相思子碱通过P53/mTOR通路缓解脂多糖对水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白合成的影响
2024-10-15周金陈肖鹏李孟琪张博郑海英杨春艳田新如黄依林杨小淦尚江华






摘要:【目的】探究相思子碱(Abrine)通过调节P53/mTOR通路缓解脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharide,LPS)对水牛乳腺上皮细胞酪蛋白合成的影响,为缓解乳房炎引起的水牛乳品质下降提供理论依据。【方法】使用脂多糖构建水牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症模型,同时使用相思子碱、P53抑制剂(Pifithrin-μ)、P53激活剂(Kevetrin hydrochloride)与水牛乳腺上皮细胞共同孵育12 h;通过HE染色观察水牛乳腺组织形态,采用CCK-8法检测细胞活性,使用ELISA试剂盒检测水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白分泌水平,利用实时荧光定量PCR测定NF-κB、IL-1β、TNFα、β-casein、mTOR、P53、JAK2、STAT5和AKT1基因相对表达量,并以Western blotting检测NF-κB、IL-1β、TNFα、β-casein、mTOR和P53蛋白相对表达量。【结果】临床型乳房炎乳腺组织间隙及腺泡腔被大量中性粒细胞浸润,部分腺泡结构呈现一定程度的萎缩。经1.0μg/mL脂多糖处理,水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力显著降低(P<0.05,下同),2.0、4.0和8.0μg/mL脂多糖处理,水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力极显著降低(P<0.001),25、50、100和200μmol/L相思子碱处理能缓解脂多糖的影响,水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力明显升高。与空白对照组相比,脂多糖处理组水牛乳腺上皮细胞NF-κB、IL-1β、TNFα和P53基因和蛋白相对表达量显著升高,β-酪蛋白表达水平显著降低;与脂多糖组相比,相思子碱+脂多糖处理组水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白水平显著升高,NF-κB、IL-1β、TNFα、P53基因和蛋白相对表达量显著降低;与脂多糖组相比,脂多糖+Pifithrin-μ组水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白表达水平显著升高,与相思子碱组相比,相思子碱+Kevetrin hydrochloride组水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白表达水平显著降低。【结论】脂多糖降低了水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白合成水平与β-酪蛋白合成相关基因及其编码蛋白的表达水平;相思子碱能通过抑制NF-κB通路缓解脂多糖诱导的水牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症,并通过调节P53/mTOR通路缓解脂多糖诱导的水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白合成减少。
关键词:水牛乳腺上皮细胞;相思子碱;脂多糖;β-酪蛋白;P53/mTOR通路
中图分类号:S853.74文献标志码:A文章编号:2095-1191(2024)07-1887-10
Abrine mitigates the effects of lipopolysaccharide onβ-caseinsynthesis in buffalo mammary epithelial cells bymodulating the P53/mTOR pathway
ZHOU Jin-chen XIAO Peng LI Meng-qi ZHANG Bo ZHENG Hai-ying YANG Chun-yan TIAN Xin-ru HUANG Yi-lin YANG Xiao-gan SHANG Jiang-hua
(1College of Animal Science and Technology,Guangxi University,Nanning,Guangxi 530004,China;2GuangxiBuffalo Research Institute/Guangxi Key Laboratory of Buffalo Genetics,Reproduction and Breeding,Nanning,Guangxi 53000 China)
Abstract:【Objective】The objective of this study was to investigate the mitigating effect of abrine on induced inhibi‐tion by lipopolysaccharide(LPS)of casein synthesis in buffalo mammary epithelial cells by modulating the P53/mTOR pathway,to provide a theoretical basis for mitigating the decline in milk quality in buffaloes caused by mastitis.【Method】The LPS-induced inflammation model was established in buffalo mammary epithelial cells,co-incubated with abrine,P53 inhibitor(Pifithrin-μ),P53 activator(Kevetrin hydrochloride)and buffab mammary epithelial cells for 12 h;morpho‐logical observations of mammary tissues were conducted using HE staining;cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 method,while the secretion levels ofβ-casein were determined using ELISA kits;real-time quantitative PCR was em‐ployed to measure the gene relative expression levels of NF-κB,IL-1β,TNFα,β-casein,mTOR,P53,JAK STAT5,and AKT1;additionally,Western blotting was used to assess the protein relative expression levels of NF-κB,β-casein,mTOR,and P53.【Result】Clinical mastitis(CMS)mammary tissues showed infiltration of neutrophils in the interstitium and alveolar cavities,accompanied by atrophy at certain degree in some alveolar structures.The buffalo mammary epithe‐lial cell viability of the 1.0μg/mL LPS treatment group was significant decreased(P<0.05,the same below),buffab mam‐mary epithelial cell viability of 2.0,4.0,and 8.0μg/mL LPS treatments extremely significantly(P<0.001).Abrine at 25,50,100,and 200μmol/L alleviated the impact of LPS,resulting in obvious increase in cell viability.Compared to the blank control group,LPS treatment group significantly elevated relative expression NF-κB,IL-1β,TNFαand P53 genes and proteins in buffalo mammary epithlial cells,while extremely significantly reducedβ-casein expression.Abrine co-treatment with LPS group resulted in significant increase inβ-casein levels in buffalo mammary epithlial cells and signifi‐cant decrease in NF-κB,IL-1β,TNFαand P53 genes and proteins relative expression compared to the LPS group.TheLPS+Pifithrin-μgroup showed significant increase inβ-casein expression in buffalo mammary epithlial cells compared to the LPS group.Conversely,abrine+Kevetrin hydrochloride group exhibited significant decrease inβ-casein expression in buffalo mammary epithlial cells compared to abrine group.【Conclusion】LPS decreasesβ-casein synthesis and expression levels of genes and their encoded proteins involved inβ-casein synthesis;abrine alleviates LPS-induced mammary epithe‐lial cells of buffalo by inhibiting NF-κB pathway,and alleviates LPS-induced reduction ofβ-casein synthesis in buffalo mammary epithelial cells by modulating P53/mTOR pathway.
