Neuroprotective effect of arundic acid on Cynomolgus macaques with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
2024-05-07WANGXiangweiZHOUYongxinEIKETSUShoCHENJiqiaoMAOJiajingZHOUJingDENGZhihaoXINGLiuliuZHOUYemingFULijie
WANG Xiangwei,ZHOU Yongxin,EIKETSU Sho,CHEN Jiqiao,MAO Jiajing,ZHOU Jing,DENG Zhihao,XING Liuliu,ZHOU Yeming,FU Lijie
[Breakthrough Pharmaceuticals (Nantong)Inc.,Nantong 226133,China]
Abstract: OBJECTlVE To evaluate the therapeutic effect of arundic acid against cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury (CIRI) Cynomolgus macaques.METHODS Nine healthy male cynomolgus monkeys were subjected to 4 h ligation of the left middle cerebral artery followed by reperfusion before they were randomly divided into model, model+calcium arundate 10 and 30 mg·kg-1 groups, with three cynomolgus monkeys in each.72 h post-cerebral infarction, the three groups were orally administrated with viehcles[20% (W:V) Solutol HS15 and 10% (V:V) PEG 400] or calcium arundate 10 and 30 mg·kg-1 twice daily for 28 consecutive days, respectively.Neurological impairment and recovery were assessed by a series of neurobehavioral tests, such as upper extremity feeding skill tests and observation of animal cage behaviour, as well as magnetic resonance data of cerebral infarction volume and cerebral edema volume during treatment.RESULTS The model group showed natural spontaneous recovery after the middle cerebral artery occlusion.After treatment with calcium arundate 30 mg·kg-1 twice daily, a remarkable neurological function recovery in terms of behavior, upper limb activity, and brain lesion volume was observed (P<0.05).Meanwhile, calcium arundate 10 mg·kg-1 group did not show convincing improvement in comparison with the model group.CONCLUSlON Arundic acid can reduce the volume of the infarct area, improve neurobehavioral activities, and skeletal muscle coordination function in the Cynomolgus macaques model of CIRI.Arundic acid has the potential to be an effective neuroprotective agent in cerebral ischemia stroke.
Key words: arundic acid;cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury;neurobehavior;Cynomolgus macaques
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and long-lasting disability in the world.However,an effective therapeutic approach in the acute phase after cerebral ischemia remains the most important clinical need.Thrombolytic therapies have shown potential for cerebral ischemia, but their limited therapeutic window means they can only be used in a small proportion of stroke patients[1].Over the past two decades, arundic acid has been widely studied as a potential pharmaceutical candidate for treating acute ischemic stroke and other neurodegenerative diseases,such as Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease[2-4].Arundic acid has been reported to suppress reactive astrocyte malfunctional production of S100B protein,which plays a significant role in the progression of brain damage[5].Although data obtained from rodent ischemic models have indicated that arundic acid can protect the periinfarct area against the expansion of ischemia lesions to prevent delayed damage, its efficacy has not been evaluated in primate cerebral ischemia models[6].
One of the biggest challenges to translating promising therapeutic treatments from the lab to human studies is the potential discrepancies between animal species used in experiments and the human body.This is a well-known issue in the field of translation, as animal models may not accurately reflect how a human body will react to treatment[7].To address these discrepancies,the Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable(STAIR) committee suggested the use of nonhuman primates (NHP) for preclinical efficacy studies and updated their recommendations in 2009[8].As a result, a validated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion NHP model was employed in this study to investigate the efficacy of arundic acid against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI).
1 MATERlALS AND METHODS
1.1 Chemicals and equipment
Calcium arundate (Fig.1) was synthesized in a chemistry lab of Wuxi Apptech Inc.(Shanghai,China).Other chemical materials such as isoflurane (RWD Life Science, Shenzhen, China),Zoletil®50 (Bless Pet Animal Protection Limited,UK), Solutol HS15 and PEG400 (Shanghai Juchuang Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Co.,Shanghai, China) were of analytical grade or above.Magnetic resonance imaging series (Panion Premium 1.5T) was from Time Medical Inc.(Hong Kong,China).
