基于反应精馏技术的乳酸乙酯工艺流程模拟与优化
2024-03-29刘春江黄江辉陈妍希尹天乐项文雨
刘春江,黄江辉,陈妍希,尹天乐,项文雨
基于反应精馏技术的乳酸乙酯工艺流程模拟与优化
刘春江,黄江辉,陈妍希,尹天乐,项文雨
(天津大学化工学院,天津 300350)
提出了一种基于反应精馏技术制备乳酸乙酯的工艺流程.通过原料乙醇过量进料及乙醇脱水预处理的方法促进反应向右进行,提高乳酸乙酯产品的纯度;根据不同的乙醇-水共沸体系分离方法,建立了3种不同的乳酸乙酯工艺流程,即反应精馏-变压精馏(RD-PSD)流程、反应精馏-萃取精馏(RD-EX)流程和反应精馏-渗透汽化(RD-PV)流程;随后采用粒子群优化算法对各工艺流程进行多参数优化,以最小年总成本(TACmin)为优化目标,优化工艺流程参数,并对各流程进行经济和环境评价.结果表明:相较于RD-PSD流程和RD-EX流程,RD-PV流程有效降低了工艺投资,是一种极具潜力的节能低碳的乳酸乙酯工艺流程,较前两者其TAC分别降低了67.89%和29.33%,全局能量消耗(GEC)分别降低了70.17%和27.85%,CO2排放量(CO2)分别降低了68.36%和25.00%.
乳酸乙酯;反应精馏;共沸物;优化设计;渗透汽化;过程强化
反应精馏(reactive distillation,RD)是将化学反应和精馏分离耦合于一个设备中实现的过程强化技术[1],通过精馏过程将反应产物及时地从体系中分离,促进反应向右进行,应用于受化学平衡限制的反应,如酯化反应[2-5]、醚化反应[6]、酯交换反应[7-9]、水解反应[10-11]时具有明显优势.
受常规反应精馏塔结构限制,分离最不利挥发度序列反应物系时,未转化的反应物会发生极端积累现象[12],学者们已经提出了针对此问题的多种应对措施,如带有外部循环结构的反应精馏塔结构[13-16]、多进料策略[17]、过量进料技术等[18-19].其中过量进料技术工艺流程简单,控制方案易行[20],仅需在后续工艺中分离出过量的反应物并循环利用.
乳酸乙酯(C5H10O3)在常压下是一种具有特殊水果香味的无色液体.乳酸乙酯的溶剂效率与石油类溶剂相当,具有来源广泛、绿色无害、经济可行等特点,是一种具有较大应用前景和市场潜力的“绿色溶剂”[21].乳酸乙酯可通过化学合成方法合成,利用乳酸与乙醇发生酯化反应制备乳酸乙酯[22-23].采用传统的“反应+分离”方法生产乳酸乙酯,乳酸转化率较低,且由于体系中存在乙醇-水共沸物,产物分离过程复杂,工艺能耗较高,不具有竞争优势[24].
本文采用反应精馏技术提高乳酸转化率,在反应精馏塔塔釜直接采出工业级乳酸乙酯,塔顶采出乙醇水混合物.采用变压精馏、萃取精馏、渗透汽化3种方式进行乙醇-水分离,提出反应精馏-变压精馏(reactive distillation-pressure swing distillation,RD-PSD)流程、反应精馏-萃取精馏(reactive distillation-extractive distillation,RD-EX)流程、反应精馏-渗透汽化(reactive distillation-pervaporation,RD-PV)流程,采用粒子群算法对各流程进行多参数优化,并对其经济、环境进行评价.
1 物系分析与优化策略
1.1 物性方法选择
原料乳酸(lactic acid,L1)和乙醇(ethanol,EtOH)发生酯化反应,生成水(H2O)和乳酸乙酯(ethyl lactate,L1E),体系中的轻组分水和乙醇从反应精馏塔塔顶采出,重组分乳酸和乳酸乙酯从塔釜采出.


当乳酸溶液质量分数高于20%时,乳酸分子会发生自聚反应[25],此时体系中会存在乳酸二聚物(dilactic acid,L2)、乳酸三聚物(trilactic acid,L3)及其与乙醇的酯化产物(L2E、L3E),是强非理想体系,且常压下体系中还会形成多种最低共沸物(表1).本文选用UNIFAC模型来描述过程的非理想性[26].
1.2 动力学
乳酸与乙醇在Amberlyst 15离子交换树脂的作用下发生酯化反应,生成乳酸乙酯和水.体系中发生的反应如下:
表1 常压下体系中存在的纯组分与共沸物

Tab.1 Pure components and azeotropes present in the system at atmospheric pressure
注:括号内为质量分数.


