牦牛肝蛋白分离纯化及其抗氧化活性研究
2012-11-23柳青海李天才
柳青海,郭 洁,李天才
1中国科学院西北高原生物研究所,西宁810008;2中国科学院研究生院,北京100049
牦牛肝蛋白分离纯化及其抗氧化活性研究
柳青海1,2,郭 洁1,2,李天才1*
1中国科学院西北高原生物研究所,西宁810008;2中国科学院研究生院,北京100049
新鲜牦牛肝匀浆、磷酸缓冲液抽提、硫酸铵分级沉淀,并采用响应面法对提取条件进行优化。在最佳提取条件下提取的粗蛋白经DEAE-52离子交换层析和Sephadex G-200凝胶柱洗脱得到7种不同的蛋白。用SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳对各蛋白的分析结果,各蛋白均成单一条带表明纯化效果较好,其分子量分布在97.2 KD-116 KD之间。采用化学发光法对其在体外抗氧化活性研究,主要包括超氧阴离子自由基、羟自由基、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼自由基的清除实验,结果表明几种蛋白均具有抗氧化作用,尤其蛋白5和蛋白1作用较为突出,在250 mg/L浓度时,对超氧阴离子的清除率为82.91%和72.92%。上述结果为牦牛肝作为抗氧化保健食品或功能食品的研究和开发提供了依据。
牦牛;肝蛋;纯化;抗氧化活性
Introduction
Yak(Bos grunniens),large ruminant herbivores inhabiting in the high altitudes,belongs to the subfamily Bovinae of family Bovidae[1-3].Yaks provide their owners with milk,meat,wool,fur and other products.They play an important role in the economic,social,cultural and religious life of the local tribal population.Their natural habitat is in and around the Himalayas and further north at altitudes ranging from 2500 to 6000 m with high solar radiation,reduced oxygen in the air and short growing seasons for herbage,where few other domestic animals can survive.Average summer temperature is about 4 to 6°C,while minimum winter temperatures are as low as minus 40 to minus 50°C[4].It is estimated that there are about 15 million Yaks in the world,of which about 92%are in China[5].However,Yak liver,a major byproduct of Yak meat processing,which is rich in proteins,has not been utilized effectively.Most Yak livers are simply treated as waste because of the living traditions of local inhabitants.Several reports have shown that active protein or poly-peptide has been extracted from other animals’liver,such as bovine liver[6,7],rat liver[8,9],Elbe-bream and Roe deer liver[10],while little work has been done on extraction protein or active poly-peptide from Yak liver.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Fresh of yak(Bos grunniens)liver were purchased from local slaughter house(Xining,China).All other chemicals and solvents used were of analytical grade.
Methods
Protein extraction
Fresh of yak(Bos grunniens)liver(2 kg)was extracted for protein with different levels of independent variables(Temperature 0-60℃,solvents of phosphate butler pH 6-8,time 2-6 h and liquid-solid ratio 3∶1-11∶1,v/w)[11,12].The protein extraction was carried out with 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer solution in Erlenmeyer flask by putting it on a water bath.The solution was continuously stirred with a magnetic stirrer for a selected period.The solution was immediately centrifuged in a cooling centrifuge(10000 rpm,10 min)at 4℃.The supernatant was added solid ammonium sulfate with different concentration(30%-60%),then centrifuged in a cooling centrifuge(10000 rpm,10 min)at 4℃.Sediment were collected and dissolved into phosphate buffer solution(pH 7.0),in the end,the volume of it was measured.
