KSKV:Key-Strategy for Key-Value Data Collection with Local Differential Privacy
2024-03-23DanZhaoYangYouChuanwenLuoTingChenandYangLiu
Dan Zhao ,Yang You ,Chuanwen Luo ,Ting Chen and Yang Liu
1Artificial Intelligence Development Research Center,Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China,Beijing,100038,China
2Industry Development Department,NSFOCUS Inc.,Beijing,China
3School of Information Science and Technology,Beijing Forestry University,Beijing,100083,China
4School of Computer Science and Engineering,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu,610054,China
5Institute of Computing Technology,China Academy of Railway Sciences Corporation Limited,Beijing,10081,China
ABSTRACT In recent years,the research field of data collection under local differential privacy(LDP)has expanded its focus from elementary data types to include more complex structural data,such as set-value and graph data.However,our comprehensive review of existing literature reveals that there needs to be more studies that engage with key-value data collection.Such studies would simultaneously collect the frequencies of keys and the mean of values associated with each key.Additionally,the allocation of the privacy budget between the frequencies of keys and the means of values for each key does not yield an optimal utility tradeoff.Recognizing the importance of obtaining accurate key frequencies and mean estimations for key-value data collection,this paper presents a novel framework:the Key-Strategy Framework for Key-Value Data Collection under LDP.Initially,the Key-Strategy Unary Encoding(KS-UE)strategy is proposed within non-interactive frameworks for the purpose of privacy budget allocation to achieve precise key frequencies;subsequently,the Key-Strategy Generalized Randomized Response(KS-GRR)strategy is introduced for interactive frameworks to enhance the efficiency of collecting frequent keys through group-anditeration methods.Both strategies are adapted for scenarios in which users possess either a single or multiple key-value pairs.Theoretically,we demonstrate that the variance of KS-UE is lower than that of existing methods.These claims are substantiated through extensive experimental evaluation on real-world datasets,confirming the effectiveness and efficiency of the KS-UE and KS-GRR strategies.
KEYWORDS Key-value;local differential privacy;frequency estimation;mean estimation;data perturbation
1 Introduction
Enterprises frequently collect data for analysis with the aim of enhancing the quality of their services.However,such data often contain sensitive information,necessitating robust privacy protection measures.Differential Privacy (DP) [1] has become thede factostandard for privacy preservation,ensuring the security of data irrespective of an adversary’s background knowledge or computational power.In environments lacking a trusted aggregator,the Local Differential Privacy (LDP) offers robust privacy assurances during the data collection phase.Under LDP,users independently apply a privacy-preserving mechanism to their data before transmission to the aggregator.Notably,several leading enterprises,including Google[2],Apple[3],and Microsoft[4],have implemented LDP.
Initial research in LDP primarily addressed basic statistical data types,focusing on frequency estimation of discrete variables and mean estimation of continuous variables.Further studies extended the paradigm to more sophisticated structured data,including set values [5–7] and graph data [8,9].Despite this progress,investigations into key-value data queries remain relatively sparse [10–12].Key-value data,prevalent in practice,necessitates simultaneous analysis of key frequencies and the means of values associated with each key.The accuracy of multidimensional data collection under LDP is particularly challenging due to the constraints of the privacy budget.Moreover,traditional LDP algorithms can significantly distort the intrinsic associations among multidimensional data.The significance of key-value data in big data analytics cannot be overstated,and the correlation between keys and their associated values is typically strong.Thus,the collection of key-value data within the stringent privacy budget constraints of LDP presents a substantial and noteworthy challenge.For example,as illustrated in Table 1,to accurately determine a movie’s rating,a sufficient number of reviews,or the frequency of keys,is first required.Subsequently,the mean of these key values represents the movie’s rating.Accurate key frequencies not only enable more precise value calculations(since the value under each key is derived from the sum of all values divided by the key’s frequency) but also facilitate a more accurate ranking of keys.

Table 1:Example for key-value
Motivations.Effective management of key-value collections critically relies on two principal factors: the frequency of keys and the mean of the values associated with each key.The primary challenge lies in maximizing the utility of key-value data within the LDP framework,while maintaining robust privacy guarantees.In LDP models,the privacy budget parameter,denoted asε,is pivotal,serving as a quantitative measure of privacy protection.Given the dual nature of key-value pairs,the privacy budget is judiciously allocated to protect the confidentiality of both the keys and their corresponding values,without compromising their intrinsic correlation.Ye et al.[10] originally proposed a method that equally divided the privacy budget between keys and values;however,this approach did not result in an optimized budget allocation within the LDP paradigm.Later,Gu et al.[12] introduced a unified privacy budget allocation strategy,employing a shared privacy budget for keys and values.Nevertheless,in the context of key-value data,an inaccurate selection of keys can render the associated values meaningless.As such,this paper advocates for a Joint Privacy Budget mechanism,oriented towards enhancing the accuracy of keys.This method not only substantiates the precision of key identification but also improves value computation by:(1)satisfying key frequency estimation requirements,and (2) enabling more accurate mean estimation due to the enhanced accuracy of frequency estimation.