Key words:buffalo mammary epithelial cells;abrine;lipopolysaccharide;β-casein;P53/mTOR pathway
Foundation items:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31872350);Guangxi Science and Technology Major Project(GuikeAA22068099);Guangxi Natural Science Foundation(2021GXNSFAA196021);Guangxi Dairy Bu-ffalo Industry Innovation Team Project of China Agriculture Research System(nycytxgxcxtd-2021-21-01)
0引言
【研究意义】水牛奶是世界乳业的重要组成部分,与牛奶相比,水牛奶总干物质含量约提高50%,乳蛋白含量约提高1.5倍(杨攀等,2020;Lin etal.,2022;Abdel-Hamid et al.,2023)。牛奶的主要蛋白是酪蛋白和乳清蛋白,其中酪蛋白占总蛋白的80%以上(Yasmin et al.,2020),且含有人体所需的8种必需氨基酸,是优质的氨基酸供给源(王玥,2017;Paz‐zola et al.,2019;张瑞明,2019)。水牛患乳房炎后,水牛奶中酪蛋白水平降低(Ahmed et al.,2021),乳腺上皮细胞酪蛋白分泌在脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharide,LPS)的影响下也呈下降趋势(Wu et al.,2020),且被污染的水牛奶还会带来潜在的食品安全问题(Sha‐run etal.,2021)。因此,探究乳房炎对水牛奶中酪蛋白含量的影响及其作用机制,对缓解乳房炎引起的乳品质下降具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】乳房炎能引起水牛产奶量及乳品质降低,给水牛养殖业带来巨大的经济损失。研究发现,饲喂辣木提取物或在乳房处涂抹由蒲公英、紫花地丁、连翘和瓜蒌等中药制剂能缓解乳房炎对奶牛的影响(Sharun etal.,2021;舒建林,2023)。鸡骨草是一种传统中药材,自古以来多用于治疗乳痈肿痛(Yang et al.,2012)。相思子碱是鸡骨草中主要的生物碱,具有抗氧化、抗炎等多种生物学活性(Yang et al.,2014),但相思子碱在水牛乳房炎防治中的应用尚无研究报道。大肠杆菌是引起乳房炎最常见的致病菌之一,而脂多糖是大肠杆菌细胞壁的主要成分(Yuetal.,2020),能通过NF-κB通路诱导猪、山羊、牛等哺乳动物乳腺上皮细胞炎症(Wang et al.,2017;Xu et al.,2023;Yan et al.,2023)。研究表明,抑制NF-κB的磷酸化及核易位,能有效缓解脂多糖诱导的细胞炎症。Wu等(2020)研究发现,脂多糖处理乳腺上皮细胞后酪蛋白的合成受到抑制。此外,脂多糖能促进P53表达(Chen et al.,2023;Zhuang et al.,2023),并抑制mTOR通路活性(Liu et al.,2015;Cui et al.,2021)。mTOR通路在酪蛋白合成中发挥关键作用(Yuan et al.,2020),mTOR通路被激活后,通过触发下游分子的磷酸化而促进酪蛋白合成(Shu et al.,2020)。进一步研究发现,P53激活同样会抑制mTOR通路表达及蛋白合成(Constantinou and Clemens,2007;Akenoetal.,2015)。【本研究切入点】P53/mTOR通路参与酪蛋白合成的调控(Akeno etal.,2015;Coronel et al.,2022),而相思子碱具有抗炎、抗氧化等生物学活性,但相思子碱能否通过P53/mTOR通路调节β-酪蛋白合成及其分子机制尚未明确。【拟解决的关键问题】通过脂多糖构建水牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症模型,使用P53抑制剂(Pifithrin-μ)和P53激活剂(Keve-trin hydrochloride)进行处理后,分别检测细胞活力、炎症水平及β-酪蛋白、P53、mTOR上下游基因和蛋白的表达情况,以探究相思子碱对脂多糖引起的水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白合成障碍的影响,为缓解乳房炎引起的水牛乳品质下降提供理论依据。
1材料与方法
1.1试验材料
