Ki-67在乳腺癌各亚型中的表达及意义
2012-05-28朱伟良谈炎王旭芬程锦玲张磊方琦谈珂岚杨澜王磊
朱伟良 谈炎 王旭芬 程锦玲 张磊 方琦 谈珂岚 杨澜 王磊
常州市第一人民医院乳腺外科,△病理科,江苏 常州 213003
Ki-67在乳腺癌各亚型中的表达及意义
朱伟良 谈炎△王旭芬 程锦玲 张磊 方琦 谈珂岚 杨澜 王磊
常州市第一人民医院乳腺外科,△病理科,江苏 常州 213003
背景与目的:目前公认的指导乳腺癌治疗和预后预测的生物学指标有雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone,PR)和人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor-2,HER-2)。近年来Ki-67逐渐成为一个新的研究热点,众多研究提示,Ki-67很可能是继HER-2之后又一个重要的生物指标。本研究旨在分析Ki-67在不同亚型的乳腺癌中的表达及临床意义。方法:收集常州市第一人民医院乳腺外科2010年1月—12月收治的252例乳腺癌患者的临床病理资料,通过免疫组化(immunohistochemistry,IHC)方法测定手术后乳腺癌组织的ER、PR、HER-2和Ki-67的表达以区分不同的乳腺癌亚型。结果:Ki-67指数在不同年龄及不同淋巴结转移状态间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。肿瘤直径>2 cm的患者Ki-67指数显著高于直径≤2 cm的患者(P=0.001)。病理分期为Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ期患者的Ki-67指数均显著高于病理分期为0期的患者(P<0.05),但是Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ期患者间的Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。ER阴性、PR阴性、HER-2阳性的患者的Ki-67指数均显著高于其对应的ER阳性、PR阳性和HER-2阴性的患者(P<0.05)。Luminal B型、HER-2过表达型和三阴型的Ki-67指数均显著高于Luminal A型(P<0.001),而Luminal B型、HER-2过表达型和三阴型三者间的Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:Ki-67结合其他生物指标对预测乳腺癌的预后有一定意义,值得和ER、PR和HER-2同时进行检测。
乳腺癌;临床病理特征;Ki-67;雌激素受体;孕激素受体;人表皮生长因子受体2
雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone,PR)和人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor-2,HER-2)是目前公认的指导乳腺癌治疗和预后预测的生物学指标。近年来,Ki-67逐渐成为一个新的研究热点。本研究通过对252例乳腺癌患者的临床资料进行分析,探讨Ki-67在乳腺癌各亚型中的表达及临床意义。
1 材料和方法
1.1 一般资料
选取常州市第一人民医院2010年1月—2010年12月接受手术治疗的乳腺癌患者,筛选出满足下列条件的病例:①女性;②可手术;③术后均经常规石蜡切片病理检查确诊为乳腺癌;④进行了腋窝淋巴结清扫;⑤术前未接受过放疗、化疗和内分泌治疗。共获得252例乳腺癌患者的临床病理资料。患者年龄20~83岁,中位年龄54岁,年龄≤35岁者11例(4.4%),>35岁者241例(95.6%)。Tis10例(4.0%),T1117例(46.4%),T2121例(48.0%),T33例(1.2%),T41例(0.4%)。腋窝淋巴结有转移者89例(35.3%),无转移者163例(64.7%)。按照第六版AJCC乳腺癌TNM病理分期标准:0期10例(4.0%),Ⅰ期85例(33.7%),Ⅱ期124例(49.2%),Ⅲ期33例(13.1%)。组织学类型:浸润性导管癌227例(90.1%),浸润性小叶癌5例(2.0%),导管原位癌10例(4.0%),其他类型10例(4.0%)。
1.2 试剂
SP9000试剂盒及免疫组化染色一抗Ki-67(ZM0166)、HER-2(ZM0065)、ER(ZA0102)、PR(ZA0255)。
1.3 免疫组化检测
采用免疫组化二步法(以PV-9000通用型二步法检测试剂盒为例)进行病理诊断。石蜡切片脱蜡,蒸馏水冲洗后,PBS浸泡5 min,置于pH为6.0的枸橼酸缓冲液中,在高压锅中,于120 ℃抗原修复6 min,冷却至室温。采用3%H2O2室温温育5~10 min,以消除内源性过氧化物酶的活性,PBS冲洗共3次,每次2 min。分别滴加Ki-67、HER-2、ER、PR一抗工作液,37 ℃温育1~2 h或4 ℃过夜。PBS冲洗3次,每次2 min。滴加试剂1(Polymer Helper),室温或37℃温育20 min,PBS冲洗3次,每次2 min。滴加试剂2(多聚过氧化物酶抗鼠及抗兔抗体),室温或37 ℃温育20~30 min,PBS冲洗3次,每次2 min。DAB显色剂显色4~8 min。自来水充分冲洗,苏木素复染,脱水透明、封片。
1.4 结果判定