Contribution.This paper aims to address the existing challenges by introducing innovative mechanisms that prioritize key strategies,aimed at increasing the utility of key-value data collection in both interactive and non-interactive environments.For non-interactive frameworks,we propose the Key-Strategy Unary Encoding(KS-UE),strategically allocating a predominant portion of the privacy budget to key frequencies to enhance utility.In interactive environments,we employ the Key-Strategy Generalized Randomized Response (KS-GRR),which uses a group-and-iteration approach across various tasks to yield superior estimation results.Furthermore,the paper thoroughly examines the flexibility of these strategies in situations where users hold either single or multiple key-value pairs.
The salient contributions of this work can be summarized as follows:
• Acknowledging the paramountcy of accurate keys in key-value collection,we advance the key-strategy mechanisms KS-UE for non-interactive frameworks and KS-GRR for interactive frameworks within the confines of LDP.
• By leveraging KS-UE and KS-GRR,we formulate algorithms tailored for contexts wherein users hold either singular or multiple key-value pairs,enhancing the adaptability of our approach.
• We provide rigorous theoretical substantiation for the minimal variance of KS-UE.Additionally,empirical evaluations corroborate that strategies KS-UE and KS-GRR can ascertain more precise frequent keys while maintaining the integrity of mean accuracy.
Roadmap.Section 2 will elaborate on related works.Subsequently,Section 3 will provide background information and the theoretical foundation for our study.In Section 4,we introduce our keystrategy algorithms for single and multiple key-value pairs within the framework of Local Differential Privacy.Section 5 will present the experimental results,while Section 6 will conclude the paper.
2 Related Work
Local Differential Privacy is a potent technique employed to safeguard sensitive user data during the data collection process.The fundamental mechanism of LDP yields a probability distribution as output rather than revealing authentic statistical information.Randomized Response (RR),first introduced in the 1960s,is recognized as a precursor to LDP methods[13]and was later formalized as a local privacy model by Dwork [14,15].Subsequent research has led to the development of methodologies such as RAPPOR [2],Optimal-RR (O-RR),Optimal-RAPPOR (O-RAPPOR) [16],Sampled Histogram(SH)[17],Optimal Unary Encoding(OUE),and Optimal Local Hashing(OLH)[18] for singleton frequency estimation.Additional studies [4,19] have focused on mean estimation with numerical attributes.More complex data structures such as set values [5,6],marginal release[20,21],numerical values [19,22],graph data [8,9,23,24],spatiotemporal data [1,25],time-series [26],distribution estimation [27],range queries [28],and machine learning [29,30] have been examined.Further,strategies to counteract attacks have been proposed [31–33].Nevertheless,only a limited number of studies[10–12,34]have concentrated on key-value data queries.
Ye et al.[10] were the first to formalize two tasks in key-value data collection under LDP:estimating the frequencies of keys and the mean of values under each key.They proposed PrivKV for non-interactive frameworks and later introduced optimized versions,PrivKVM and PrivKVM+,for interactive frameworks.Ye et al.further improved PrivKVM+in[34].Sun et al.[11]offered another approach within the PrivKV framework,but they did not analyze the impact of the correlation between perturbations on the tighter budget composition.Gu et al.[12]addressed this issue by proposing an optimized budget allocation and an advanced’padding-and-sampling’mechanism.They used budget allocation to optimize privacy parameters for better estimation results.In this paper,we propose a more effective scheme,termed key-strategy frameworks,for key-value data collection under LDP.
3 Preliminaries
In this section,we initially delineate the problem,followed by an introduction to the concept of LDP.The notations used in this paper are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2:Notations
3.1 Problem Definition and Challenge
Key-Value Data Collection.The issue of key-value data collection under LDP was first put forth by[10].Assume there arenusers(denoted asui∈Uwherei=1,2,...,n).Each useruipossesses either a single or a set of key-value data.The key-value pair is denoted asPi:=
•Frequency Estimation:The purpose of this task is to estimate the frequency of each keyk,defined as:
•Mean Estimation:The goal of this task is to estimate the mean of values associated with each keyk,defined as:
In practical application scenarios,most users possess multiple valuesPi:={
3.2 Local Differential Privacy
LDP is a localized model of DP intended for data collection without a trustworthy aggregator[5,18,35,36].An LDP algorithm,denoted asψ,ensures that the probability of one value being transmitted to the aggregator closely approximates the probability of any other values being sent.The notion ofε-LDP is defined as follows.
