AGK2 pre-treatment protects against thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure via regulating the MFN2-PERK axis and ferroptosis signaling pathway
2024-03-04QingQiZhangQianChenPanCaoChunXiaShiLuYiZhangLuWenWangZuoJiongGong
Qing-Qi Zhang,Qian Chen,Pan Cao,Chun-Xia Shi,Lu-Yi Zhang,Lu-Wen Wang,Zuo-Jiong Gong
Department of Infectious Diseases, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, China
Keywords: SIRT2 inhibitor AGK2 Acute liver failure MFN2 Ferroptosis
ABSTRACT Background: Acute liver failure (ALF) is an unpredictable and life-threatening critical illness.The pathological characteristic of ALF is massive necrosis of hepatocytes and lots of inflammatory cells infiltration which may lead to multiple organ failure.Methods: Animals were divided into 3 groups,normal,thioacetamide (TAA,ALF model) and TAA+AGK2.Cultured L02 cells were divided into 5 groups,normal,TAA,TAA+mitofusin 2 (MFN2)-siRNA,TAA+AGK2,and TAA+AGK2+MFN2-siRNA groups.The liver histology was evaluated with hematoxylin and eosin staining,inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1),activating transcription factor 6 β (ATF6 β),protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) and phosphorylated-PERK (p-PERK).C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP),reactive oxygen species (ROS),MFN2 and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) were measured with Western blotting,and cell viability and liver chemistry were also measured.Mitochondriaassociated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs) were measured by immunofluorescence.Results: The liver tissue in the ALF group had massive inflammatory cell infiltration and hepatocytes necrosis,which were reduced by AGK2 pre-treatment.In comparison to the normal group,apoptosis rate and levels of IRE1,ATF6 β,p-PERK,CHOP,ROS and Fe2+ in the TAA-induced ALF model group were significantly increased,which were decreased by AGK2 pre-treatment.The levels of MFN2 and GPX4 were decreased in TAA-induced mice compared with the normal group,which were enhanced by AGK2 pretreatment.Compared with the TAA-induced L02 cell,apoptosis rate and levels of IRE1,ATF6 β,p-PERK,CHOP,ROS and Fe2+ were further increased and levels of MFN2 and GPX4 were decreased in the MFN2-siRNA group.AGK2 pre-treatment decreased the apoptosis rate and levels of IRE1,ATF6 β,p-PERK,CHOP,ROS and Fe2+ and enhanced the protein expression of MFN2 and GPX4 in MFN2-siRNA treated L02 cell.Immunofluorescence observation showed that level of MAMs was promoted in the AGK2 pre-treatment group when compared with the TAA-induced group in both mice and L02 cells.Conclusions: The data suggested that AGK2 pre-treatment had hepatoprotective role in TAA-induced ALF via upregulating the expression of MFN2 and then inhibiting PERK and ferroptosis pathway in ALF.
Introduction
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a potentially catastrophic condition that always requires specialized clinical treatment [1].ALF is characterized by massive necrosis of hepatocytes and a lot of inflammatory cells infiltration which may lead to multiple organ failure [2].Currently,there is lack of effective medications for ALF.It is reported that single-dose administration of thioacetamide (TAA)can induce central necrosis of liver lobules [3].After TAA enters the liver,toxic metabolites such as TAA sulfur dioxide are formed which result in lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress,destruction of ultrastructure and function in liver tissue,and necrosis and apoptosis of hepatocytes.Therefore,TAA was selected as a classical and common drug in animal and cell experiment to induce ALF.
Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes(MAMs) link the interaction between mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) [4].It provides a valuable platform for various exchanges of biological molecules and signal transduction between the two essential organelles.To be specific,calcium (Ca2+)homeostasis,autophagy,apoptosis,and tumor growth are implemented that require MAMs [5].The study has shown that mitofusin 2 (MFN2) is a MAMs protein which is responsible for connecting mitochondria and ER [6].MFN2 can act as an upstream modulator of protein kinase R-like ER kinase (PERK),which locates in the ER membrane [7].Knockdown of MFN2 promotes cardiac fibroblast activation by upregulating the PERK/ATF4 pathway [8].In addition,ablation of MFN2 in liver disrupts ER-mitochondrial phosphatidylserine transfer [9].And one demonstrated that the level of MFN2 in liver biopsies from patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is decreased [10].The expression of MFN2 is reduced in D-galactosamine (D-Gal)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced ALF mice [11].
