萨福克羊主要经济性状的遗传参数估计及非遗传因素分析
2024-12-31陈胜磊孙国智张国威马海玉刘玲玲张维忠刘武军
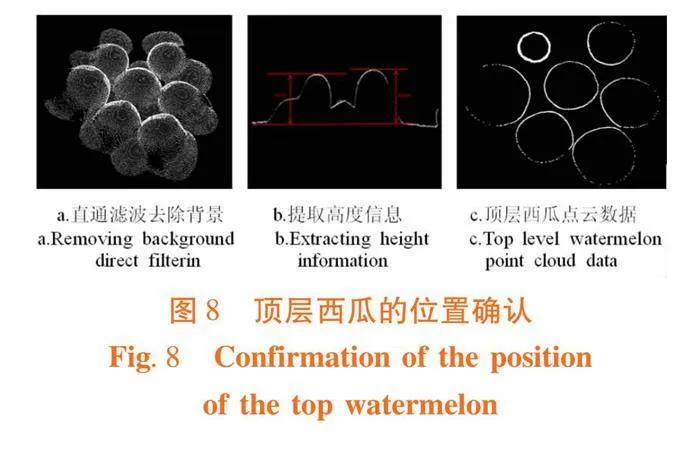

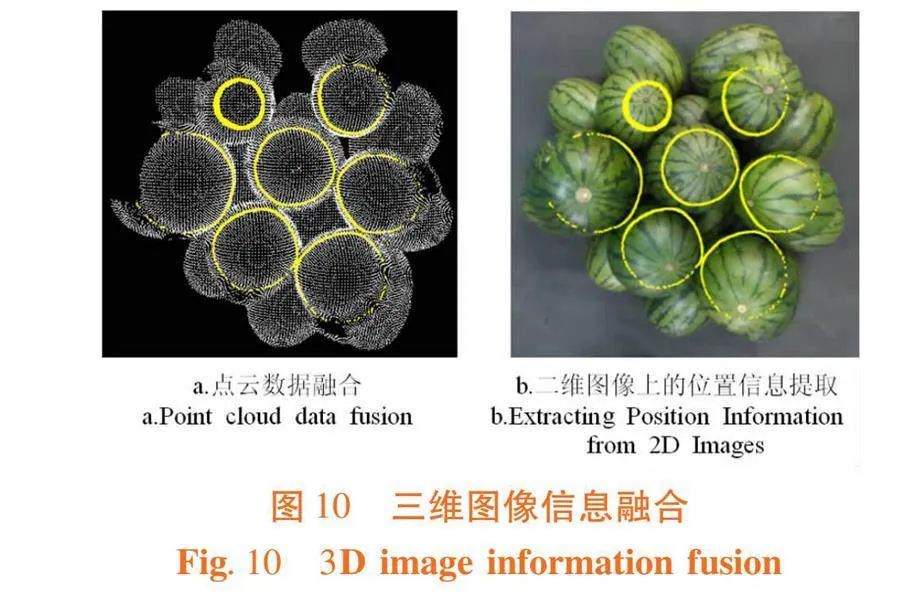
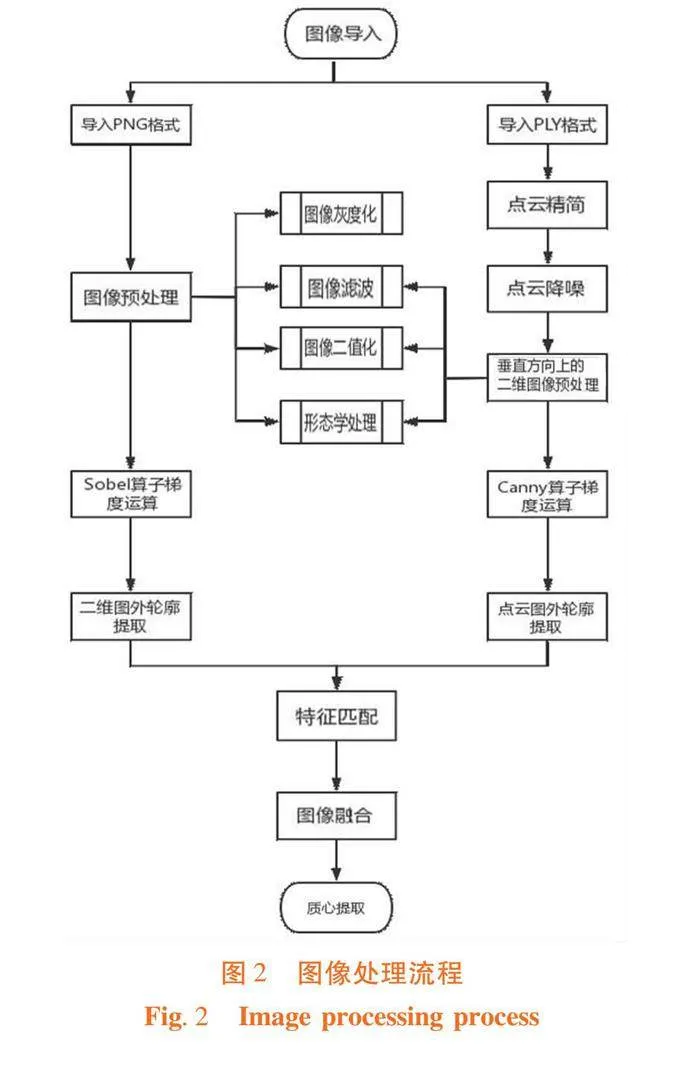




摘 要:【目的】分析萨福克羊主要经济性状的遗传参数,研究非遗传因素对萨福克羊主要经济性状的影响。
【方法】2017~2023年共收集新疆玛纳斯种羊场萨福克羊4 156只,并进行个体鉴定记录,利用DMU软件估计主要经济性状遗传参数,并使用SAS软件分析萨福克羊出生类型、出生年份、群别、胎次和母羊年龄等5个固定效应对各性状的影响。
【结果】萨福克羊初生重、周岁重、胸围的遗传力分别为0.17、0.27和0.31,属于中等遗传力;日增重遗传力为0.05,属于低遗传力;体高、体长遗传力为0.38和0.41,属于高遗传力。除了胸围与体高、体长之间存在遗传负相关外,其余性状均呈正相关,体高和胸围与日增重存在较强遗传相关和表型相关性,且两者遗传力均较高。单胎的初生重、日增重、周岁重、体长、胸围均显著高于双胎;初生重、日增重处于上升趋势,群1中初生重、日增重、周岁重显著高于群2,群2中体高、体长、胸围显著高于群1;2、3、4胎次的羊初生重、日增重、体高显著高于1、5胎次;母羊年龄在2、3、4岁时初生重显著高于1岁,日增重、周岁重1、2岁显著高于3、4岁,其他性状间无显著差异。
【结论】萨福克羊体高、体长属于高遗传力,初生重、周岁重、胸围属于中等遗传力,日增重属于低遗传力,除了胸围与体高、体长之间存在遗传负相关外,其余性状均呈正相关。该场萨福克羊群体2017~2019年早期生长性状呈上升趋势,2胎或3胎母羊繁殖性均达到最佳水平。
关键词:萨福克羊;遗传参数;非遗传参数;经济性状