水牛奶样由广西水牛研究所水牛种畜场提供;水牛乳腺上皮细胞由广西水牛研究所水牛繁殖遗传重点实验室分离培养提供;PBS(P2272)、氢化可的松(386698)、孕酮(P-069)、胰岛素(Y0001717)、转铁蛋白(T8158)、表皮生长因子(E4127)及脂多糖(L2630-25MG)购自美国Sigma公司;DMEM/F-12培养基(C11330500BT)和胎牛血清(10100147C)购自美国Gibco公司;相思子碱(B21358)购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司;Pifithrin-μ(HY10940)和Kevetrin hydrochloride(HY16271)购自美国MedChemExpress公司;苏木素和伊红(BP-DL001)购自南京森贝伽生物科技有限公司;CCK-8试剂盒(C008-2)购自上海七海复泰生物科技有限公司;牛β-casein ELISA试剂盒(M55158)购自上海酶联生物科技有限公司;RT-qPCR试剂盒(AUQ-01)购自天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;CK-18、β-Actin、mTOR、P53、IL-1β、TNFα蛋白一抗及HRP标记山羊抗兔IgG(二抗)购自武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司;β-casein一抗购自北京博奥森生物技术有限公司。
1.2试验方法
1.2.1奶样检测选择65头处于泌乳中期、且体况和精神状态相近的摩拉水牛。上午5:00—7:00,通过手工挤奶方式无菌采集奶样并置于50 mL离心管中。过滤后使用体细胞计数仪检测奶中体细胞数(Somatic cell count,SCC),并以多功能乳成分分析仪检测水牛奶中酪蛋白含量。根据SCC对乳房炎程度进行划分(刘鸽等,2017),其中,SCC≤20万/mL为健康,20万/mL<SCC≤50万/mL为隐性型乳房炎,SCC>50万/mL为临床型乳房炎。
1.2.2细胞处理及组别使用添加10%胎牛血清、10 ng/mL表皮生长因子、1µg/mL氢化可的松、1µg/mL孕酮、5µg/mL胰岛素和5µg/mL转铁蛋白的DMEM/F-12培养基,在37.5℃、5%CO2培养箱中培养水牛乳腺上皮细胞。以不同浓度脂多糖(0.5、1.0、2.0、4.0和8.0μg/mL)处理水牛乳腺上皮细胞12h后检测细胞活力;然后,以不添加脂多糖和相思子碱为空白对照组(CK),使用不同浓度相思子碱(6.25、12.5、25、50、100和200μmol/L)和脂多糖共同处理水牛乳腺上皮细胞12 h后检测细胞活力。试验分为4组:空白对照组(CK)、脂多糖组(LPS)、相思子碱组(Abrine)和脂多糖+相思子碱组(LPS+Abrine)。后续试验通过添加Pifithrin-μ和Kevetrin hydrochloride分别抑制和激活P53探究相思子碱在水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白合成中的作用,试验分为6组:空白对照组(CK)、脂多糖组(LPS)、脂多糖+Pifithrin-μ组(LPS+Pifithrin-μ)、脂多糖+相思子碱组(LPS+Abrine)、相思子碱+Kevetrin hydrochloride组(Abrine+hydrochloride)和相思子碱组(Abrine)。
1.2.3细胞活力测定0.25%胰蛋白酶消化水牛乳腺上皮细胞,按4×103个/孔的密度将细胞铺在96孔细胞板中培养12 h。培养结束后,用相思子碱和脂多糖处理12h;每孔加入10.0μL细胞增殖与毒性检测试剂,37.5℃培养箱中孵育3h后使用自动微孔板读取仪读取吸光度。细胞活力计算公式如下:
细胞活力(%)=(As-Ab)/(Ac-Ab)×100
式中,As表示试验组吸光度;Ac表示对照组吸光度;Ab表示空白组吸光度。
1.2.4 HE染色组织切片固定到载玻片上,载玻片垂直放置于65℃烘箱中烘干;载玻片置于二甲苯中浸泡2次,每次10 min;然后依次在100%、95%、85%和75%乙醇中浸泡3 min,过水2 min;脱蜡复水,将载玻片置于苏木素染液中浸染8 min,分化液中分化10 s,水中蓝化20min;随后将载玻片置于伊红染液中染色5 min;将载玻片依次在75%、85%、95%和100%乙醇中浸泡3 s,在100%乙醇中浸泡1 min;随后在二甲苯中浸泡2次,每次1min;在载玻片上滴加中性树脂,盖玻片封片,尼康共聚焦显微镜(Nikon A1)下采集图像。
1.2.5β-酪蛋白含量检测使用牛β-casein ELISA试剂盒检测水牛乳腺上皮细胞培养液中β-酪蛋白含量。在酶标板上设定标准品孔、样本孔和空白孔,其中,标准品孔加入50.0μL不同浓度标准品;待测样品孔加入40.0μL样品稀释液和10.0μL待测样品,空白孔不加样品及酶标试剂。轻轻晃动混匀,封板置于37.5℃下孵育30min;孵育后加入洗涤液,静置30 s,重复5次后拍干;加入50.0μL酶标试剂,再次孵育30min;孵育结束后每孔加入洗涤液,静置30 s,重复5次;每孔加入50.0μL显色剂A和50.0μL显色剂B,轻轻振荡混匀,37.5℃避光显色15min;随后加入50.0μL终止液并检测吸光度。
1.2.6免疫荧光染色4%多聚甲醛固定细胞20 min;用含0.1%Triton X-100和0.05%Tween-20的PBS洗涤2次,每次5 min;然后以0.5%Triton X-100的PBS处理细胞30 min;洗涤2次,然后以含1%牛血清白蛋白的PBS封闭30 min;然后与一抗CK18(1∶400)在4℃下孵育过夜,孵育结束后洗涤3次,每次5 min;加入二抗(1∶1000)室温下避光孵育1h,洗涤3次,每次5 min;以Hoechst 33342(1∶1000)染色10 min,洗涤3次,每次2 min;尼康共聚焦显微镜下采集图像。
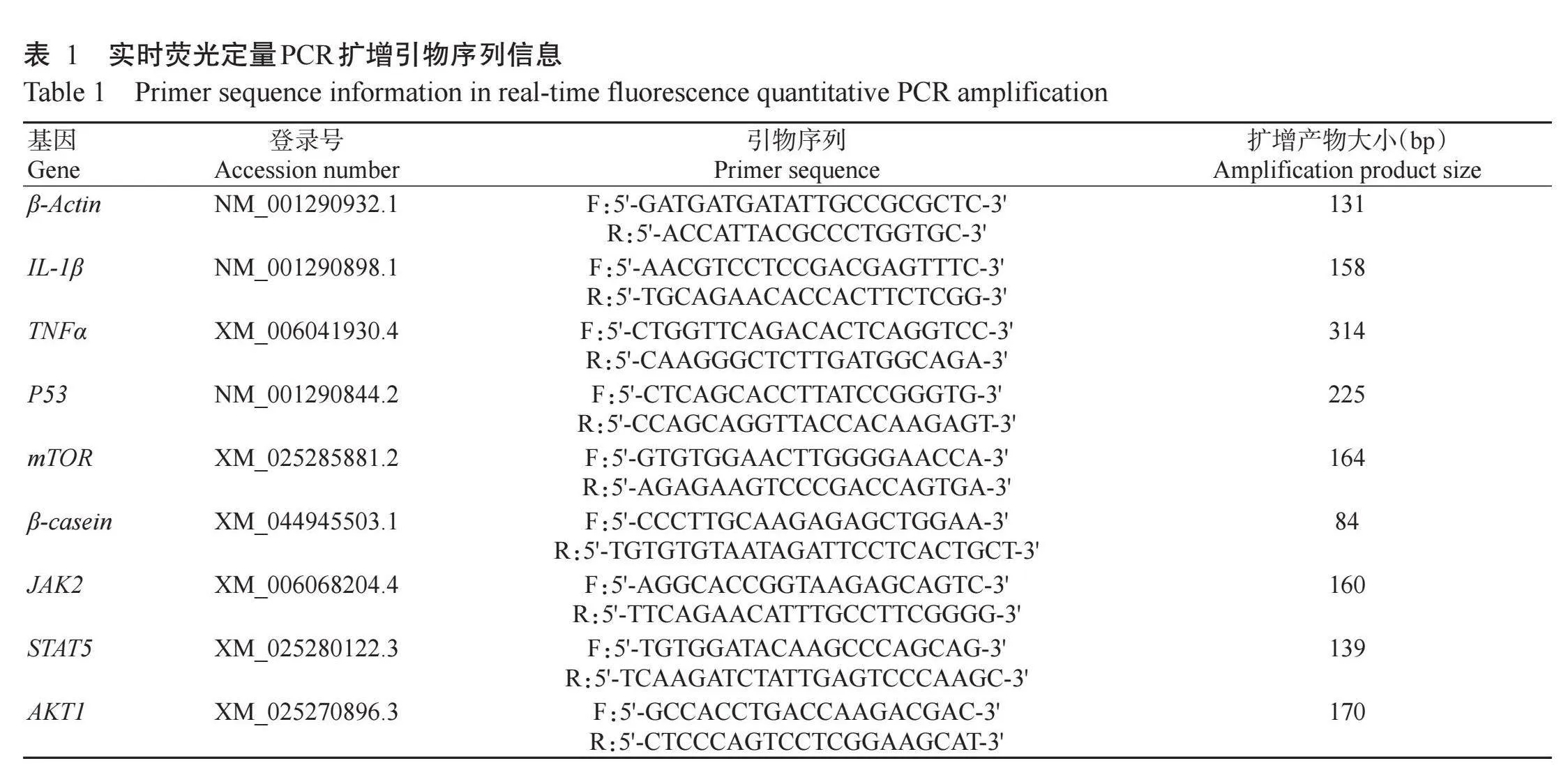