Protein determination
Protein concentration was measured by the Bradford method using bovine serum albumin(BSA)as the standard[13].The binding of the dye to protein causes a shift in the absorption maximum of the dye from 465 to 595 nm,and it is an increase in absorption at 595 nm which is monitored.This assay was very reproducible and rapid with the dye binding process virtually complete in approximately two minutes with good color stability for one hour.The protein yield was expressed as:
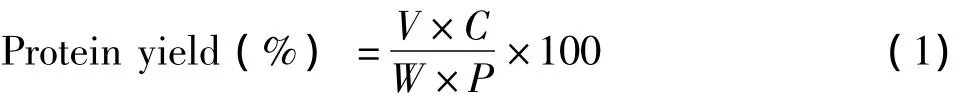
Where V is the volume of protein crude,C is the concentration of crude protein,W is the weight of fresh yak liver,P is the proportion of protein in fresh yak liver.Experimental design
The quantitative effects of extraction time,phosphate buffer pH,liquid-solid ratio and extraction temperature on yield of yak(Bos grunniens)liver protein were investigated using response surface methodology(RSM).The four factors chosen for the present investigation were based on the results of a single-factor test.The independent variables Xiwere coded as xi,which were defined as dimensionless,according to the equation:

where xiis the coded value of an independent variable,Xiis the real value of an independent variable,X0is the real value of an independent variable at the center point,and△Xiis the step change value[14].Experiments were randomized in order to minimize bias.Extraction yield of protein was taken as the response,Y.Protein purification byDEAE-52
The crude protein was dialyzed by dialysis tubing 3500 (φ27,USA),at 4℃ overnight,then concentrated by Polyethylene Glycol 20000(PEG20000).Crude was subjected to ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-52 column(80×3.6 cm)and gradient eluted by 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer(pH7.2)containing NaCl (0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5mol/L)at the flowing rate of 2 mL/min and 5 mL for a tube,then each tube absorbance was measured under 280 nm.After DEAE-52 ion-exchange chromatography was performed,the fractions containing proteins were dialyzed against 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer(pH7.2)for 24 h at least three to four changes of buffer,concentrated to 5 mL,loaded onto a gel filtration chromatography on Sephadex G-200 column(50×2.0 cm).Sample buffer and eluted buffer was 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer(pH7.2).The desired protein was eluted at the flowing rate of 1 mL/min and collected 2 mL for a tube,and then each tube absorbance was measured at 280 nm.
SDS-Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis(SDS-PAGE)
The protein samples were run on discontinuous sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gelelectrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)[15].The sample was dissolved in de-monized water and boiled for 5 min in SDS and β-mercaptoethanol.Electrophoresis was performed using 12% (v/v)separating gel and 5%stacking gel[16].The gels were run for 165 min.The voltage was initially 80 V,raised to 140 V once the samples had entered the resolving gel.The gels were stained with a commassie brilliant blue R250 of 0.05%(w/v),50%(v/v) methanol and 12%(v/v)acetic acid.The gel destained using the same buffer without commassie brilliant blue R250.
Antioxidant assay
Determination of antioxidant activity by the DPPH radical scavenging method
The antioxidant activity of each protein was measured in terms of hydrogen donating or radical scavenging ability,according to the stable radical,DPPH· method[17].Using ascorbic acid as the positive control.The percent scavenging effect was calculated as:
Scavenging effect(%)=[(A0-A1)/A0]×100
A0was the absorbance without sample and A1was the absorbance with sample.
Hydroxyl(OH)radical scavenging activity
Hydroxyl radical(·OH)was assayed using Salicylic acid colorimetric method,adopt Fenton reaction system[19].Absorbance was taken after 30 min at 510 nm.U-sing ascorbic acid as the positive control.The scavenging activity on·OH was expressed as:
Scavenging effect(%)=[(A0-A1)/A0]×100 A0was the absorbance without sample and A1was the absorbance with sample.
Results and Discussion
Protein extraction
The effect of different extraction time on the protein yields
Extraction time is not constant during the extraction stages.Here,extraction time was,respectively,set at 2,3,4,5 and 6 h to examine the influence of extraction time on the purity of protein when other reaction conditions were as follows:extraction temperature 30℃,Liquid-solid ratio at 7 mL/g,and phosphate buffer solution(pH 7.0).As shown in Fig.1(A),after 4 h,the purity of protein no longer obviously changed,when the time of extraction increased.Therefore,extraction time range of 3-5 h was considered in the present work.
The effect of different phosphate buffer solution pH on the protein yields
Fig.1(B)presented the influence of phosphate buffer solution pH on the forward extraction efficiency.When pH varied from 6 to 8(other three conditions were as follows:extraction temperature 30℃,Liquid-solid ratio 7 mL/g,and extraction time 4 h),the purity of protein reached a maximum percentage of 73.39 when the pH was 7.0.After this point,the purity of protein started to decline when increasing the pH.The yak liver protein isoelectric point had measured 4.2,the protein was negatively charged above the isoelectric point,and electrostatic interaction cannot be a major driving force causing protein transfer at this time.From the investigation,when the protein was negatively charged above the isoelectric point,it may be deduced that hydrophobic interaction between protein and surfactant leads to protein solubilization[20].Therefore,phosphate buffer solution pH range of 6.5-7.5 was considered in this work.The effect of different ratio of Liquid-solid ratio on the protein yields
The effect of different liquid-solid ratio(3,5,7,9 and 11)on the purity of protein was seen in Fig.1C,when the other three conditions were as follows:extraction temperature 30℃,phosphate buffer solution pH7.0,and extraction time 4 h.After liquid-solid ratio 7 mL/ g,there was a little rise when Liquid-solid ratio continued to increase.If continue to increased Liquid-solid ratio,not only a waste of raw materials,but also increased workload.