Definition 3.1(ε-local differential privacy.).A randomized mechanismψwith domainDom(ψ)and rangeRan(ψ)isε-local differential private if for any input itemsv,v′∈Dom(ψ),and any outputs∈Ran(ψ),the following inequality holds:
The privacy budget,ε,can be adjusted to strike a balance between data availability and privacy intensity.LDP can offer a stronger level of privacy protection than a centralized framework as each user reports only the perturbed data.
3.3 Mechanism under LDP
We assume the size of domainDisd,each user has one item ofD.
Randomized Response(RR)/Generalized Randomized Response(GRR).The perturbation function of GRR[18]is
where RR is the special situationd=2.
Unary Encoding(UE).[18]Each user transforms her item into a vector of lengthd,where only the mapped position is 1,and all others are 0s.Subsequently,each bit is independently perturbed through the function
wherep+qneed not be equal to 1.
Whenp=andq=,the variance of frequency is minimized;therefore,under these conditions,it is termed as Optimized Unary Encoding(OUE).
Optimal Local Hashing(OLH).[18]The OLH protocol was developed to ameliorate the challenges posed by attributes with extensive categories.Initially,the client-side algorithm transforms the user’s actual valuevto a diminished hash value domaingutilizing a precise hash function.Subsequent to this transformation,the algorithm applies a randomized response to the hash value within this condensed domain.The parametergrepresents a balanced compromise between the information loss occurring during the hashing and the subsequent randomization step;the balance is deemed optimal wheng=eε+1.The temporal complexity of this algorithm is characterized asO(logn),while the spatial complexity is quantified asO(nlog|D|).
3.4 Padding-and-Sampling Protocol
Originally utilized for itemset data [6],the ‘padding-and-sampling’protocol was first adopted for key-value data in [12].In this setup,each user samples a single key-value pair from their set.A crucial parameter,denoted asl,ensures a consistent sampling rate whileldummy key-value pairs are generated.A key-value pair from the user’s set Si is selected randomly with a probability of,and a dummy key-value pair is chosen with the remaining probability.
3.5 Competitor
PrivKV.Ye et al.[10]proposed PrivKV and improved version PrivKVM and PrivKVM+on keyvalue data collection under LDP first time.The primary process comprises: (a) encoding the keyvalue pair to a position of a vector,leaving all other positions as<0,0>;(b) the key is perturbed first at each vector position,followed by the value perturbation,with the privacy budget split equally between them.
PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR.Gu et al.[12]proposed PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR,leveraging the privacy budget in a more efficient manner.They employed a joint perturbation strategy,rather than dividing the privacy budget evenly.The value’s perturbation is contingent upon the key’s perturbation,which optimizes the privacy budget composition.Both methods,theoretically and experimentally,outperform those proposed by Ye et al.Thus,we have excluded the PrivKV series from our experiment.The variances of keys and means in PCKV-UE are as follows:
It is noteworthy that both theoretically and experimentally,Gu et al.have demonstrated that PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR are superior to the series of PrivKV algorithms under equivalent conditions.Even after the conditions in [34] were collectively altered,PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR still showcased excellent performance.Therefore,this paper solely compares PCKV-UE and PCKVGRR.
For multiple key-value.In[12],when PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR address multiple key-value pairs,they pre-set an average lengthl,yielding favorable results for datasets conforming to this specified length,while performance deteriorates for those that do not align with the set length.In contrast,PrivKV[10],when dealing with multiple key-value pairs,directly employs a“padding-and-sampling”approach to simplify multidimensional data into unidimensional data.Given that PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR outperform PrivKV significantly,this paper solely compares the superior PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR algorithms.
4 Key-Strategy and Mechanisms
Our mechanisms aim to gather the frequencies of keys and the mean of values under each key.If most keys have low frequencies,the mean values corresponding to these keys are largely irrelevant.Hence,if the domain is large,it becomes essential to reduce the domain in order to find top frequent keys.In this section,we introduce two key-strategy mechanisms for asingletonkey-value pair under LDP: key-strategy unary encoding (KS-UE) in non-interactive frameworks and key-strategy generalized randomized response (KS-GRR) in interactive frameworks.When each user possessesmultiplekey-value pairs,padding-sampling is utilized to convert them into a singleton key-value pair.Subsequently,each user can implement the aforementioned two mechanisms.
4.1 KS-UE for Singleton Pair in Non-Interactive Frameworks
In non-interactive frameworks,users transmit their perturbed data to the aggregator using a oneway communication model.Here,the unary encoding (UE) mechanism comes into play,encoding each pair into a bit vector with only the bit corresponding to the key set to a value,and all others to zero.Building upon previous algorithms,KS-UE skews the privacy budget in favor of key frequencies to improve utility.The KS-UE methodology unfolds in three distinct phases:Discretization,Encoding and Perturbation,andDecoding,as delineated in Algorithm 2.
