基于2-氯-6-甲基苯甲酸和N-甲基咪唑铜(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、晶体结构和电化学性能
2010-11-09邓月义刘法谦刘保成
邓月义 刘法谦 刘保成
(青岛科技大学新材料研究重点实验室,青岛 266042)
基于2-氯-6-甲基苯甲酸和N-甲基咪唑铜(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、晶体结构和电化学性能
邓月义 刘法谦*刘保成
(青岛科技大学新材料研究重点实验室,青岛 266042)
合成了标题配合物Cu(Cmba)2(Mim)2(Cmba为2-氯-6-甲基苯甲酸阴离子,Mim为N-甲基咪唑),并用X射线单晶衍射仪测定了其晶体结构。晶体属单斜晶系,P21/n 空间群,晶胞参数为:a=0.7389(15)nm,b=2.1379(4)nm,c=0.8150(16)nm,β=112.41(3)°,V=1.1902(4)nm3,Z=2,Dc=1.582 g·cm-3。 最后精修结果为:R1=0.0682,wR2=0.1740。 在配合物结构中每个 Cu(Ⅱ)原子分别与来自 2个羧酸根离子中的2个氧原子、2个N-甲基咪唑分子中的2个N原子进行配位,形成了1个平面四边形结构。电化学研究显示配合物中的Cu2+/Cu+对的氧化还原是一个准可逆的过程。
铜(Ⅱ)配合物;N-甲基咪唑;晶体结构;循环伏安法
Copper(Ⅱ)complexes based on Carboxylic acids and N-donor ligands for mimicking the Cu-containing enzymes,such as Superoxide dismutase(SOD),peroxidase,catalase,hemocyanin,have attracted much attention[1-7].A general survey of the literature reveals that a considerable amount of work has been carried out on the preparation and characterization of complexes of Copper(Ⅱ)carboxylates with nitrogen donors.These complexes give three different stoichiometries,viz.,1∶1,1∶2,and 1∶4 (metal∶carboxylic acid)[8].Some adducts of Copper(Ⅱ)chlorobenzoate were prepared with propanodiamine[9-10],pyridine[11],and imdazole[8].In this paper,as a continuous study on the structure and properties of metal complexes with chlorobenzoic acids and N-donor ligands,we report the synthesis,crystal structure,electrochemical properties of[Cu(Cmba)2(Mim)2].
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and instruments
All the chemical reagents for synthesizing the title compound were purchased commercially and used without further purification.Elemental analyses(C,H and N)were carried out on a Perkin-Elmer 1400C analyzer.Voltammetry was performed by using a CHI 832B electrochemical analysis system (China)with a three-electrode system consisting of a glass carbon(GC)electrode(U=3 mm)as the working electrode,a saturated calomel electrode(SCE)as the reference electrode,and a platinum wire as the auxiliary electrode.All the electrochemical measurements were carried out in a 10 mL electrolyte cell with 0.01 mol·L-1pH 6.86 KH2PO4-Na2HPO4buffer solution as electrolyte.TG curve was recorded on a NETZSCH-TG209 GmbH thermoanalyser in flow of N2,in the temperature range from 20~900℃,with a heating rate of 5 ℃·min-1.
1.2 Preparation
CuCl2·6H2O(0.34 g,2 mmol),KOH(0.224 g,4 mmol),and Cmba (0.53 g,2 mmol)were added to ethanol(40 mL),and the mixture was stirred for half an hour.The resulting blue solution was added Mim(0.164,2 mmol),then refluxed for 3 h and filtered.The filtrate was allowed to stay at ambient temperature for a period of about 3 d,gave 0.32 g (31%yields)of blue block crystals suitable for structural determinations.Anal.Calcd.for C24H24Cl2CuN4O4(%):C 57.26,H 4.81,N 11.13;found(%):C 57.19,H 4.57,N 11.36.
1.3 Crystal structure determination
A block shaped crystal with dimensions of 0.20 mm ×0.10 mm ×0.10 mm was mounted on a Bruker SMART 1000 CCD area detector X-ray single crystal diffractometer with graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.071073 nm)and a φ-ω scanning mode at 293(2)K.Intensities was corrected for Lorentz and polarization effects and empirical absorption.