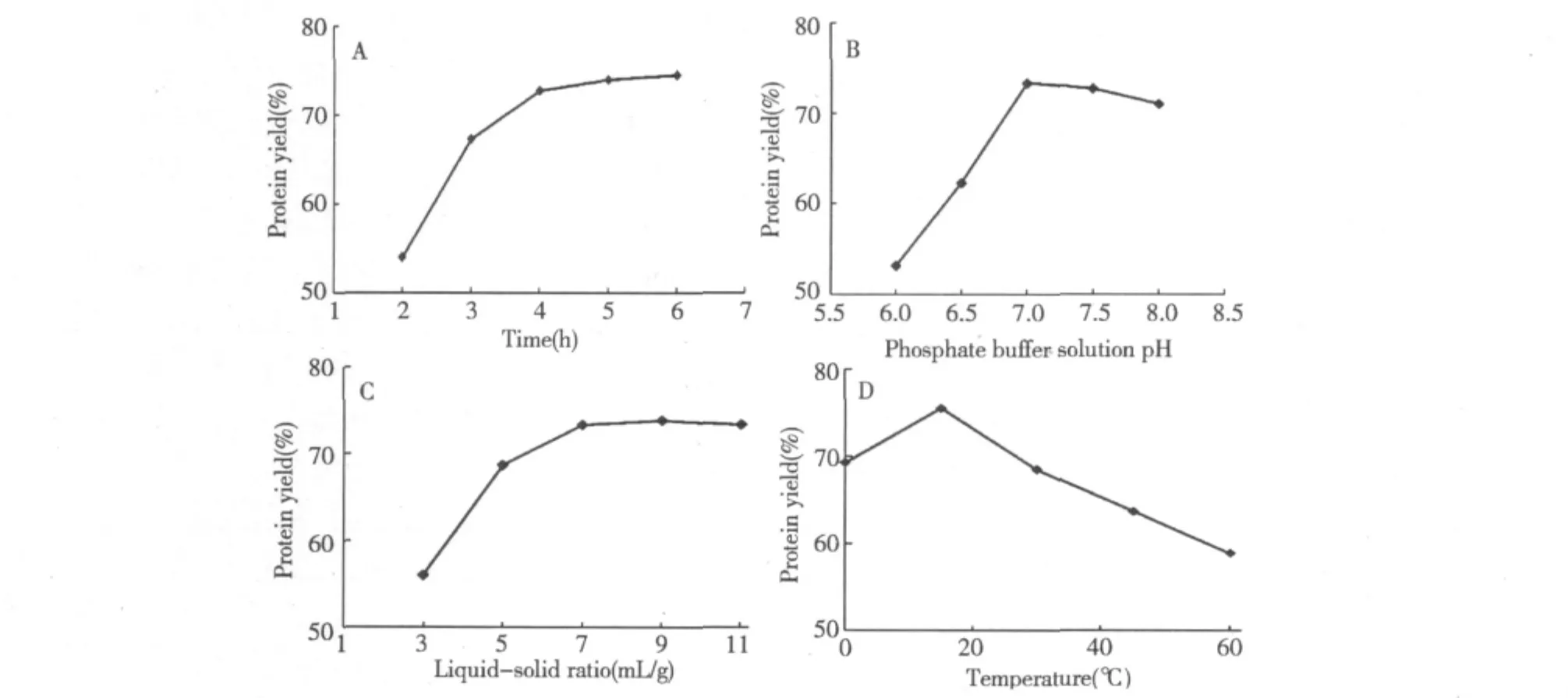
Fig.1 Effect of different extraction parameters on the purity of protein
The effect of different extraction temperature on the polysaccharides yields
Different extraction temperature was set at 0,15,30,45 and 60℃,respectively,to investigate the influence of extraction temperature on the purity of protein when the other reaction conditions were set as follows:Liquidsolid ratio7 mL/g,phosphate buffer solution pH7.0,
and extraction time 4 h.Fig.1D indicated that the maximum purity of protein was reached a maximum percentage of 75.53when extraction temperature 15℃.And then there was no increase when extraction temperature continued to rise[21].Therefore,the range of 0-30℃was adopted to be optimal extraction temperature in this work.