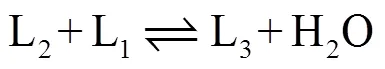





式(2)为体系中发生的主反应,式(3)~(9)为体系中发生的副反应.在反应体系中只含有微量的L2E、L3E,根据Dai等[26]的研究可知,式(2)~(4)足以描述该反应过程,其他反应对系统的影响可以忽略.动力学参数如表2[27]所示.
表2 动力学参数

Tab.2 Parameters of the kinetics
1.3 工艺流程

本文假设进料乳酸流量为1kmol/h,根据工业乳酸浓度确定乳酸原料进料流量,再依据醇酸比计算所需乙醇原料进料流量.
从反应平衡角度考虑,水作为乙醇乳酸酯化反应的生成物,应尽可能降低其在反应体系中的浓度以促进反应向右进行,提高乳酸的转化率.根据是否对乙醇原料进行脱水预处理,存在两种可选的工艺流程方案,如图1所示.

(a)原料乙醇不进行脱水预处理

(b)原料乙醇进行脱水预处理
图1 不同乙醇进料位置工艺流程方案
Fig.1 Processes for different ethanol feed locations
1.4 工艺流程评价方法
年总成本(total annual cost,TAC)是一种常用的化工设备经济成本评价方法.反应精馏塔的TAC计算需要在传统精馏塔的基础上另考虑催化剂费用,其计算公式[28]如下:






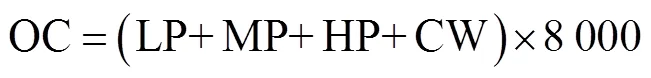
式中:OC为操作费用,包括低压蒸汽、中压蒸汽、高压蒸汽和冷凝水的费用,万元/a;CI为固定投资费用,包括塔壳及内件、催化剂费用、换热器费用,万元/ a;PR为投资回收期,通常假设为3a;、、分别为塔高、塔径和总塔板数;、分别为每块塔板上的催化树脂的体积及密度,催化树脂的价格为5000 元/m3;con、reb分别为冷凝器和再沸器的换热面积,m2;LP、MP、HP、CW分别为低压蒸汽、中压蒸汽、高压蒸汽和冷凝水每小时的费用,万元/h.假设1年工作8000h.
选取全局能量消耗(global enengy consumption,GEC)来评价生产单位产品的能量消耗,计算式[29]为

式中:L、M、H、C分别为低压蒸汽、中压蒸汽、高压蒸汽和冷凝水的热负荷,kW;为产品流量,kmol/h.


式中:fuel为燃料燃烧释放的能量,kW;根据式(19)进行计算;NHV为燃料的净热值,kJ/kg;为燃料的碳含量,%;为CO2与C摩尔质量之比,取3.67.选用天然气为燃料,其NHV为51600kJ/kg,为75.4%.

式中:proc和proc分别为蒸汽的潜热和焓,kJ/kg;proc为工艺流程的再沸器热负荷,kW;FT为锅炉火焰的温度,℃;stack为烟囱温度,℃;0为环境温度,℃.
1.5 优化策略
反应精馏流程通常由反应精馏塔和后续分离设备组成,难以通过单参数优化方法寻找全局最优解.因此,本文采用粒子群优化算法(图2),在满足生产任务要求的前提下,以最小的年总成本(TACmin)为优化目标,通过改变总塔板数、进料位置feed、回流比等参数对乳酸乙酯反应精馏工艺流程进行多参数优化.

图2 精馏塔粒子群优化算法流程


反应精馏工艺流程的优化是典型的混合整数非线性优化过程,且设备之间存在物质能量交换,全流程同时优化难以收敛.采用规定循环流股组成的方法简化工艺过程,将序贯优化策略用于全流程优化.
2 工艺流程模拟
2.1 反应精馏塔进料乙醇浓度确定
反应精馏塔反应段中水含量对酯化反应的化学平衡有重大影响,需要先分析进料乙醇浓度对产品乳酸乙酯纯度的影响,以此判断是否需要对原料乙醇进行脱水预处理.