The structure was solved by direct methods via SHELXS 97 program[12]and refined by full-matrix least squares on F2via SHELXL 97 program[13].The benzene ring exhibits disorder and restraints were applied to the anisotropic displacement parameters(ISOR and DELU restrains)of atoms C1-C6 of the benzene ring.H atoms were positioned geometrically (C-H=0.093 and 0.096 nm)and allowed to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H)=1.2 times Ueq(C).Crystalographic data for the title complex are listed in Table 1.
CCDC:778482.
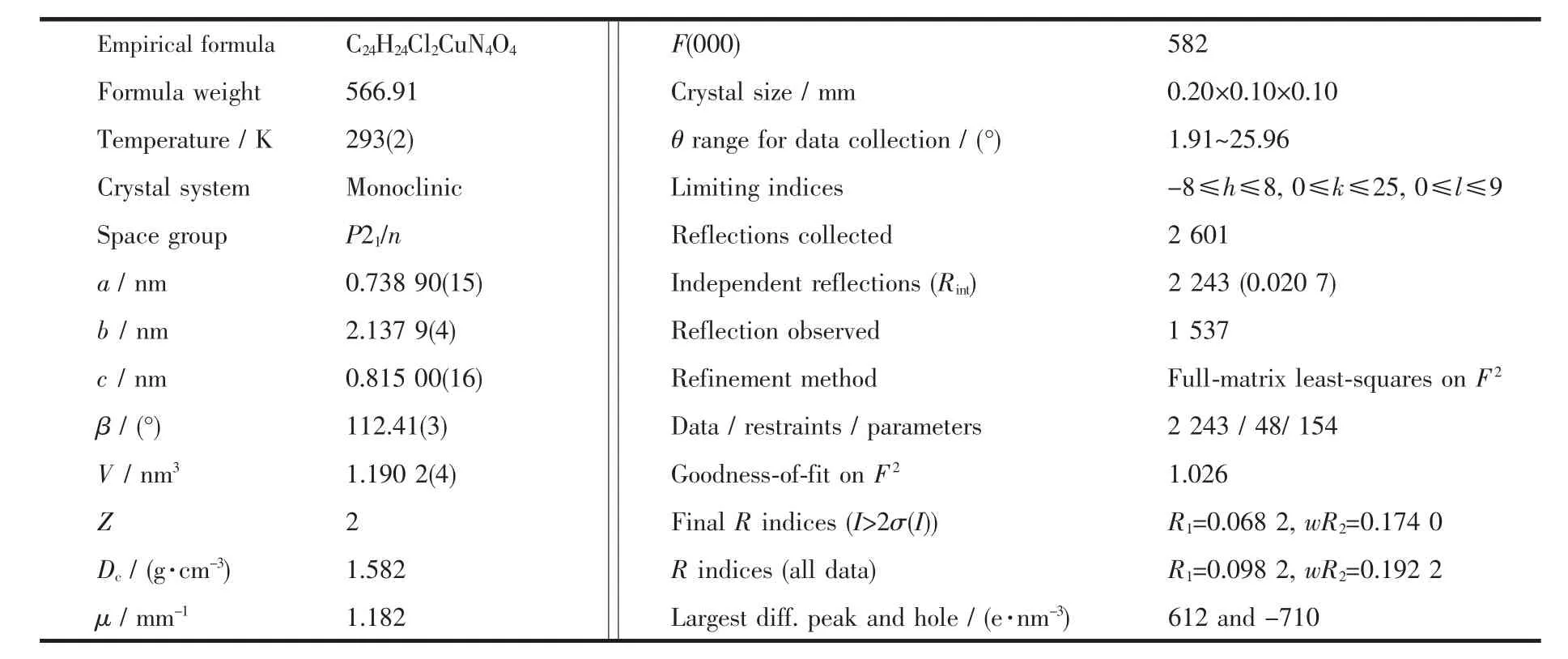
Table 1 Crystal and structure refinement data for the title complex
2 Result and discussion
2.1 Explanations to the crystal structure
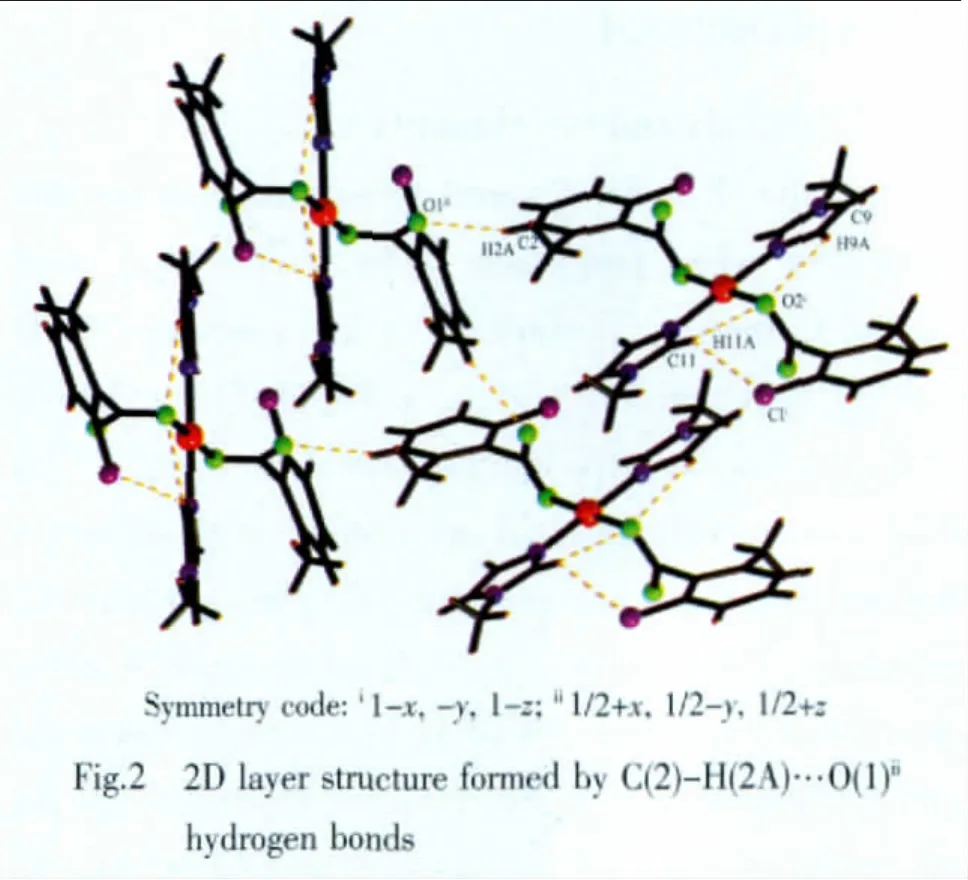
Fig.1 shows the structure of the title compound,showing 30%probability displacement ellipsoids and theatom-numberingscheme,andFig.2showsa perspective view of the crystal packing in the unit cell.Selected bond lengths and bond angles are presented in Table 2.Hydrogen-bonds are presented in Table 3.
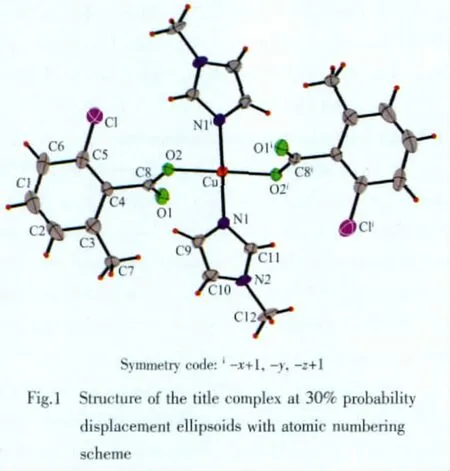