1.2.7 RNA提取与实时荧光定量PCR检测使用TRIzol试剂提取水牛乳腺上皮细胞总RNA,OD260 nm/OD280 nm介于1.8~2.0的RNA样品可用于后续试验。根据Perfect Start Uni RT&qPCR试剂盒说明进行反转录,反转录体系10.0μL:RNA 1.0μg,5×All-in-One Reaction Mix for qPCR 4.0μL,gDNA Remover 1.0μL,RNase-free H2O补足至10.0μL。使用SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix试剂盒进行实时荧光定量PCR检测,反应体系10.0μL:2×PerfectStart®Green qPCR SuperMix 5.0μL,上、下游引物各0.2μL,cDNA模板1.0μL,Nuclease-free H2O 3.6μL;扩增程序:94℃预变性30 s;94℃5 s,60℃15 s,72℃10 s,进行45个循环。以β-Actin为内参基因,采用2−ΔΔCt法计算目的基因相对表达量。实时荧光定量PCR扩增引物序列信息见表1。
1.2.8 Western blotting检测采用99%RIPA和1%PMSF的蛋白裂解液提取细胞总蛋白,以BCA蛋白浓度试剂盒对蛋白浓度进行定量和均一化处理;将蛋白样品与上样缓冲液按4∶1混合,100℃加热8 min;蛋白样品经SDS-PAGE电泳分离后,通过湿转法将蛋白转移到硝酸纤维素膜上,并用5%脱脂奶粉封闭3 h;与一抗(β-Actin、TNFα、IL-1β、β-casein、mTOR和P53采用1∶1500稀释)在4℃下孵育过夜;回收一抗,使用1×TBST洗膜3次;再与1∶1000稀释的二抗室温避光孵育1h,孵育结束后洗涤3次,通过化学发光成像仪捕获蛋白条带。
1.3统计分析
试验数据采用GraphPad Prism 8.0进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)和制图。
2结果与分析
2.1乳房炎对水牛奶酪蛋白含量的影响
水牛奶样检测结果如图1所示。与健康组相比,隐性型乳房炎组水牛奶酪蛋白含量呈下降趋势,但无显著差异(P>0.05,下同),临床型乳房炎组水牛奶酪蛋白含量则显著降低(P<0.05,下同)。
2.2乳房炎对水牛乳腺组织形态学的影响
如图2所示,健康水牛乳腺组织的腺泡结构完整且饱满;隐性型乳房炎水牛乳腺组织中部分腺泡腔有中性粒细胞浸润;临床型乳房炎水牛乳腺组织的腺泡腔被大量中性粒细胞浸润,部分腺泡结构呈现一定程度的萎缩,甚至被破坏。
2.3水牛乳腺上皮细胞鉴定结果
采用CK18对水牛乳腺上皮细胞进行免疫荧光染色,结果如图3所示。视野内大部分细胞胞质呈现特异性绿色荧光,表明CK18反应呈阳性,即该细胞为水牛乳腺上皮细胞。
2.4相思子碱和脂多糖浓度筛选结果
如图4-A所示,与空白对照组相比,1.0μg/mL脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力显著降低,2.0、4.0和8.0μg/mL脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力极显著降低(P<0.001),为防止脂多糖引起水牛乳腺上皮细胞过度损伤,故选择1.0μg/mL脂多糖用于后续试验。如图4-B所示,12.5、25、50和100μmol/L相思子碱组水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力均极显著升高(P<0.01或P<0.001),200μmol/L相思子碱组水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力显著升高;将不同浓度的相思子碱与1.0μg/mL脂多糖共同孵育水牛乳腺上皮细胞12h,结果表明,与空白对照组相比,25、50和100μmol/L相思子碱组水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力均极显著升高(P<0.01或P<0.001),200μmol/L相思子碱组水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力显著升高,其中50μmol/L相思子碱能最大程度缓解脂多糖对水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力的影响,因此选择50μmol/L相思子碱用于后续试验。
2.5相思子碱对脂多糖诱导水牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症及酪蛋白合成的影响