(a)反应精馏塔总理论板数 (b)乳酸进料位置 (c)乙醇进料位置

(d)反应段起始位置 (e)反应段终止位置 (f)回流比
图3 反应精馏塔决策变量分析
Fig.3 Analysis of the decision variables related to the reactive distillation column
表3 反应精馏塔决策变量取值范围

Tab.3 Value range of the decision variables for the reac-tive distillation column
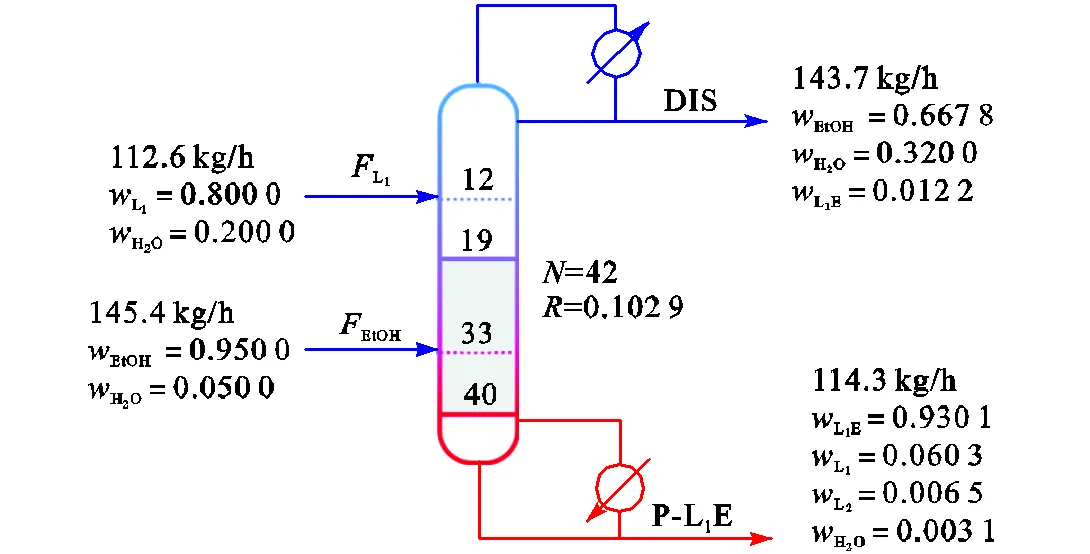
图4 95%乙醇进料反应精馏塔最优结构
根据优化结果可知,原料乙醇在反应精馏塔直接进料时,乳酸乙酯产品浓度无法达到乳酸乙酯工业品标准,后续仍需复杂的乳酸乙酯产品精制过程.因此,采用对原料乙醇进行脱水预处理的工艺流程(图1(b)).
保持如图4所示的最优反应精馏塔结构,分析乙醇进料浓度对乳酸乙酯产品浓度的影响.由图5可知,乳酸乙酯产品浓度随进料乙醇浓度增加而增加,乙醇质量分数高于0.995时,可获得工业品标准的乳酸乙酯产品.

图5 进料乙醇质量分数对乳酸乙酯含量的影响
2.2 反应精馏过程稳态模拟
在表3决策变量的取值范围内,以TACmin为优化目标对99.5%进料乙醇的反应精馏塔结构进行粒子群算法优化,反应精馏塔的参数优化结果如图6所示,此时塔釜乳酸乙酯质量分数为0.9826,反应精馏塔的TAC为35.87万元/a.
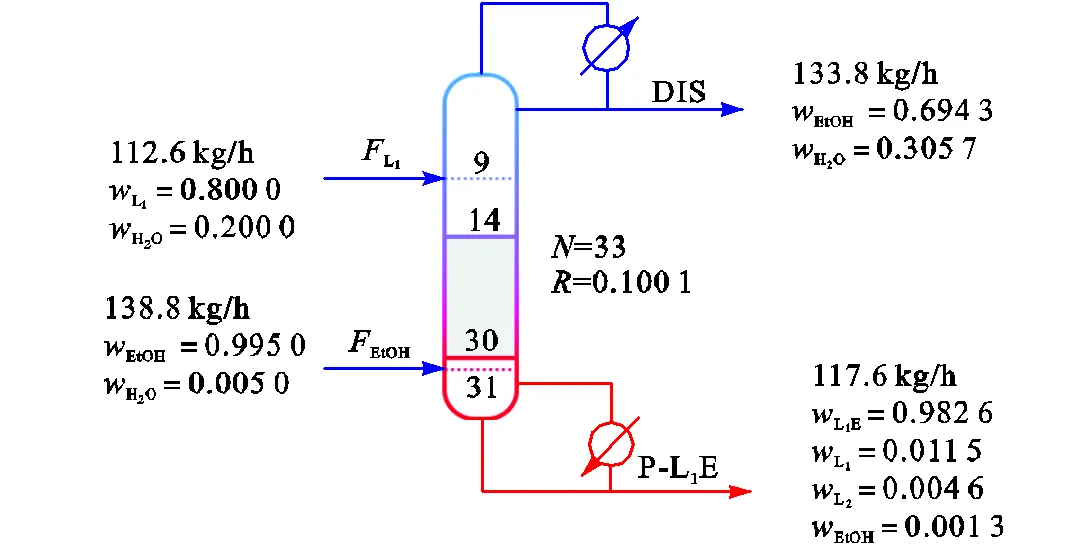
图6 99.5%乙醇进料反应精馏塔最优结构
2.3 乙醇-水分离单元稳态模拟
2.3.1 变压精馏
变压精馏是一种常用的共沸物分离方法.图7为不同压力下乙醇-水体系的气液平衡曲线,分别选取101.3kPa和1013.0kPa作为变压精馏的低压塔和高压塔操作压力,对应压力下共沸物的乙醇质量分数分别为0.955、0.916.
以两塔塔釜热负荷之和最小为目标[28],确定低压塔和高压塔的塔顶采出乙醇质量分数分别为D1=0.949、D2=0.918(图8).