Ferroptosis is considered an oxidative,iron-dependent and peroxidation-driven form of cell-regulated death [12].Accumulating studies demonstrate that ferroptosis plays a crucial part in the development and occurrence of various pathologies of the liver disease [13].High-iron diet will augment the susceptibility to liver fibrosis in mice by ferroptosis [14].Besides,ferroptosis inducers can exert cytotoxicity against hepatocellular carcinoma [15].Ferrostatin-1 effectively attenuates ferroptosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) [10].The study revealed that MFN2 interacted with inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1)α,and ultimately led to ferroptosis in NaAsO2-induced L02 cells [10].
Sirtuin2 (SIRT2) is implicated in various immune and inflammatory diseases,including asthma,colitis and renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis [16–18].AGK2 is an inhibitor for SIRT2 that has an inhibitory effect on inflammatory response [19].Furthermore,Wang et al.showed that AGK2 pre-treatment mitigates serum aminotransferase,hepatocellular necrosis and apoptosis,and neutrophil infiltration in hepatic ischemia reperfusion (I/R) mouse model [20].Our previous study has verified that AGK2 has a hepatoprotective effect via inhibition of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways [21].The present study aimed to explore the possible hepatoprotective influence of AGK2 in ALF.
Methods
Animals and treatments
Wild-type C57BL/6 male mice (6-7 weeks,obtained from Experimental Animal Center of Wuhan University) were used for the study.Protocols of this study were approved by the Ethics Committee of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University [Certificate Numbers:WDRM (F) 20181018].In our study,30 mice were separated into 3 groups: normal (n=10),TAA-induced ALF model (n=10),and TAA+AGK2 (n=10).In TAA+AGK2 group,AGK2 was administrated by intraperitoneal injection (1 μmol/mouse,Selleckchem,Houston,USA).After 2h,TAA (600 mg/kg;Sigma,St.Louis,USA)was intraperitoneally injected in TAA group and TAA+AGK2 group.The same volume of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was given to the normal group.All experimental mice were sacrificed after 24 h of TAA administration.
Cell culture and transfection
L02 cells were grown in DMEM (HyClone,Logan,USA) including 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (GIBCO,NY,USA).The cells were grown at 37 °C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2.First,different TAA concentrations (0 mmol/L,30 mmol/L,60 mmol/L,90 mmol/L,120 mmol/L,and 150 mmol/L) were used to stimulate L02 cells to detect the apoptosis rate and select the appropriate concentration of TAA for ALF modelinginvitroexperiment.Then L02 cells were divided into the normal,TAA,MFN2-siRNA,TAA+AGK2,and TAA+AGK2+MFN2-siRNA groups.Except for the normal group,TAA (90 mmol/L) was added to each group medium for 24 h.AGK2 (1 μmol/L) was applied to the medium 2 h before adding TAA (90 mmol/L) in the AGK2 and AGK2+MFN2-siRNA groups.MFN2-siRNA (RiboBio,Guangzhou,China) transfection was done 24 h prior to TAA administration.According to instructions,the transfection was accomplished by Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen,CA,USA).The knockdown interference sequence of MFN2-siRNA was 5’-GGC CAA ACA TCT TCA TCC T-3’.Each group of cells was collected 24 h after TAA administration.
Histopathological analysis and biochemical examination
A part of fresh liver specimens of mice were fixed using 10% neutral-buffered formalin and were used for histology[hematoxylin-eosin (HE) stain].Liver sections were observed in BX 51 light microscope (Olympus,Tokyo,Japan).And a part of fresh liver specimens of mice were fixed in 4% glutaraldehyde.After dehydration by ethanol and acetone,tissues were embedded with epoxy resin and sliced,the slices were double stained with saturated uranium acetate and lead citrate.The ultrastructure of liver tissues was observed by transmission electron microscope (HIT ACHI HT7700,Tokyo,Japan).Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were measured by automated Aeroset chemistry analyzer (Abbott Co.Ltd.,Chicago,USA).