Fitting the models
The independent variables and their levels are presented in Table 1.Experiments were randomized in order to minimize bias.Extraction yield of Protein was taken as the response,Y.

Table 1 Independent variable and their levels employed in Box-Behnken experimental design
As seen from table 2,the complete design consisted of 27 experimental points,and the experiment was carried out in a random order.

Table 2 Response surface Box-Behnken design and results for the purity of protein
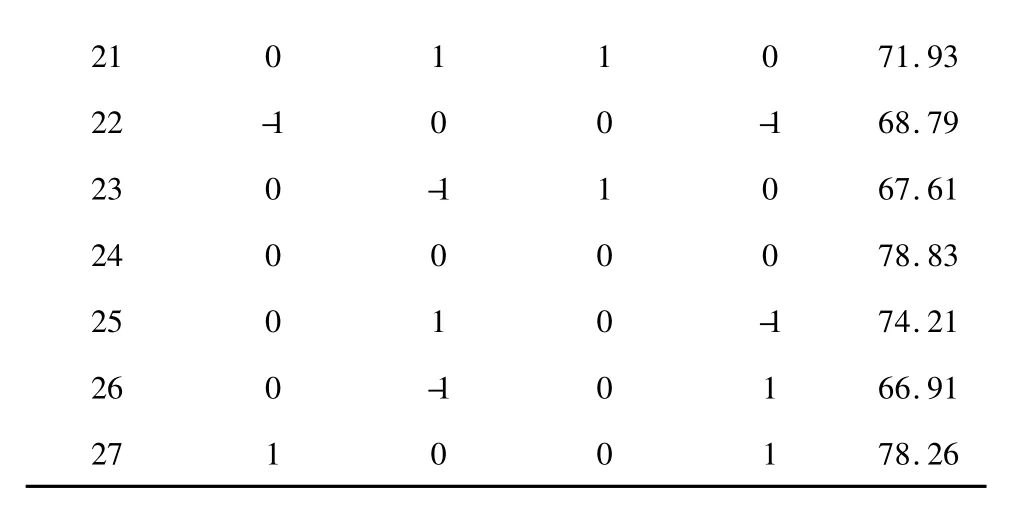
21 0 1 1 0 71.93 22 -1 0 0 -1 68.79 23 0 -1 1 0 67.61 24 0 0 0 0 78.83 25 0 1 0 -1 74.21 26 0 -1 0 1 66.91 27 1 0 0 1 78.26
The study utilized RSM to develop a prediction model for optimizing the conditions of protein extraction from yak liver.The experimental conditions and the corresponding response values from the experimental design were presented in Table 2.Predicted response Y for the yield of yak liver protein could be expressed by the following second-order polynomial equation in terms of coded values:

The predicted values of protein yields were calculated using regression model and compared with experimental values.Coefficient of determination (R2)was 93.14%,which indicates the adequacy of the applied model.
The effect of treatment variables as the linear,quadratic and interaction terms were tested foradequacy and fitness by analysis of variance(ANOVA)(Table 3).The probability(P)value of the regression model was less than 0.0001,with no significant lack-of fit(P <0.0001).The determination coefficient(R2=0.9314) was satisfactory,having a low experimental error according to ANOVA(Table 3).The time(X1)and time-phosphate buffer solution pH interaction(X1X2),and the quadratic terms(X1,X2,X3,X4)had a highly significant effect(P<0.001).The phosphate buffer solution pH(X2),Temperature(X4),the time-Liquidsolid ratio interaction term(X1X3),the time-temperature interaction term(X1X4),and the quadratic terms (X1,X2)had a significant effect(P <0.05).R(adjusted determination coefficient)is the correlation measure for testing the goodness-of-fit of the regression equation.Higher it is the better degree of correlation between the observed and predicted values[22].The value ofwas 0.8729,it confirmed that the model was highly significant and indicated a high degree of correlation between the observed and predicted data.Coefficient of variation(CV)indicates the degree of precision with which the experiments are compared.A relatively low value of CV(2.14)in Table 3,which showed a better precision and reliability of the experiments were carried out[23].