图7 乙醇-水体系气液平衡曲线

图8 低压塔和高压塔塔顶采出浓度对变压精馏流程再沸器总热负荷的影响

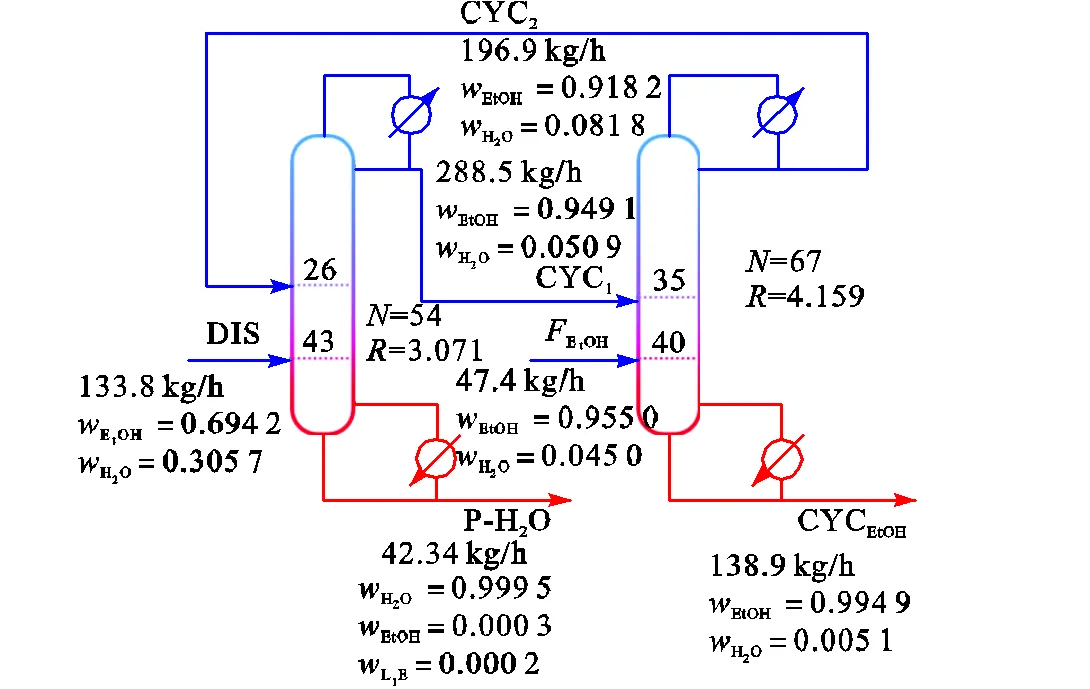
图9 变压精馏流程最优结构

(a)低压塔总理论板数 (b)DIS进料位置

(c)CYC2进料位置 (d)高压塔总理论板数

(e)原料乙醇进料位置 (f)CYC1进料位置
图10 变压精馏流程决策变量分析
Fig.10 Analysis of decision variables of the pressure-swing distillation process
表4 变压精馏决策变量取值范围

Tab.4 Value range of the decision variable of the pres-sure-swing distillation process

2.3.2 萃取精馏
本文选取乙二醇(ethylene glycol,EG)作为乙醇-水体系分离的萃取剂.萃取精馏流程如图11所示,萃取塔选取萃取塔总理论板数EX、DIS进料位置DIS、原料乙醇进料位置EtOH、萃取剂EG进料位置EG、萃取剂用量EG为决策变量,考察决策变量对萃取塔TAC及塔顶采出乙醇质量分数的影响(图12),并确定各决策变量的范围(表5);萃取剂回收塔选取萃取剂回收塔总理论板数RE-EX、萃取塔塔釜采出进料位置EX-BOT、萃取剂回收塔回流比RRRE-EX为决策变量,考察各决策变量对萃取剂回收塔TAC及塔顶采出水质量分数的影响,确定各决策变量的变化范围(表5).

