二维配合物{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n的水热合成、晶体结构和荧光性质研究
2010-11-10刘光祥黄荣谊任小明
刘光祥 黄荣谊 任小明
(安庆师范学院化学化工学院,功能配合物安徽省重点实验室,安庆 246003)
研究简报
二维配合物{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n的水热合成、晶体结构和荧光性质研究
刘光祥*黄荣谊 任小明
(安庆师范学院化学化工学院,功能配合物安徽省重点实验室,安庆 246003)
镉配合物;晶体结构;4,4′-联苯二磺酸;荧光
0 Introduction
There has been significant interest in the design and synthesis ofmixed inorganic-organic hybrid materials owing to their potential application in catalysis,gas storage and separation,ion exchange and magnetism[1-5].Metal phosphonates have been extensively studied due to their inorganic-organic lamellar structures which possess potential functionality of host-guest interactions[6-9].The sulfonate group,R-SO3,bearing a structural analogue of phosphonate R-PO3,could be utilized as a synthon to build inorganic-organic lamellar structure similar to that of its phosphonate analog.On the other hand,the coordination chemistry of sulfonatesis a less-well explored territory,as is also indicated by the limited number of references on structures of metal sulfonates,and sulfonate anions show weak coordination strength with transition metals[10-15].Most of the transition metal sulfonates obtained from aqueous solution are aqua-metal sulfonate salts[16-17].However,after introducing other organic ligands as auxiliaries to the metal centers,sulfonate anions can compete with water molecules and coordinate with transition metals[18-19].This observation indicates that the coordination strength of sulfonate anions is tunable.With the infinite number of organic auxiliary ligands available,it opens up a novel research area that could produce numerous materials with interesting coordination and structural features.4,4′-Biphenyldisulfonate anions are rigid spacers with potential multiple binding sites which can be used to construct coordination polymers with multiple dimensions and variant topologies,as demonstrated previously[14-15,18-19].Herein,we report its synthesis,crystal structure and luminescent properties of a new coordination polymer{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n(1)based on 4,4′-biphenyldisulfonic acid(H2bpds)and 1,3-bis(4-pyridyl)propane(bpp).
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and general methods
All the reagents and solvents for syntheses and analyses were commercially available and employed as received without further purification.Elemental analyses(C,H and N)were performed on a Vario ELⅢelemental analyzer.Infrared spectra were performed on a Nicolet AVATAR-360 spectrophotometer with KBr pellets in the 400~4 000 cm-1region.The luminescent spectra for the powdered solid samples were measured at room temperature on a Hitachi F-4500 fluorescence spectrophotometer with a xenon arc lamp as the light source.In the measurements of emission and excitation spectra the pass width is 5 nm.All the measurements were carried out under the same experimental conditions.Thermal gravimetric analyses(TGA)were performed on a Netzsch STA-409PC instrument in flowing N2with a heating rate of 20 ℃·min-1.
1.2 Synthesis of{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n(1)
The single crystals of 1 were prepared by hydrothermal reaction.A mixture of bpp(0.20 g,1.00 mmol),H2bpds(0.31 g,1.0 mmol),Cd(OAc)2·2H2O (0.27 g,1.00 mmol),NaOH (0.08 g,2.00 mmol),and H2O(10 mL)was stirred for 1 h and then sealed in a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel container.The container was heated to 150℃and held at that temperature for 96 h,then cooled to room temperature at a rate of 5℃·h-1.Colorless block crystals of 1 were collected in 43%yield based on Cd(OAc)2·2H2O.Anal.Cacld.for C38H40N4O8S2Cd(%):C 53.24,H 4.70,N 6.54;found(%):C 53.20,H 4.75,N 6.51.IR spectrum:3 427,3 109,3 085,2 031,1 923,1 634,1 595,1 485,1 319,1 243,1 157,1 185,1 062,1 035,1 005,912,873,838,815,773,734,712,676 and 631 cm-1.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
A colorless block single crystal of 1 with 0.24 mm×0.22 mm ×0.18 mm was carefully selected under a polarizing microscope and glued at the tip of a thin glass fiber with cyanoacrylate (super glue)adhesive.Single crystalstructure determination by X-ray diffraction was performed on a Bruker Smart ApexⅡCCD diffractometer equipped with a normal focus,3 kW sealed tube X-ray source (Mo Kα radiation,λ=0.071073 nm)operating at 50 kV and 30 mA.A total of 4,906 reflections were collected in the range(2.04 ≤θ≤25.50,-10≤h≤9,-13≤k≤12,-13≤l≤11),of which 3468 are unique(Rint=0.0195)and 3384 with I>2σ(I)were used in the refinement of the structure of 1.Absorption corrections were applied using multiscan technique[20].The structure was solved by the direct method and refined by full-matrix least squares on F2using the SHELX 97 software[21-22].All of the nonhydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.The hydrogen atoms of the ligands were placed in the geometrically calculated positions.The hydrogen atoms of the water molecule were located in a difference Fourier map.The detailed crystallographic data and structure refinement parameters for 1 are summarized in Table 1.Selected bond lengths and bond angles for 1 are listed in Table 2.