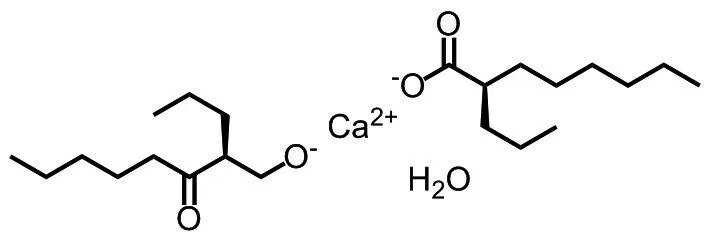
Fig.1 Chemical structure of calcium arundate
1.2 Animals
Nine male cynomolgus monkeys (Guangzhou Xusheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou,China.License #: SCXK2019-0045) ages 4-5 and weighing between 5-8 kg were used in this study.The monkeys were housed individually in a temperature-controlled environment of 18-26 ℃,with a relative humidity of 40%-70% and a 12-hour light/dark cycle.They were fed twice daily with regular monkey chow supplemented with various fruits and provided with wateradlibitum.All applicable portions of the study were conducted in accordance with the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC)international guidelinesintheGuidefortheCare andUseofLaboratoryAnimals(National Research Council 2011) as well astheRegulationsforthe AdministrationofAffairsConcerningExperimental Animals(Ministry of Science & Technology, China 1988).
1.3 Preparation of test article
Calcium arundate is calcium salt of arundic acid [(R)-(-)-2-propyloctanoic acid] that can be easily absorbed after oral administration.Calcium arundate presents in an acid form upon entering blood circulation and takes effects.The test article for oral administration was prepared by dissolving into Solutol HS15 (W:V, 20%) to get a clear solution then adding PEG400 (V:V, 10%) and distilled water (V:V, 70%) and stored in 2-8 ℃refrigerator,protected from light and used within 48 h.
1.4 Model establishment, animal grouping and drug administration
Prior to one-side middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) surgery, all monkeys underwent a 3-week training period to adapt to the experimental apparatus.This training involved a task-oriented scoring system that evaluated upper limb motor function impairment and recovery.Specifically, the monkeys were rated on their ability to grasp fruit (apple in this study) within a 5 min time frame.The efficiency and speed of their task performance were recorded as baseline data.Throughout this study, all monkeys were monitored at least twice daily and received appropriate veterinary care from trained personnel.
The establishment of ischemic-reperfusion NHP model was adapted from the literature[9].All monkeys were fasted overnight (8-12 h) before the surgery.On the day of the operation, atropine sulfate was injected intramuscularly, and anesthesia was induced by Zoletil®50.The Sugita vascular clip was used to block the blood flow of the left middle cerebral artery completely with the monkeys being confirmed under deep anesthesia that was then maintained by a respiratory anesthesia machine.After 4 h of ischemia, the vascular clip was removed, and recovery of the blood flow was secured.After the monkeys were fully awake, they were moved back to the original single-caged environment.Model establishment success criteria: the volume of brain injury in the ischemic side (left side) was no less than 15% of the total volume of the injured cerebral hemisphere (same side).72 h after cerebral infarction, each monkey was randomly assigned to one of three groups:the model group(n=3),model+calcium arundate 10 and 30 mg·kg-1groups (n=3).Three groups were orally administrated with viehcles (20% (W:V)Solutol HS15 and 10% (V:V)PEG400) or calcium arundate 10 and 30 mg·kg-1,twice daily, for 28 consecutive days , respectively.The volume of drug administration was 2 mL·kg-1.Neurological examinations were conducted three times weekly and magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) was performed biweekly after the first drug administration.A schematic diagram of the alendic acid regimen was shown in Fig.2.