图11 萃取精馏流程最优结构
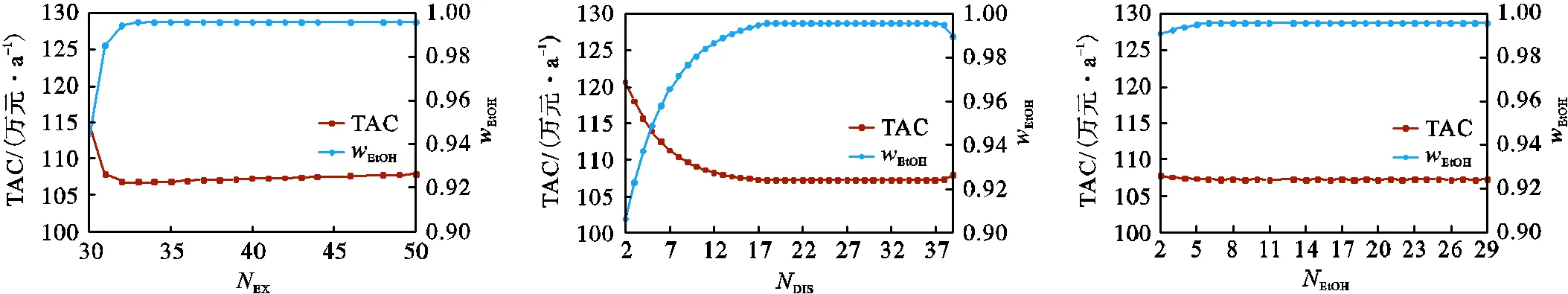
(a)萃取塔总理论板数 (b)DIS进料位置 (c)乙醇进料位置

(d)萃取剂进料位置 (e)萃取剂用量 (f)萃取剂回收塔总理论板数

(g)萃取塔塔釜采出进料位置 (h)萃取剂回收塔回流比
图12 萃取精馏流程决策变量分析
Fig.12 Analysis of decision variables in the extractive distillation process

表5 萃取精馏决策变量取值范围

Tab.5 Value range of the decision variable of the extrac-tive distillation process
2.3.3 渗透汽化
本文渗透汽化过程的模型方程由质量守恒方程、能量守恒方程及扩散方程构成,即

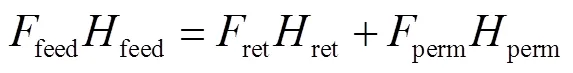


式中:feed、ret、perm分别为进料、滞留侧、渗透侧的流量,mol/h;x,feed、x,ret、x,perm分别为进料、滞留侧、渗透侧各组分的摩尔分数;feed、ret、perm分别为进料、滞留侧、渗透侧的摩尔焓,J/mol;D,j为各组分渗透表观活化能,kJ/mol;J为各组分的渗透量,kg/(h·m2);1、2、3、4均为指前因子;为除水以外的其他组分.
本文选用Sulzer Chemtech®提供的PERVAP®2201用于渗透汽化过程,膜面积为30m2,模型方程中涉及的参数见表6[32].
渗透汽化流程如图13所示,初分塔选取总理论板数PRE、DIS进料位置DIS、CYC进料位置CYC、回流比PRE为决策变量,考察决策变量对初分塔TAC及塔釜采出乙醇质量分数的影响(图14),并确定各决策变量的范围(表7).
表6 渗透汽化模型参数

Tab.6 Pervaporation model parameters

图13 渗透汽化流程最优结构

(a)初分塔总理论板数 (b)DIS进料位置

(c)CYC进料位置 (d)回流比
图14 渗透汽化流程决策变量分析
Fig.14 Analysis of decision variables in the pervaporation process
表7 渗透汽化流程决策变量取值范围

Tab.7 Value range of the decision variable of the per-vaporation process

3 结果与讨论
3.1 全流程计算
在反应精馏制备乳酸乙酯的全流程中,反应精馏塔塔顶采出流股DIS进入乙醇-水分离单元,乙醇-水分离单元的乙醇采出流股CYCEtOH循环至反应精馏塔.在全流程计算过程中,设置这两个流股为撕裂流股.根据共沸体系分离方法的不同,提出3种不同的工艺流程,分别为RD-PSD流程、RD-EX流程、RD-PV流程,如图15~图17所示.
3.2 结果与讨论