CCDC:769593.
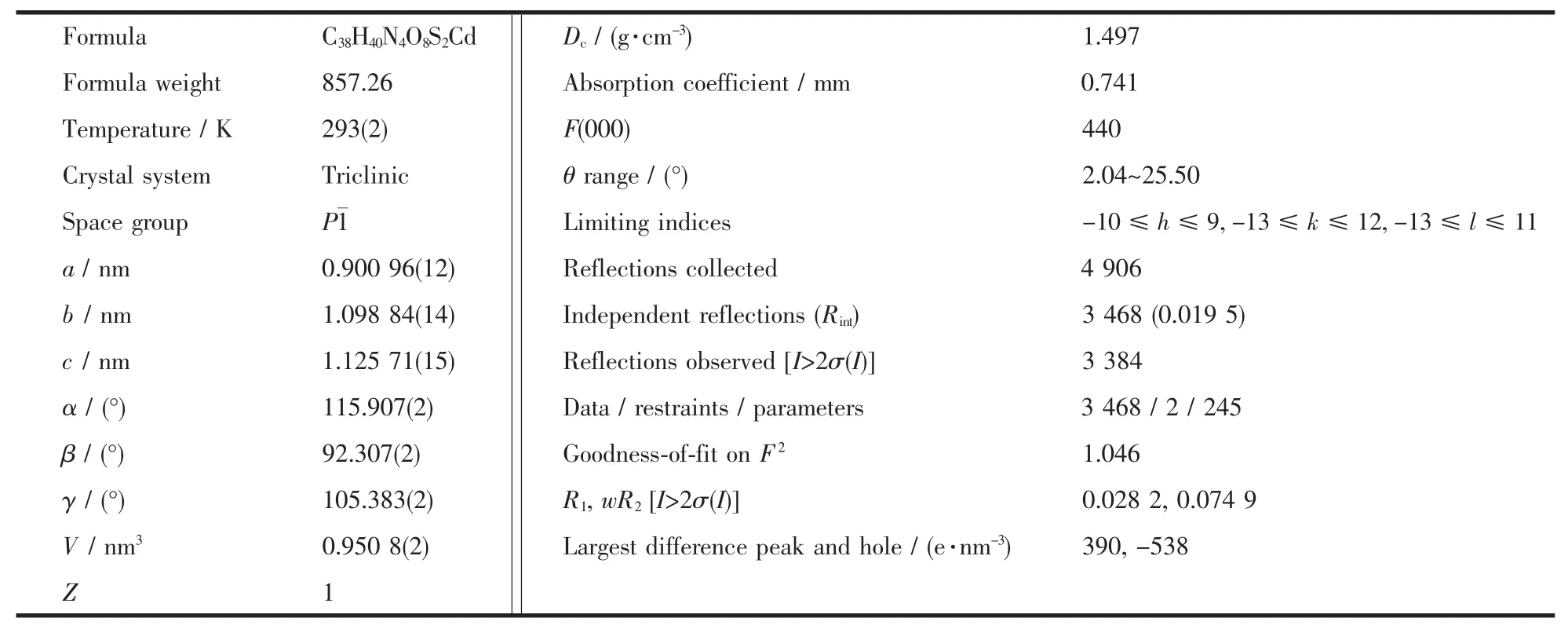
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for 1
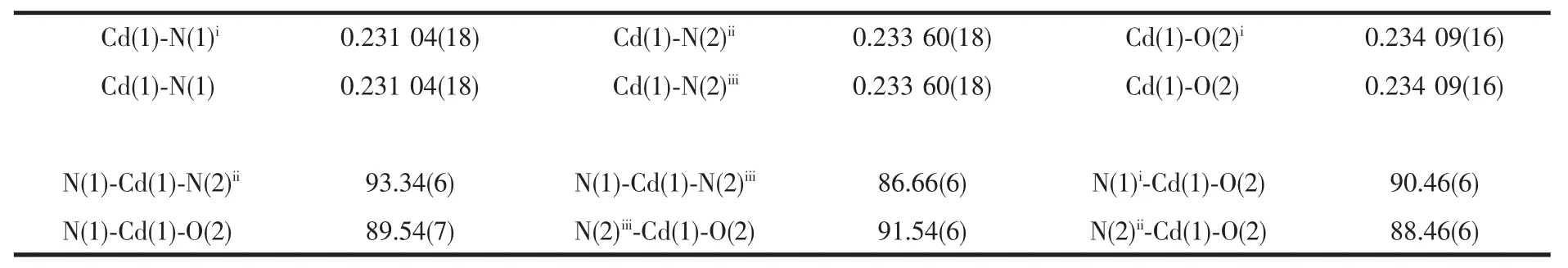
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for 1
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Structure description of{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n
Complex 1 crystallizes in the triclinic with space group P1.The asymmetric unit contains one unique Cdatom,one unique bpp ligand,a half of bpds dianion and one solvated water molecule.As shown in Fig.1,Cdlies on an inversion center and shows a slightly distorted octahedral geometry with four nitrogen atoms from four different bpp ligands in the equatorial basal plane and two oxygen atoms from different bpds at the axial positions.The Cd-N distances are in the range of 0.231 04(18)~0.233 60(18)nm and the Cd-O distance is 0.23409(16)nm,which are similar to the reported Cd-O and Cd-N distances in other Cdcoordination polymers[14].The angles of cis O(N)-Cd-O(N)are in the range of 86.66(6)°~93.34(6)°.