Terminal dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay
Liver specimen section was incubated with 20 μg/mL proteinase K for 10 min.Then TUNEL reaction mixture (TdT:dUTP,1:9) was added for 1 h in the dark at 37 °C.Finally,staining conditions were observed under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus).
Western blotting
Protein lysates (30 μg/sample) were subjected to 12% SDSPAGE.Then proteins were transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride(PVDF) membranes.Primary antibodies against MFN2 (Proteintech,Wuhan,China),PERK (Proteintech),p-PERK (Affinity Biosciences,Changzhou,China),IRE1 (Affinity Biosciences),ATF6β(Proteintech),CHOP (Cell Signaling Technology,Boston,USA),GPX4 (Cell Signaling Technology) and GAPDH (Proteintech) were used.
The apoptosis rate of L02 cells
PE Annexin V apoptosis detection kit (BD,New Jersey,USA) was used to determine the apoptosis rate of L02 cell.The dosage of TAA (0 mmol/L,30 mmol/L,60 mmol/L,90 mmol/L,120 mmol/L, and 150 mmol/L) was given to each well of a 6-well plate.Cells were collected 24 h after TAA administration.Then the cells were washed twice,added with 5 μL PE Annexin V and 5 μL 7-AAD,and gently vortexed and incubated.Finally,400 μL of binding buffer was added and the apoptosis rate was measured by flow cytometry (BD).
Immunofluorescence detection of MAMs expression
TOM20 marks mitochondria and calreticulin (CRT) marks (Abcam,Cambridge,MA,USA) the ER.A total of 1×104L02 cells/500 μL per plate were grown in 24-well plates with circular slides placed.After treatment,the slides were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and treated with 0.2% Triton X-100.Slides were incubated with polyclonal antibodies against TOM20 and CRT overnight at 4 ˚C.Slides were incubated with Cy3 and FITC–labeled antibodies for 1 h.Cells were stained with 5 μg/mL DAPI for 3 min in a dark environment.The slides were performed under a confocal microscopy (Olympus,#FV1200).After mice liver tissues paraffin sections were deparaffinized and hydrated in ethanol,the antigen was recovered.The remaining steps were similar with method of L02 cell immunofluorescence detection.Observations were performed with a confocal microscopy (Olympus,#FV1200).
Detection of the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), glutathione(GSH), and Fe2 +
The ROS (Beyotime institute of Biotechnology,Wuhan,China),GSH (Naijing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute,Nanjing,China),and Fe2+(Abcam) were measured with pertinent ELISA kits.The values for the levels of ROS,GSH,and Fe2+in the L02 cells and liver tissue were detected with the multimode plate reader.
Statistical analysis
Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD).All values were compared by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).APvalue<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software,Inc.,La Jolla,CA,USA).
Results
AGK2 ameliorated pathological damage in ALF mice
HE staining showed that liver lobules have complete structure,obvious sinusoid and without hepatocellular necrosis nor neutrophil infiltration in the normal group.Compared with the normal group,liver lobules showed disturbed structures,a lot of hepatocellular necrosis and neutrophil infiltration in TAA group.However,AGK2 ameliorated the liver tissue damage (TAA group,Fig.1 A).Electron microscopy results showed that TAA destroyed the mitochondrial double membrane of hepatocytes and reduced the number of ER significantly (Fig.1 B).AGK2 pre-treatment improved the integrity of mitochondria inner and outer membranes and increased the number of ER in mice hepatocytes (Fig.1 B).The apoptosis cells in liver tissue were measured by TUNEL assay.TAA increased the number of TUNEL positive cells (Fig.1 C),whereas AGK2 pre-treatment reduced the number of TUNEL positive cells compared with the TAA group.The level of hepatic enzymes was assessed as well.TAA significantly increased the serum levels of ALT and AST,while AGK2 prominently decreased the serum levels of ALT and AST compared with the TAA group (Fig.1 D,E).