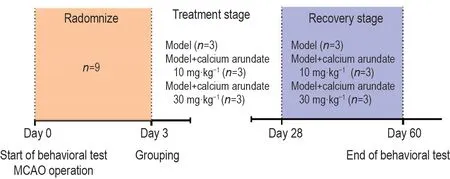
Fig.2 Schematic representation of therapy schedule for calcium arundate therapy.On day 0, all Cynomolgus macaques accepted behavioral test and then middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) surgical operation.On day 3, the monkeys were separated into 3 groups: the model group (n=3), model+calcium arundate 10 and 30 mg·kg-1 group (n=3).Three groups were orally administrated with vehcles [20% (W:V) Solutol HS15 and 10% (V:V) PEG400] or calcium arundate (calcium salt of arundic acid) 10 and 30 mg·kg-1 twice daily until day 28, respectively.On day 28, all monkeys were given the last dose but the behavioral test continued until day 60.Neurological examinations were conducted three times weekly and magnetic resonance imaging imaging was performed biweekly after the first drug administration.
1.5 Neurological function assessment
Neurological examinations were conducted by two independent observers to assess the neurobehavioral function in accordance with the standard neurological assessment score sheet (Tab.1)that was adapted from reference resources[10-13].In addition, the task-oriented scoring system with fruit grasping success rates was used as a classic proxy of motor impairment and recovery in the whole study.The task-oriented scoring system was established by having a monkey chaired in a special device where the fruits could only be reached and grasped by moving the impaired arm.The successfulness of fruit grasping is a reliable way in investigating neurological and motive recovery of MCAO model animals.

Tab.1 Adapted standard neurological assessment scale sheet[10-13].
1.6 MRl acquisition for determination of cerebral lesion volume
2D high-resolution fast spin echo (FSE) T2-weighted imaging series was used to determine the extent of the lesion.Data such as locations and areas of the cerebral infarction and development as well as the changes of cerebral vascular structure were collected and analyzed by 3D imaging analysis.
1.7 Statistical analysis
The data were presented as±sfrom three independent experiments and all statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0.Differences between groups were analyzed for statistical significance using two way ANOVA.LSD test was conducted only whenFachievedP<0.05 and homogeneity of variance was observed.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2 RESULTS
2.1 Effect of calcium arundate on neurobehavioral function of Cynomolgus macaques ischemic model
To explore the therapeutic effect of arundic acid therapy, we established a cerebral ischemiareperfusionCynomolgusmacaquesmodel.We first assessed the effects of the arundic acid therapy on neurobehavioral function impairment and recovery of macaques models.After the left-side MCAO operation, all monkeys displayed severe but consistent neurological impairment in both motor and behavioral functional activities such as stooped posture and episodes of rotation to the side of the lesion.Starting from the second week after the modeling operation, the clinical signs gradually improved in all groups with monkeys in model+calcium arundate 30 mg·kg-1group demonstrating a remarkable improvement (P<0.05), and model group displaying natural recovery (Fig.3A).Model+calcium arundate 10 mg·kg-1group, however, did not show a significant difference compared with the model group.
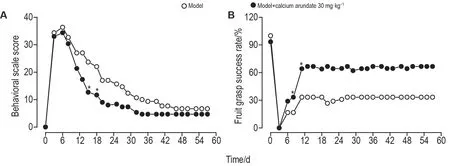
Fig.3 Effect of calcium arundate on neurobehavioral function (A) and task-oriented neurologic function (B) in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion Cynomolgus macaques model.See Fig.2 for the animal treatment.The behavioral scale score is the mean value of the summary of four categories of data from each individual, i.e., consciousness, sensory system, motor system,and skeletal muscle coordination.Fruit grasp success rate is the average fruit grasp success rating score of right upper limbs.±s,n=2-3.*P<0.05,compared with model group.
2.2 Effect of calcium arundate on task-oriented neurologic function of Cynomolgus macaques ischemic model
In the current study, the motor function impairment and recovery were further evaluated by testing the monkey′s ability to reach out its upper arm and grasp the fruit.During the pre-experiment training, all monkey′s grasp success rates were almost 100% for both upper limbs.After MCAO surgery on the left side, the clinical neurological deficits came out in all animals with spastic paralysis, musculoskeletal movement incoordination on the contralateral side (right side) that was vividly reflected in the fruit grasping test (Fig.3B).These data showed that monkeys in all three groups failed to finish the task in the first 3 d after surgery.The grasp success rate for the model group grew to 16.67% on day 6 and 33.33% on day 11 while the success rates for the model+calcium arundate 30 mg·kg-1group were 28.89% on day 6 and 64.10% on day 11, respectively.Consistently, improvement stopped at day 12 and since then the grasp success rate remained unchanged.This remarkably faster recovery demonstrated in the model+30 mg·kg-1group over the model group was of statistical significance (P<0.05).Meanwhile, the model+10 mg·kg-1group did not display visible improvement in aim-oriented arm motor function until 27 d in comparison with the model group.