The crystal structure of the title compound is built of monomeric[Cu(Cmba)2(Mim)2]molecules.The Cu atom in the complex is coordinated by two O atoms from two carboxylate anions and two N atoms from two Mim molecules in a square-planar geometry.The trans angles are all 180°for symmetry requirement and the cis ones are 90.80(16)°and 89.20(17)°for N-Cu-O,respectively.The d(Cu-O)is 0.198 5(4)nm,and d(Cu-N)is 0.1972(4)nm.These bond lengths are shorter than those of the structurally analogous complex[Cu(Cba)2(Im)3](Cba=chlorobenzoic acid,Im=imdazole,d(Cu-O)=0.211 3(2)nm and d(Cu-N)=0.199 4(3)and 0.201 9(3)nm)[8].O(1)and its symmetry-related atom are located above the coordinate square planar or below,respectively.The dihedral angle between the carboxylate plane C(8)O(1)O(2)and the phenyl ring plane is 58.8(1)°,and the corresponding one of the complex[Cu(Cba)2(Im)3]is 58.8(1)°.The dihedral angles between the planes of the carboxylate groupC(8)O(1)O(2)and the Mim ring and the CuO2N2 plane are 91.20(3)°and 13.91(3)°,respectively.The O-C-O angle in the carboxylate groups is 125.1(5)°,characteristic of chelating carboxylate groups.