中图分类号:S826"" 文献标志码:A"" 文章编号:1001-4330(2024)07-1814-07
0 引 言
【研究意义】萨福克羊是肉用绵羊品种,具有早熟、生长发育快、适应性强、肉质优良等特点,广泛用于纯种羊繁育和杂交和改良地方绵羊品种[1]。分析研究萨福克羊高遗传力的性状及其与性状有较强正相关性状,对提高萨福克羊的生产力、经济效益和新品种选育有重要意义。【前人研究进展】北京、河北、甘肃、新疆等地利用萨福克羊改良本土羊品种取得较好效果[2]。随着我国肉羊产业市场需求旺盛,迫切需要提高羊肉生产水平[3]。【本研究切入点】肉羊的初生重、日增重、周岁重和体高等性状决定其生产效益,其中遗传因素对羊各性状起着关键作用,管理水平、地理位置和环境条件等非遗传因素的差异亦对肉羊的经济性状有重要影响[4]。中等遗传力h2指0.1≤h2≤0.35[5]。
因此在利用萨福克羊的优良特性进行精确选种和利用时,亦需充分分析非遗传因素对肉羊经济性状的影响。【拟解决的关键问题】以萨福克羊经济性状为研究对象,估算各繁殖性状的遗传参数,分析出生类型、出生年份、群别、胎次等因素对羊经济性状的影响,为萨福克羊新品种选育提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
2017~2023年收集新疆日发新西域玛纳斯牧业有限公司玛纳斯种羊场4 156只萨福克羊。
记录系谱信息及有关经济性状(初生重、日增重、周岁重、体高、体长、胸围等)。
1.2 方 法
1.2.1 固定效应水平的划分
出生类型效应划分2个水平,即单胎、双胎;出生年份效应5个水平,即2017~2023每年1个水平;群别效应划分2个水平,即群1、群2;胎次效应划分5个水平,即1、2、3、4和5胎次;母羊年龄划分6个水平,即1、2、3、4、5和6岁。
1.2.2 统计模型
1.2.2.1 固定效应分析模型
Yijklm=u+mi+cj+xk+cl+qm+eijklm.