2.3 Effect of calcium arundate on neurobehavioral lesion volume of Cynomolgus macaques ischemic model
MRI imaging scan was conducted on the third day after the establishment of cerebral infarction model and data showed significant necrosis in the left cerebral cortex and basal ganglia area with the lesions ranging from the left parietal lobe to the temporal lobe but not affecting the midbrain, pons or cerebellum.The brain tissue structure on the contralateral side (right) was clear and healthy (Fig.4).The volume of left cerebral infarction was calculated by integration of the area measured at each infarcted surface for the section over the number of slices that encompassed the potion of the lesion being evaluated.The analysis results showed that after ischemia-reperfusion of the cerebral artery, the volume of lesion areas was highly correlated with the behavioral score(r2=0.9944) and there was a natural self-recovery process in the stroked hemisphere with the percentage of the infarct area decreasing gradually until a stable level was attained (17.15% in this study)(Fig.5).

Fig.4 Effect of calcium arundate on magnetic resonance imaging and T2-weighted images of cerebral ischemiareperfusion Cynomolgus macaques model.See Fig.2 for the animal treatment.A:T2 2D flash fluid attenuated inversion recovery(FLAIR)phase of coronal section prior to ischemia-reperfusion.B:T2 2D fast spin echo axial phase of coronal section 16 days after ischemia-reperfusion.C:T2 2D flash FLAIR phase of coronal section 16 d after ischemia-reperfusion.1:the right hemisphere of the brain(the health side);2:the left hemisphere of the brain(the stroked side);3:the ischemic area.

Fig.5 Effect of calcium arundate on leision volume percentage in stroked hemisphere cerebral of ischemiareperfusion Cynomolgus macaques model.See Fig.2 for the animal treatment.±s,n=3.*P<0.05, compared with model group.
3 DlSCUSSlON
Our study aimed to evaluate the neuroprotective effects of calcium arundate on a NHP ischemic model by administering it for 4 consecutive weeks and continuously monitoring the animals using a standard neurological assessment scoring system and MRI.The data collected covered the full process of an ischemic stroke, from the acute phase to recovery and stable disability, indicating that this ischemia-reperfusion model was successful and reliable.The model animals exhibited selective impairment of motor function in the contralateral arm, and the degree of impairment and recovery correlated with the final size of the lesion volume.This model was ideal for longterm stroke outcome studies because the animals appeared otherwise normal except for the impairment in one side of their limbs.However, brain and blood biomarkers such as protein S100B and glial fibrillary acidic protein, which could help elucidate the mechanisms of calcium arundate effects, were not detected in this study.Researchers should consider using other specific,reliable, and clinically useful stroke biomarkers in future studies.
The results indicate that the NHP MCAO model animals have a natural spontaneous recovery after ischemia-reperfusion operation that is apparent in the early stages and attenuates later,leaving some permanent impairment.This is consistent with previous literature.In this study,when treated with calcium arundate at 30 mg·kg-1twice daily,the NHP model animals demonstrated a remarkably faster neurological function recovery in the early stage of oral administration, indicating that calcium arundate did have an effect in accelerating the natural self-recovery process but had no effect in ameliorating the impairment essentially.As data shows, the motor and neurobehavioral function scores of all animals in the three groups gradually reached a similar level with no significant differences.
In conclusion, this study has validated the NHP model as a reliable method to evaluate pharmaceutical agents for ischemic disease.Additionally, calcium arundate has been shown to display an anti-infarction effect on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in the NHP model.However,further studies are needed to better understand the mechanism underlying this effect.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the animal study team at Jiangsu KMQ Biotech, Inc.for their excellent expertise and assistance in establishing the NHP model.