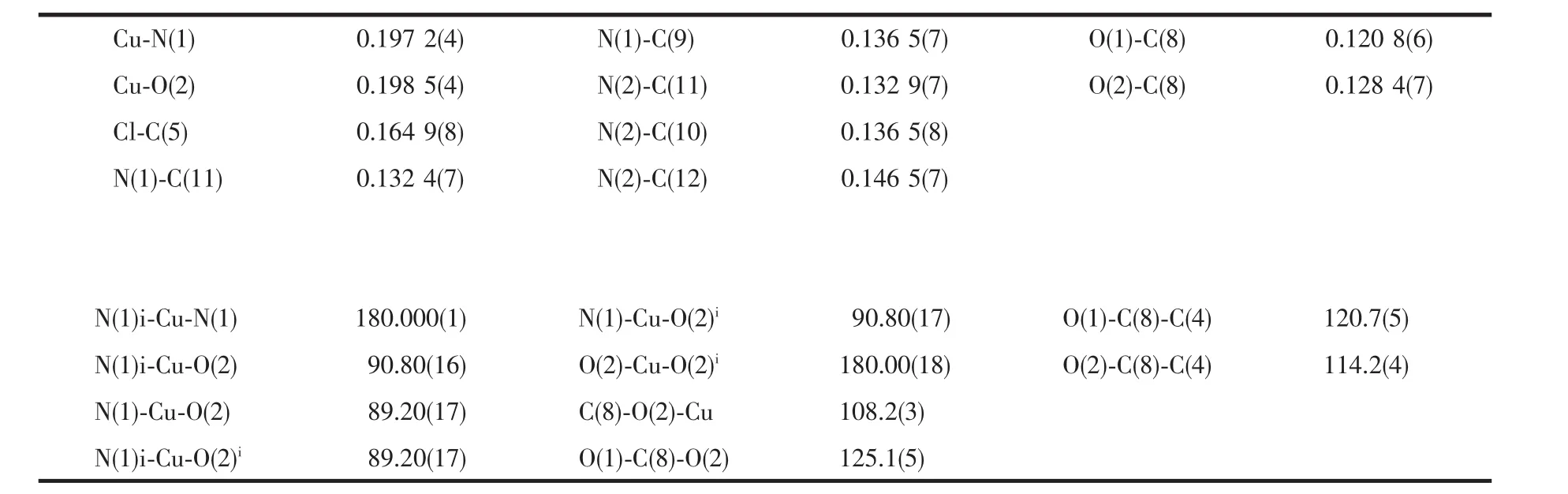
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)for the complex
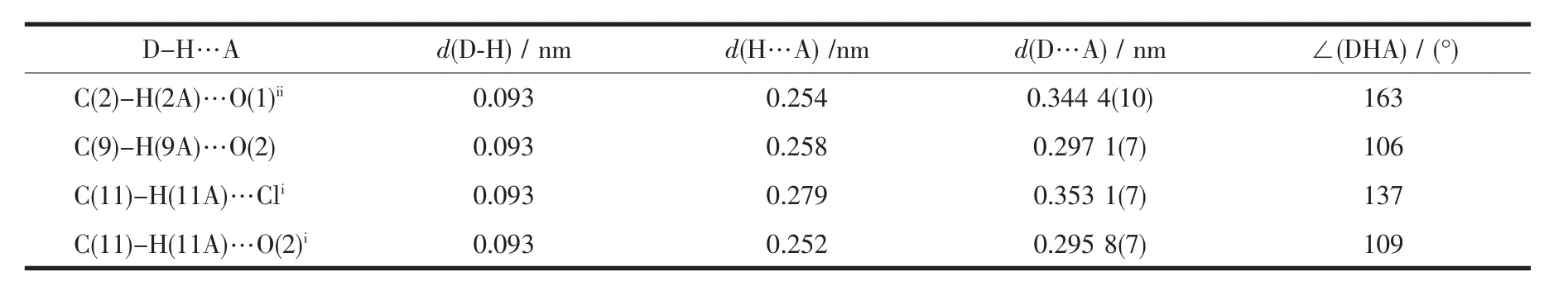
Table 3 Hydrogen bonds of the complex
Some potentially weak(C-H…O and C-H…Cl)intramolecular and intermolecular interactions exist in the lattice[14-15].The C(2)atoms with O(1)atoms form weak intermolecular interactions (the donor and the acceptor distance is 0.344 4(10)nm),which link the complex units into a 2D layer structure(Fig.2 and Table 3).The C(9),C(11)atoms with O(2)and C(11)atoms with Cl atoms form weak C-H…O and C-H…Cl intramolercular interactions(the donor and the acceptor distances are 0.297 1(7),0.295 8(7),0.353 1(7)nm,respectively)(Table 3).These weak interactions further stabilize the crystal structure.