式中,Yijklm为个体表型观察值,u为群体均值效应,mi为出生类型效应,cj为出生年份效应,xk为群别效应,cl胎次效应,qm为母羊年龄效应,eijklm为随机残差效应。
1.2.2.2 遗传参数估计模型
Y=Xβ+Za+e.
式中,Y为性状观察值,β为固定效应,a为随机加性遗传效应,X、Z分别是固定效应、随机加性效应的关联矩阵,e是随机残差效应。
h2=σ2aσ2p.
式中,h2为遗传力,σ2a为加性遗传效应,σ2p为表型方差。
1.3 数据处理
利用Excel 2016对原始数据的质控,剔除表型值异常,以平均值±3倍标准差作为正常值的范围,剔除正常值以外的数据。使用SPSS 26.0软件对数据进行描述性统计,使用SAS软件(version6.2)对羊出生类型、出生年份、群别、胎次、母羊年龄5个固定效应对数据进行最小二乘分析,运用DMU软件(version6.5)AIREML模块结合EM算法估计经济性状的方差组分。
2 结果与分析
2.1 萨福克羊生长性状统计
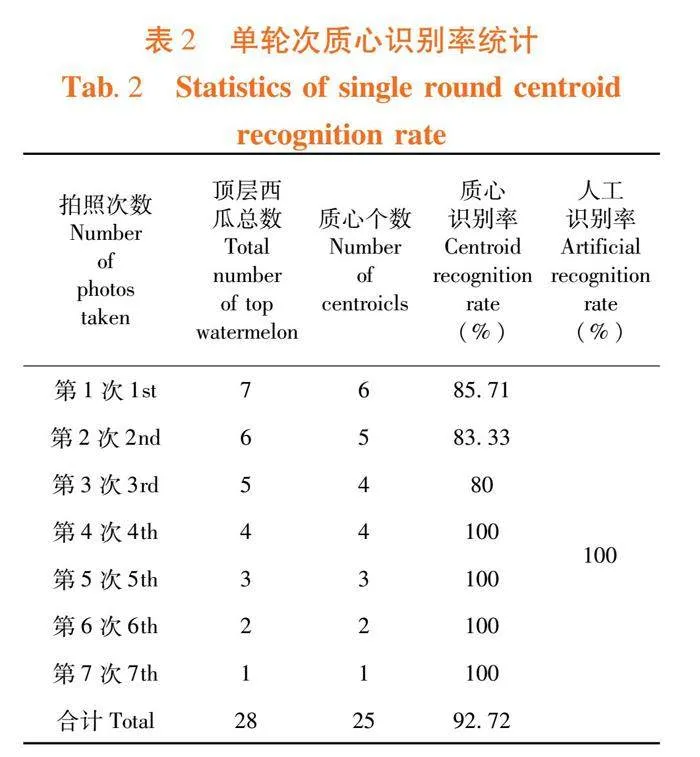
研究表明,萨福克羊各性状的均值分别为初生重4.47 kg、平均日增重0.19 kg、周岁重76.64 kg、体高65.58 cm、体长66.89 cm、胸围94.24 cm。表1
2.2 萨福克羊各性状方差比较
研究表明,出生类型对初生重、日增重、体高、体长差异极显著(P<0.01)、对周岁重、胸围差异显著(P<0.05);出生年份对初生重、周岁重差异极显著(P<0.01);群别对初生重、日增重周岁重、胸围差异极显著,对体高、体长差异显著;胎次对初生重、日增重、周岁重、体高差异极显著;母羊年龄对初生重、日增重、周岁重差异极显著。表2
2.3 萨福克羊各性状最小二乘均方差
研究表明,出生类型单胎的初生重、日增重、周岁重、体长、胸围均显著高于双胎;出生年份在2017~2023年间初生重、日增重处于上升趋势;群1中初生重、日增重、周岁重显著高于群2,群2中体高、体长、胸围显著高于群1;胎次中2、3、4胎次的初生重、日增重、体高显著高于1、5胎次;母羊年龄在2、3、4岁时初生重显著高于1岁,日增重、周岁重1、2岁显著高于3、4岁,其他性状间差异不显著(P>0.05)。表3
2.4 遗传力估计、性状间的遗传相关性和表型相关性
研究表明,萨福克羊主要经济性状中初生重、周岁重、胸围的遗传力分别为0.17、0.27和0.31,属于中等遗传力;日增重为0.05,属于低遗传力;体高、体长遗传力为0.38、0.41,属于高遗传力。表4
表型相关系数在0.23~0.97,其中日增重于体高之间最大(0.97),胸围体长与胸围之间最小(0.23);遗传相关系数在-0.49~0.86,其中日增重与周岁重之间遗传相关性最高(0.86),初生重于日增重之间遗传相关性最低(0.14),体高、体长与胸围呈负相关,其余各阶段体重之间均呈正相关,各性状间除日增重于与体长、胸围不显著,其余性状均呈极显著正相关(Plt;0.01)。表5
3 讨 论
3.1 非遗传因素对萨福克羊主要经济性状的影响
研究结果表明,出生类型对萨福克羊单羔和多羔类型的初生重差异极显著(P<0.01),此结论与黄锡霞等[6]、刘旭光等[7]、Hernandez等[8]、Corner等[9]报道双胎羔羊初生重降低是由于胚胎期胎儿之
间存在对营养物质竞争的结果一致。一般双胎羔在胚胎发育阶段从母体吸收的营养要少于单胎羔羊,双胎羔羊在出生时的体重较低。
在萨福克羊出生年份中,2017~2019年间早期生长性状呈上升趋势,而2019~2022年呈缓慢下降的趋势直至2023年恢复平稳状态,同样在早期生长性状群1高于群2,俞春山等[10]研究表明,出生年份对中卫山羊羔羊初生重的影响差异显著(Plt;0.05);王东劲等[11]研究表明,出生年份、出生类型和出生性别对海南黑山羊初生重均差异极显著;赵晓平等[12]研究表明,所有早期性状和主要经济性状均受到群别的极显著影响,该研究结果与试验研究结果一致。
