一株海洋杆菌属新菌种XAAS-72T的植物促生功能分析及ACC脱氨酶蛋白结构预测
2024-12-31王慧楠朱静谢文何子璇柏晓玉朱艳蕾张志东

摘 要:【目的】研究海洋杆菌属新菌种XAAS-72的植物促生功能,挖掘其潜在功能基因。
【方法】通过对菌株全基因组测序,分析相关功能基因组成,挖掘ACC脱氨酶合成相关的候选基因,并进行功能预测。
【结果】海洋杆菌属新种Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72菌悬液处理可显著提高盆栽小麦麦苗生长,其基因组长度为5 054 860 bp,含1个环形质粒,总GC含量为54.52%,注释的基因数目为4 391个,编码蛋白数4 261个,具有多种抗逆和促生相关基因。其与Pontibacter sp. BAB1700的ACC脱氨酶(1-aminoeyclopropane-1-earboxylate-deaminase)相似度最高为72.48%。该蛋白属于不稳定亲水性蛋白,不具备跨膜结构,且无信号肽结构。
【结论】海洋杆菌属新种XAAS-72蕴藏着丰富的抗逆和植物促生相关基因。
关键词:海洋杆菌属;植物促生特性;ACC脱氨酶;结构预测
中图分类号:S188"" 文献标志码:A"" 文章编号:1001-4330(2024)07-1778-08
0 引 言
【研究意义】土壤盐分是影响农作物产量的主要非生物胁迫,能抑制植物的种子萌发且对植株生长发育有显著影响[1]。治理和改良盐碱地的方法包括物理法、化学法及生物法,其中,利用具有耐盐、促生活性的菌剂,不仅能够提高土壤肥力,提升植物盐碱抗性及植物生长效率,部分产品还可降低作物病害指数[2],已成为了改善中低盐碱土壤的重要方法之一。【前人研究进展】盐生植物根际中蕴含着丰富盐碱及干旱耐受性的菌株[3-4],如盐单胞菌属(Halomonas)、芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)、根瘤菌属(Rhizobium)[5-6]。部分微生物能够耐受10%的NaCl,可用作生物肥料,能改善盐胁迫下的小麦产量,并降低病害及经济损害[7-8]。新型微生物辅助技术可以增强植物的耐盐性,并在盐胁迫条件下提高作物产量[9],表现出耐盐促生菌株的重大应用前景。部分环境分离获得的耐盐促生菌株缺少评价[10-11]。因此,利用基因编辑、基因克隆等现代分子学手段,强化耐盐促生菌株关键基因的挖掘和利用,已成为重要的生物安全风险规避的技术方法。1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸脱氨酶(1-aminoeyclopropane-1-earboxylate- deaminase,ACC脱氨酶,简称ACCD酶)在促进植物生长、保护植物抵御非生物和生物胁迫中起到重要作用[12]。