如图5所示,与空白对照组相比,脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞NF-κB、IL-1β和TNFα基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著升高;与脂多糖组相比,相思子碱+脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞NF-κB、IL-1β和TNFα基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著降低(图5-A,图5-B,图5-D~5-G)。与空白对照组相比,脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白含量显著降低;与脂多糖组相比,相思子碱+脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白含量显著升高(图5-C,图5-J,图5-K),表明相思子碱能缓解脂多糖对β-酪蛋白合成的抑制作用。如图5-H和图5-I所示,与空白对照组相比,脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞P53基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著升高;与脂多糖组相比,相思子碱+脂多糖组水牛乳腺上皮细胞P53基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著降低。
2.6相思子碱调控P53/mTOR通路促进β-酪蛋白合成
如图6所示,与脂多糖组相比,脂多糖+Pifithrin-μ组水牛乳腺上皮细胞P53基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著降低,β-casein、mTOR基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著升高,JAK2、STAT5和AKT1基因相对表达量显著升高。与相思子碱组相比,相思子碱+Kevetrin hydrochloride组水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-casein、mTOR基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著降低,JAK2、STAT5和AKT1基因相qMuSSv1ZsgtvVLxPLqlPeg==对表达量显著降低,P53基因及其编码蛋白相对表达量显著升高。综上所述,相思子碱能通过抑制脂多糖对P53的促进作用,而缓解脂多糖诱导β-酪蛋白合成相关基因及其编码蛋白表达降低。
3讨论
乳房炎能引起水牛产奶量及乳品质下降,严重制约着乳制品行业的高质量发展(Chen et al.,2022)。酪蛋白是水牛奶中的主要蛋白,占总蛋白的80%以上,其中β-酪蛋白占酪蛋白的38%,是水牛奶中重要的蛋白组分(顾鑫,2015)。本研究发现乳房炎能降低水牛奶酪蛋白含量,与Bobbo等(2017)的研究结果一致。大肠杆菌是水牛乳房炎的主要致病菌,而脂多糖是大肠杆菌细胞壁的主要毒力因子,可诱导多种动物乳腺上皮细胞炎症(Tsugami et al.,2021)。本研究结果表明,脂多糖能造成水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力降低,而相思子碱可显著改善脂多糖对水牛乳腺上皮细胞活力的影响,说明相思子碱可能是治疗水牛乳房炎的潜在药物。
NF-κB通路在脂多糖介导的细胞炎症过程中发挥关键作用,脂多糖能通过促进NF-κB的磷酸化和核易位而引起NF-κB依赖性炎症因子的释放,进而导致细胞炎症水平升高(Dai et al.,2020;Jianget al.,2022;Che etal.,2023)。Jiang等(2022)研究表明,抑制NF-κB信号通路能缓解脂多糖诱导的细胞炎症水平。在本研究中,相思子碱缓解了脂多糖诱导的水牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症水平,可能与qMuSSv1ZsgtvVLxPLqlPeg==NF-κB P65磷酸化被抑制有关。此外,本研究发现脂多糖能诱导β-酪蛋白相对表达量降低,P53相对表达量升高,与Wu等(2020)、Lin等(2023)的研究结果相符,提示乳房炎水牛脂多糖水平的增加可能是导致水牛奶中酪蛋白含量降低的主要原因。
酪蛋白合成受多种因素调控,其中JAK/STAT和AKT/mTOR信号通路在酪蛋白合成中发挥重要作用(Zhang et al.,2018)。在水牛哺乳期,体内催乳素水平升高,催乳素与催乳素受体相互作用诱导催乳素受体二聚化,导致JAK2的快速磷酸化,激活的JAK2通过其SH2结构域招募细胞质STAT5,导致磷酸化的STAT5从单体状态转变为二聚体状态,并易位到细胞核与酪蛋白启动子的转录因子结合位点结合,诱导酪蛋白基因转录(Geng et al.,2021)。催乳素还可协同氨基酸激活AKT/mTOR信号通路,活化的PI3K能通过磷酸化激活下游分子AKT(Wang et al.,2018);AKT被激活后,信号传递至下游靶点mTOR(Zhu et al.,2021),触发下游分子的磷酸化,而促进翻译过程和酪蛋白的合成(Shu et al.,2020)。脂多糖能抑制JAK/STAT和AKT/mTOR通路(Liu et al.,2015;Genget al.,2021;Lin etal.,2023)。本研究也发现,脂多糖处理能降低JAK2、STAT5、AKT1和mTOR的相对表达量。相思子碱处理缓解了脂多糖对酪蛋白合成的影响,可能与相思子碱上调JAK2、STAT5、AKT1和mTOR的表达而导致转录和翻译水平提高有关(Wu et al.,2020)。P53能抑制蛋白质的合成(He et al.,1995)。本研究中,Pifithrin-μ抑制P53后,β-casein、JAK2、STAT5、AKT1和mTOR的相对表达量显著升高,Kevetrin hydrochloride激活P53后,β-casein、JAK2、STAT5、AKT1和mTOR的相对表达量显著降低,表明P53在酪蛋白合成中发挥抑制作用。P53对酪蛋白合成通路的抑制作用与脂多糖的作用结果一致,提示P53可能在脂多糖抑制酪蛋白合成的过程中担任重要角色,但具体作用机制还需进一步探究。