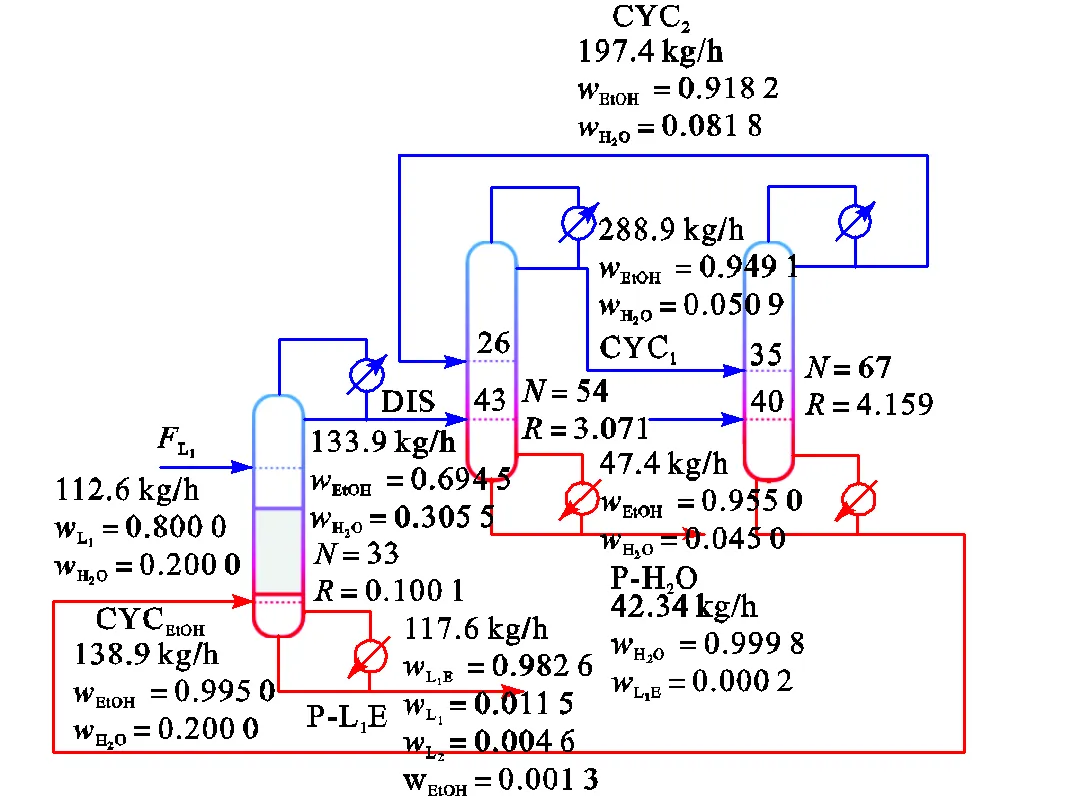
图15 反应精馏-变压精馏流程

图16 反应精馏-萃取精馏流程

图17 反应精馏-渗透汽化流程
表8 不同工艺流程计算结果汇总

Tab.8 Summary of calculation results of different proc-esses
4 结 论
本文根据不同的乙醇-水共沸物分离方法,提出了3种基于反应精馏技术的乳酸乙酯工艺流程.首先,对进料乙醇进行脱水预处理并确定了最佳进料乙醇质量分数;随后,采用粒子群优化算法对各流程进行多参数优化,以最小的年总成本(TACmin)为优化目标,优化工艺流程参数;最后,从经济、环境两方面对流程进行评价.主要结论如下.
(1) 采用95%乙醇作为反应精馏塔进料时,受反应平衡限制,反应精馏塔无法直接得到合格的乳酸乙酯产品.计算结果表明,对原料乙醇进行脱水预处理,反应精馏塔进料乙醇的质量分数高于99.5%时,反应精馏塔塔釜可得到合规产品.