2.2 Thermal properties
Thermal analyses reveal that the title complex retain stability below 89.5 ℃.On further heating the compound underwent five weight loss processes in a temperature range of 89.5~900 ℃.The first weight loss of 29.12%around 89.5 ~162 ℃ via two unidentified steps corresponds to the loss of two N-methylimidazole molecules (calculated 28.93%).In the temperature range of162~900 ℃ weight loss of 59.47% was ascribed to the release of two 2-Chloro-6-methylbenzoic anion through three steps(calculated 58.39%),to give expected Cu(observed 11.42%,calculated 11.20%).
2.3 Electrochemistry
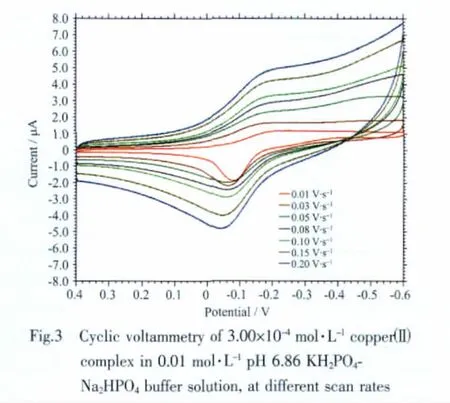
Cyclic voltammetry curve for the title complex in 0.01 mol·L-1pH 6.86 KH2PO4-Na2HPO4buffer solutions at different scan rates is shown in Fig.3.
The complex at 0.1 V·s-1has a anodic peak at-0.059 V and an cathodic peak at-0.170 V,corresponding to the electrochemical process of Cu2+/Cu+[16].The separation of the cathodic and anodic peak potential,ΔE=0.111 V,indicates that the electrochemical behavior of the title complex on the glass carbon electrode is an quasi-reversible process.