4结论
脂多糖降低了水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白分泌水平与β-酪蛋白合成相关基因及其编码蛋白的表达水平;而相思子碱能通过抑制NF-κB通路缓解脂多糖诱导的水牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症,并通过调节P53/mTOR通路缓解脂多糖诱导的水牛乳腺上皮细胞β-酪蛋白合成减少。
参考文献(References):
顾鑫.2015.中国人乳β-酪蛋白克隆表达及功能分析[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学.[Gu X.2015.Clonaing,expression and functional analysis ofβ-casein from Chinese human[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University.]doi:10.7666/d.Y2621452.
刘鸽,张培生,于会举,张倩,屈勇刚.2017.用测SCC法调查石河子某奶牛场隐性乳房炎的发病情况[J].中国乳业,(1):54-57.[Liu G,Zhang P S,Yu H J,Zhang Q,Qu Y G.2017.The incidence of latent mastitis in a dairy farm inShihezi was investigated by SCC[J].China Dairy,(1):54-57.]doi:10.16172/j.cnki.114768.2017.01.015.
舒建林.2023.中草药在奶牛乳房炎中的治疗效果[J].现代畜牧科技,(5):88-90.[Shu J L.2023.Therapeutic effect of Chinese herbal medicine in cow mastitis[J].Modern Animal Husbandry Science&Technology,(5):88-90.]doi:10.19369/j.cnki.2095-9737.2023.05.024.
王玥.2017.豌豆淀粉与酪蛋白复合物在水相体系中的相互作用及稳定性研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学.[Wang Y.2017.Study on the interaction and stability of pea starch and casein complex in water system[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University.]doi:10.7666/d.Y3231456.
杨攀,黄丽,黄子珍,王海军.2020.水牛乳营养特性与产业发展状况[J].中国乳业,(3):3-6.[Yang P,Huang L,Huang Z Z,Wang H J.2020.Nutritional characteristics and indus-trial development of buffalo milk[J].China Dairy,(3):3-6.]doi:10.16172/j.cnki.114768.2020.03.002.
张瑞明.2019.酪蛋白在脂肪球膜再构建中作用的机理研究[D].天津:天津科技大学.[Zhang R M.2019.Study on the mechanism of casein in the reconstruction of milk fat glo-bule membrane[D].Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology.]doi:10.27359/d.cnki.gtqgu.2019.000168.
Abdel-Hamid M,Huang L,Huang Z Z,Romeih E,Yang P,Zeng Q K,Li L.2023.Effect of buffalo breed on the detailed milk composition in guangxi,China[J].Foods,12(8):1603.doi:10.3390/foods 12081603.
Ahmed H F,Hegazy Y M,Ibrahem S A.2021.Interrelationship of milk acute-phase proteins and casein percentage in cows and buffaloes subclinical mastitis[J].Veterinary Research Forum,12(4):409-414.doi:10.30466/vrf.2020.113022.2687.
