中立型Cohen-Grossberg神经网络概周期解的存在唯一性
2011-01-24何丹华
何丹华
(浙江外国语学院理工学院,浙江杭州310012)
1 引言
考虑如下中立型Cohen-Grossberg神经网络概周期解的存在唯一性:

其中,xi(t)表示第i个神经元,αi(xi(t))表示第i个神经元的放大函数,βi(xi(t))表示适当的运行函数,gj,fj表示第j个神经元的激活函数,aij(t),bij(t)表示在t时刻神经元之间相互联络的权重,0≤τij(t)≤τ(τ是常数,i,j=1,2,…,n)表示传输时滞,Ii(t)表示外部输入.另外αi(xi(t)),βi(xi(t)),aij(t),bij(t),Ii(t)(i,j=1,2,…,n)都是关于t的概周期函数.
近年来,带有常数时滞或变时滞或分布时滞的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络得到了广泛研究[1-4].这些研究主要依赖于平衡点的存在唯一性及其稳定性.然而因为外界干扰的影响,神经网络有时会出现周期振荡,概周期振荡,甚至不稳定.因此我们有必要研究神经网络的概周期振荡现象.
同时,各种中立型时滞微分系统的研究已经得到关注[5-8],因为它们在自动化控制,人口系统和与弹性杆相关的振动人群的研究中有广泛运用.出现在几乎无损失传输的高速电脑中的电子网络经常用于连接开关电路,然而大量包含无损失传输线的电子网络的方程可以简化为中立型时滞微分方程.因此,我们对中立型时滞微分系统的研究具有理论和实际意义.
在文献[9-11]中,带有变系数的Cohen-Grossberg神经网络的概周期解已经利用反导数方法得到研究.因为中立型时滞的存在,所以利用反导数方法构建gj的条件非常困难.因此,受文献[9]和[12]启发,我们通过建立线性辅助方程,利用指数二分性及不动点定理,得到了一类中立型Cohen-Grossberg神经网络概周期解的存在唯一性的充分条件.
2 预备知识
定义1[13-14]称连续函数x(t):R→Rn在R上是概周期的,如果对任意的ε>0,都能找到一个实数l=l(ε)>0,且在任意长度为l(ε)的区间上存在一个数δ=δ(ε),使得(t+δ)-x(t )<ε,t∈R.
定义2[13-14]称x(t)是连续可微的概周期函数,如果x(t):R→Rn关于t连续可微,且x(t)和x'(t)在R上是概周期的.
定义3[13-14]令x(t)∈Rn,C(t)是一个定义在R上的n×n连续矩阵,称系统

在R上具有指数二分性,如果存在正常数k,l,映射S和基础矩阵X(t)满足

引理1[12,15]假设ci(t)是R上的一个概周期函数,且

则线性系统x'(t)=diag{-c1(t),…,-cn(t)}x(t)在R上具有指数二分性.
引理2[12,15]如果线性系统x'(t)=C(t)x(t)具有指数二分性,则概周期系统x'(t)=C(t)x(t)+g(t)存在一个概周期解x(t),可表示为

3 主要结果
给出以下假设条件:
(A1)放大函数αi(x)是连续∀x,y∈R,i∈N.
(A2)存在正常数ωi,μi,使
(A3)存在正常数Fj,Gj,Mj,Nj,使
(A4)核函数kij≥0分段连续,且满数.
定理1 假设条件(A1)~(A4)成立,则式(1)存在唯一的概周期解,如果存在常数d>0,使得0≤
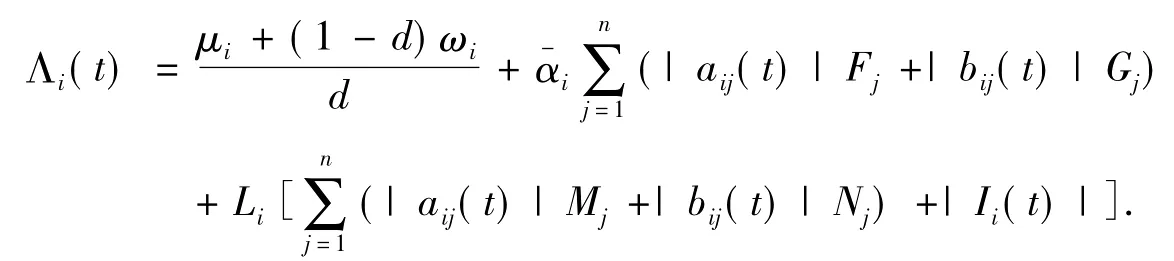
证明令Ξ={u(t)=col{ui(t)}|u(t):R→Rn是连续可微概周期函数}.对任意的u(t)∈Ξ,定义范数:

因此(Ξ,‖·‖)是一个巴拿赫空间.
与文献[12]中的分析类似,对任意的u(t)∈Ξ,考虑如下的辅助线性概周期微分系统


根据引理1,得到

在R上具有指数二分性.所以根据引理2,系统(3)存在一个概周期解xu(t)=col{xui(t)}表示为

定义一个映射Γ:Ξ→Ξ,Γ(u(t))=xu(t),∀u∈Ξ,其中
Γ(u(t))=col{Γi(u(t))}.接下来证明映射Γ:Ξ→Ξ是压缩映射.对任意的u,v∈Ξ,有
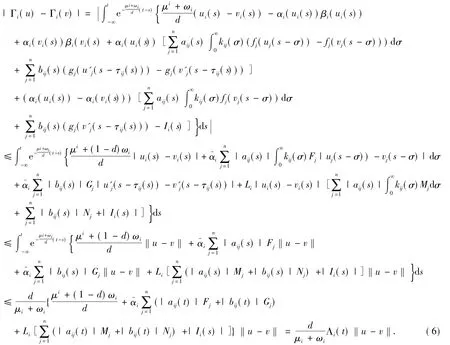
另一方面,