Discretization.To alleviate communication and time complexity,the initial step discretizes the value of the key-value pair from float type to binary {1,-1} using formula(2).Consequently,the domain for all key-value pairs becomes {<1,1>,<1,-1>,<0,0>}.In an attempt to further reduce communication costs,we simplify them to three single values{1,-1,0}.If a value is zero,the key is also set to zero;otherwise,the key is set to one.
Encoding and Perturbation.The first operation here is to employ UE to create a bit vectorbof sized.The position inbcorresponding to the key isv∗,and all other positions are set to zero.Subsequently,each bit of the vector undergoes perturbation in accordance with formula(3)(b[j]=0)and formula(4)(b[j]0).

Having estimated the frequency of keyk,the mean value under keyk,can be estimated.
4.2 KS-GRR for Singleton Pair in Interactive Frameworks
Within interactive frameworks,users are systematically assembled into random group,and the entirety of the privacy budget is meticulously allocated to facilitate involvement in two distinct tasks for each assembly,as depicted in Fig.1:(1)the estimation of the most prevalent keys within key-value pairs;(2)the computation of the frequencies of the aforementioned prevalent keys,as well as the mean of the values corresponding to these keys.Then,the aggregator is enabled to process and extrapolate the preliminary results from the initial group,subsequently deriving the conclusive frequencies of the superior keys and the corresponding mean values from the subsequent group.The KS-GRR model employs a sophisticated grouping methodology,aiming to optimize the efficacy of the data collection process,thereby contributing to enhanced accuracy and utility in the realization of key-value collection goals.
Top frequent keys.In the context of top frequent keys,the value in key-value pairs is deemed irrelevant,as the focus here is solely on estimating the frequencies of keys.Thus,this stage transforms the collection of key-value pairs into a singleton keys collection under LDP,directly utilizing the OLH algorithm.To obtain the top-tfrequent keys,the top frequent-2tkeys should be identified and used as a candidate setTKSin this task.

Figure 1:Illustration of KS-GRR for singleton key-value pair
Frequency and mean.The aggregator transmits the top-2tcandidate keys setTKSto the remaining users for final estimation.If the key is withinTKS,each user retains their key-value pair;otherwise,a dummy key-value pair<⊥,±1>is used to replace the original key-value pair.Since the potential number of keys is currently 2t+1,we setTKS∩{⊥} asK′.Subsequently,discretizes the value of the key-value pair from float type to binary {1,-1} using formula(2).Then,each user with value

4.3 KS-UE and KS-GRR for Multiple Key-Value Pairs
The scenario of multiple key-value pairs indicates that each user possesses a set of such pairs.In order to accommodate this situation,we employ an advanced protocol known as ‘padding-andsampling’as described in Gu et al.[12],specifically designed to enhance the performance of key-value data analysis.
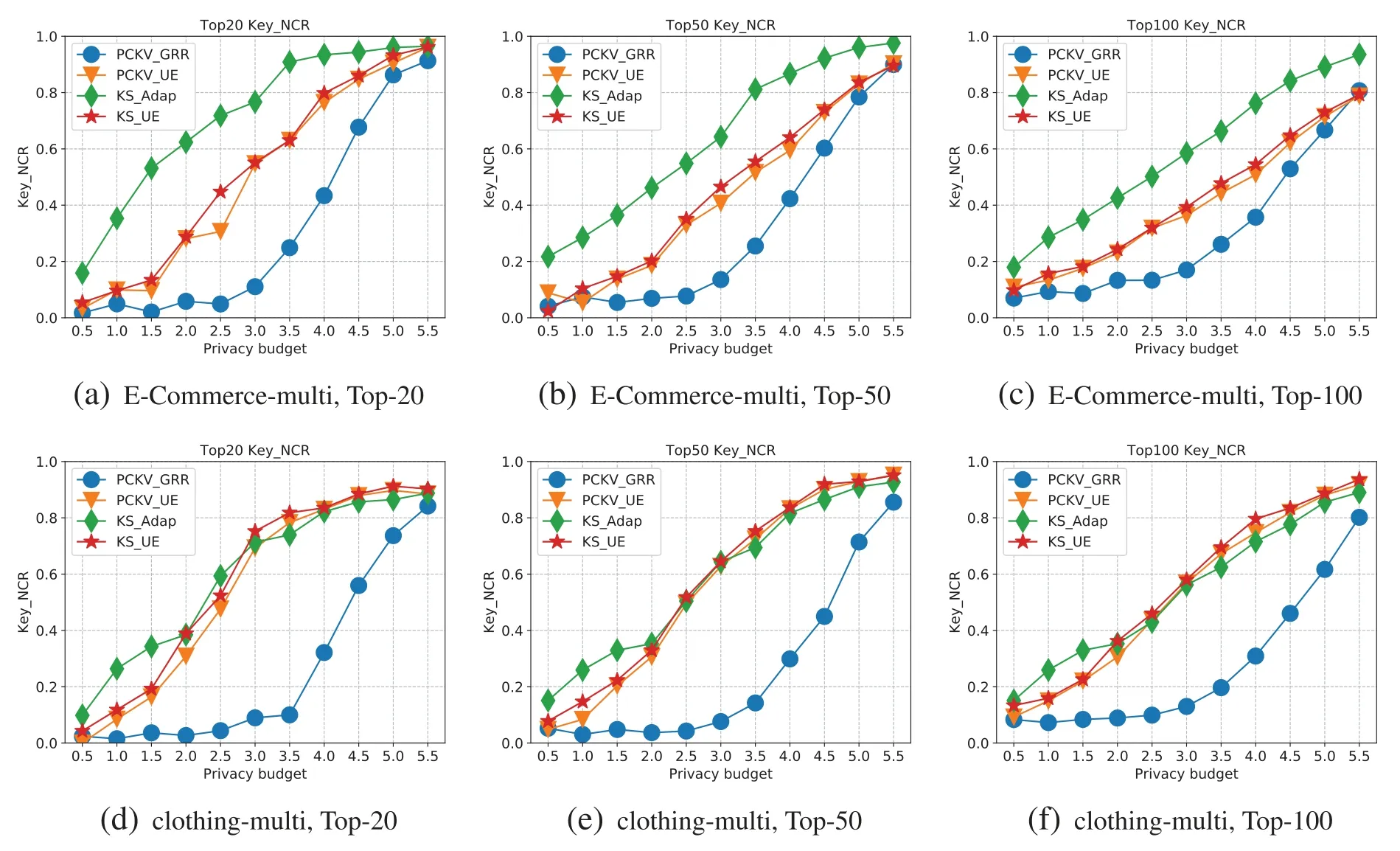
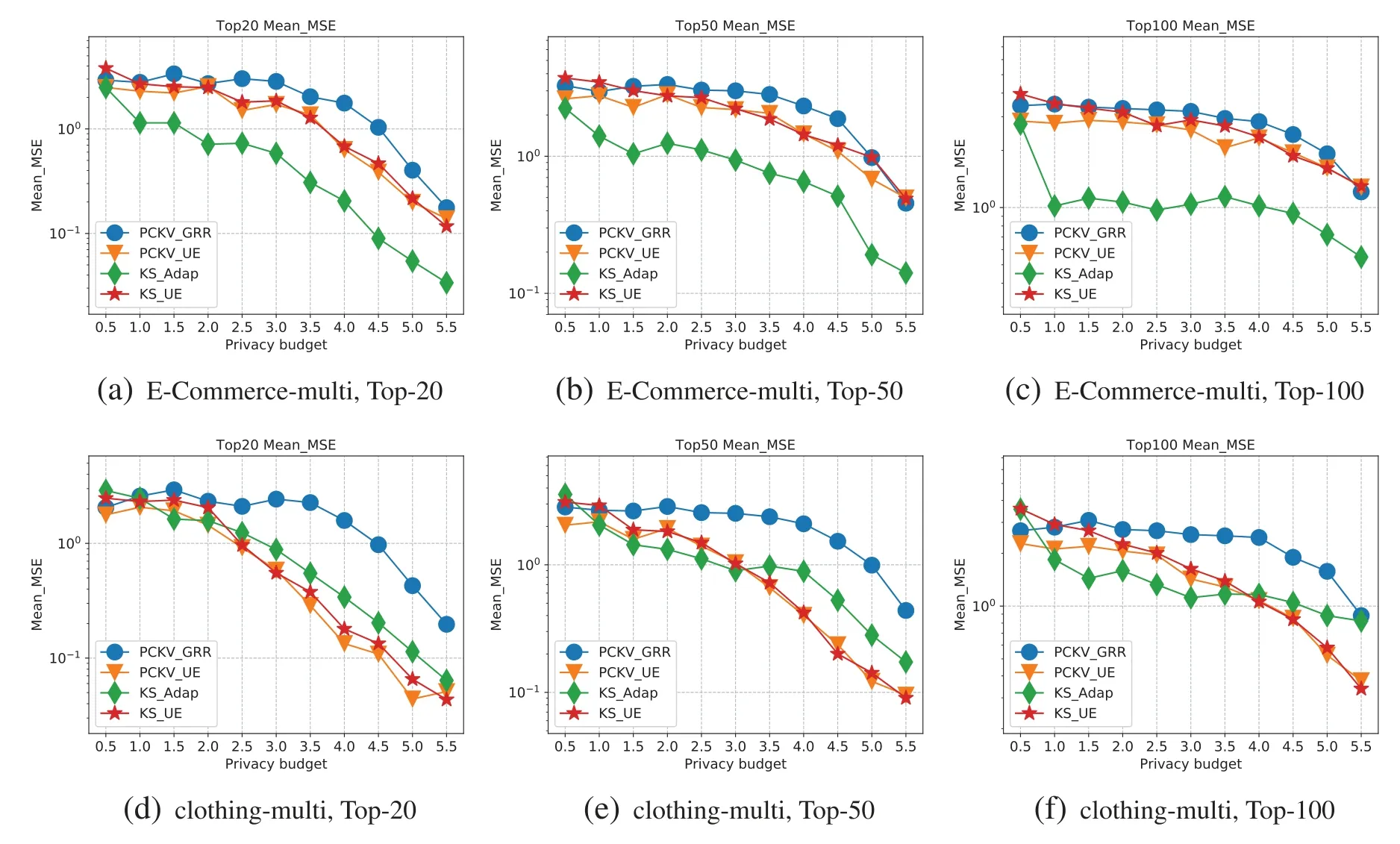
