配合物Pb(cbba)2(phen)2的水热合成、晶体结构与荧光性能研究
2010-11-09王庆伟李秀梅王志涛
王庆伟 李秀梅 王志涛 刘 博
(1吉林师范大学化学学院,四平 136000)(2通化师范学院化学系,通化 134002)
研究简报
配合物Pb(cbba)2(phen)2的水热合成、晶体结构与荧光性能研究
王庆伟*,1李秀梅2王志涛2刘 博1
(1吉林师范大学化学学院,四平 136000)
(2通化师范学院化学系,通化 134002)
水热合成;晶体结构;铅配合物;荧光
0 Introduction
As we know,lead is a heavy and toxic metal,so the study of Pb(Ⅱ)model complexes in biological systems and removal of lead by chelating agents through coordination is very important[1].Lead(Ⅱ)possesses a large radius,a variable stereochemical activity,and a flexible coordination environment,which provide unique opportunities for the construction of novel metal-organic frameworks(MOFs)[2].Recently,increasing investigations have been focused on the construction of coordination polymers using heterocyclic carboxylic acids like pyridine-[3],pyrazine-[4]and imidazolecarboxylic acids[5]as building blocks.These building blocks contain multi-oxygen and nitrogen atoms and can coordinate with metal ions in different ways,resulting in the formation of various metal-organic frameworks(MOFs)with specific topologies and useful properties.
We are interested in the solid-state coordinationchemistry of 2-(4′-chlorine-benzoyl)benzoic acid,which shows an excellent building block with charge and multi-connecting ability.As far as we are aware,there has been only one report on the structures of transition metal complexes with 2-(4′-chlorine-benzoyl)benzoic acid ligand[6],but those based on metal Pb and mixed ligands of 2-(4′-chlorine-benzoyl)benzoic acid and chelate phen ligand,to the best of our knowledge,have not been previously investigated.Of particular interest to us is the construction of metal of main group polymers with new structural features by the utilization ofhydrothermalsynthesis.We reporthere the preparation and crystal structure of the title complex Pb(cbba)2(phen)2(1).
1 Experimental
1.1 Synthesis of Pb(cbba)2(phen)2
The title compound was prepared from a mixture of Pb(NO3)(0.030 g),H2cbba(0.052 g),phen(0.036 g)and H2O (18 mL)in a 30 mL Teflon-lined autoclave under autogenous pressure at 170 ℃ for five days.After cooling to room temperature,colorless block crystals were collected by filtration and washed with distilled water in 38%yield (based on Pb).Anal.Calcd.for C52H32Cl2N4O6Pb(%):C,57.46;H,2.97;N,5.15.Found(%):C,57.45;H,2.95;N,5.14.IR(KBr,cm-1):3056w,1 659s 1 601w,1 583s,1 557s,1 429w,1 418w,1 379s,1347w,1299w,1 286m,1 247w,1 142w,1 091m,1 015 w,932s,857m,840m,774w,750m,730w,675w,651w,636w,529w,478w.
1.2 Structure determination
A single crystal of the title compound with dimensions of 0.235 mm ×0.138 mm ×0.095 mm was mounted on a Bruker Smart ApexⅡCCD diffractometer equipped with a graphite-monochromatic Mo Kα(λ=0.071 073 nm)radiation using an φ-ω scan mode at 273(2)K.In the range of 3.86°<2θ<52.06°,a total of 22 551 reflections were collected and 4 198 were independent with Rint=0.017 3,of which 3 582 were observed with I>2σ(I).The correction for Lp factors was applied.The structure was solved by direct methods with SHELX-97 program[7]and refined by full-matrix least-squares techniques on F2with SHELXL-97[8].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically and hydrogen atoms isotropically.All H atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding with Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(C).The final R=0.0184 and wR=0.0476(w=1/=1.125,(Δρ)max=506 e·nm-3,(Δρ)min=-629 e·nm-3and(Δ/σ)max=0.001.The selected important bond parameters are given in Table 1.
CCDC:792222.