研究中随着母羊年龄增长和胎次的增多,羔羊初生重、日增重也同样增加,是因为母羊已经历了多次产羔,其繁殖性能所提升,与Gardner、Petrovic[13-14]结论随着母羊年龄的增长,生产过的母羊子宫变大,与未熟的母羊相比,可以分配更多的营养物质给子宫内的羔羊,有效地提高羔羊的初生重的研究结果一致。
3.2 萨福克羊经济性状遗传参数估计
遗传力代表了性状从父母传递给子女的可遗传的部分[15],遗传力可评估不同性状的育种价值,然而不同性状的遗传力可靠性存在差异,受到品种、环境等多种因素的影响。研究中萨福克羊各性状遗传力分别为初生重(0.17)、日增重(0.05)、周岁重(0.27)、体高(0.38)、体长(0.41)、胸围(0.31),与Simm等[16]研究报道的萨福克羊直接加性遗传效应初生重的遗传力为0.054,陶林等[17]估计鲁中肉羊初生体尺体重的遗传力初生重(0.16)、体高(0.44)、体长(0.43)、胸围(0.46),陈世尧等[18]、张国俊等[19]、孙国智等[20]研究的鲁中肉羊、南江黄羊、多浪羊等肉羊的初生重、日增重、周岁重、体高、体长、胸围的遗传力范围为0.11~0.32、0.19~0.35、0.15~0.47研究结果相近,各性状遗传力大小在以上肉羊品种遗传力的范围之内。遗传力受数据量、应用软件、计算方法等多种因素的影响[21]。研究结果显示高遗传力性状可在萨福克羊选育提高中通过表型进行选择。
遗传相关和表型相关在萨福羊经济性状选育和经济效益优化非常重要[5],研究结果发现,在萨福克羊各性状中,除胸围与体高、体长,其余均为遗传正相关,仅有日增重与体长、胸围差异不显著,其余均差异显著(Pgt;0.05),其余各性状间均呈极显著表型相关(Plt;0.01),各经济性状的遗传相关系数为-0.53~0.86,表型相关系数为0.12~0.97。较高于陶林等[17]报道的鲁中肉羊初生阶段的体尺体重的遗传相关范围-0.196~0.59一致,与王大广[22-23]、陈世尧[18]报道的萨福克羊表型测定值遗传参数的估计的遗传相关系数0.52~0.89、巴什拜羊各经济性状遗传力范围0.11~0.63基本一致,部分差异与环境、研究对象、数据量、计算、分析软件等因素有关。羊体高和胸围与日增重存在较强遗传相关和表型相关,且两者遗传力较高,在早期选择时重点关注上述性状加强饲料提供均衡的营养,以满足羔羊生长的需要。
4 结 论
萨福克羊体高、体长遗传力属于高遗传力;初生重、周岁重、胸围、属于中等遗传力;日增重遗传力属于低遗传力。除了胸围与体高、体长之间存在遗传负相关外,其余性状均呈正相关。该场萨福克羊群体在2017~2019年期间早期生长性状呈上升趋势。2胎或3胎母羊繁殖性能达到最佳水平,可将高遗传力且与其他性状具有较强正相关性的特征作为目标性状,以提高羊群的生产力。
参考文献(References)
[1]
李佳蓉, 贾超, 姜怀志. 萨福克羊种质特性及利用状况[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2017, 37(3): 51-55.
LI Jiarong, JIA Chao, JIANG Huaizhi. Germplasm characteristics and utilization of Suffolk[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2017, 37(3): 51-55.