The ‘padding-and-sampling’protocol necessitates a global parameterlto ensure uniform sampling rate across all users.Consequently,ldummy key-value pairs are introduced into the key-value pairs domain.When |Si| KS-UE for multiple key-value pairs.In order to allow for a comparison with PCKV-UE,KSUE employs the same ‘padding-and-sampling’protocol as PCKV-UE.Consequently,following the‘padding-and-sampling’protocol,each user will have a singleton key-value pair.The KS-UE algorithm(discussed in Section 4.1)is utilized to ascertain the frequencies of the top-tfrequent keys and the mean under these keys. KS-GRR for multiple key-value pairs.The process of KS-GRR is recalibrated for the case of multiple key-value pairs,as depicted in Fig.2.Given the tripartite tasks involved in KS-GRR,the users are accordingly segmented into three groups,each group catering to a specific task. •Task 1:Users in this group bypass the‘padding-and-sampling’protocol and opt to randomly select one of their keys to be transmitted to the aggregator via the OLH algorithm.This technique does not ascertain the frequencies of the keys;however,it reliably preserves the ordinal information of the keys.Notably,the estimations remain stable and unaffected by variations in the value ofl. •Task 2:For the users engaged in this task,the aggregator provides feedback on the top keys setTKS.This task requires a limited number of users to identify an appropriatel.Moreover,the data essential for this task pertains to the size of each user’s set,not the key-value pair.Initially,every user generates her new key-value pairs set,ensuring that the keys belong toTKS.Subsequently,each user submits the size of the private set,and the aggregator identifies the smallestlsuch that>0.9. •Task 3:For the users participating in this task,the aggregator provides feedback on the top keys setTKSas well as the adjustedl.Users maintain key-value pairs if the keys are found inTKS,and subsequently implement the‘padding-and-sampling’protocol with theldetermined in task 2.This facilitates the estimation of the frequencies of top frequent keys and the mean under these keys. Figure 2:Illustration of KS-GRR for multiple key-value pairs In this section,we will initially provide evidence to confirm that KS-UE satisfiesε-LDP.Subsequently,we will conduct an analysis on the estimation error of KS-UE.The error yielded by KS-UE is demonstrably less than that produced by preceding algorithms. Theorem 4.1.KS-UE satisfiesε-LDP. Proof.LetSbe a key-value pair set,and each key-value pair Then,PiandPjare indistinguishable at most through KS-UE: Theorem 4.2.(Estimation Error Analysis).The expectation and variances ofare as following: For formula(9).Next,we calculate the variance of: For formulas(10)and(11).We calculate the expectation and variance of mean estimation.From the multivariate Taylor Expansions of functions of random variables,the expectation of quotient of two random variablesXandYcan be approximated by The variances are E[X],E[Y],Var[Y]andCovX,Yare computed by their exact values. The proof is completed. In this section,we set up experiments on real datasets to validate our analysis with different approaches. Datasets.We ran experiments on the following datasets: • E-Commerce(Ecommerce rating dataset)1https://www.kaggle.com/nicapotato/womens-ecommerce-clothing-reviews:This dataset contains the merchant transactions of 23,486 users with 1,206 keys.Each user has only one key-value pair.This