ACC脱氨酶可分解ACC(乙烯的前体)为氨和α-丁酮酸,使植物体内乙烯浓度降低,减少对植物造成的不良影响,从而保证植物正常生长[13]。植物根际促生菌能够在盐胁迫条件下通过提高ACC脱氨酶的利用率来维持小麦的生长,主要是通过表达acdS基因来促进植物的生长并提高耐盐性[14-15]。如将该基因导入到不含ACC脱氨酶的菌株内,能通过提高植物抗性来促进植物生长;或导入到根瘤菌中,以增强根瘤菌的侵染能力,促进结瘤[16-18]。【本研究切入点】从盐爪爪(Kalidium foliatum)根际土壤分离出一株海洋杆菌属菌株XAAS-72并命名为Pontibacter kalidii,其具有ACC脱氨酶活性,目前有关海洋杆菌属菌株的促生作用鲜有报道。需研究海洋杆菌属新菌种XAAS-72的植物促生功能。【拟解决的关键问题】通过对菌株XAAS-72处理后的小麦盆栽试验,验证其促生效果,并从基因组中分析挖掘其潜在促生基因,对其ACC脱氨酶编码基因分析,为进一步开发和利用菌株功能基因及构建相关工程菌株奠定了基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
1.1.1 菌种来源
菌株Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T分离自盐爪爪(Kalidium foliatum)根际土壤,并保存于中国普通微生物菌种保藏管理中心(CGMCC),菌保号CGMCC 16594。实验室冻存的菌株接种于1/3 2216E(MA)琼脂培养基上,置于28℃恒温培养箱中培养3 d。
1.1.2 培养基
2216E培养基、TSB培养基、无机磷细菌培养基,均购自青岛海博生物技术有限公司。DF培养基购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
1.1.3 主要仪器设备
紫外分紫外分光光度计,日本岛津公司(shimadzu);高速冷冻离心机,德国Sigma公司;酶标仪,美国伯腾仪器有限公司;磁力搅拌器,上海梅颖浦仪器制造有限公司。
1.2 方 法
1.2.1 菌株促生特性的测定
菌株解磷能力:菌株接种于解磷(无机磷和有机磷)细菌培养基上,30℃,培养7 d,观察透明圈的大小。
菌株产IAA能力:菌株接种于含L-色氨酸(100 mg/L)的2% NaCl的TSB培养基中,摇床培养(30℃,180 r/min)1 d后,取50 μL菌悬液滴于白色陶瓷板上,同时加入等体积的Salkowski比色液(50 mL 35% HClO4+1 mL 0.5 mol/L FeCl3),将白色陶瓷板于室温避光放置30 min后,观察颜色变红的情况。以加入2% NaCl的TSB培养基为阴性对照。