Table 3 ANOVA for quadratic model
Analysis of response surface
The tri-dimensional response surface and two-dimensional contour plots are the graphical representations of regression equation 3.They provide a method to visualize the relationship between responses and experimental levels of each variable and the type of interactions between two test variables.The shapes of the contour plots,circular or elliptical,indicate whether the mutual interactions between the variables are significant or not.Circular contour plot indicates that the interactions between the corresponding variables are negligible; while elliptical contour plot indicates that the interactions between the corresponding variables are significant[24].The relationship between independent and dependent variables was illustrated in tri-dimensional representation of the response surfaces and two-dimensional contour plots generated by the model for yield of protein(Figs.2-7),two variables were depicted in one tridimensional surface plots while the other variable kept at level zero.It is clear that the yield of protein was sensitive to minor alterations of the test variables(Extraction time,phosphate buffer solution pH,Liquid-solid ratio and extraction temperature).
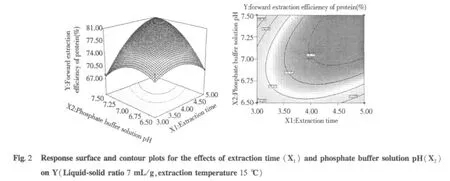
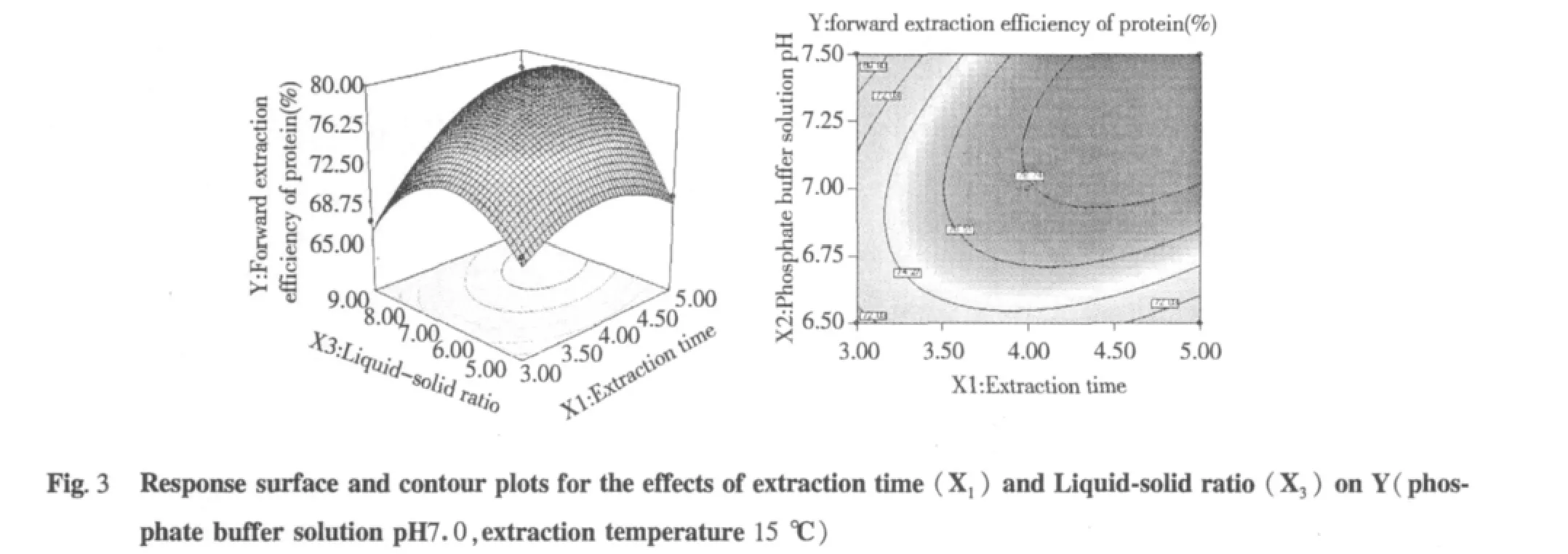


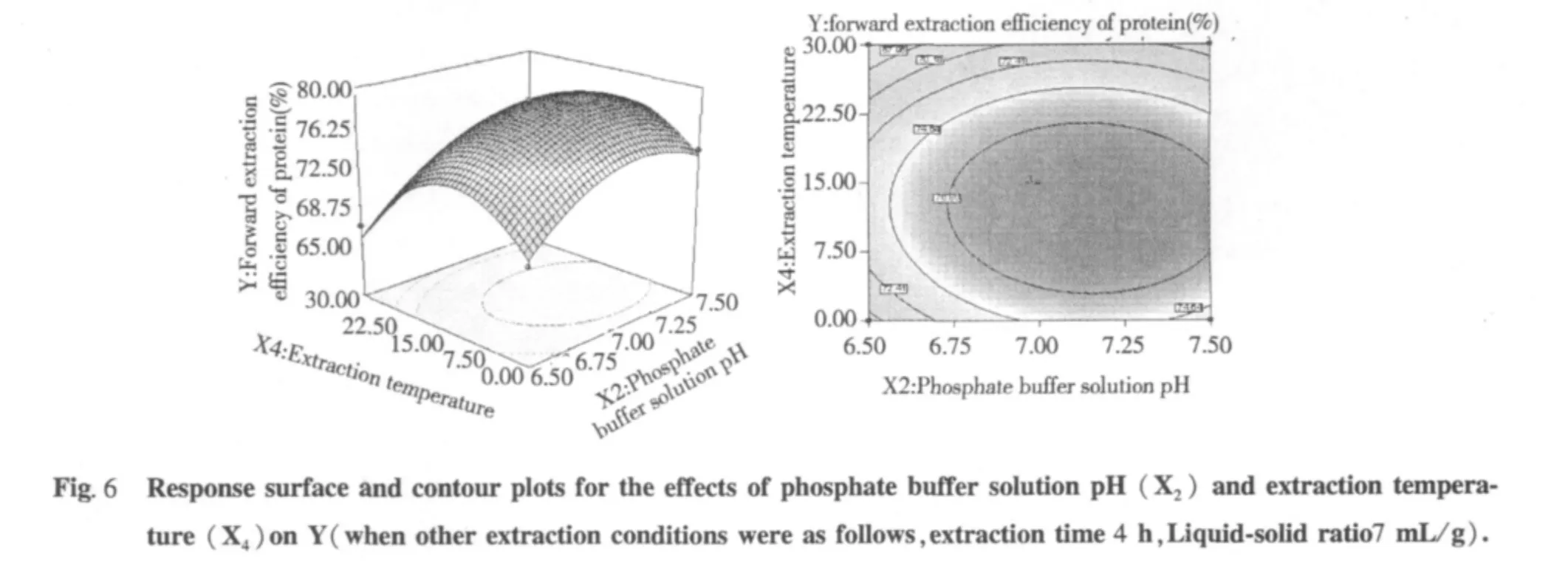
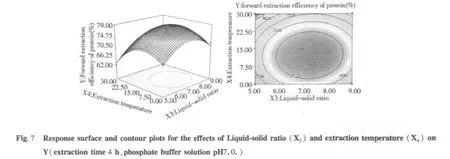
Optimum conditions and model frication