dataset is used in both singleton and multiple scenarios. • Clothing(Clothing fit and rating dataset)2https://www.kaggle.com/rmisra/clothing-fit-dataset-for-size-recommendation:This dataset contains the merchant transactions of 47,959 users with 5,850 keys.Each user has multiple key-value pair.For singleton key-value pair collection,we treat each key-value pair as a individual record.Thus,clothing-singleton dataset has 82,789 records with 5,850 keys. Metrics.This study aimed to find the frequent itemsets together with their frequencies,which requires different metrics to evaluate their utilities.We adopted the normalized cumulative rank(NCR)[6,18]and squared error(SE)to assess the frequent itemsets and frequencies,respectively. 1).Normalized Cumulative Rank(NCR).The quality function with the mosttkeys ranked is as follows:Score(kj)=t-j+1 forj-th highest-ranked key,and all other non-top keys have scores 0.To normalize this into a value between 0 and 1,we divide the sum of scores by the maximum possible score.Thus,a higher score indicates better identification. 2).Squared Error(Var).We measured the estimation accuracy for both frequency and mean by using averaged Mean Squared Error.That is wherefkandmkare the real set of frequency and mean of keyk.Note that we account only for top-tfrequent keys that are successfully identified by the algorithm,i.e.,Xis the intersection of the real top-tkeys set and the estimated top-tkeys set.Thus,lower variance means more accurate estimation. Parameter settings.In KS-GRR for multiple pairs,we use 40% of all users to find top-2tfrequent keysTFK,10% to report the size of their key-value pairs whose keys are inTFK,and 50% to obtain final results. Selected approaches.We compare our KS-UE and KS-GRR with the following approaches.The approaches used in the evaluation are as follows: (i)PCKV-UE[12].PVKV-UE is the state-of-the-art approach for key-value pairs collection. (ii)PVKV-GRR[12].PCKV-GRR can obtain benifit from‘padding-and-sampling’than PCKVUE,but only performs well when|K|is small. (iii)KS-Adap.KS-Adap is a manifestation for multiple key-value pairs of KS-GRR.We use 40% of all users to find top-2tfrequent keysTFK,10% to report the size of their key-value pairs whose keys are inTFK,and 50% to obtain final results for multiple pairs. For KS-UE,PCKV-UE and PCKV-GRR,we setl=2 for multiple key-value pairs.For KS-GRR,two groups of users are equally divided for singleton pair. All experiments were conducted on an Intel Core(TM)i7-6700 3.40 GHz PC with 16 GB RAM.The results are averaged over 10 runs. Singleton key-value pair.Figs.3–5 depict the metric evaluation on the E-Commerce and Clothing singleton key-value pair datasets. Figure 4:Key-MSE for single dataset Figure 5:Mean-MSE for single dataset Firstly,Fig.3 presents the trendlines of NCR for keys with an increasing privacy budget(ε)when selecting the top 20,50,and 100 values.As per the NCR definition,higher trendlines correlate with more accurate identification.Our analysis revealed that KS-UE consistently outperforms PCKV-UE.Similarly,KS-GRR notably surpasses PCKV-GRR,exhibiting the best performance at smaller values ofε.Therefore,both KS-UE and KS-GRR demonstrate robust performance in terms of the NCR of. Secondly,Fig.4 illustrates the trendlines of MSE for keys with an incrementing