[1] 王晓达,陈 宇,王清莲,等. 醚化反应精馏研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2021,40(4):1797-1811.
Wang Xiaoda,Chen Yu,Wang Qinglian,et al. Review on etherification by reactive distillation[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(4):1797-1811(in Chinese).
[2] Grisales D V H,Willis M J. Ethyl acetate production from dilute bioethanol with low energy intensity[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,376:134137.
[3] Wang Z W,Liu R Q,Liu X N. Influence of side reactions and catalytic packing geometry on acrylic acid esterification with butanol by reactive distillation using amberlyst 15[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2022,61(40):14951-14961.
[4] Patan A K,Thamida S K. Modeling and Simulation of a batch reactive distillation process with column heating[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology,2021,44(12):2365-2373.
[5] 陈强强. 反应精馏法合成苯甲酸异丁酯的工艺研究[J]. 化学研究,2020,31(5):409-415.
Chen Qiangqiang. Study on synthesis of isobutyl benzoate by reactive distillation[J]. Chemical Research,2020,31(5):409-415(in Chinese).
[6] Gao X,Wang F Z,Li H,et al. Heat-integrated reactive distillation process for TAME synthesis[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2014,132:468-478.
[7] 宋振兴,崔现宝,张 缨,等. 混合离子液体催化反应精馏合成乙酸正己酯[J]. 化工学报,2021,72(8):4155-4165.
Song Zhenxing,Cui Xianbao,Zhang Ying,et al. Synthesis of-hexyl acetatereactive distillation catalyzed by mixed ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal,2021,72(8):4155-4165(in Chinese).
[8] Geng X L,Ding Q Y,Na J,et al. Enhanced transesterification reactive distillation for producing isopropanol:From kinetics,pilot-scale experiments,and process design to sustainability evaluation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2022,302:122108.
[9] Hu Y Q,Sun H,Li C L,et al. Design of reaction region of reactive dividing wall column based on cross-wall heat transfer[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2023,62(12):5430-5444.
[10] Si Z H,Chen H,Cong H F,et al. Intensification of methyl acetate hydrolysis process:A novel transformation using steam-driven vapor recompression[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2022,301:121958.
[11] 吴 妍. 二氧戊环类化合物水解反应动力学及反应精馏新工艺设计[D]. 天津:天津大学化工学院,2020.
Wu Yan. Hydrolysis Reaction Kinetics of Dioxolane Compounds and New Process Design of Reactive Distillation[D]. Tianjin:School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,2020(in Chinese).
[12] 杨 宇. 双隔离壁反应精馏塔的结构与分析[D]. 北京:北京化工大学信息科学与技术学院,2021.
Yang Yu. Structure and Analysis of Double-Wall Reactive Distillation Column[D]. Beijing:School of Information Science and Technology,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,2021(in Chinese).
[13] 陈海胜,王腾飞,黄克谨,等. 外部环流反应精馏塔的分散控制方案设计[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(2):440-449,790.
Chen Haisheng,Wang Tengfei,Huang Kejin,et al. Decentralized control system designs for reactive distillation columns with external recycle[J]. CIESC Journal,2019,70(2):440-449,790(in Chinese).
[14] 郝阳洋,马 超,熊小然. 外部环流强化乙酸丁酯反应隔离壁蒸馏塔[J]. 化学工程,2017,45(12):26-29.
Hao Yangyang,Ma Chao,Xiong Xiaoran. Reactive dividing-wall distillation columns employing an external recycle to strengthen process of transesterification of butyl acetate with ethanol[J]. Chemical Engineering (China),2017,45(12):26-29(in Chinese).
[15] 熊小然,苑 杨,陈海胜,等. 乙酸甲酯外部环流隔离壁反应蒸馏塔的设计与比较[J]. 现代化工,2017,37(10):148-151.
Xiong Xiaoran,Yuan Yang,Chen Haisheng,et al. Design and comparison of methyl acetate external circulation dividing-wall reactive distillation column[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2017,37(10):148-151(in Chinese).
[16] 谢沈强. 定量比较双反应段和外部环流反应精馏塔的性能[J]. 化学工程,2016,44(9):11-17.
Xie Shenqiang. Quantitative comparison of performance of RDC-TRS and RDC-TBER[J]. Chemical Engineer-ing(China),2016,44(9):11-17(in Chinese).
[17] Nicolas M E,Harro V B. Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations for biodiesel production by reactive distillation[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy,2013,32(2):373-376.
[18] 朱 超,陈海胜,苑 杨,等. 过量进料反应隔离壁蒸馏塔的设计与比较[J]. 现代化工,2019,39(9):204-207.
Zhu Chao,Chen Haisheng,Yuan Yang,et al. Design and comparison of dividing-wall reactive distillation column with excess feed[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2019,39(9):204-207(in Chinese).
[19] 孔 倩,陆佳伟,王 琼,等. 乳酸过量进料反应精馏合成乳酸甲酯研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报,2021,35(2):280-286.
Kong Qian,Lu Jiawei,Wang Qiong,et al. Study on reactive distillation process for synthesis of methyl lactate with overfeeding[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities,2021,35(2):280-286(in Chinese).
[20] 李海英. 反应精馏合成乙酸异丁酯的经济优化与动态控制[D]. 青岛:青岛科技大学化工学院,2019.