Fig.1 ORTEP drawing of 1 showing the labeling of atoms with thermal ellipsoids at 30%probability
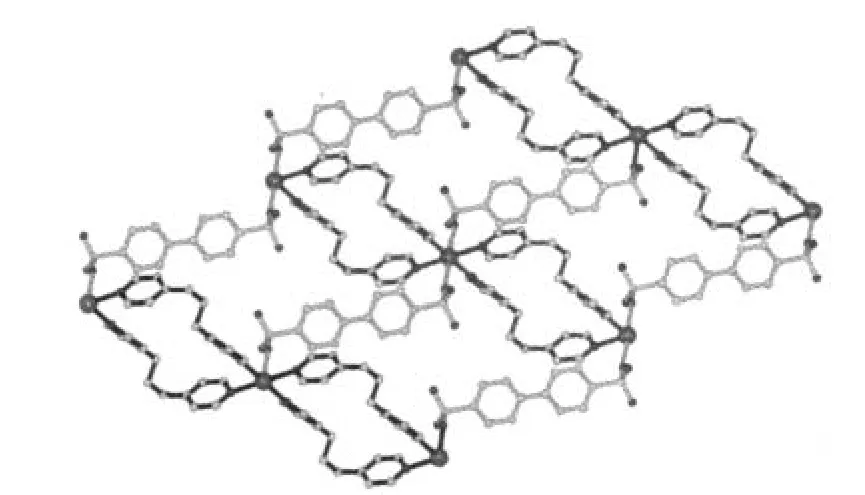
Fig.2 View toward the bc plane of the two-dimensional lamellar structure in 1
Bpds in a bis-monodentate fashion bridges two Cdatoms forming a one-dimensional zigzag chain.The shortest Cd…Cd distance within a chain is 1.3082 nm,which is similar to those in other bpds complexes[14,19].The zigzag chains are further linked by bpp into a two-dimensional lamellar structure (Fig.2),the Cd…Cd distances separated by bpp is 1.180 6 nm.The pyridyl rings of bpp are twisted with dihedral angle of 61.87°.Crystalline water molecules reside in adjacent layers and extend the 2D layer into a 3D architecture through extensive hydrogen-bonding interactions.Hydrogen-bonding details for 1 are given in Table 3.