菌株产ACC能力:菌株接种于含3 mM ACC的DF液体培养基,传代3次后,观察其在ACC为唯一氮源培养基上的生长情况,生长的菌株为产脱氨酶阳性菌株。
1.2.2 菌株XAAS-72对小麦促生作用
选择颗粒饱满且无明显破损的小麦种子,0.1%的升汞消毒5 min,无菌水洗净,晾干后,室温浸于106 CFU/mL浓度菌液4 h。对照处理为蒸馏水浸种。将试验组和对照组小麦种子分别点植于穴栽盆,每穴为4粒,深度约1.5 cm,置于人工气候室中培养。培养条件20℃、无光照8 h;22℃、30%光照2 h;25℃、100%光照12 h;30%光照2 h。每日浇1次水,浇水量控制一致。待发芽后,每隔5 d浇灌1次(每穴约10 mL)。生长15 d后测量试验组和对照组小麦植株的相关参数,包括发芽率、鲜重和株高。
1.2.3 全基因组测序
采用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵法(CTAB)对样本的基因组DNA进行提取,使用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA的纯度和浓度,交由北京诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司完成扩增测序。
菌株基因组在北京基因组研究所(中国深圳)使用Illumina NovaSeq PE150测序。配对端片段文库根据Illumina NovaSeq PE150系统的流程进行测序。来自配对测序的低质量原始读段(连续碱基覆盖少于5个读段的原始读段)被丢弃。测序后的读段使用SMRT Link(版本5.0.1)进行组装,使用Glimmer(版本3.0)对XAAS-72基因组组装进行基因预测。使用blast对齐工具进行功能注释。采用京都基因和基因组百科全书数据库(KEGG)、同源蛋白簇数据库(COG)、非冗余蛋白数据库(NR)、Swiss-Prot数据库、基因本体论数据库(GO)、碳水化合物活性酶数据库(CAZy)数据库等6个数据库进行一般功能注释。采用基因组测序法测定DNA的G+C含量。除非另有说明,否则所有软件都使用默认参数。
1.2.4 目标基因编码蛋白
使用纽普生物平台(https://www.novopro.cn/tools/)对蛋白质亲疏水性分析;使用ProtParam 在线软件进行蛋白质理化性质分析;使用Signal-P4.1在线软件(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-4.1/)进行信号肽预测;使用在线跨膜结构预测程序 TMHMM2.0 Server 对蛋白质氨基酸序列进行跨膜结构分析;使用 SOPMA 在线软件对蛋白质进行二级结构预测;使用 SWISS-MODEL 在线软件(https://swissmodel.expasy.org/)对蛋白质进行三维结构预测;使用 MEGA 11.0 软件建立系统发育树。