[2] 李佳蓉, 贾超, 姜怀志. 优良肉用羊品种——萨福克羊[J]. 农村百事通, 2019, (21): 36.
LI Jiarong, JIA Chao, JIANG Huaizhi. Excellent meat sheep breed - Suffolk sheep [J]. Nongcun Baishitong," 2019(21): 36.
[3]甘春艳, 李军, 金海, 等. 2021年我国肉羊产业发展概况、未来发展趋势及建议[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58(3): 258-263.
GAN Chunyan, LI Jun, JIN Hai, et al. Overview of China's meat sheep industry development in 2021, future trends, and recommendations [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58(3): 258-263.
[4] 刘静, 毛静艺, 吴翠玲, 等. 非遗传因素对鲁中肉羊不同生长阶段体尺体重性状的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2023, 59(4): 108-113.
LIU Jing, MAO Jingyi, WU Cuiling, et al. Effects of non-genetic factors on body size and weight traits of luzhong mutton sheep at different growth stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2023, 59(4): 108-113.
[5]张沅.家畜育种学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2018.
ZHANG Yuan. Animal Breeding[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press 2018.
[6] 黄锡霞, 巴德娃木·道别克, 张亚军, 等. 影响中国美利奴羊(新疆型)羔羊初生重的非遗传因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2010, 47(10): 2027-2030.
HUANG Xixia, Badewamu Daobieke, ZHANG Yajun, et al. Analysis of Non-genetic factors affecting birth weight of Chinese merino sheep (Xinjiang type)[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences," 2010, 47(10): 2027-2030.
[7] 刘旭光, 刘文, 吴宓, 等. 影响波尔山羊初生重的因素分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2005, 32(10): 32-33.
LIU Xuguang, LIU Wen, WU Mi, et al. Analysis of factors affecting the birth weight of Boer goat[J]. Animal Science Abroad," 2005, 32(10): 32-33.