Li Haiying. Economic Optimization and Dynamic Control of Reactive Distillation to Produce Isobutyl Acetate[D]. Qingdao:School of Chemical Engineering,Qingdao University of Science and Technology,2019(in Chinese).
[21] Paul S,Pradhan K,Das A R. Ethyl lactate as a green solvent:A promising bio-compatible media for organic synthesis[J]. Current Green Chemistry,2016,3(1):111-118.
[22] Komesu A,Jaimes F J,Rios L F,et al. Evaluation of operational parameters for ethyl lactate production using reactive distillation process[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions,2015,43:1141-1146.
[23] Ding Q Y,Li H,Liang Z P,et al. Reactive distillation for sustainable synthesis of bio-ethyl lactate:Kinetics,pilot-scale experiments and process analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2022,179:388-400.
[24] 黄志红,高 静,周丽亚,等. 乳酸乙酯合成研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 化工进展,2009,28(1):150-154.
Huang Zhihong,Gao Jing,Zhou Liya,et al. Progress and development trend of ethyl lactate synthesis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2009,28(1):150-154(in Chinese).
[25] Pereira C S M,Silva V M T,Rodrigues A E. Ethyl lactate as a solvent:Properties,applications and production processes—A review[J]. Green Chemistry,2011,13:2658.
[26] Dai S B,Lee H Y,Chen C L,et al. Design and economic evaluation for the production of ethyl lactate via reactive distillation combined with various separation configurations[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2019,58(15):6121-6132.
[27] Navinchandra S A,Aspi K K,Dung T V,et al. A kinetic model for the esterification of lactic acid and its oligomers[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2006,45:5251-5257.
[28] William L L. Distillation Design and Control Using Aspen™ Simulation[M]. 2nd ed. Canada:John Wiley & Sons,Inc.,2012.
[29] Liu J Y,Ren J Y,Yang Y L,et al. Effective semicontinuous distillation design for separating normal alkanes via multi-objective optimization and control[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2021,168:340-356.
[30] 彭 珂. 环戊烷分离隔壁精馏塔的设计与优化[D]. 大连:大连理工大学化工学院,2021.
Peng Ke. Design and Optimization of Divided Wall Distillation Column for the Separation Process of Cyclopen-tane[D]. Dalian:School of Chemical Engineering,Dalian University of Technology,2021(in Chinese).
[31] 郭廉洁. 夹带剂促进反应精馏过程多稳态分析与控制研究[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东),2017.
Guo Lianjie. Multiple Steady-States Analysis and Control in Entrainer-Enhanced Reactive Distillation Process[D]. Qingdao:China University of Petroleum(East China),2017(in Chinese).
[32] Delgado P,Sanz M T,Beltrán S. Pervaporation of the quaternary mixture present during the esterification of lactic acid with ethanol[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2009,332(1/2):113-120.
Simulation and Optimization of the Ethyl Lactate Synthesis Process Based on Reactive Distillation Technology
Liu Chunjiang,Huang Jianghui,Chen Yanxi,Yin Tianle,Xiang Wenyu
(School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300350,China)
This study presents a novel approach for synthesizing ethyl lactate based on reactive distillation technology. This approach employs ethanol dehydration pretreatment and excess raw ethanol feeding to overcome chemical equilibrium limitations,consequently enhancing the purity of ethyl lactate. Three different ethyl lactate processes were developed based on different methods of separating the ethanol-water azeotrope:reactive distillation-pressure swing distillation(RD-PSD)process,reactive distillation-extractive distillation(RD-EX)process,and reactive distillation-pervaporation(RD-PV)process. Particle swarm optimization was employed to optimize the parameters of each process for the minimum total annual cost(TACmin). Subsequent economic and environmental evaluations performed for each process indicate that the RD-PV process is a promising,low-carbon approach for ethyl lactate synthesis that requires lower investment than either the RD-PSD or the RD-EX processes. The adoption of RD-PV reduced the TAC by 67.89% and 29.33%,respectively,as compared to the RD-PSD and RD-EX processes;a reduction of 70.17% and 27.85%,respectively,in the global energy consumption;and a reduction of 68.36% and 25.00%,respectively,in the CO2emissions(CO2).
ethyl lactate;reactive distillation;azeotrope;optimized design;pervaporation;process intensification
TQ028.8
A
0493-2137(2024)04-0382-12
10.11784/tdxbz202302007
2023-02-06;
2023-04-12.
刘春江(1970— ),男,博士,教授,cjliu@tju.edu.cn.
项文雨,xwywenwen@163.com.
天津市自然科学基金资助项目(21JCQNJC00470).
the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin,China(No. 21JCQNJC00470).
(责任编辑:田 军)