Laviron′s approach was used to determine the energy transfer coefficient α and the rate constant k[17].The anodic(Epa)and the cathodic(Epc)peak potentials are expressed by this approach as follows:
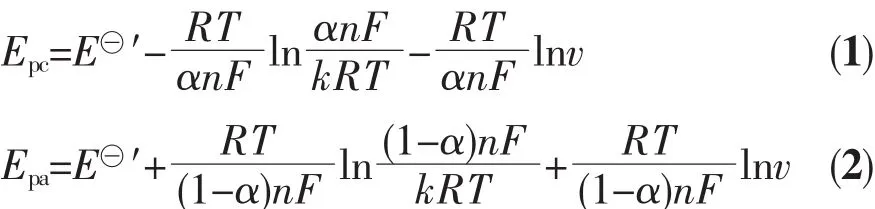
where E⊖′(V)is the formal potential,F is Faraday constant(96 487 C·mol-1),R is universal gas constant(8.314 J·K-1·mol-1),and T is Kelvin temperature.So,plots of Epcand Epaversus lnν should have two straight lines with slopes scand saas-RT/(αnF)and RT/[(1-α)nF)],respectively(see data in Fig.4).Then α value can be calculated by the following relationships:
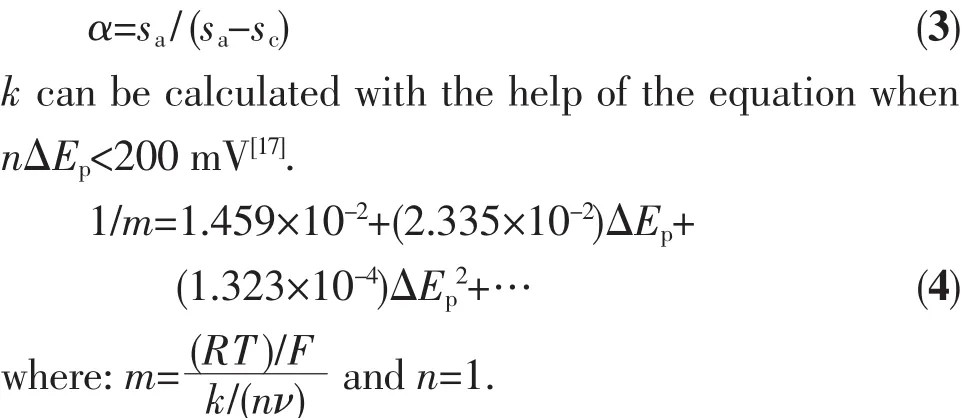
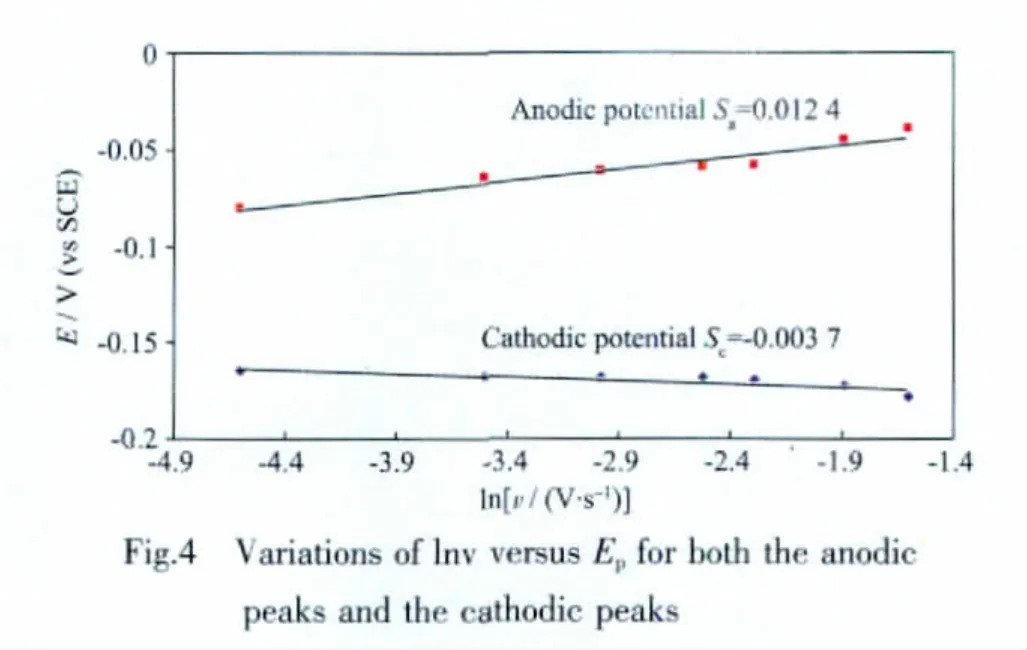
The redox potential,ΔEp,and ipa/ipcat different scan rates were shown in Table 4.The scand savalueswere attained by Fig.4.Finally,an energy transfer coefficient α value of 0.77 for this electrochemical process can be obtained by the equtation (3).When a scan rate is 0.05 V·s-1,and ΔEp=107 mV,k was estimated to be 115.1 s-1by the equation(4).