From the model,optimum conditions for protein extraction were obtained as presented in extraction time 4.77 h,phosphate buffer solution pH 7.2,Liquid-solid ratio 7.22 mL/g and extraction temperature 15.04℃.Under the optimum conditions,a maximum response of 79.98%protein was predicted.But this optimum conditions was not convenient to control,so optimum conditions were recommended to extraction time 4.8 h,phosphate buffer solution pH 7.2,liquid-solid ratio 7 mL/g and extraction temperature 15℃.Additional independent experiments using the recommended conditions,the results indicated that the experimental protein value(84.23%)was not significantly different from the predicted protein value(84.98%).Therefore we used recommended conditions for our work.
Protein purification by DEAE-52
Chromatography under no denaturing conditions,its elues as seven peaks(Fig.8),is indicating that the purity is very high.In the present study,proteins in the main peak were recovered for further analysis.To confirm the different peaks,the fraction was analyzed by SDS-PAGE.From the gel we can see that the protein was well separated(Fig.9).


DPPH·scavenging activity
Fig.10 shows the results of scavenging DPPH·ability of VC and each BGP at various concentrations.BGP scavenged as much as 16.67%t o 75%of DPPH·at a concentrate on of 50 to 250 mg/L.It showed dose-dependent DPPH· scavenging activity.Different BGP scavenging DPPH· ability have obvious difference.The BGP5 and BGP1 scavenging DPPH·ability obvious when the concentrations on of 200 to 250 mg/L,but the BGP2 scavenging DPPH· ability not obvious when concentrations on of 250 mg/L,it only 43.75%.
