发挥着重要的作用。
[1]Abramson J,Giraud M,Benoist C,et al.Aire’s partners in the molecular control of immunological tolerance[J].Cell,2010,140(1):123-135.
[2]Kogawa K,Nagafuchi S,Katsuta H,et al.Expression of AIRE gene in peripheral monocyte/dendritic cell lineage[J].Immunol Lett,2002,80(3):195-198.
[3]Schaller CE,Wang CL,Beck-Engeser G,et al.Expression of Aire and the early wave of apoptosis in spermatogenesis[J].J Immunol,2008,180(3):1338-1343.
[4]Suzuki E,Kobayashi Y,Kawano O,et al.Expression of AIRE in thymocytes and peripheral lymphocytes[J].Autoimmunity,2008,41(2):133-139.
[5]Zhu W,Yang W,He Z,et al.Overexpressing autoimmune regulator regulates the expression of toll-like receptors by interacting with their promoters in RAW264.7 cells[J].Cell Immunol,2011,270(2):156-163.
[6]Mathis D,Benoist C.Aire[J].Annu Rev Immunol,2009,27(3):287-312.
[7]Liiv I,Rebane A,Org T,et al.DNA-PK contributes to the phosphorylation of AIRE:importance in transcriptional activity[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2008,1783(1):74-83.
[8]Ju BG,Lunyak VV,Perissi V,et al.A topoisomeraseⅡβmediated dsDNA break required for regulated transcription[J].Science,2006;312(5781):1798-1802.
[9]Zhang S,Schlott B,Gorlach M,et al.DNA-dependent protein kinase(DNA-PK)phosphorylates nuclear DNA helicaseⅡ/RNA helicase A and hnRNP proteins in an RNA-dependent manner[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2004,32(1):1-10.
[10]Giffin W,Gong W,Schild-Poulter C,et al.Ku antigen-DNA conformation determines the activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase and DNA sequence-directed repression of mouse mammary tumor virus transcription[J].Mol Cell Biol,1999,19(6):4065-4078.
[11]Finnish-German APECED Consortium. An autoimmune disease,APECED,caused by mutations in a novel gene featuring two PHD-type zinc-finger domains[J].Nat Genet,1997,17(4):399-403.
[12]Halonen M,Kangas H,Ruppell T,et al.APECED-causing mutations in AIRE reveal the functional domains of the protein[J].Hum Mutat,2004,23(3):245-257.
[13]Heo K,Kim H,Choi SH,et al.FACT-mediated exchange of histone variant H2AX regulated by phosphorylation of H2AX and ADP-ribosylation of Spt16[J].Mol Cell,2008,30(1):86-97.
[14]Smith GC,Jackson SP. The DNA-dependent protein kinase[J].Genes Dev,1999,13(8):916-934.
[15]Romani L.Immunity to fungal infections[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2011,11(4):275-288.
Expression of Toll like receptor regulated by DNAPKcs and autoimmune regulator in peritoneal macrophages in mice and its significance
WU Jing1,2,FU Hai-ying1,ZHANG Ying-lin1,SUN Ji-tong1,YANG Wei1
(1.Department of Immunology,Norman Bethune College of Medicine,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China;2.Institute of Translational Medicine,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China)
Objective To study the expression levels of the Toll like receptor(TLRs)regulated by DNA-PKcs and autoimmune regulator in peritoneal macrophages in mice,and to clarify the function and significance of autoimmune regulator in peripheral immune system.Methods The macrophages were divided into p EGFPC1/m Aire transfection group,p EGFPC1/m Aire and negative control siRNA co-transfection group,p EGFPC1/m Aire and DNA-PKcs siRNA co-transfection group,p EGFPC1 and negative control siRNA co-transfection group,and p EGFPC1 and DNA-PKcs siRNA co-transfection group;the expression levels of TLR1-9 in peritoneal macrophages of the mice in various groups were detected by RT-PCR.The expression levels of TLR1-9 in peritoneal macrophages were detected by RT-qPCR after transfected with p EGFPC1/m Aire and pEGFPC1 into the peritoneal macrophages in mice;the expression levels of TLRs in the transfected cells before and after silencing DNA-PKcs were detected by RT-qPCR.Results The peritoneal macrophages in mice could express TLR1-9.Compared with p EGFPC1/m Aire transfection group,the expression levels of TLR1,3 and 8 were increased in peritoneal macrophages after transfected with autoimmune regulator(P<0.05)and those in the other groups did not changed significantly(P>0.05).After silencing DNA-PKcs,the expression levels of TLR1,3,and 8 were decreased(P<0.05)in peritoneal macrophages in p EGFPC1/m Aire transfection group than thoes in unsilenced group,but the expression levels of TLR1-9 didn’t have significant changes in macrophages transfected with p EGFPC1 before and after silence(P>0.05).Conclusion Autoimmune regulator can regulate the expression levels of TLR1,3,and 8 in peritoneal macrophages in mice,and the mechnism may be associated with DNA-PKcs interaction effect.
autoimmune regulator;macrophages;Toll-like receptor;partner
R392.12
A
1671-587Ⅹ(2012)06-1063-05
2012-07-12
国家自然科学基金资助课题(81001304)
吴 静(1980-),女,吉林省白山市人,医学博士,主要从事免疫耐受机制方面的研究。
杨 巍(Tel:0431-85619476,E-mail:ywei@jlu.edu.cn)