2 结果与分析
2.1 菌株及菌株植物促生功能
2.1.1 菌株特征
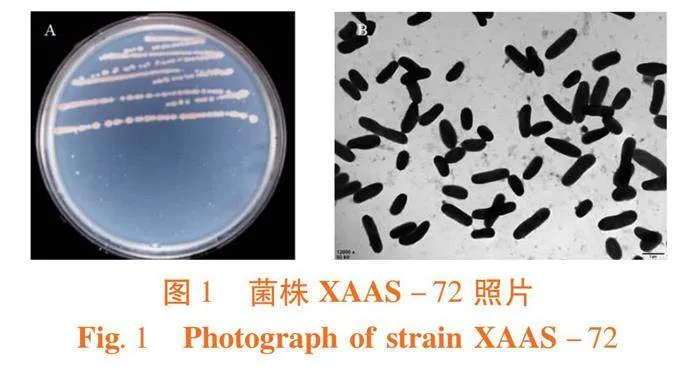
研究表明,菌株分离自盐爪爪根际土壤,由本课题组命名为Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72并保存,保藏号为CGMCC 16594T=KCTC 72095T。菌株XAAS-72为革兰氏阴性,需氧,运动,杆状。在1/3 MA培养基上培养3 d,菌落呈圆形,凸状,光滑,粉红色。细胞大小为0.5~0.6 μm×1.0~1.8" μm,无鞭毛。菌株可在8%的NaCl下生长,具有解磷、产IAA和ACC特性。图1
2.1.2 菌株促生效果的盆栽试验验证
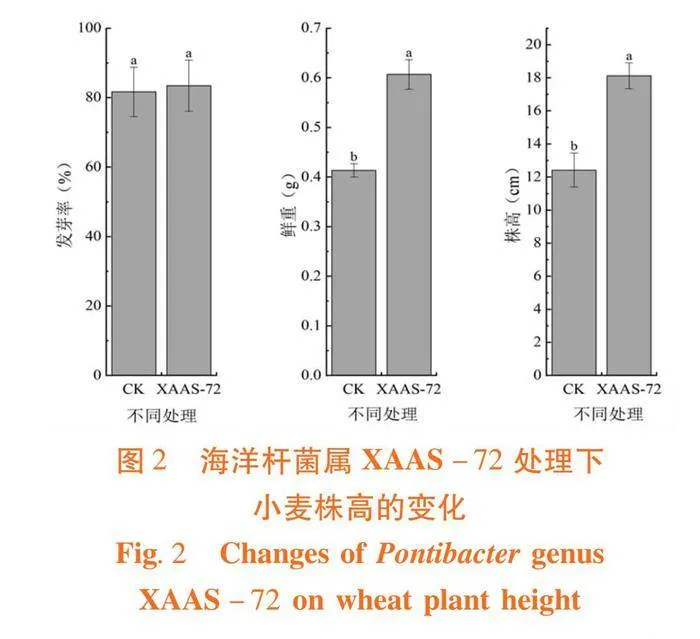
研究表明,小麦种子经XAAS-72菌悬液处理,盆栽生长15 d后,出现显著的促生作用,与对照处理相比,处理组小麦株高显著增加了45.1%,植株鲜重增加了46.3%,但菌悬液处理对小麦种子发芽率无显著影响,发芽率提高了2.3%。图2
2.2 菌株基因组基本信息
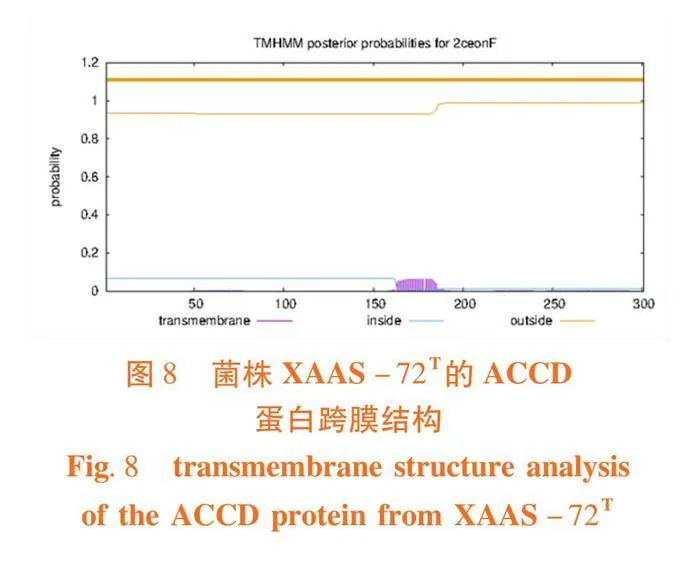
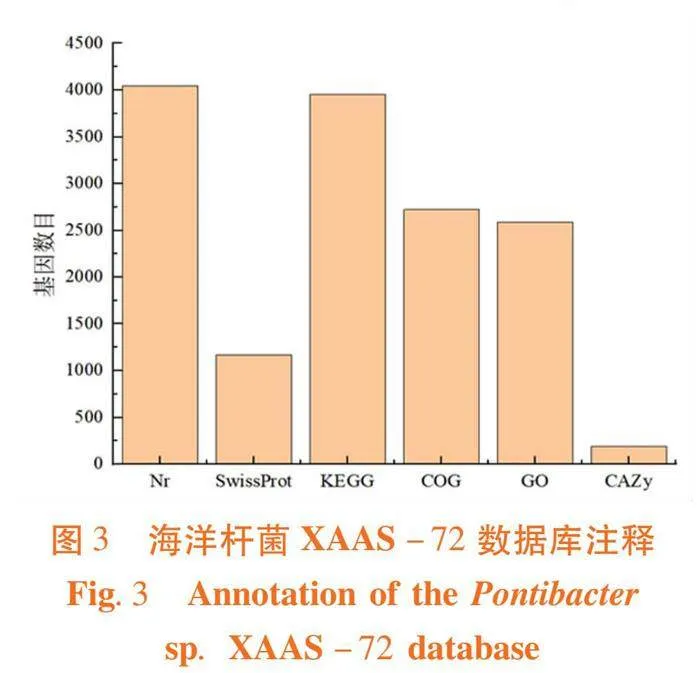
研究表明,菌株Pontibacter sp. XAAS-72含1个环形质粒,全基因组大小为5 054 860 bp,GC含量为54.52%,注释的基因数目为4 391,注释得到的基因总长度为4 256 406 bp,基因平均长度为969 bp,注释的蛋白质数目为4 261。将菌株的全基因组测序数据提交至NCBI数据库,登录号为CP111079.1。经KEGG数据库比对,有3 953个基因得到注释,占基因总数的90.03%,分别在细胞过程、环境信息处理、遗传信息处理、人类疾病、新陈代谢和生物系统共6个功能,41个通路上得到注释。其中有1 086个基因在代谢通路上得到注释,全局和概述图谱有417个基因,氨基酸代谢通路相关的基因有120个,占代谢通路的11.05%,与碳水化合物相关的基因有116个,占代谢通路基因总数的10.68%。图3,图4
2.3 菌株抗逆促生相关基因的挖掘
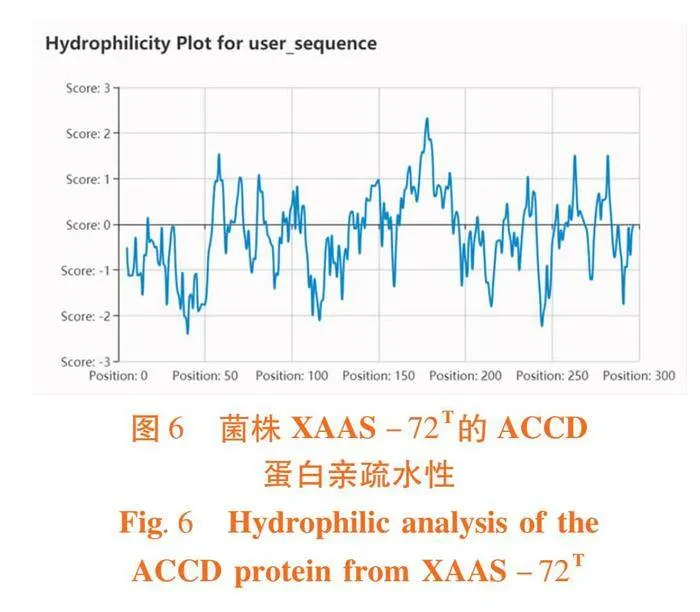
研究表明,从XAAS-72菌株基因组中初步筛选出植物促生、菌株抗逆和应激等功能基因33个,相关基因包括ACC 脱氨酶基因1个、耐盐渗透调节基因4个、生物膜形成基因2个、促植物生长基因3个、固氮基因3个、磷酸盐代谢基因5个、硫同化和代谢基因5个、根定植基因2个。该基因组中存在多种参与氧化应激和耐旱性的酶,DNA损伤修复基因。表1
2.4 菌株XAAS-72T的ACCD酶分析