Table 3 Distance and angles of hydrogen-bonding for 1
2.2 IR spectra
The IR spectral data show features attributable to the sulfonate stretching vibrations of the complex.The broad bands centered at ca.3 427 cm-1indicate the OH stretching of water.The well-resolved frequencies of aromatic rings span over the regions of 1250~1750 and 600~900 cm-1.Bands characteristic of the fundamental and split ν3S-O stretching modes are observed in the range of 1000~1240 cm-1[23].
2.3 Thermogravimetric analyses
Thermal gravimetric analyses(TGA)were carried out to examine the thermal stability of 1.The samples were heated up in flowing N2with a heating rate of 20℃·min-1,as shown in Fig.3.The weight loss of 4.15%(calcd.4.20%)below 100 ℃ is attributed to the release of two solvated water molecules per formula.Then a sharp weight-loss step was observed between 280 and 550℃,which can be attributed to the decomposition of organic ligands.
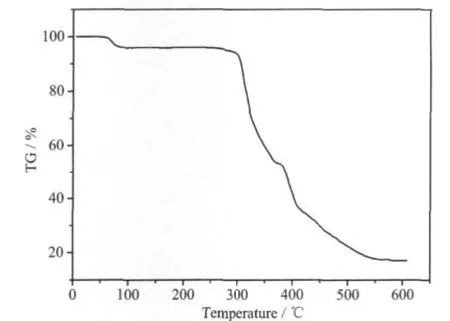
Fig.3 TG curve of complex 1
2.4 Luminescent properties
Luminescent compounds are of great current interest because of their various applications in chemical sensors,photochemistry,and electroluminescent(EL)displays[24-27].The luminescent properties of cadmium carboxylate complexes have been investigated extensively[28-30],however,studies concerning cadmium sulfonates are limited[14,19].As shown in Fig.4,complex 1 exhibits both blue photoluminescence with an emission maximum at 476 nm upon excitation at 338 nm and the strongest excitation peak at 342 nm upon emission at 472 nm.The main emission peaks of H2bpds and bpp are at 312 and 369 nm,respectively.The removal of a proton from H2bpds and the coordination of the bpds2-anion and bpp to the cadmiumcenters play important roles in the red shift of the emission.The luminescence of complex 1 should originate from the transitions between the energy levels of sulfonate anion,neutral ligand,or both.The shifts of the emission bands are attributed to both the deprotonation of the sulfonic acid and the coordination action of the sulfonate anion and neutral ligand to cadmiumions[31].These observations indicate that 1 may be excellent candidates for potential photoactive materials.