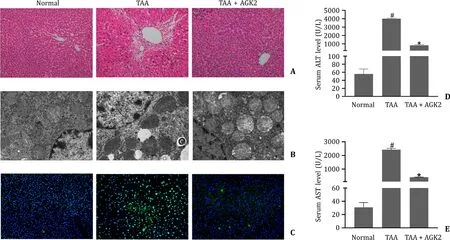
Fig.1. AGK2 ameliorated liver pathological damage and improved liver function in TAA-induced ALF mice.A:HE staining of liver tissues (original magnification×200).B:Ultrastructural changes of hepatocytes in ALF mice observed by transmission electron microscopy micrographs.C:TUNEL staining of the liver tissues (original magnification×200).D and E:Serum levels of ALT and AST in mice.# P < 0.05,compared with normal group.∗P < 0.05,compared with TAA group.TAA: thioacetamide;ALF: acute liver failure;HE: hematoxylin and eosin;TUNEL: terminal dUTP nick-end labeling;ALT: alanine aminotransferase;AST: aspartate aminotransferase.
AGK2 affected the MFN2-PERK axis and increased the MAMs in ALF mice
TAA significantly decreased the protein level of MFN2 and number of MAMs,and significantly increased protein levels of IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK and CHOP (Figs.2 A-C and 3).AGK2 increased the levels of MFN2 and MAMs,and decreased the levels of IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK and CHOP compared with the TAA group.There was no significant difference of the protein expression of PERK among the three groups.
AGK2 inhibited the ferroptosis pathway in ALF mice
The levels of GPX4 and GSH were negatively whereas ROS and Fe2+positively related to ferroptosis.TAA reduced the levels of GPX4 and GSH,and enhanced the levels of ROS and Fe2+(Fig.2 A,C and 2D-F,respectively).AGK2 increased the levels of GPX4 and GSH,and inhibited the levels of ROS and Fe2+compared with the TAA group.
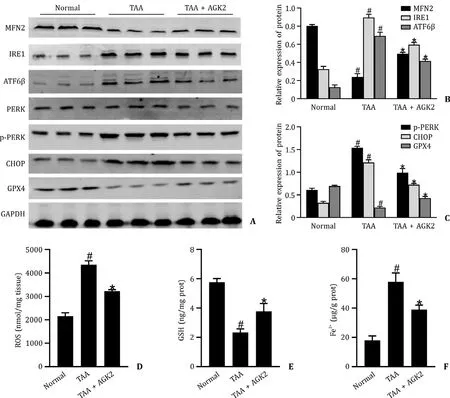
Fig.2. AGK2 affected the MFN2-PERK axis and inhibited the ferroptosis in TAA-induced ALF mice.A-C:The levels of MFN2,IRE1,ATF6 β,PERK,p-PERK,CHOP and GPX4 in mice liver tissue.D-F:The level of ROS,GSH,and Fe2+ in mice liver tissue.# P < 0.05,compared with the normal group;∗P < 0.05,compared with TAA group.TAA:thioacetamide;ALF: acute liver failure;MFN2: mitofusin 2;PERK: protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase.
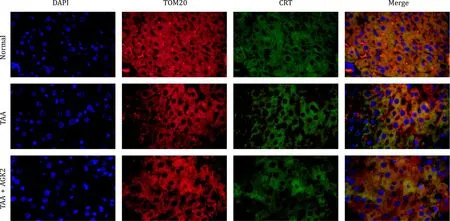
Fig.3. AGK2 increased the MAMs in TAA-induced ALF mice.DAPI marked the nucleus of hepatocytes which was shown as blue.TOM20 marked mitochondria which was shown as red.CRT marked the endoplasmic reticulum which was displayed as green.The overlapping area of TOM20 and CRT represented MAM which was shown as yellow(original magnification×1000).The normal group had the largest area of yellow,followed by TAA+AGK2 group,and the TAA group has the least in mice liver tissue.TAA:thioacetamide;ALF: acute liver failure;MAM: mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
Effects of different TAA concentrations on L02 cell apoptosis rate
To determine an appropriate treatment dosage of TAA for modeling of L02 cell,the apoptosis rate of TAA on L02 cells was measured by flow cytometry.Apoptosis in TAA-induced L02 cells showed a concentration-dependent manner.As shown in Fig.4,the apoptosis rates were 5.63%,13.62%,34.14%,55.47%,73.34% and 84.55% respectively when treating L02 cell with TAA dosage of 0 mmol/L,30 mmol/L,60 mmol/L,90 mmol/L,120 mmol/L,and 150 mmol/L.When treated with 90 mmol/L TAA,the apoptosis rate of L02 cell was over 50%.Therefore,we selected the TAA dosage of 90 mmol/L in the following study.