[8] Hernandez V R, Vega Murillo V, Costa R G, et al. Evaluation of genetic parameters of growth of pelibuey and blackbelly sheep through pedigree inMexico[J]. Animals: an Open Access Journal from MDPI, 2022, 12(6): 691.
[9] Corner R A, Mulvaney F J, Morris S T, et al. A comparison of the reproductive performance of ewe lambs and mature ewes[J]. Small Ruminant Research, 2013, 114(1): 126-133.
[10] 俞春山, 张振伟, 叶勇. 影响中卫山羊初生重的非遗传因素研究[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2013, 34(1): 30-31.
YU Chunshan, ZHANG Zhenwei, YE Yong. Study on the non-genetic factors that affected the birth weight of Zhongwei goat[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2013, 34(1): 30-31.
[11] 王东劲, 徐铁山, 周汉林, 等. 影响海南黑山羊初生重的非遗传因素初探[J]. 华南热带农业大学学报, 2006, 12(2): 10-13.
WANG Dongjin, XU Tieshan, ZHOU Hanlin, et al. A preliminary Probe into Non-genetic factors that Influence Birth Weight of Hainan Black Goats[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2006, 12(2): 10-13.
[12] 赵晓平, 何小龙, 荣威恒. 非遗传因素对敖汉细毛羊12个性状表现的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2008, 37(11): 121-125.
ZHAO Xiaoping, HE Xiaolong, RONG Weiheng. Effects of non-genetic factors on the traits of Inner Mongolian Aohan merino sheep[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 37(11): 121-125.
[13] Gardner D S, Buttery P J, Daniel Z, et al. Factors affecting birth weight in sheep: maternal environment[J]. Reproduction, 2007, 133(1): 297-307.
[14] Petrovic M, Muslic D, Petrovic V, et al. Influence of environmental factors on birth weight variability of indigenous Serbian breeds of sheep[J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2011, 10.
[15] 吴仲贤. 统计遗传学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1977.
WU Zhongxian. Statistical genetics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1977.
[16] Simm G, Lewis R M, Grundy B, et al. Responses to selection for lean growth in sheep[J]. Animal Science, 2002, 74(1): 39-50.
[17] 陶林, 潘林香, 王金文, 等. 鲁中肉羊初生体尺体重的遗传参数估计[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2019, 39(2): 17-19, 27.
TAO Lin, PAN Linxiang, WANG Jinwen, et al. Estimation of genetic parameters for body measurements and weight at birth in luzhong mutton sheep[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2019, 39(2): 17-19, 27.
[18]陈世尧. 不同生长期的巴什拜羊体尺体重遗传参数估计[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2022.
CHEN Shiyao. Estimation of genetic parameters for body measurements and weights at different growth stages of Bashbay sheep [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.
[19] 张国俊, 陈瑜, 谭玉祥. 南江黄羊早期生长发育性状遗传参数的估计[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2012, 32(S1): 210-212.
ZHANG Guojun, CHEN Yu, TAN Yuxiang. Estimation of genetic parameters of early growth and development traits of Nanjiang yellow sheep[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2012, 32(S1): 210-212.
[20]孙国智, 樊殊, 何海迎, 等. 多浪羊主要性状遗传参数及育种值估计[J]. 中国畜牧杂志: 1-12.
SUN Guozhi, FAN Shu, HE Haiying, et al. Estimation of genetic parameters and breeding values for major traits in Duolang sheep [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science: 1-12.
[21] 乔国艳, 袁超, 李文辉, 等. 高山美利奴羊重要经济性状遗传参数估计[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2019, 55(10): 58-62.
QIAO Guoyan, YUAN Chao, LI Wenhui, et al. Estimation of genetic parameter for important economic traits of alpine merino sheep[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2019, 55(10): 58-62.
[22]王大广, 赵志辉, 赵玉民, 等. 萨福克羊表型测定值遗传参数的估计[J]. 中国草食动物, 2003, (S1): 67-68.
WANG Daguang, ZHAO Zhihui, ZHAO Yumin, et al. Estimation of genetic parameters for phenotypic measurements in Suffolk sheep [J]. Chinese Herbivores," 2003, (S1): 67-68.