2.4.1 氨基酸序列同源性
研究表明,菌株基因组中一个编码ACC脱氨酶(EC:3.5.99.7)编码基因,全长为906 bp,编码301个氨基酸,其与Pontibacter sp. BAB1700的ACC脱氨酶编码氨基酸(1-aminoeyclopropane-1-earboxylate-deaminase)相似度最高为72.48%,两者在一个大分支上。图5
2.4.2 蛋白质理化性质
研究表明,编码ACCD酶的氨基酸数目为301,分子量约为33.6 kDa,理论等电点为6.27,其值小于7为酸性蛋白质。带负电荷的残基总数 (Asp + Glu)33,
带正电荷的残基总数 (Arg + Lys)29,分子式C 1521 H 2358 N 406 O 434 S 11,原子总数4 730,不稳定指数44.80,
脂肪族指数89.80,亲水性总平均值-0.226。
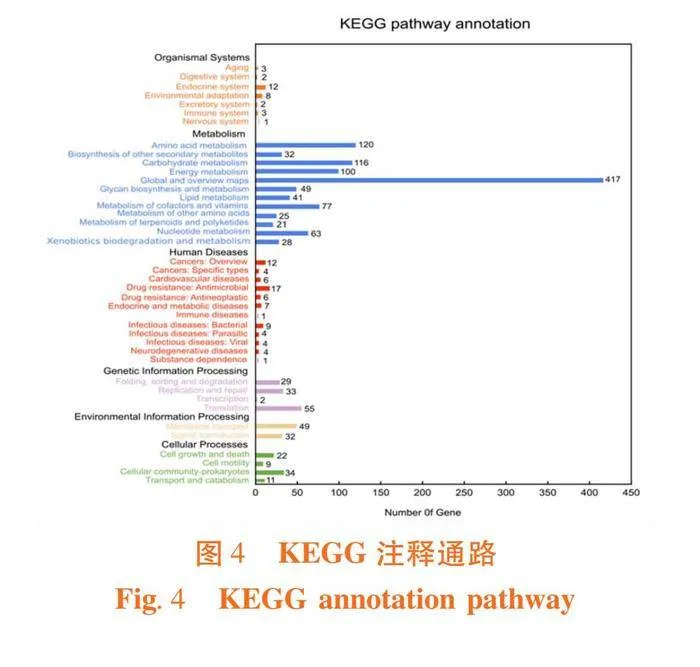
不稳定性指数预测值为44.80(不稳定系数小于40时,预测蛋白质稳定,反之则不稳定),该蛋白为不稳定蛋白,ACCD蛋白亲疏水分布中小于0的部分占比为65%,明显高于50%,其中疏水性分数数值最高为4.5,最低为-4.5,此蛋白为酸性亲水性不稳定蛋白。图6
2.4.3 信号肽
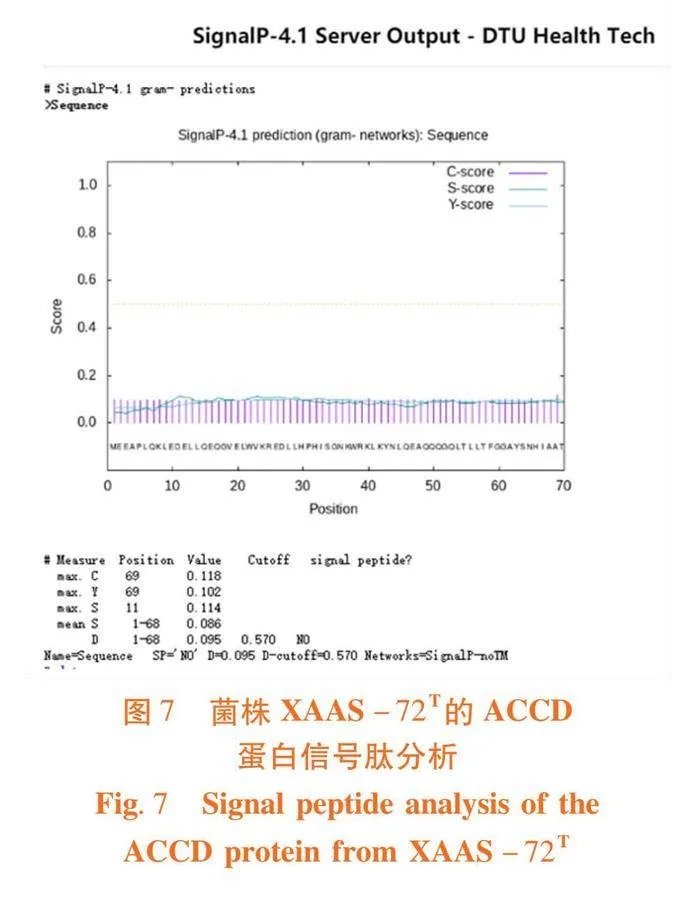
研究表明,信号肽切割位点C的最高值为0.118,位于第69位氨基酸;信号肽分数S值的最高值为0.114,位于第11位氨基酸;合并后切割位点Y值的最高值位于第69位氨基酸,为0.102;S平均值为0.086,C,S,Y值比较平缓。图7
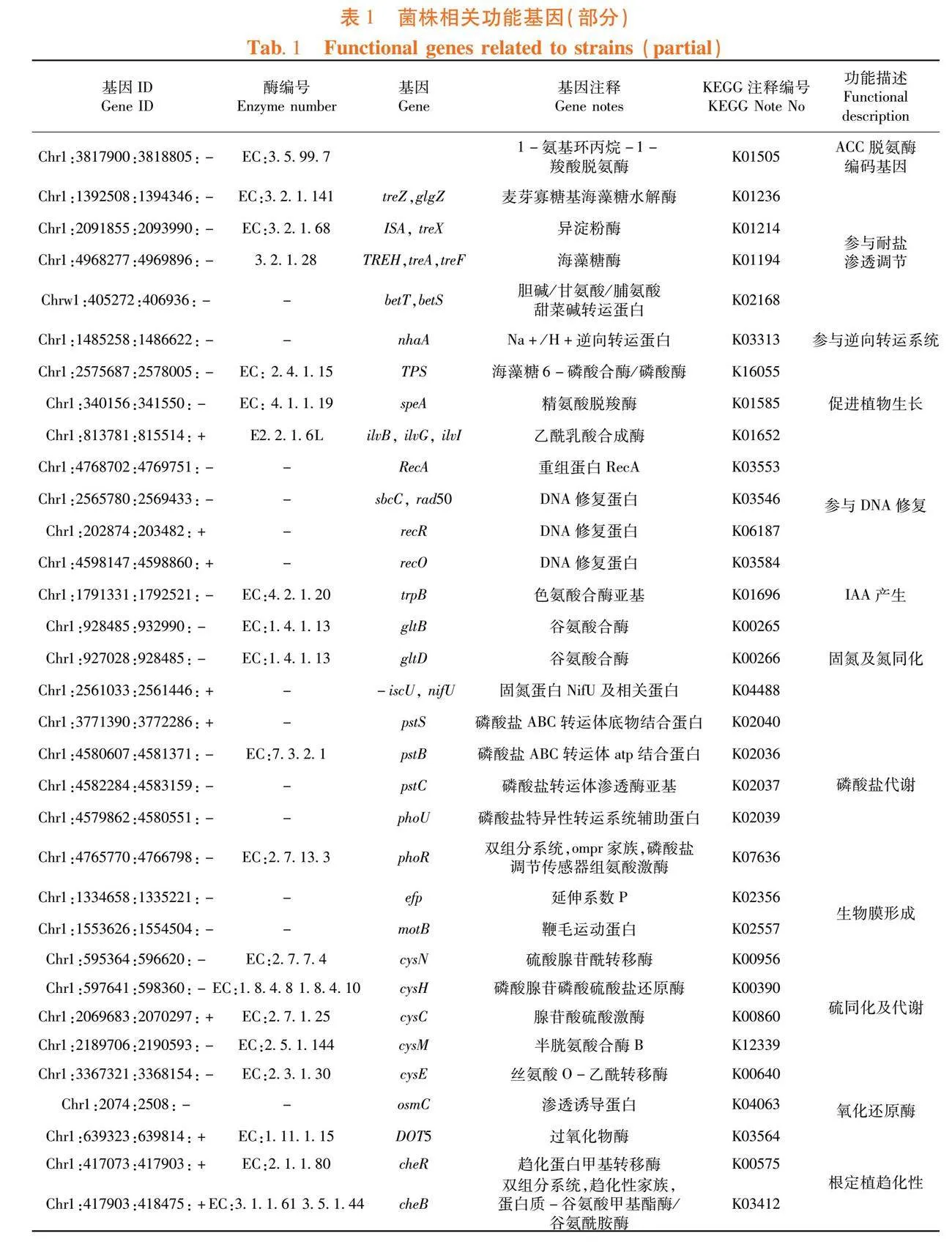
2.4.4 跨膜结构
研究表明,蛋白质无跨膜结构。图8
2.4.5 蛋白质结构预测
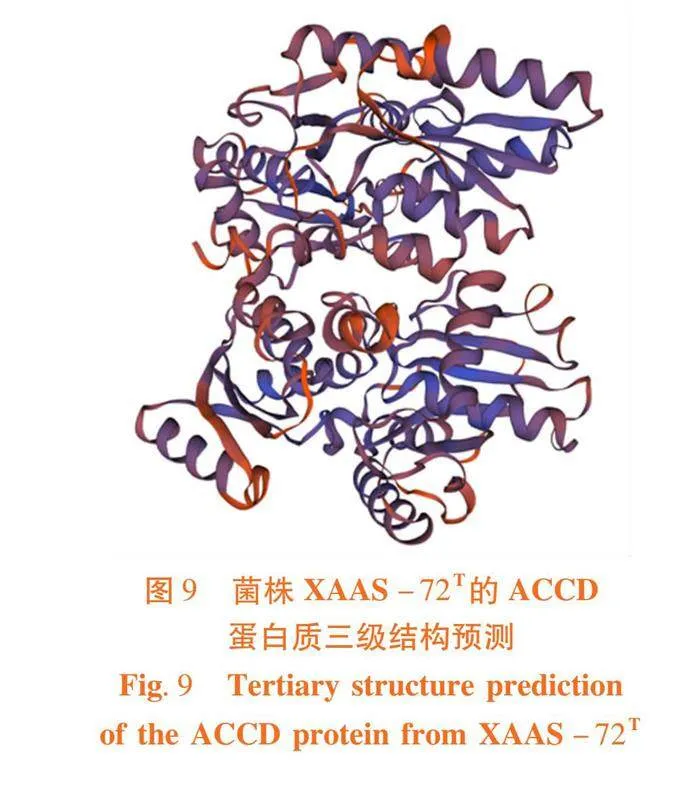
研究表明,ACCD结构中α-螺旋和无规则卷曲所占百分比最多,分别为38.87%和36.21%。而另两个结构所占比例相对较小,β-转角仅占比7.64%,蛋白质三级结构分析也与二级结果相互验证,蛋白质三级结构中也以α-螺旋和无规则卷曲为主。图9
3 讨 论
3.1
海洋杆菌属最初由Nedashkovskay等[19]提出的,归属于拟杆菌门中膜杆菌科。目前,对于海洋杆菌属的研究主要集中在功能产物方面,包括产类胡萝卜素、虾青素、硝酸盐还原活性、α-半乳糖苷酶的盐适应性及转糖基化活性[20-23]。研究采用的海洋杆菌属新菌种Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T分离自盐爪爪根际土壤中,并由团队命名。该菌株可在8%的NaCl下生长,具有解磷、产IAA和ACC特性。该菌具有明显的促生作用。
