基于自由权矩阵的时滞神经网络系统时滞相依全局稳定性分析
2012-01-09毛凯时宝
毛凯,时宝
(海军航空工程学院,a.系统科学与数学研究所;b.基础部,山东烟台264001)
基于自由权矩阵的时滞神经网络系统时滞相依全局稳定性分析
毛凯a,时宝b
(海军航空工程学院,a.系统科学与数学研究所;b.基础部,山东烟台264001)
在激励函数有界且满足扇区条件的情形下研究了一类同时具有时变时滞和无穷分布时滞的神经网络系统全局稳定性.通过构造一个包含更多信息的新的Lyapunov泛函,利用自由权矩阵更好地描述Newton-Leibniz公式中各项以及系统各项之间的关系,充分利用状态变量、时滞函数、状态变量以及Lyapunov泛函导数中出现的负项中隐藏的信息,并结合S-Procedure等方法以线性矩阵不等式(LMI)的形式给出了系统时滞相依全局指数稳定充分条件.文中结果去掉了以往文献对时变时滞函数的导数具有不超过1的上界的限制条件,具有更低的保守性,且利用Matlab工具箱极易验证条件的正确性,并推广改进了相关文献的结果.
时变时滞;无穷分布时滞;自由权矩阵;S-Procedure;Lyapunov泛函
0 引言
众所周知,时滞通常是引起系统不稳定或振荡的重要原因,对于时滞神经网络系统稳定性的研究无论在理论上还是在实践中都具有重要意义.文献[1-4]研究了离散定常时滞神经网络的稳定性.文献[5-9,13-14,17-18]研究了具有时变时滞的神经网络的稳定性.文献[10-11,18]研究了具有时变时滞和有限分布时滞的神经网络系统的稳定性.文献[12,19]研究了含有形gj(uj(s))ds的无穷分布时滞项的神经网络系统的稳定性.但对于含有形的无穷分布时滞项的神经网络系统的稳定性研究却很少见.
一方面已有文献[5-9,18]中对于时变时滞函数通常都要求其导数具有不超过1的上界的限制条件.另一方面如何降低稳定性判据的保守性已成为研究热点.时滞相依的稳定性判据利用了时滞长度的信息,通常比时滞不相依的稳定性判据具有更低的保守性.而文献[13-16]引入了自由权矩阵法,用以描述Newton-Leibniz公式中各项之间的关系.它充分利用状态变量、状态变量的导数、时滞函数以及Lyapunov泛函导数中出现的负项中隐藏的信息,能够极大降低保守性.
基于以上分析,文中将通过构造一个新的恰当的Lyapunov泛函,利用自由权矩阵法以及SProcedure[15,21-22]研究同时具有时变时滞和形无穷分布时滞系统的全局渐近稳定性和全局指数稳定性,其中不再要求时变时滞函数的导数具有不超过1的上界,并以线性矩阵不等式(LMI)给出系统时滞相依全局指数稳定充分判据.
1 模型描述
考虑如下具有时变时滞和无穷分布时滞的系统:对于系统(1),我们作如下假设:
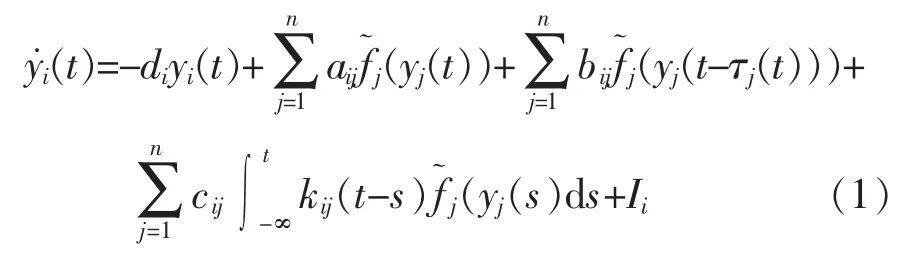
H1:时变时滞函满足0≤τ1≤τ(t)≤τ2,τ觶(t)≤μ.
H2:激励函数有界且满
H3:核函数kij(s)非负,
注1:通常文献都假设0≤τ(t)≤τ2,τ觶(t)≤μ<1.文中无论对于时变时滞函数的下界还是其导数的上界的要求都更具一般性.
注2:关于激励函数的假设H2最早出现在文献[23]中,现在已经被广泛采用.常以为正数,负数或零,相对于Sigmoid型和Lipschitz型激励函数而言,显然H2更具一般性,这样的假设被广泛应用于相关文献.
由假设H2知系统存在平衡点,记为y*.作变换yj(t)=xj(t)-,则系统(1)变为