[23] 王大广, 苏秀侠, 杨德新, 等. 萨福克肉用种羊体型测定值遗传参数的估计[J]. 吉林农业科学, 2002, 27(5): 45-46.
WANG Daguang, SU Xiuxia, YANG Dexin, et al. Genetic coefficient evaluation of body conformation measured value of Suffolk mutton buck[J]. Jilin Agricultural Sciences, 2002, 27(5): 45-46.
Estimation of genetic parameters and analysis of the
effects of non-genetic factors on major economic traits in Suffolk sheep
CHEN Shenglei1, SUN Guozhi1, ZHANG Guowei1, MA Haiyu1,
LIU Lingling1, ZHANG Weizhong2, LIU Wujun1,2
(1. College of Animal Science, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi 830052, China; 2. Rifa New Xiyu Manas Animal Husbandry Co. Ltd., Manas Xinjiang 832200, China)
Abstract:【Objective】 This project aims to estimate the genetic parameters of the main economic traits of Suffolk sheep and to analyze the effects of non-genetic factors on the main economic traits. traits
【Methods】" In this experiment, a total of 4,156 individual identification records of Suffolk sheep from 2017-2023 in Xinjiang Manas breeding farm were collected, and the DMU software was used to estimate the genetic parameters of the main economic traits, and the SAS software was used to analyze the effects of five fixed effects, including birth type, year of birth, group, litter size, and age of the ewe on each trait.
【Results】"" The heritability of the main economic traits in Suffolk sheep was 0.17, 0.27, 0.31 in birth weight, weekly weight and chest circumference, respectively, while the heritability of 0.05 for daily weight gain was low, and the heritability of 0.38 for body height and 0.41 for body length were high, except for the negative correlation of chest circumference with body height and body length, the other traits showed positive correlation and the correlation of body height and chest circumference with daily weight gain was low. There were strong genetic and phenotypic correlations between height and chest circumference and daily weight gain, and the heritability of both was high. The birth weight, daily weight gain, weekly weight, body length and chest circumference of single fetuses were significantly higher than those of twin fetuses; the birth weight and daily weight gain of single fetuses were in an upward trend during the period of birth year; the birth weight, daily weight gain and weekly weight of group 1 were significantly higher than those of group 2, and the body height, length and chest circumference of group 2 were significantly higher than that of group 1; in the number of litters, the birth weight, daily weight gain and body height of litters 2, 3 and 4 were significantly higher than those of litters 1 and 5; The age of ewes at 2, 3 and 4 years old was significantly higher than that of 1 year old, daily weight gain and weekly weight at 1 and 2 years old were significantly higher than those of 3 and 4 years old, and there was no significant difference among other traits.
【Conclusion】 Soffolk sheep are tall,the heritability of body length is high,weight at birth,weight at the age of one year,chest circumference belongs to medium heritability.The heritability of daily weight gain was low.There was a negative genetic correlation between chest circumference and body height and body length.The other traits were positively correlated.The soffolk sheep herd 2017-2019 early growth traits showed an upward trend.The fecundity of 2 or 3 ewes reached the best level.
Key words:Suffolk sheep; genetic parameters; non-genetic parameters; economic
Fund projects:National Key R amp; D Program Project (2021YFD1600702-1); Dolang Sheep Breed Selection and Promotion Technology System of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2021XJXQZY-DLY-01);Rural Revitalization Industry Development Science and Technology Action Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2021NC024)
Correspondence author: LIU Wujun (1966-), female, from Henan, Ph.D., professor, research direction: animal genetic breeding, (E-mail)lwj_ws@163.com
收稿日期(Received):
2023-12-10
基金项目:
国家重点研发计划项目(2021YFD1600702-1);新疆维吾尔自治区多浪羊品种选育推广技术体系(2021XJXQZY-DLY-01);新疆维吾尔自治区乡村振兴产业发展科技行动(2021NC024)
作者简介:
陈胜磊(1998-),男,新疆伊犁人,硕士研究生,研究方向为动物遗传育种,(E-mail)1046167066@qq.com
通讯作者:
刘武军(1966-),女,河南人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为动物遗传育种,(E-mail)lwj_ws@163.com