3.2
通过对菌株XAAS-72基因组测序注释,发现该基因组中含有多个与植物促生相关的基因。查找的关键基因包括ACC 脱氨酶基因1个,耐盐渗透调节基因4个,参与生物膜形成基因2个,植物生长促进基因3个,固氮基因3个,磷酸盐代谢基因5个,硫同化和代谢基因5个,氧化还原酶基因2个,与根定植相关的基因2个,同时也预测到了与DNA修复和植物冷害等非生物胁迫的关键基因,菌株XAAS-72具有较强的抵抗逆境条件及促生长活性。其中,ACC脱氨酶可广泛用于植物生长,Holguin等[24]将阴沟肠杆菌UW4的ACC脱氨酶基因 (acdS) 导入巴西固氮螺菌中在lac启动子的控制下表达,结果显著增加了IAA合成能力并提高了细菌生长速度,同时促进了番茄幼苗的生长。acdS基因的过表达也提高了矮牵牛对非生物胁迫的耐受性[25]。此外ACC脱氨酶还可作为植物防御和病原体毒力的调节剂[26]。
3.3
近期对于ACC脱氨酶的研究主要集中于编码ACC脱氨酶的结构基因acdS[27],其中以假单胞菌属的报道最为广泛,基因大小在1 014~1 017 bp,编码338个氨基酸,预测亚单位重量为36.6 KDa[28],假单胞菌[12]和中根瘤菌[28]中的编码蛋白等电点均小于7,不稳定指数低于40,为酸性亲水性不稳定蛋白,且均没有跨膜结构和信号肽结构,蛋白质二三级结构均以α螺旋和无规则卷曲结构为主。研究菌株基因组中发现的ACCD编码基因大小为906 bp,编码301个氨基酸,约为33.6 KDa,其与NCBI已知菌株Pontibacter sp. BAB1700的ACC脱氨酶(1-aminoeyclopropane-1-earboxylate-deaminase)相似度最高为72.48%,其为编码ACC脱氨酶的候选基因。
4 结 论
海洋杆菌属新种Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T具有明显耐盐、促生特性,其全基因组全长为5 054 860 bp,含1个环形质粒,具有多种抗菌、抗逆和促生相关基因。其ACC脱氨酶与Pontibacter sp. BAB1700的相关酶蛋白序列相似度最高为72.48%。该蛋白属于不稳定亲水性蛋白质,不具备跨膜结构,且无信号肽结构。
参考文献(References)
[1]
Liang W J, Cui W N, Ma X L, et al. Function of wheat Ta-UnP gene in enhancing salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis and rice [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2014, 450(1): 794-801.