privacy budget(ε),selecting the top 20,50,and 100 values.As per the MSE definition,lower trendlines are indicative of higher accuracy.It is observed that KS-UE continuously outstrips PCKV-UE.Moreover,KSGRR considerably outperforms PCKV-GRR.Consequently,KS-UE and KS-GRR display robust performance regarding the MSE of. Lastly,Fig.5 demonstrates the trendlines of MSE for the mean values with an increasing privacy budget (ε),while selecting the top 20,50,and 100 values.The trendlines of KS-UE and PCKV-UE closely intersect.Although KS-UE matches the utility of PCKV-UE,the allocated budget for the value is smaller and a higher NCR implies more identified keys.Therefore,KS-UE exhibits exceptional performance.Forε >3,the variance of KS-GRR is lower than that of PCKV-GRR.Moreover,forε≥6,KS-GRR even surpasses both PCKV-UE and KS-UE.When combined with the NCR and MSE of,theof KS-GRR demonstrates an improvement over PCKV-GRR,though it does not exhibit a significant advantage over PCKV-UE.On the whole,KS-UE and KS-GRR exhibit effectiveness and efficiency,which is consistent with our theoretical results. Multiple key-value pairs.Figs.6–8 present the metric evaluation for the E-Commerce and Clothing datasets featuring multiple key-value pairs. Figure 6:NCR for multiple dataset Figure 7:Key-MSE for multiple dataset Figure 8:Mean-MSE for multiple dataset Firstly,Fig.6 depicts the trendlines for the NCR of keys,corresponding to the increasing privacy budget (ε),for the top 20,50,and 100 selected values.By definition,a higher trendline suggests more accurate identification.KS-UE consistently outperforms PCKV-UE,and KS-GRR significantly surpasses PCKV-GRR.In particular,KS-GRR exhibits the best performance across allεvalues for the E-Commerce-multiple dataset,and performs optimally under smaller privacy budgets for the clothingmultiple dataset.Hence,both KS-UE and KS-GRR demonstrate excellent performance in terms of the NCR of. Secondly,Fig.7 illustrates the MSE trendlines for keys,with respect to the incrementing privacy budget (ε),for the top 20,50,and 100 selected values.In line with the definition of MSE,lower trendlines equate to more accurate identification.Here,KS-UE consistently surpasses PCKV-UE,and KS-GRR considerably outperforms PCKV-GRR,even showing the best performance for large privacy budgets on the E-Commerce-multiple dataset.Thus,both KS-UE and KS-GRR excel in relation to the MSE of. Lastly,Fig.8 presents the MSE trendlines for the mean values with increasingε,for the top 20,50,and 100 selected values.The trendlines of KS-UE and PCKV-UE closely intertwine.Although KSUE attains equivalent utility with PCKV-UE,the budget allocation for value is smaller and a higher NCR implies more identified keys,signifying excellent performance by KS-UE.KS-GRR generally performs optimally for smallεvalues.For largeεvalues,KS-GRR exhibits the best performance for E-Commerce-multiple and is relatively efficient in the clothing-multiple dataset.Combined with the NCR and MSE of,theof KS-GRR demonstrates improvement over PCKV-GRR,although it does not hold a significant advantage over PCKV-UE.Overall,KS-UE and KS-GRR both exhibit effectiveness and efficiency,which aligns with our theoretical findings. Analysis.The experimental outcomes reveal that the KS-UE and KS-GRR algorithms predominantly surpass