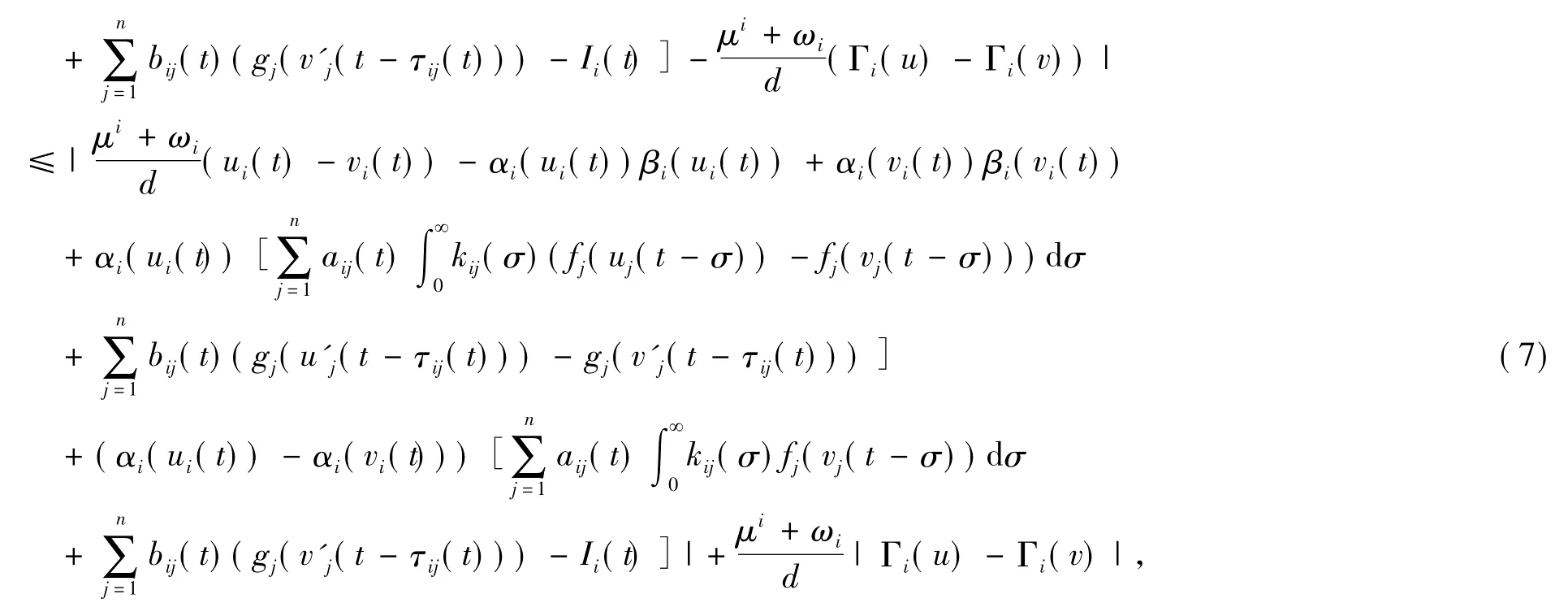
由式(6),得到

所以由式(2),(6)和(8),得到

因为0≤ρ<1,所以映射Γ是一个压缩映射.根据巴拿赫不动点定理,存在唯一的不动点u*(t)∈Ξ,使得Γ(u*(t))=u*(t),进而得到系统(1)存在唯一的概周期解.证毕.
[1] Li T,Fei S,Guo Y,et al.Stability analysis on Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with both time-varying and continuously distributed delays[J].Nonlinear Anal RWA,2009,10:2600-2612.
[2] Su W,Chen Y.Global robust stability criteria of stochastic Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with discrete and distributed time-varying delays[J].Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat,2009,14:520-528.
[3] Cui B,Wu W.Global exponential stability of Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with dis-tributed delays[J].Neurocomputing,2008,72:386-391.
[4] Lu K,Xu D,Yang Z.Global attraction and stability for Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with delays[J].Neural Networks,2006,19:1538-1549.
[5] Hale J,Verduyn Lunel S M.Introduction to Functional Differential Equations[M].Springer-Verlag,New York,1993.
[6] Deimling K.Nonlinear Functional Analysis[M].Berlin:Springer,1985.
[7] Fang H,Li J.On the existence of periodic solutions of a neutral delay model of single-species population growth[J].J Math Anal Appl,2001,259(1):8-17.
[8] Xu L,Xu D.Exponential stability of nonlinear impulsive neutral integro-differential equa-Tions[J].Nonlinear Anal,2008,69:2910-2923.
[9] Zhao H,Chen L,Mao Z.Existence and stability of almost periodic solution for Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with variable coeffcients[J].Nonlinear Anal RWA,2008,9:663-673.
[10] Xiang H,Cao J.Almost periodic solution of Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with bounded and unbounded delays[J].Nonlinear Anal RWA,2009,10:2407-2419.
[11] Li Y,Fan X,Existence and globally exponential stability of almost periodic solution for Cohen-Grossberg BAM neural networks with variable coeffcients[J].Appl Math Model,2009,33:2114-2120.
[12] Chen Z,Zhao D,Ruan J.Almost periodic attractor for Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with delay[J].Phys Lett A,2009,373:434-440.
[13] Fink A M.Almost Periodic Differential Equations[M].Berlin:Springer, 1974:80-112.
[14] He C Y.Almost Periodic Differential Equation[M].Beijing:Higher Education Publishing House,1992:90-100.
[15] Xiao B.Existence and uniqueness of almost periodic solutions for a class of Hopfeld neural networks with neutral delays[J].Appl Math Lett,2009,22:528-533.