Akeno N,Miller A L,Ma X,Wikenheiser-Brokamp K A.2015.P53 suppresses carcinoma progression by inhibiting mTOR pathway activation[J].Oncogene,34(5):589-599.doi:10.1038/onc.2013.589.
Bobbo T,Ruegg P L,Stocco G,Fiore E,Gianesella M,Mor-gante M,Pasotto D,Bittante G,Cecchinato A.2017.Asso-ciations between pathogen-specific cases of subclinical mastitis and milk yield,quality,protein composition,and cheese-making traits in dairy cows[J].Journal of Dairy Science,100(6):4868-4883.doi:10.3168/jds.2016-12353.
Che H Y,Zhou C H,Lyu C C,Meng Y,He Y T,Wang H Q,Wu H Y,Zhang J B,Yuan B.2023.Allicin alleviated LPS-induced mastitis via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,24(4):3805.doi:10.3390/ijms 24043805.
Chen X S,An M,Zhang W Q,Li K,Kulyar M F,Duan K,Zhou H,Wu Y,Wan X,Li J L,Quan L T,Mai Z H,Bai W X,Wu Y.2022.Integrated bacteria-fungi diversity analysisreveals the gut microbial changes in buffalo with mastitis[J].Frontiers in Veterinary Science,9:918541.doi:10.3389/fvets.2022.918541.
Chen Z,Li J,Peng H,Zhang M L,Wu X,Gui F,Li W,Ai F,Yu B,Liu Y J.2023.Meteorin-like/Meteorin-βprotects LPS-induced acute lung injury by activating SIRT1-P53-SLC7A11 mediated ferroptosis pathway[J].Molecular Me-dicine,29(1):144.doi:10.1186/s 10020-023-00714-6.
Constantinou C,Clemens M J.2007.Regulation of translation factors eIF4GI and 4E-BP1 during recovery of protein syn-thesis from inhibition by p53[J].Cell Death and Differen-tiation,14(3):576-585.doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402045.
Coronel L,Häckes D,Schwab K,Riege K,Hoffmann S,Fischer M.2022.p53-mediated AKT and mTOR inhibition requires RFX7 and DDIT4 and depends on nutrient abun-dance[J].Oncogene,41(7):1063-1069.doi:10.1038/s41388-021-02147-z.
Cui D R,Qu R R,Liu D,Xiong X F,Liang T B,Zhao Y C.2021.The cross talk between p53 and mTOR pathways in response to physiological and genotoxic stresses[J].Fron-tiers in Cell and Developmental Biology,9:775507.doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.775507.
Dai H,Coleman D N,Hu L,Martinez-Cortés I,Wang M,Parys C,Shen X,Loor J J.2020.Methionine and arginine supple-mentation alter inflammatory and oxidative stress responses during lipopolysaccharide challenge in bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro[J].Journal of Dairy Science,103(1):676-689.doi:10.3168/jds.2019-16631.
Geng Z J,Shan X F,Lian S,Wang J F,Wu R.2021.LPS-induced SOCS3 antagonizes the JAK2-STAT5 pathway and inhibitsβ-casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithe-lial cells[J].Life Sciences,278:119547.doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119547.
He C,Merrick B A,Patterson R M,Selkirk J K.1995.Altered protein synthesis in p53 null and hemizygous transgenic mouse embryonic fibroblasts[J].Applied and Theoretical Electrophoresis:The Official Journal of the International Electrophoresis Society,5(1):15-24.
Jiang M C,Lv Z Y,Huang Y H,Cheng Z Q,Meng Z T,Yang T Y,Yan Q,Lin M,Zhan K,Zhao G Q.2022.Quercetin alle-viates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in bovine mammary epithelial cells by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J].Frontiers in Veterinary Scien-ce,9:915726.doi:10.3389/fvets.2022.915726.
Lin H,Ji F,Lin K Q,Zhu Y T,Yang W,Zhang L H,Zhao J G,Pei Y H.2023.LPS-aggravated ferroptosis via disrupting circadian rhythm by Bmal1/AKT/p53 in sepsis-induced myocardial injury[J].Inflammation,46(4):1133-1143.doi:10.1007/s 10753-023-01804-7.
Lin Y X,Sun H,Shaukat A,Deng T X,Abdel-Shafy H,Che Z X,Zhou Y,Hu C M,Li H Z,Wu Q P,Yang L G,Hua G H.2022.Novel insight into the role of ACSL1 gene in milk production traits in buffalo[J].Frontiers in Genetics,13:896910.doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.896910.
Liu L X,Lin Y,Lin L L,Bian Y J,Zhang L,Gao X J,Li Q Z.2015.14-3-3γregulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflam-matory responses and lactation in dairy cow mammary epi‐thelial cells by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs and up-regulating mTOR signaling[J].International Journal of Mo-lecular Sciences,16(7):16622-16641.doi:10.3390/ijms 160716622.
Pazzola M,Stocco G,Dettori M L,Bittante G,Vacca G M.2019.Effect of goat milk composition on cheesemaking traits and daily cheese production[J].Journal of Dairy Science,102(5):3947-3955.doi:10.3168/jds.2018-15397.