Fig.4 Solid-state excitation and emission spectra of 1 at room temperature
[1]Li J R,Kuppler R J,Zhou H C.Chem.Soc.Rev.,2009,38:1477-1504
[2]Chae H K,Siberio-Pérez D Y,Kim J,et al.Nature,2004,427:523-527
[3]Wang Z,Chen G,Ding K L.Chem.Rev.,2009,109:322-359
[4]Cramb D T,Shimizu G K H.Nature Mater.,2008,7:229-235
[5]Ockwig N W,Delgado-Friederichs O,O′Keeffe M,et al.Acc.Chem.Res.,2005,38:176-182
[6]Gadenne B,Semeraro M,Yebeutchou R M,et al.Chem.Eur.J.,2008,14:8964-8971
[7]Shimizu G K H,Vaidhyanathan R,Taylor J M.Chem.Soc.Rev.,2009,38:1430-1449
[8]Miller S R,Pearce G M,Wright P A,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2008,130:15967-15981
[9]Guo L R,Zhu F,Chen Y,et al.Dalton Trans.,2009:8548-8554
[10]Cté A P,Ferguson M J,Khan K A,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2002,41:287-292
[11]Kosnic E J,McClymont E L,Hodder R A,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,1992,201:143-151
[12]Wu H,Dong X W,Liu H Y,et al.Dalton Trans.,2008:5331-5341
[13]Li F F,Ma J F,Song S Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2005,44:9374-9383
[14]Chen C H,Cai J W,Liao C Z,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2002,41:4967-4974
[15]Lian Z X,Cai J W,Chen C H,et al.CrystEngComm,2007,9:319-327
[16]Shubnell A J,Kosnic E J,Squattrito P J.Inorg.Chim.Acta,1994,216:101-112
[17]Gunderman B J,Kabell I D,Squattrito P J,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,1997,258:237-246
[18]Cai J W,Chen C H,Liao C Z,et al.J.Chem.Soc.,Dalton Trans.,2001:1137-1142
[19]Cai J W,Chen C H,Liao C Z.J.Chem.Soc.,Dalton Trans.,2001:2370-2375
[20]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,Program for Bruker Area Detector Absorption Correction,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[21]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,Program for Crystal Structure Solution,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[22]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structure,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[23]Nakamoto K.Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordinated Compounds.5th Ed.New York:Wiley&Sons,1997.
[24]Wu Q G,Esteghamatian M,Hu N X,et al.Chem.Mater.,2000,12:79-83
[25]McGarrah J E,Kim Y J,Hissler M,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2001,40:4510-4511
[26]Santis G D,Fabbrizzi L,Licchelli M,et al.Angew.Chem.,Int.Ed.Engl.,1996,35:202-204
[27]Zheng S L,Yang J H,Yu X L,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2004,43:831-836
[28]Li S L,Lan Y Q,Ma J F,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2008,8:1610-1616
[29]Kulkarni P,Padhye S,Sinn E.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2001,321:193-199
[30]Wang Y X,Perez W J,Zheng G Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1998,37:2227-2234
[31]Valeur B.Molecular Fluorescence:Principles and Applications.Weinheim:Wiley-VCH,2002.
Hydrothermal Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Photoluminescence of a Novel Two-Dimensional CadmiumComplex:{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n
LIU Guang-Xiang*HUANG Rong-YiREN Xiao-Ming
(Anhui Key Laboratory of Functional Coordination Compounds,School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Anqing Normal University,Anqing,Anhui 246003)
A novel two-dimensional cadmiumcomplex{[Cd(bpds)(bpp)2]·2H2O}n(1)with 4,4′-biphenyldisulfonic acid(H2bpds)and 1,3-bis(4-pyridyl)propane(bpp)has been synthesized by means of hydrothermal method and characterized by elemental analysis,IR spectrum,thermal analysis and single-crystal X-ray diffraction.The crystal is of triclinic,space group P1 with a=0.90096(12)nm,b=1.09884(14)nm,c=1.12571(15)nm,α=115.907(2)°,β=92.307(2)°,γ=105.383(2)°,V=0.9508(2)nm3,Dc=1.497 g·cm-3,Z=1,F(000)=440,Goof=1.046,R1=0.0282,wR2=0.074 9.Complex 1 shows a novel two-dimensional (2D)lamellar structure and further extended into a 3D supramolecular structure through O-H…O and C-H…O hydrogen bonding interactions.Luminescent studies show that complex 1 exhibits intense blue fluorescent emission.CCDC:769593.
Cadmiumcomplex;crystal structure;4,4′-biphenyldisulfonic acid;luminescence
O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2010)09-1680-05
2010-04-12。收修改稿日期:2010-05-23。
国家自然科学基金项目(No.20971004)和教育部科学技术研究重点项目(No.210102)资助。*
。 E-mail:njuliugx@gmail.com
刘光祥,男,39岁,博士,教授;研究方向:功能配合物。