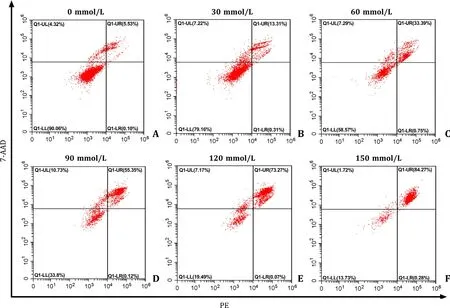
Fig.4. Effects of different concentrations of TAA on apoptosis rate of L02 cell.The L02 cell apoptosis rate which stimulated by different dosage of TAA was detected by flow cytometry.TAA: thioacetamide.
AGK2 decreased the apoptosis rate in TAA-induced L02 cell
TAA increased the apoptosis rate in L02 cells.MFN2-siRNA further aggravated the apoptosis of L02 cell when compared with TAA only.AGK2 pre-treatment reduced the apoptosis rate in both TAA and TAA+MFN2-siRNA groups (Fig.5).
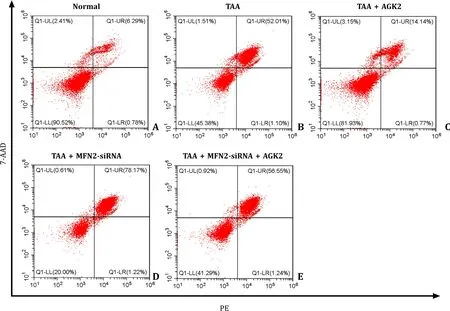
Fig.5. AGK2 decreased the apoptosis rate in both TAA-induced and TAA+MFN2-siRNA-induced L02 cell.The apoptosis rate of L02 cell was measured by flow cytometry.TAA: thioacetamide.
AGK2 increased the expression of MFN2 and inhibited the level of p-PERK and ferroptosis pathway in TAA-induced L02 cell
Levels of MFN2,GPX4 and GSH were significantly reduced and levels of IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK,CHOP,ROS and Fe2+were significantly increased in the TAA group.AGK2 pre-treatment upregulated the levels of MFN2,GPX4 and GSH and downregulated the levels of IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK,CHOP,ROS and Fe2+in the TAA group.Moreover,MFN2-siRNA decreased the protective effect of AGK2 by suppressing the levels of MFN2,GPX4 and GSH and promoting IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK,CHOP,ROS and Fe2+levels in cells treated with TAA+AGK2 (Fig.6 A-F).
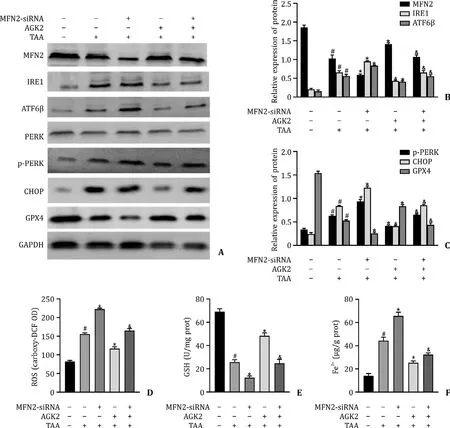
Fig.6. AGK2 promoted the expression of MFN2 and inhibited the level of p-PERK and ferroptosis pathway in TAA-induced L02 cell.A-C:The protein expression of MFN2,IRE1,ATF6 β,PERK,p-PERK,CHOP and GPX4 in L02 cells.D-F:The levels of ROS,GSH,and Fe2+ in L02 cells.# P < 0.05,compared with normal group;∗P < 0.05,compared with TAA group.&P < 0.05,compared with the TAA+AGK2 group.