Table 1 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)
2 Results and discussion
2.1 IR spectrum
The COO-is coordinated with its asymmetric and symmetric stretching appearing at 1583 cm-1(ν(OCO)assym)and 1 379 cm-1(ν(OCO)sym)[9],respectively.The Δν(ν(OCO)assym-ν(OCO)sym)is 204 cm-1(>200 cm-1),showing the presence of monodentate linkage of carboxylates in the dianions.Thus the carboxylates coordinate to the metal as monodentate ligands via the carboxylate groups[10].The absence of the characteristic bands at abound 1700 cm-1in compound 1 attributed to the protonated carboxylic group indicates that the complete deprotonation of cbba ligand upon reaction with Pb ions[11].In addition,X-ray diffraction analysis further indicates the existence of monodentate coordination manners of the carboxylate groups and prence deprotonation of cbba ligands.
2.2 Description of the structure
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that compound Pb(cbba)2(phen)2(1)crystallizes in Pbcn space group and consistsofa zero-dimensional structure.The molecular structure of the compound 1 is shown in Fig.1.There are one Pb (Ⅱ) ion,two phen ligands and two cbba ligands in the asymmetric unit.The Pb1 ion is six-coordinated by two carboxylate oxygen atoms(O1,O2A)from two different cbba ligands and four nitrogen atoms(N1,N2,N1A,N2A)from two different phen ligands,showing a distorted octahedral geometry.One carboxylate oxygen (O2)and three nitrogen (N1A,N2,N2A)atoms define an equatorial plane,while the axial coordination sites are occupied by the other carboxylate oxygen atom (O2A)and nitrogen atom (N1).The bond distances of Pb-O in compound 1 are 0.269 51(19)nm,and the Pb-N bond distances in the crystal are in the range of 0.2551(2)~0.26457(18)nm.

One coordination mode of the cbba ligand is present in the structure of compound 1,namely monodentate bridging mode.
There are significant π-π interactions in the packing diagram between the neighboring phen or cbba ligands.The centroid-to-centroid and perpendicular distances between ring plane C4C5C6C7C11C12 and in the adjacent molecule ring plane N2C1C2C3C4C12 are 0.371 2 nm and 0.336 2 nm,respectively.While the centroid-to-centroid and perpendicular distances between two neighboring rings C21C22C23C24C25C26 and C21′C22′C23′C24′C25′C26′(symmetry code:1-x,1-y,1-z)are 0.417 3 and 0.328 1 nm,respectively.By virtue of these π-π interactions,compound 1 forms an interleaving three-dimensional supramolecular network(Fig.2).These supramolecular interactions together with coordinate-covalent interactions between metal ions and organic ligands strengthen the stability of the 3D network structure.

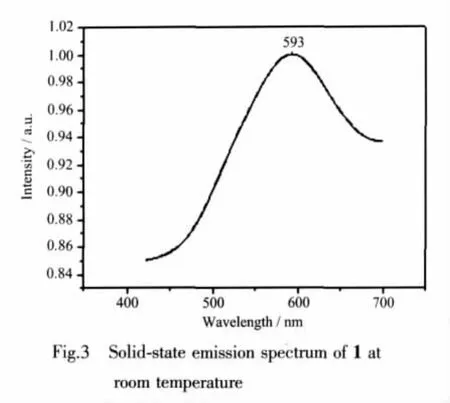
2.3 Photoluminescent properties
The emission spectrum of compound 1 in the solid state at room temperature is shown in Fig.3.It can be observed that compound 1 exhibits yellow photoluminescence with an emission maximum at ca.593 nm upon excitation at 325 nm.In order to understand the nature of these emission bands,we first analyzed the photoluminescence properties of free phen,and confirmed that it does not emit any luminescence in the range of 400~800 nm.And then we investigated the emission spectrum of H2cbba itself and the resultindicated thatitdoesnotemitany luminescence in the range 400~800 nm,which has also been confirmed previously[12].Thus,according to the previous literature[13],the emission band could be assigned to the emission of ligand-to-metal charge transfer(LMCT).