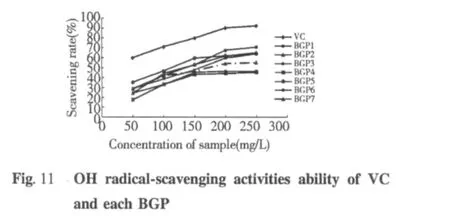
·OH scavenging activity
As we know,·OH is the strongest oxidant,·OH is the most reactive and severely damages adjacent bimo lecular such as all proteins,nucleic acid,and almost any biological molecule it touches.This damage causes aging,cancer and several diseases.Therefore,the removal of·OH is probably one of the most effective defenses of a living body against various diseases.Fig.11 shows the results of scavenging·OH ability of VC and each BGP at various concentrations.BGP scavenged as much as 17.8%t o71.11%of·OH at a concentrate on of 50 to 250 mg/L.It showed dose-dependent·OH scavenging activity.Different BGP scavenging·OH ability have obvious difference.The BGP5 and BGP1 scavenging·OH ability obvious when the concentrations on of 200 to 250 mg/L,but the BGP4 scavenging ·OH ability not obvious when concentrations on of 250 mg/L,it only 45.56%.According to the present findings,it shows that BGP has excellent·OH scavenging effects.It suggested BGP might be used to food additive or health foods as a good natural antioxidant.

Fig.10 DPPH radical-scavenging activities ability of VC and each BGP
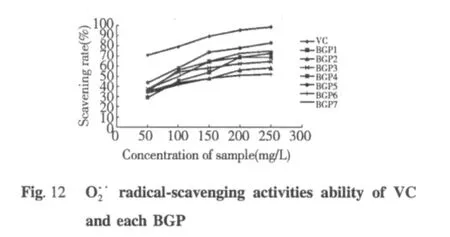
Conclusions
The response surface method proved to be useful for optimization of technology of yak liver protein extraction.Statistical analysis proved to be a useful and powerful tool in developing optimum extraction conditions.The statistical analysis based on a Box-Behnken design showed that an extraction time 4.8 h,phosphate buffer solution pH 7.2,liquid-solid ratio 7 mL/g and extraction temperature 15℃ were the best conditions to extraction protein from yak liver.Under the optimum conditions,maximum yield of proteins 84.23%can be achieved.The crude protein purification by Ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-52 and gel filtration chromatography on Sephadex G-200,obtained seven proteins.Each protein gave a single band on SDS-PAGE and the molecular weight of those proteins was from 97.2 KD to 116 KD.The results of antioxidant activities showed that each protein scavenging(DPPH·),superoxide (O)and hydroxyl(·OH)were obvious,especially,BGP5 and BGP1 on scavenging oxygen free radical were obvious.The results indicated that proteins may be exploited as health food or functional food,to alleviate oxidative stress.
Acknowledgements This work was financially supported by Qinghai Science and technology department,China(No:2007-G-523).
1 Groves CP.(1981).Systematic relationships in the Bovini (Artiodactyla,Bovidae).J Zool Syst Evol Res,19:264-2781.
2 Olsen SJ.Fossil ancestry of the yak,its cultural significance and domestication in Tibet.Acad Nat Sci Phila,1990,1142:73-100.
3 Sasaki M.Yak:Hardy multi-purpose animal of Asia highland.In proceedings 1st international congress on Yak(pp.1-5),1-6 August,1994,Lanzhou,China.
4 Wiener G,Han JL,Long RJ.The yak(2nd Ed).Bangkok Thailand:Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific of the Food and Agriculture.2003,2,150-156.
5 Zhang ZG,Xia L,Yang QS.Distribution and conservation of Yak(Bos grunniens).Chin J Zool,2009,44:148-150.
6 Mitchell DC,Maler T,Jourdian GW.Detergent dissociation of bovine liver phosphomannosyl binding protein.J Cell Biochem,1984,24,319-330.
7 Shibusawa Y,Fujiwara T,Shindo H,et al.Purification of alcohol dehydrogenase from bovine liver crude extract by dyeligand affinity counter-current chromatography.J Chromatogr B,2004,799:239-244.
8 Gao MX,Li N,Zhang J,et al.The study of three extraction methods for pre-separation and enrichment:Application to the complex proteome separation in rat liver.Sep Purif Technol.,2006,52:170-176.