ER和PR阳性判断标准:肿瘤细胞无细胞核棕黄染色或少于5%的细胞核较弱棕黄染色为阴性,>5%的细胞核棕黄染色则为阳性。Ki-67阳性染色定位于细胞核,按视野中阳性细胞所占的比例进行计数,以任意5个高倍镜视野中阳性细胞所占比例的平均值定义为阳性细胞百分比并作为评定依据。HER-2阳性判断标准:细胞膜棕黄染色为阳性。无细胞染色或<10%的细胞膜较弱染色为(-);>10%的细胞膜部分较弱染色为(+);>10%的细胞膜完全较弱到中等染色为(++);>10%的细胞膜完全强染色为(+++)。由于未对HER-2(++)的病例进一步进行FISH检测,本研究将检查结果(++)及以下者定义为阴性,(+++)者定义为阳性。
1.5 统计学处理
采用SPSS 16.0统计软件包进行统计处理,采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 Ki-67指数与临床病理特征的关系
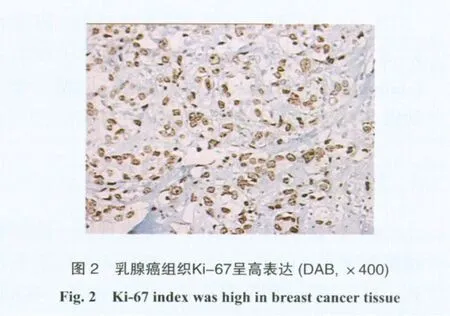
Ki-67在乳腺癌组织和正常乳腺组织中的表达情况见图1和图2。年龄≤35岁和>35岁的患者间Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P=0.087)。肿瘤直径>2 cm的患者Ki-67指数高于肿瘤直径≤2 cm者(P=0.001)。淋巴结无转移和有转移间Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P=0.297)。病理分期为Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ期者的Ki-67指数均显著高于病理分期为0期者(P<0.05),但Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ期三者间的Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。ER(-)者的Ki-67指数显著高于ER(+)者(P<0.001)。PR(-)者的Ki-67指数显著高于PR(+)者(P<0.001)。HER-2(+)者的Ki-67指数显著高于HER-2(-)者(P=0.013,表1)。
2.2 Ki-67指数与乳腺癌亚型的关系
Luminal A型76例(30.2%),Ki-67指数均值为7.28。Luminal B型98例(38.9%),Ki-67指数均值为33.21。HER-2过表达型16例(6.3%),Ki-67指数均值为35.31。三阴型62例(24.6%),Ki-67指数均值为36.0(表2)。
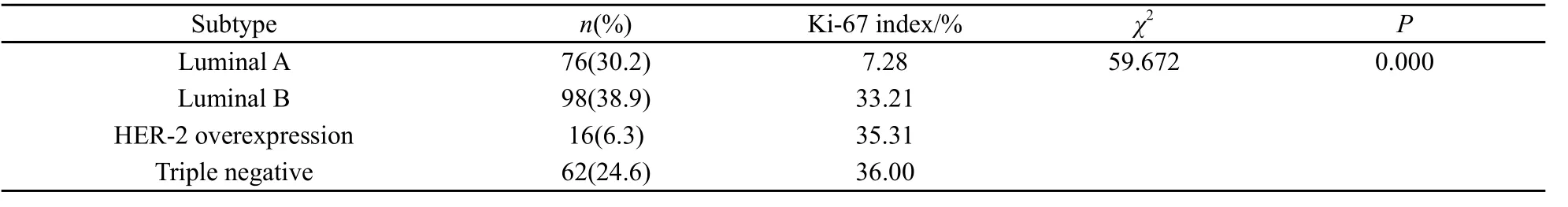
表 2 Ki-67与乳腺癌亚型的关系Tab. 2 The relationship between Ki-67 and subtype of breast cancer
Luminal B型、HER-2过表达型和三阴型的Ki-67指数均显著高于Luminal A型(P<0.001)。Luminal B型、HER-2过表达型和三阴型三者间的Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
3 讨 论
Ki-67是1983年由Gerdes等发现的一种在增殖细胞中表达的核抗原。Ki-67抗原在G0期不表达,在G1期和S期早期表达水平比较低,在S期后期和G2期表达明显增加,在M期达到高峰,在细胞分裂的后期和末期迅速下降。鉴于Ki-67的这个特点,其被认为是有效评估细胞增殖的一个重要指标。有研究发现,Ki-67在正常乳腺组织和乳腺癌组织中的表达存在差异,正常乳腺组织和临近乳腺纤维腺瘤的乳腺组织中Ki-67呈低表达(<3%)[1-3]。Fasanella等[4]报道315例乳腺癌的Ki-67阳性指数为36%±14%,与本研究结果有一定差异。
本研究结果显示,Ki-67在不同年龄的患者之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.087)。关于Ki-67和肿瘤大小的关系,有研究结果显示,两者呈正相关[5-6],亦有研究结果显示,两者间无关[7]或者呈负相关[8]。本研究结果显示,肿瘤较大者Ki-67指数较高(P=0.001)。对于Ki-67和腋窝淋巴结转移的关系,大部分研究认为,Ki-67和淋巴结转移呈正相关[8],也有研究认为两者无关[7,9-10],还有研究报道呈负相关[11]。本研究的结果显示,Ki-67与淋巴结转移无明显相关(P=0.297)。Ki-67与病理分期相关(P=0.027),进一步分析的结果显示,病理分期为Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ期的患者Ki-67指数均显著高于病理分期为0期者(P<0.05),但Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ期三者间的Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结果提示,Ki-67指数主要与肿瘤局部的增殖相关,不能反应区域淋巴结的状态。
目前,多数研究认为Ki-67与ER、PR呈负相关[5,9-10,12-14],也有报道呈正相关[15]。本研究结果显示,ER、PR表达阴性者Ki-67指数显著高于ER、PR表达阳性者(P<0.001)。由于ER、PR阳性的乳腺癌对内分泌治疗敏感,预后较ER、PR阴性的乳腺癌好,可以推测Ki-67高表达的乳腺癌患者预后可能较差。目前已有数个研究证实,Ki-67和HER-2表达呈正相关[10,13,16],但也有负相关的报道[17-18]。本研究结果显示,HER-2阳性者Ki-67指数显著高于HER-2阴性者(P=0.013)。由于HER-2过度表 达的乳腺癌患者预后较差已成定论,可以由此推测Ki-67高表达的乳腺癌患者预后较差。