[1]Fan S R,Zhu L G.Inorg.Chem.,2007,46:6785-6793,and references therein
[2]Yang J,Ma J F,Liu Y Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2007,46:6542-6555
[3](a)Li X M,Niu Y L,Wang Q W,et al.Acta Cryst.,2007,E63:m1737-m1738
(b)Li X M,Niu Y L,Wang Q W,et al.Acta Cryst.,2007,E63:m2443-
(c)Li X M,Wang Q W,Cui Y C,et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.,2009,10:1317-1320
(d)Li X M,Niu Y L,Wang Q W,et al.Acta Cryst.,2007,E63:m487-m488
(e)Tong M L,Hu S,Wang J,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2005,5:837-839
(f)Xu Y,Han L,Lin Z Z,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2004:4457-4462
(g)Ciurtin D M,Smith M D,zurLoye H C.J.Chem.Soc.,Dalton Trans.,2003:1245-1250
(h)Zeng M H,Feng X L,Chen X M.J.Chem.Soc.,Dalton Trans.,2004:2217-2223
(i)Luo J H,Jiang F L,Wang R H,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2004,707:211-216
(j)Ghosh S K,Savitha G,Bharadwaj P K.Inorg.Chem.,2004,43:5495-5497
(k)Zhao B,Yi L,Dai Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2005,44:911-920
(l)Kang Y,Zhang J,Qin Y Y,et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.,2006,3:374-377
[4](a)Li X M,Niu Y L,Liu B,et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.,2009,1:29-32
(b)Xu H T,Zheng N W,Yang R Y,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2003,349:265-268
(c)Xu Z L,Li X Y,Che G B,et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.,2008,5:593-597
[5](a)Li X M,Dong Y H,Wang Q W,et al.Acta Cryst.,2007,E63:m1274-m1276
(b)Rajendiran T M,Kirk M L,Setyawati I A,et al.Chem.Commun.,2003:824-825
(c)Zhang X,Huang D G,Chen F,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2004,7:662-663
(d)Wang C F,Gao E Q,He Z,et al.Chem.Commun.,2004:720-721
(e)Wang Y L,Yuan D Q,Bi W H,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2005,5:1849-1855
(f)Lu J Y,Ge Z H.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2005,358:828-833
(g)Wang X L,Qin C,Wang E B,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2005,749:45-50
[6]Wang Q W,Li X M,Meng Q L,et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.,2009,28:335-337
[7]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS97,Program for the Solution of Crystal Structure,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[8]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS97,Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structure,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[9]Devereux M,Shea D O,Kellett A,et al.Inorg.Biochem.,2007,101:881-892
[10]Farrugia L J,Wing X A.Windows Program for Crystal Structure Analysis,University of Glasgow,Glasgow,UK,1988.
[11]Bellamy L J.The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules.New York:Wiley,1958.
[12]Rendell D.Fluorescence and Phosphorescence.New York:John Willey&Sons,1987.
[13]Zheng S L,Chen X M.Aust.J.Chem.,2004,57:703-712
Hydrothermal Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Luminescent Property of Pb(cbba)2(phen)2
WANG Qing-Wei*,1LI Xiu-Mei2WANG Zhi-Tao2LIU Bo1
(1Jilin Normal University,Siping,Jilin 136000)
(2Department of Chemistry,Tonghua Teachers College,Tonghua,Jilin 134002)
A new metal-organic complex Pb(cbba)2(phen)2(1,H2cbba=2-(4′-chlorine-benzoyl)benzoic acid,phen=1,10-phenanthroline)has been hydrothermally synthesized and structurally characterized by elemental analysis,IR,fluorescence spectrum and single-crystal X-ray diffraction.The compound crystallizes in orthorhombic,space group Pbcn with a=1.474 49(7)nm,b=0.953 90(4)nm,c=3.031 65(14)nm,V=4.264 1(3)nm3,C52H32Cl2N4O6Pb,Mr=1086.91,Dc=1.693 g·cm-3,μ(Mo Kα)=4.141 mm-1,F(000)=2144,Z=4,the final R=0.0183 and wR=0.0457 for 3582 observed reflections(I>2σ(I)).In the crystal structure,the lead atom is six-coordinated with two carboxylate oxygen atoms from different cbba ligands and four nitrogen atoms from different phen ligands,showing a distorted octahedral geometry.Furthermore,1 shows yellow photoluminescent property at room temperature.CCDC:792222.
hydrothermal synthesis;crystal structure;lead complex;luminescence
O614.43+3
A
1001-4861(2010)11-2101-04
2010-05-24。收修改稿日期:2010-07-26。
吉林省教育厅科学技术研究项目资助(No.2009.272)。
*通讯联系人。 E-mail:lixm20032006@yahoo.com.cn
王庆伟,男,48岁,教授;研究方向:无机-有机杂化配合物。