9 Ichikawa A,Ishizaki J,Morita M,et al.Identification of new amine acceptor protein substrate candidates of Transglutaminase in rat liver extract:Use of 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine as a probe,Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2008,72,1056-1062.
10 Profrock D,Prange A,Schaumloffel D,et al.Optimization of capillary electrophoresis-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for species analysis of metallothionein-like proteins extracted from liver tissues of Elbe-bream and Roe deer.Spectrochim Acta,Part B,2003,58:1403-1415.
11 Oomah BD,Mazza G,Cui W.Optimization of protein extraction from fiaxseed meal.Food Res Int,1994,27,355-361.
12 Qiu H,Guo XL,et al.Isolation and purification catalase from Anas platyrhynchos liver and analysis of some its properties.J Southwest Univ(Nat Sci Ed),2008,30:163-168.
13 Bradford MM.A rapid and sensitive method for the quantization of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal Chem,1976,72:248-254.
14 Guan X,Yao HY.Optimization of viscozyme L-assisted extraction of oat bran protein using response surface methodology.Food Chem,2008,106,345-351.
15 Unden G,Hackenberg H.,Kroger A.Isolation and functional aspects of the fumarate reductase involved in the phosphorylative electron transport of Vibrio succinogenes.Biochim Biophys Acta,1980,591,275-288.
16 Laemmli UK.Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature,1970,277: 680-685.
17 Zhong YG,Lin N,Wang SQ,et al.Study on antioxidative and antimicrobial activities of lentinan.Food Sci Technol,2007,32:141-144.
18 Shimada K,Fujiyama K,Yahara K,et al.Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autoxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion.J Agric Food Chem,1992,40,945-948
19 Singh N,Rajini PS.Free radical scavenging activity of an aqueous extract of potato peel.Food Chem,2004,85:611-616.
20 Paradkar VM,Dordick JS.Mechanism of extraction of chymotrypsin into isooctane at very low concentrations of aerosol OT in the absence of reverse micelles.Biotechnol Bioeng,1994,43,529-540.
21 Paraman I,Hettiarachchy NS,Schaefer C,et al.Hydrophobicity,solubility,and emulsifying properties of enzyme-modified rice endosperm protein.Cereal Chem,2007,84:343-349.
22 Mundra P,Desai K,Lele SS.Application of response surface methodology to cell immobilization for the production of palatinose.Bioresour Technol,2007,98,2892-2896.
23 Ahmad AL,Ismail S,Bhatia S.Optimization of coagulationflocculation process for palm oil mill effluent using response surface methodology.Environ Sci Technol,2005,39,2828-2834.
24 Cheison SC,Wang Z,Xu SY.Use of response surface methodology to optimize the hydrolysis of whey protein isolate in a tangential flow filter membrane reactor.J Food Eng,2007,80,1134-1145.
25 Zhu KX,Zhou HM,Qian HF.Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH)prepared with alcalase.Process Biochem,2006,41: 1296-1302.
July 5,2011;Accepted October 9,2011
Isolation and Purification of Proteins in Liver of Yak (Bos grunniens)and Its Antioxidant Activities
LIU Qing-hai1,2,GUO Jie1,2,LI Tian-cai1*1Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology,Chinese Academy of Science,Xining 810008,China;2Graduate University,Chinese Academy of Science,Beijing 100049,China
Seven proteins(BGP1,BGP2,BGP3,BGP4,BGP5,GBP6,and BGP7)were isolated respectively from the liver of yak(Bos grunniens)by homogenizing,step precipitating with ammonium sulfate,ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-52 and gel filtration chromatography on Sephadex G-200.Each protein gave a single band on SDS-PAGE and the molecular weight of those proteins were from 97.2 KD to 116 KD.The anti-oxidant activities of proteins were evaluated using the method of chemistry luminescence,including 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl(DPPH·),superoxide(O-·2) and hydroxyl(·OH)radical scavenging assays.The proteins could scavenge superoxide radical,hydroxyl radical and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl(DPPH·).Especially,the effects of BGP5 and BGP1 on scavenging superoxide free radical were obvious,with scavenging ability 82.91%and 72.92%at the concentrations of 250 mg/L.The results indicated that proteins may be exploited as health food or functional food.
yak;liver protein;purification;antioxidation
1001-6880(2012)05-0581-10
*Corresponding author Tel:86-013897242213;E-mail:tcli@nwipb.ac.cn
Q58;R282.74
A