本研究中的三阴型乳腺癌患者共62例(24.6%),其比例与周波等[19]报道的26.8%接近。进一步发现不同的乳腺癌亚型的Ki-67指数有一定区别。Luminal B型、HER-2过表达型和三阴型的Ki-67指数均显著高于Luminal A型(P<0.001),而Luminal B型、HER-2过表达型和三阴型三者间的Ki-67指数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
本研究结果提示,在乳腺癌的发生、发展过程中,Ki-67与ER、PR、HER-2之间可能存在着特殊的关系,Ki-67高表达可能是一个不良预后因素。由于目前尚缺乏统一的Ki-67检测和评估方案,而且缺乏大样本的前瞻性研究,Ki-67还不能作为公认的乳腺癌预后指标。尽管如此,Ki-67很可能是继HER-2之后的又一个重要的生物指标[20],将在乳腺癌的预后和指导治疗方面发挥越来越重要的作用。
[1]HARPER-WYNNE C, ROSS G, SACKS N, et al. Effects of the aromatase inhibitor letrozole on normal breast epithelial cell proliferation and metabolic indices in postmenopausal women: a pilot study for breast cancer prevention[J].Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2002, 11(7): 614-621.
[2]CLARKE R B, HOWELL A, POTTEN C S, et al. Dissociation between steroid receptor expression and cell proliferation in the human breast[J]. Cancer Res, 1997, 57(22): 4987-4991.
[3]de LIMA G R, FACINA G, SHIDA J Y, et al. Effects of low dose tamoxifen on normal breast tissue from premenopausal women[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2003, 39(7): 891-898.
[4]FASANELLA S, LEONARDI E, CANTALONI C, et al.Proliferative activity in human breast cancer: Ki-67 automated evaluation and the influence of different Ki-67 equivalent antibodies[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2011, 6(Suppl 1): 7.
[5]LIU S, EDGERTON S M, MOORE D H 2ND, et al. Measures of cell turn over (proliferation and apoptosis) and their association with survival in breast cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2001, 7(6): 1716-1723.
[6]MOLINO A, MICCIOLO R, TURAZZA M, et al. Ki-67 immunostaining in 322 primary breast cancers: associations with clinical and pathological variables and prognosis[J].Int J Cancer, 1997, 74(4): 433-437.
[7]BHATAVDEKAR J M, PATEL D D, SHAH N G, et al.Prognostic significance of immunohistochemically localized biomarkers in stage Ⅱ and stage Ⅲ breast cancer: a multivariate analysis[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2000, 7(4): 305-311.
[8]BROWN R W, ALLRED C D, CLARK G M, et al. Prognostic value of Ki-67 compared to S-phase fraction in axillary nodenegative breast cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 1996, 2(3):585-592.
[9]SPYRATOS F, FERRERO-POUS M, TRASSARD M, et al.Correlation between MIB-1 and other proliferation markers:clinical implications of the MIB-1 cut off value[J]. Cancer,2002, 94(8): 2151-2159.