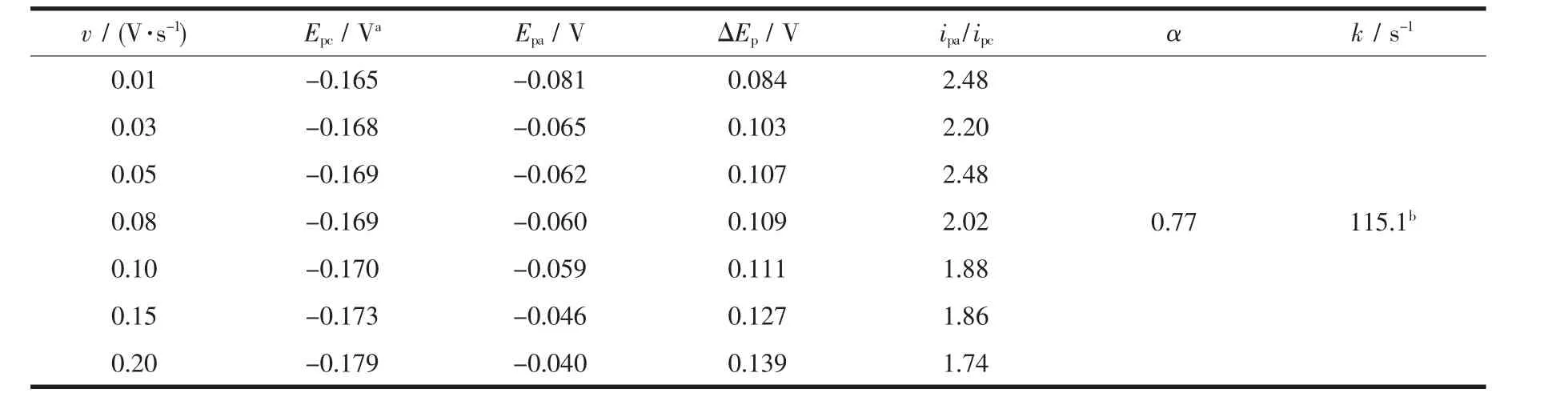
Table 4 Redox potential,ΔEp,ipa/ipcand other calculated parameters from the CV data
[1]Sigel H.Inorg.Chem.,1980,19:1411-1413
[2]Bernarducci E E,Bharadwaj P K,Lalancette R A,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1983,22:3911-3920
[3]Sorrel T N,Garrity M L.Inorg.Chem.,1991,30:210-217
[4]Adams H,Neil A B,Crane J D,et al.J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.,1990:1727-1732
[5]Kaiser J,Csonka R,Speier G,et al.J.Mol.Catal.A:Chem.,2005,236:12-16
[6]Kaiser J,Csonka R,Speier G,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2006,9:1037-1043
[7]Devereux M,O′Shea D,O′Connor,et al.Polyhedron,2007,26:4073-4084
[8]Wolodkiewicz W.J.Coord.Chem.,2002,55(7):727-734
[9]Uggla R,Orama O,Sundberg N,et al.Finn.Chem.Lett.,1974:185-189
[10]Alten H L,Koten G,Riethorat E,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1989,26:4141-4145
[11]Nakatani K,Slecten J,Halut-Desporte S,et al.Inorg.Chem.,1991,30:164-168
[12]Sheldrick G M.Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.A,1990,46:467-478
[13]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,Program for X-ray Crystal Structure Refinement,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[14]Karunakaran C,Thomas K R J,Shunmugasundram A,et al.J.Chem.Cryst.,1999,29:423-420
[15]Steiner T.Cryst.Rev.,1996,6:1-34
[16]Mandal S K,adikary B,Nag K.J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.,1986:175-181
[17]Laviron E.J.Electroanal.Chem.,1979,101:19-21
Synthesis,Crystal Structure,Electrochemical Studies of Copper(Ⅱ)Complex with 2-Chloro-6-methylbenzoic Acid and N-Methylimidazole
DENG Yue-YiLIU Fa-Qian*LIU Bao-Cheng
(Key Laboratory of Advanced Materials,Qingdao University of Science and Technology,Qingdao,Shandong 266042)
The title complex Cu(Cmba)2(Mim)2(Cmba=2-Chloro-6-methylbenzoic anion,Mim=N-Methylimdazole)has been synthesized and structurally characterized by X-ray single crystal diffractometry.The complex crystallizes in monoclinic system,P21/n space group with the cell parameters of a=0.738 9(15)nm,b=2.137 9(4)nm,c=0.8150(16)nm,β=112.41(3)°,V=1.1902(4)nm3,Z=2,and Dc=1.582 g·cm-3,the final R1=0.0682,wR2=0.1740.In the structure of the complex each Cu(Ⅱ)ion is coordinated by two O atoms from two carboxylate anions and two N atoms from two Mim molecules in a square-planar geometry.The electrochemical studies reveal that redox of Cu2+/Cu+in the complex is a quasi-reversible process.CCDC:778482.
copper(Ⅱ)complex;N-Methylimdazole;crystal structure;cyclic voltammetry
O614.121
A
1001-4861(2010)11-1944-05
2010-06-07。收修改稿日期:2010-08-02。
国家自然科学基金(No.20871072),山东省博士启动基金(No.2007BS04023),青岛科技大学博士启动基金资助项目。
*通讯联系人。 E-mail:qdplastics@163.com
邓月义,男,28岁,博士研究生;研究方向:功能配合物。