[2] Zhang C Y, Wang W W, Hu Y H, et al. A novel salt-tolerant strain Trichoderma atroviride HN082102.1 isolated from marine habitat alleviates salt stress and diminishes cucumber root rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum [J]. BMC Microbiology," 2022, 22(1):67-80.
[3] Salma M, Samia A, Aftab B, et al. Identification of plasmid encoded osmoregulatory genes from halophilic bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere of halophytes - Science Direct [J]. Microbiological Research," 2019,228:126307-126307.
[4] Zhang M, Yang L, Hao R Q, et al. Drought-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba) and their potential to enhance drought tolerance [J]. Plant and Soil, 2020,(1/2):452,423-440.
[5] 张志东,顾美英,唐琦勇,等.盐爪爪根际耐盐促生菌的筛选及穴栽验证 [J].中国农业科技导报,2021,23(3):186-192.
ZHANG Zhidong, GU Meiying, TANG Qiyong, et al. Screening and cavity planting of salt-tolerant probiotic bacteria in inter-rhizosphere of salt pawpaw [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology," 2021,23(3):186-192.
[6] Mohammad K H, John A M, Jarrod J, et al. Pectin-Rich Amendment Enhances Soybean Growth Promotion and Nodulation Mediated by Bacillus Velezensis Strains [J]. Plants, 2019, 8(5):120-134.
[7] Zhou Y Y, Hao L P, Ji C, et al. The Effect of Salt-Tolerant Antagonistic Bacteria CZ-6 on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community of Winter Jujube (Mill. “Dongzao”) in Saline-Alkali Land [J]. BioMed Research International,2021.
[8] Zahra S T, Tariq M, Abdullah M, et al. Dominance of Bacillus species in the wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere and their plant growth promoting potential under salt stress conditions [J]. PeerJ, 2023,11: e14621.
[9] Kumar A, Singh S, Gaurav A K, et al. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Biological Tools for the Mitigation of Salinity Stress in Plants [J]. Frontiers in microbiology," 2020,11:1216-1256.
[10] Farzad B A, Davoud F, Ali B, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of canola leaf inoculated with a plant growth-promoting bacterium, Pseudomonas fluorescens, under salt stress [J]. BBA - Proteins and Proteomics, 2016,1864(9):1222-1236.
[11] Swapmil S, Lti G M, Sharad T. Klebsiella sp. confers enhanced tolerance to salinity and plant growth promotion in oat seedlings (Avena sativa) [J]. Microbiological Research," 2018,206:25-32.
[12] Glick B R, Nascimento F X. Pseudomonas 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) Deaminase and Its Role in Beneficial Plant-Microbe Interactions [J]. Microorganisms, 2021,9(12): 2467.
[13] 张典利,孟臻,亓文哲,等.植物根际促生菌的研究与应用现状[J].世界农药,2018,40(6):37-43,50.
ZHANG Dianli, MENG Zhen, QI Wenzhe, et al. Research and application status of plant rhizosphere growth promoting bacteria [J]. World Pesticides, 2018,40(6):37-43,50.
[14] Muhammad S A, Amna, Sumaira, et al. Induction of tolerance to salinity in wheat genotypes by plant growth promoting endophytes: Involvement of ACC deaminase and antioxidant enzymes [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019,139:569-577.
[15] Rubén P R, Jessica LCA, José L B, et al. Halophilic rhizobacteria from Distichlis spicata promote growth and improve salt tolerance in heterologous plant hosts [J]." Symbiosis," 2017,73(3):179-189.
[16] Muhammad T, Lftikhar A, Muhammad S, et al. Regulation of antioxidant production, ion uptake and productivity in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plant inoculated with growth promoting salt tolerant Bacillus strains [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019,178:33-42.
[17] Liu C H, Siew W Y, Hung Y T, et al.1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) Deaminase Gene in Pseudomonas azotoformans Is Associated with the Amelioration of Salinity Stress in Tomato [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021,69(3):913-921.
[18] Tavares M J, Nascimento F X, Glick B R, et al. The expression of an exogenous ACC deaminase by the endophyte Serratia grimesii BXF1 promotes the early nodulation and growth of common bean [J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2018,66(3):252-259.
[19] Chhetri G, Yang D, Choi J, et al. Edaphorhabdus rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from soil in South Korea [J]. AntonieVan Leeuwenhoek, 2018a,111(12):2385-2392.
[20] Chhetri G, Kim J, Kim H, et al. Pontibacter oryzae sp. nov., a carotenoid-producing species isolated from a rice paddy field [J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2019,112(11):1705-1713.