Sharun K,Dhama K,Tiwari R,Gugjoo M B,Iqbal Yatoo M,Patel S K,Pathak K,Karthik K,Khurana S K,Singh R,Puvvala B,Amarpal,Singh R,Singh K P,Chaicumpa W.2021.Advances in therapeutic and managemental approa-ches of bovine mastitis:A comprehensive review[J].Vete-rinary Quarterly,41(1):107-136.doi:10.1080/01652176.2021.1882713.
Shu X,Fang Z Y,Guan Y,Chen X Y,Loor J J,Jia H D,Dong J H,Wang Y Z,Zuo R K,Liu G W,Li X B,Li X W.2020.High levels of fatty acids inhibitβ-casein synthesis through suppression of the JAK2/STAT5 and mTOR signaling path‐ways in mammary epithelial cells of cows with clinical ketosis[J].Journal of Dairy Research,87(2):212-219.doi:10.1017/s0022029920000175.
Tsugami Y,Wakasa H,Kawahara M,Nishimura T,Kobayashi K.2021.Lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid influen-ce milk production ability via different early responses in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J].Experimental Cell Research,400(2):112472.doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112472.
Wang M Y,Wang Z K,Yang C,Liu L,Jiang N.2018.Protein14-3-3εregulates cell proliferation and casein synthesis via PI3K-mTOR pathway in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,66(45):12000-12008.doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04590.
Wang Y N,Zhang X,Wei Z K,Wang J J,Zhang Y,Shi M Y,Yang Z T,Fu Y H.2017.Platycodin D suppressed LPS-induced inflammatory response by activating LXRαin LPS-stimulated primary bovine mammary epithelial cells[J].European Journal of Pharmacology,814:138-143.doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.07.037.
Wu Y J,Sun Y W,Dong X W,Chen J B,Wang Z L,Chen J C,Dong G Z.2020.The synergism of PGN,LTA and LPS in inducing transcriptome changes,inflammatory responses and a decrease in lactation as well as the associated epigene-tic mechanisms in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J].To-xins,12(6):387.doi:10.3390/toxins 12060387.
Xu S Y,Jiang X J,Liu Y L,Jiang X M,Che L Q,Lin Y,Zhuo Y,Feng B,Fang Z F,Hua L,Li J,Wang J P,Ren Z H,Sun M M,Wu D.2023.Silibinin alleviates lipopolysaccharide induced inflammation in porcine mammary epithelial cells via mTOR/NF-κB signaling pathway[J].Molecular Nutri‐tion&Food Research,67(14):e2200715.doi:10.1002/mnfr.202200715.
Yan Y T,Zhu K Y,Fan M Z,Wan W J,Zhao X E,Pan M H,Ma B H,Wei Q.2023.Immunolocalization of antibacterial peptide S100A7 in mastitis goat mammary gland and lipo‐polysaccharide induces the expression and secretion of S100A7 in goat mammary gland epithelial cells via TLR4/NFκB signal pathway[J].Animal Biotechnology,34(7):2701-2713.doi:10.1080/10495398.2022.2112689.
Yang M,Al Zaharna M,Chen Y S,Li L,Cheung H Y.2014.In vitro antioxidant activities and anti-proliferative properties of the functional herbAbruscantoniensis and its main alka‐loid abrine[J].Food&Function,5(9):2268-2277.doi:10.1039/c4fo00217b.
Yang M,Cho S H,Cheung H Y.2012.Biochemical-and biological-based studies of Abri Herba[J].Editiorial Com‐mittee,2012:73.
Yasmin I,Iqbal R,Liaqat A,Khan W A,Nadeem M,Iqbal A,Chughtai M F J,Rehman S J U,Tehseen S,Mehmood T,Ahsan S,Tanweer S,Naz S,Khaliq A.2020.Characteriza‐tion and comparative evaluation of milk protein variants from pakistani dairy breeds[J].Food Science of Animal Resources,40(5):689-698.doi:10.5851/kosfa.2020.e44.
Yu S,Liu X S B J,Yu D,E C Y,Yang J H.2020.Piperine pro‐tects LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting inflammatory re-sponse[J].International Immunopharmacology,87:106804.doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106804.
Yuan X H,Zhang L,Cui Y J,Yu Y B,Gao X J,Ao J X.2020.NCOA5 is a master regulator of amino acid-induced mTOR activation andβ-casein synthesis in bovine mam‐mary epithelial cells[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Re-search Communications,529(3):569-574.doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.193.
Zhang M C,Zhao S G,Wang S S,Luo C C,Gao H N,Zheng N,Wang J Q.2018.D-glucose and amino acid deficiency inhibits casein synthesis through JAK2/STAT5 and AMPK/mTOR signaling pathways in mammary epithelial cells of dairy cows[J].Journal of Dairy Science,101(2):1737-1746.doi:10.3168/jds.2017-12926.
Zhu C,Wang L L,Zhu J R,Jiang Y,Du X Y,Duan Q Y,Yin H,Huang X R,Song Y X,Cao B Y,Li G,An X P.2021.OGR1 negatively regulatesβ-casein and triglyceride syn‐thesis and cell proliferation via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR sig‐naling pathway in goat mammary epithelial cells[J].Ani‐mal Biotechnology,32(5):627-636.doi:10.1080/10495398.2020.1737099.
Zhuang C C,Zhao J H,Zhang S Y,Shahid M.2023.Esche-richia coli infection mediates pyroptosis via activating p53-p21 pathway-regulated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J].Microbial Patho‐genesis,184:106338.doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106338.
(责任编辑兰宗宝)