other algorithms in most situations.The advantages of KS-UE have already been discerned in the error analysis in Section 4.4;its Mean Squared Error (MSE) is lower than prior algorithms,thus reflecting more superior results in the experiments.KS-GRR,by adopting a keypriority strategy,ensures the accuracy in collecting keys and the validity of the values under such keys,once accurate keys have been obtained by collecting the frequency of keys. In this research,we explore methods for key-value data collection under the constraint of local differential privacy to obtain key frequencies and corresponding mean values.We design two innovative strategies,namely,Key Strategy KS-UE and KS-GRR,applicable in interactive and non-interactive frameworks,respectively.Since mean estimation is intrinsically dependent on key frequencies,precise key collection is vitally important not only for estimating key frequencies but also for deriving accurate mean values.KS-UE is specifically designed to tilt the privacy budget towards the key,thereby enhancing the estimation of keys,while KS-GRR implements a group-and-interactive strategy to identify the top frequent keys,subsequently enabling accurate frequency and mean estimation.Empirical validation supports our theoretical analysis,demonstrating the effectiveness of both KSUE and KS-GRR.In terms of future work,we aim to enhance the efficiency of the candidate domain and reduce both communication and time complexity.These refinements will potentially allow for the broader implementation of these methodologies in practical applications,thereby contributing significantly to the field of privacy protection. Acknowledgement:This papers logical organisation and content quality have been enhanced,so the authors thank anonymous reviewers and journal editors for assistance. Funding Statement:This work is supported by a grant from the National Key R&D Program of China. Author Contributions:The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows:study conception and design:Dan Zhao,Chuanwen Lu;data collection:Dan Zhao,Yang Liu;analysis and interpretation of results: Dan Zhao,Yang You;draft manuscript preparation: Dan Zhao,Chuanwen Luo,Ting Chen,Yang Liu.All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript. Availability of Data and Materials:The data is from https://www.kaggle.com/nicapotato/womensecommerce-clothing-reviews and https://www.kaggle.com/rmisra/clothing-fit-dataset-for-size-recom mendation. Conflicts of Interest:The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
4.4 Privacy and Analysis
5 Experimental Evaluation
5.1 Experimental Setup



6 Conclusions
杂志排行
Computer Modeling In Engineering&Sciences的其它文章
- A Study on the Transmission Dynamics of the Omicron Variant of COVID-19 Using Nonlinear Mathematical Models
- Novel Investigation of Stochastic Fractional Differential Equations Measles Model via the White Noise and Global Derivative Operator Depending on Mittag-Leffler Kernel
- Saddlepoint Approximation Method in Reliability Analysis:A Review
- A Review of the Tuned Mass Damper Inerter(TMDI)in Energy Harvesting and Vibration Control:Designs,Analysis and Applications
- Recent Advances on Deep Learning for Sign Language Recognition
- A Survey on Blockchain-Based Federated Learning:Categorization,Application and Analysis