[21] Abirami P, Giji S, Mohan K, et al. Biomedical Potential of Astaxanthin from Novel Endophytic Pigment Producing Bacteria Pontibacter korlensis AG6 [J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2020,12.2119-2129.
[22] Philippon T, Tian JH, Bureau C, et al. Denitrifying bio-cathodes developed from constructed wetland sediments exhibit electroactive nitrate reducing biofilms dominated by the genera Azoarcus and Pontibacter [J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2021,140:107819.
[23] Zhou J P, Liu Y, Lu Q, et al. Characterization of a Glycoside Hydrolase Family 27 α-Galactosidase from Pontibacter Reveals Its Novel Salt-Protease Tolerance and Transglycosylation Activity [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016,64(11):2315-24.
[24] Holguin G, Glick B R. Transformation of Azospirillum brasilense Cd with an ACC deaminase gene from enterobacter cloacae UW4 fused to the Tet r gene promoter improves its fitness and plant growth promoting ability [J]. Microbial Ecology, 2003,46(1) 46(1):122-33.
[25] Naing A H, Jeong H Y, Jung S K, et al. Overexpression of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid Deaminase (acdS) Gene in Petunia hybrida Improves Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021,12:737490.
[26] Tsolakidou M D, Pantelides L S, Tzima A K, et al. Disruption and Overexpression of the Gene Encoding ACC (1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid) Deaminase in Soil-Borne Fungal Pathogen Verticillium dahliae Revealed the Role of ACC as a Potential Regulator of Virulence and Plant Defense [J]. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions Mpmi,, 2019,32(6):639-653.
[27] 李,傅培龙,贾颜,等.含ACC脱氨酶的螃蟹脚内生细菌筛选及其acdS基因克隆与分析[J].分子植物育种2021-12-27 17:19
LI Qian, FU Peilong, JIA Yan, et al. Screening of Endophytic Bacteria from Viscum liquidambaricolum Containing ACC Deaminase and Cloning and Analysis of acdS Gene [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021-12-27 17:19.
[28] Krishnendu P, Tithi S, Soumik M, et al. In silico structural and functional analysis of Mesorhizobium ACC deaminase [J]. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 2017,68:12-21.
Structure prediction of the ACC protein from
Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T with the plant
growth-promoting character
WANG Huinan1,2, ZHU Jing2, XIE Wenwen2,3, HE Zixuan2,3,
BAI Xiaoyu1," ZHU Yanlei1, ZHANG Zhidong1,2,3
(1." College of Life Sciences, Xinjiang Normal University, Urumqi 830054, China; 2. Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Special Environmental Microbiology/Institute of Applied Microbiology, Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Urumqi 830091, China; 3. College of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China)
Abstract:【Objective】 To explore the plant growth promotion function of a novel strain Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T, and investigate the potential functional genes.
【Methods】" The strain whole genome was sequenced, and the composition of function genes were analyzed. A candidate gene related to ACC deaminase synthesis was obtained, and the enzyme protein characteristics were predicted.
【Results】" The results showed that the growth of wheat seed treated with Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T was promoted significantly in pots.The genome length of strain XAAS-72 (accession no. CP111079) was 5,054,860 bp, containing one circular plasmid. A total GC content was 54.52%, and the number of annotated genes was 4,391, coding for 4,261 proteins. A variety of resistance and growth-promoting related genes was observed. It had the highest similarity of 72.48% to the ACC deaminase of Pontibacter sp. BAB1700. It an unstable hydrophilic protein, with none of transmembrane structure and signal peptide structure.
【Conclusion】" Pontibacter kalidii XAAS-72T harbors a lot of genes related to the stress resistance and the plant growth-promoting.
Key words:Pontibacter;plant growth-promoting character;ACC deaminase;structure prediction
Fund projects: \"Outstanding Youth Fund\" of Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang (2022D01E19); Key Science and Technology Innovation Incubation Project of Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences(xjkcpy-2022004);Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences Scientific and technological innovation support(xjnkywdzc-2023005)
Correspondence author: ZHU Yanlei (1980-), female, from Jiangsu, associate professor, research direction: microbial ecology, (E-mail) zhuyanlei1226@163.com
ZHANG Zhidong (1977-), male, from Xinjiang, researcher, research direction: special environmental microorganisms and probiotic resources, (E-mail) zhangzheedong@sohu.com
收稿日期(Received):
2023-10-11
基金项目:
新疆维吾尔自治区自然科学基金项目“杰出青年基金”(2022D01E19); 新疆农业科学院科技创新重点培育专项(xjkcpy-2022004);新疆农业科学院农业科技创新稳定支持专项(xjnkywdzc-2023005)
作者简介:
王慧楠(1999-),女,吉林长春人,硕士研究生,研究方向为微生物生态,(E-mail)18946303350@163.com
通讯作者:
朱艳蕾(1980-),女,江苏沛县人,副教授,博士,研究方向为微生物生态,(E-mail)zhuyanlei1226@163.com
张志东(1977-),男,新疆乌鲁木齐人,研究员,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为特殊环境微生物资源挖掘与利用,(E-mail)zhangzheedong@sohu.com