[10]BOTTINI A, BERRUTI A, BERSIGA A, et al. Relationship between tumour shrinkage and reduction in Ki-67 expression after primary chemotherapy in human breast cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2001, 85(8): 1106-1112.
[11]WEIKEL W, BECK T, MITZE M, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of growth fractions in human breast cancers using monoclonal antibody Ki-67[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat,1991, 18(3): 149-154.
[12]BADER AA, TIO J, PETRU E, et al. T1breast cancer:identification of patients at low risk of axillary lymph node metastases[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2002, 76(1): 11-17.
[13]TRIHIA H, MURRAY S, PRICE K, et al. Ki-67 expression in breast carcinoma: its association with grading systems, clinical parameters, and other prognostic factors--a surrogate marker?[J]. Cancer, 2003, 97(5): 1321-1331.
[14]URRUTICOECHEA A, SMITH I E, DOWSETT M.Proliferation marker Ki-67 in early breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2005, 23(28): 7212-7220.
[15]PINDER S E, WENCYK P, SIBBERING D M, et al.Assessment of the new proliferation marker MIB1 in breast carcinoma using image analysis: associations with other prognostic factors and survival[J]. Br J Cancer, 1995,71(1): 146-149.
[16]RUDOLPH P, OLSSON H, BONATZ G, et al. Correlation between p53, c-erbB-2, and topoisomerase Ⅱ alpha expression, DNA ploidy, hormonal receptor status and proliferation in 356 node-negative breast carcinomas:prognostic implications[J]. J Pathol, 1999, 187(2): 207-216.
[17]GASPARINI G, POZZA F, MELI S, et al. Breast cancer cell kinetics: immunocytochemical determination of growth fractions by monoclonal antibody Ki-67 and correlation with flow cytometric S-phase and with some features of tumor aggressiveness[J]. Anticancer Res, 1991, 11(6): 2015-2021.
[18]NICHOLSON R I, MCCLELLAND R A, FINLAY P, et al.Relationship between EGF-R, c-erbB-2 protein expression and Ki-67 immunostaining in breast cancer and hormone sensitivity[J]. Eur J Cancer, 1993, 29(7): 1018-1023.
[19]周波, 谢菲, 王思源, 等. 紫杉类联合蒽环类的新辅助化疗方案治疗三阴乳腺癌的疗效及预后[J]. 中国癌症杂志,2009, 19(2): 129-132.
[20]CUZICK J, DOWSETT M, PINEDA S, et al. Prognostic value of a combined estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor,Ki-67, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 immunohistochemical score and comparison with the genomic health recurrence score in early breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(32): 4273-4278.
The expression and significance of Ki-67 in different subtype of breast cancer
ZHU Wei-liang,TAN Yan, WANG Xu-fen, CHENG Jin-ling, ZHANG Lei, FANG Qi, TAN Ke-lan, YANG Lan, WANG Lei(Department of Breast Surgery, The First People’s Hospital of Changzhou, Changzhou Jiangsu 213003, China)
ZHU Wei-liang E-mail:lancezwl@sina.com
Background and purpose:The established prognostic and predictive parameters of breast cancer were estrogen-receptor (ER), progesterone-receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2) status.The Ki-67 is now becoming a new research focus, and many researches showed that Ki-67 is an important biomarker after HER-2. This research aimed to study the expression and significance of Ki-67 in different subtypes of breast cancer.Methods:Clinical and pathological data of breast cancer patients, treated in Department of Breast Surgery, The First People’s Hospital of Changzhou from Jan. 2010 to Dec. 2010, were collected and analyzed. Immunohistochemical method was used to detect the expression of ER, PR, HER-2 and Ki-67 of these patients.Results:There were no correlations between the expression of Ki-67 and age or node metastasis of breast cancer patients, although there were significant differences in different tumor size of patients (P=0.001). The expressions of Ki-67 in stage Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲpatients were significantly higher than those in stage 0 patients, while there was no significant difference between the three mutually. The expressions of Ki-67 in ER negative patients were significantly higher than ER positive patients,and this trendency extended to PR negative and HER-2 positive patients (P<0.05). The expressions of Ki-67 in Luminal B subtype, HER-2 over-expression subtype and basal like subtype were significantly higher than in Luminal A subtype(P<0.001), but there was no significant difference between the three mutually.Conclusion:Ki-67 provides prognostic information combined with other biologic markers, and co-detection of Ki-67, ER, PR and HER-2 may be useful.
Breast cancer; Clinicopathological characteristics; Ki-67; ER; PR; HER-2
10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2012.05.005
R737.9
A
1007-3639(2012)05-0347-05
朱伟良 E-mail:lancezwl@sina.com
2011-12-02
2012-04-02)