写成矩阵向量形式即为

为方便,记Ij为第j行元素全部为1而其余元素全部为零的n×n矩阵,Ijj是第j行j列元素为1,其余元素全部为零的n×n矩阵L=diag(l1,l2,…,ln),

引理1[21]对于任意的正定常数矩阵M,常数r〉0和向量值函数x:[0,r]→Rn有

引理2(S-procedure[15,21-22])设Ti(i=0,1,2,…,k)为对称矩阵,若存在τi≥0(i=1,2,…,p)使立,则对于任意满足ξTTiξ≥0(i=1,2,…,k)的ξ≠0都
2 主要结果
定理假设H1~H3成立.对于给定的τ1,τ2,μ,若存在正定矩阵P,Qi(i=1,2,3,4),Ri(i=1,2,3),正对角阵E=diag(e1,e2,…,en),H=diag(h1,h2,…,hn),半正定对角矩阵Λi=diag(λi1,λi2,…,λin),λij≥0,i=1,2;j=1,2…,n以及任意适当维数的矩阵NT=(,,…,),M1,M2使得矩阵Π<0,则系统(2)的零解全局指数稳定.其中:

证明:作Lyapunov泛函V(t)=V1(t)+V2(t)+V3(t)+V4(t),其中:

对V(t)沿系统(2)的轨迹对t求导数,并利用引理1有:



对于任意适当维数的矩阵M1,M2显然还有下式成立.


另外,由假设H2知有:

则由引理2知,若存在Λi=diag(λi1,λi2,…,λin),λij≥0,i=1,2;j=1,2,…,n使得对任意的η(t)≠0都有下式成立,则系统(2)的零解全局渐近稳定.

由定理条件Π<0知,上式成立,从而系统(2)的零解全局渐近稳定性得证.
下面进一步证明系统(2)的零解全局指数稳定.由式(10)以及Π<0有:

再由V(t)的构造容易得:

其中α1=λmax(P)+λmax(LE),L=diag(l1,l2,…,ln),

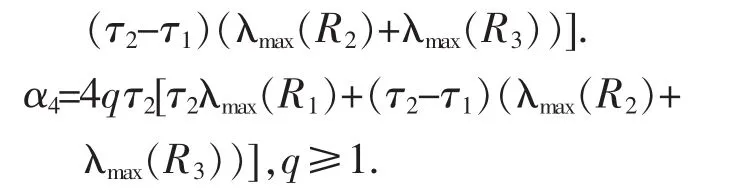
考察函数e2λtV(t),其中λ〉0待定.有

将上式从0到t积分,得

对于上式中的二重积分和三重积分,只要交换积分次序并适当放大积分区域,不难得到:

同理,
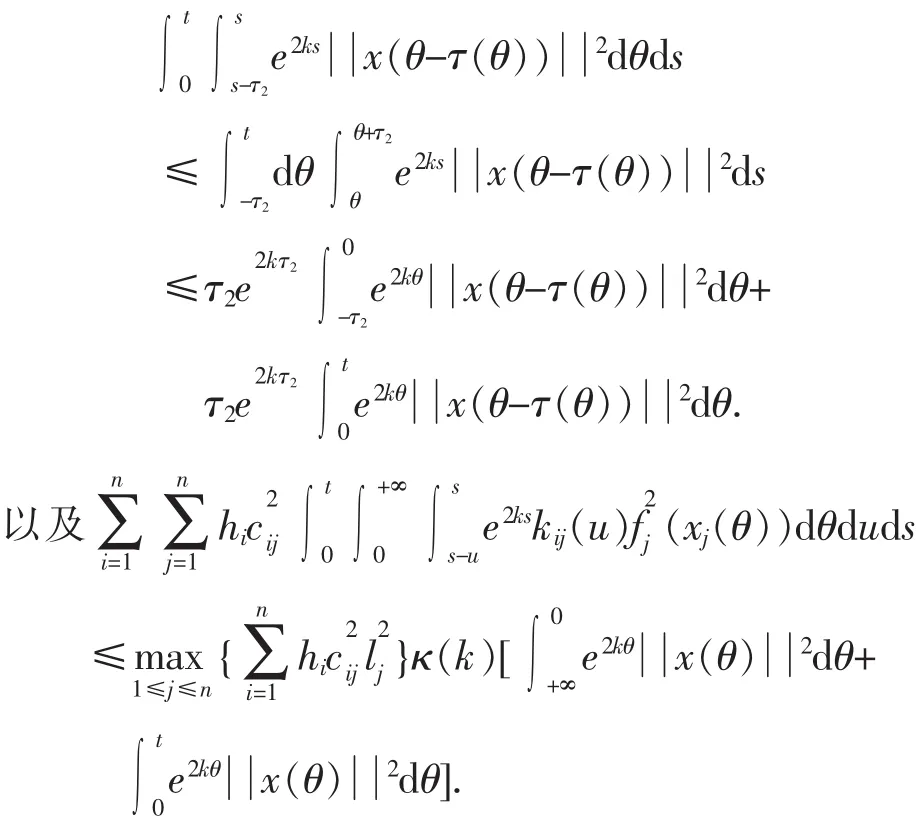
于是,

只要取λ满足下列条件

则由式(15)知:
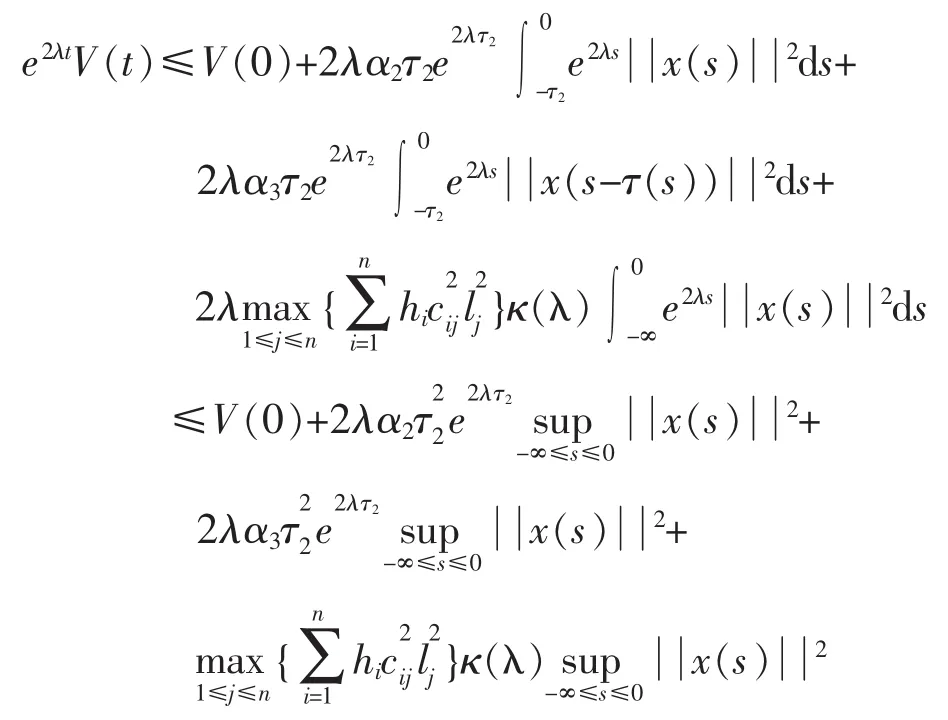
由式(12)有:

利用Cauchy-Schwartz不等式,有


另外,显然还有:

由V(t)的表达式以及式(16),式(17),式(18)得到:


3 结论
通过构造一个新的Lyapunov泛函,并利用自由权重矩阵法和S-Procedure研究了一类同时具有时变时滞和无穷分布时滞的细胞神经网络的全局指数稳定性,以LMI形式给出了系统全局渐近稳定以及指数稳定的充分判据,由Matlab工具箱能非常方便地对判据进行验证.文章去掉了时变时滞函数的导数具有不超过1的上界的严格要求.自由权重矩阵的引入有利于更好地描述Newton-Leibnitz公式中各项之间、以及系统各项之间的关系,能更好地利用状态变量、各时滞状态变量以及状态变量的导数之间隐藏的信息,从而极大地减少了稳定性判据的保守性,改进了相关文献的结果.
[1]Liao X F,Chen G R,Sanchez E N.Delay-dependent exponential stability analysis of delayed neural networks:an LMI approach[J].Neural Networks,2002,5(7):855-866.
[2]Li C D,Liao X F,Zhang R.Delay-dependent exponential stability analysis of bi-directional associative memory neural networks with time delay:an LMI approach[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2005,24(4):1119-1134.
[3]Xu S Y,Lam J,Ho D W C,et al.Novel global asymptotic stability criteria for delayed cellular neural networks[J].IEEE Trans Circ Syst II,2005,52(6):349-353.
[4]Xu S Y,Lam J,Ho D W C.A new LMI condition for delaydependentasymptoticstabilityofdelayedHopfieldneural networks[J].IEEE Trans Circ Syst,2006,53(3):230-234.
[5]Arik S.An analysis of exponential stability of delayed neural networks with time-varying delays[J].Neural Networks,2004,17(7):1027-1031.
[6]Zhang Q,Wei X P,Xu J.Delay-dependent exponential stability of cellular neural networks with time-varying delays[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2005,23(4):1363-1369.
[7]Zhang H B,Li C D,Liao X F.A note on the robust stability of neural networks with time delay[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2005,25(2):357-360.
[8]Liu Jiang.Global exponential stability of Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with time-varying delays[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2005,26(3):935-945.
[9]He Y,Wang Q G,Zheng W X.Global robust stability for delayed neural networks with polytopic type uncertainties[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2005,26(5):1349-1354.
[10]Li H Y,Chen B,Zhou Q,et al.Robust exponential stability for
uncertain stochastic neural networks with discrete and distributed
time-varying delays[J].Physics Letters A,2008,372(19):3385-3394.[11]RRakkiyappan,PBalasubramaniam,SLakshmanan.Robuststability results for uncertain stochastic neural networks with discrete interval and distributed time-varying delays[J].Physics Letters A,2008,372(32):5290-5298.
[12]Ju H Park.On gobal stability criterion of neural networks with continuously distributed delays[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2008,37(2):444-449.
[13]Song Q K,Wang Z D.A delay-dependent LMI approach to dynamics analysis of discrete-time recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays[J].Physics Letters A,2007,368(1-2):134-145.
[14]Liu H L,Chen G H.Delay-dependent stability for neural networks with time-varying delay[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2007,33(1):171-177.
[15]Jiang Y H,Yang B,Wang J C,et al.Delay-dependent stability criterion for delayed Hopfield neural networks[J].Chaos,Solitons&Fractals,2009,39(5):2133-2137.
[16]Park P.A delay-dependent stability criterion for systems with uncertain time-invariant delays[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,1999,44(4):876-877.
[17]Poogyeon Park,Jeong Wan Ko.Stability and robust stability for systems with a time-varying delay[J].Automatica,2007,43(10):1855-1858.
[18]Li T,Luo Q,Sun C Y,et al.Exponential stability of recurrent neural networks with time-varying discrete and distributed delays[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Real World Applications,2009,10(4):2581-2589.
[19]Su Huan,Li Wenxuw,Wang Ke,et al.Stability for stochastic neural network with infinite delay[J].Neurecomputing 2011,74(10):1535-1540.
[20]宫大为,王占山,黄博南.一类带有混合时滞的神经网络全局渐近稳定分析[J].东北大学学报:自然科学版,2011,32(6):773-776.
[21]S Boyd,L EI Ghaoui,E Feron,et al.Linear matrix inequalities in system and control theory[M].SIAM,Philadelphia,PA,1994.
[22]S Udpin,P Niamsup.Robust stability of discrete-time LPD neural networks with time-varying delay[J].Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat,2009,14(11):3914-3924.
[23]Liu Y R,Wang Z D,Liu X H.Global exponential stability of generalizedrecurrentneuralnetworkswithdiscreteand distributed delays[J].Neural Networks,2006,19(5):667-675.
On the delay-dependent global stability analysis of delayed neural networks based on the free-weighting matrix method
MAO Kaia,SHI Baob
(a.Institute of Systems Science and Mathematics;b.Department of Basic Science,Naval Aeronautical and Astronautically University,Yantai 264001,China)
The global stability of the neural networks with both time-varying and infinite distributed delays is studied based on the condition that the activation functions satisfy the sector condition.By constructing a new Lyapunov functional which contains more information,utilizing the free-weight matrices which can better describe the relations among the terms of Newton-Leibnitz formula and the system,taking advantage of the information hidden in the state variable,the time delay functions,the derivative of the state variable and the Lyapunov functional,combining with the S-procedure,a delay-dependent sufficient condition for guaranteeing the globally exponential stability of the system is derived in form of LMI,which can be easily checked by the Matlab toolbox.The result obtained in this article improves the previous ones on which it threw off the constraint that the derivative of the time-varying function has an upper bound no larger than 1 and is less conservative than the relevant ones.
time-varying delays;infinite distributed delays;free-weighting matrix;S-Procedure;Lyapunov functional
O175.13
A
2012-06-05
海军航空工程学院专业技术拔尖人才基金(名师工程)
毛凯(1972-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事神经网络动力学等方面的研究,E-mail:maokaif@hotamil.com.
2095-3046(2012)05-0082-06