AGK2 improved the level of MAMs in TAA-induced L02 cell
The number of MAMs in TAA treated cells was lower than that of the normal and AGK2 groups.MFN2-siRNA further reduced the number of MAMs in TAA treated and TAA+AGK2 treated cells(Fig.7).
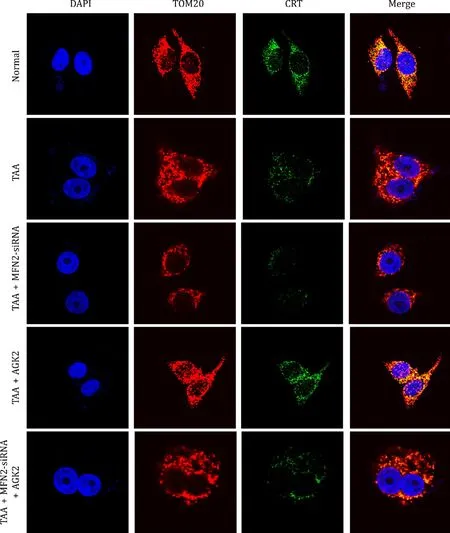
Fig.7. AGK2 promoted the level of MAMs in TAA-induced L02 cell.DAPI marked the nucleus of L02 cell which was shown as blue.TOM20 marked mitochondria which was shown as red.CRT marked the endoplasmic reticulum which was displayed as green.The overlapping area of TOM20 and CRT represented MAMs which was shown as yellow (original magnification×1000).The normal group had the largest area of yellow,and the TAA+MFN2-siRNA group had the least in L02 cell.The yellow area in the TAA+AGK2 group was larger than the TAA group or TAA+AGK2+MFN2-siRNA group.TAA: thioacetamide;MAM: mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
Discussion
ALF is a life-threatening and catastrophic clinical syndrome accompanied by hepatocyte apoptosis and necrosis [22].TAA has an obvious liver-damaging effect,which acts as a classic hepatotoxin applied in ALF modeling in animals [23].Increasing evidence reveals that short-term high dose of TAA can lead to oxidative stress and ROS-induced NF-κB activation in rats liver[24].Our findings demonstrated that TAA caused a remarkable destruction of liver structure and function in mice and increased the apoptosis rate of L02 cell which presented in a dosedependent manner.Meanwhile,TAA could decrease the expression of MFN2 and the number of MAMs.The PERK/IRE1/ATF6βand ferroptosis pathway is activated in TAA-induced mice and L02 cells.
MAMs provide physical interaction between the ER and mitochondria which has pivotal roles in cellular housekeeping functions [25].MFN2 is a mitochondrial fusion protein.Meanwhile,MFN2 is a MAMs protein that connects the ER and mitochondria.Mitochondria swell and fragment in MFN2 knockout cells [26].PERK,IRE1 and ATF6βare three proteins located in ER membrane which respond to ER stress via triggering unfolded protein response (UPR) [27].In addition,PERK-stimulated CHOP activates apoptosis [28].In PERK knockout cells,the ROS level is decreased and mitochondrial morphology is improved [29].In our study,the protein expression of MFN2 and number of MAMs were decreased in TAA-induced mice and L02 cell.However,levels of IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK and CHOP were increased in TAA-induced mice and L02 cell.After MFN2-siRNA was transfected,the protein levels of IRE1,ATF6β,p-PERK and CHOP were further increased in TAA-induced mice and L02 cell.These results also supported the notion that MFN2 could act as an upstream molecule of regulating PERK.
Ferroptosis is a new type of cell death which charters with accumulation of lipid ROS and decrease in antioxidant capacity [30].In ferroptosis process,the intracellular level of GSH is lessened and the activity of GPX4 is reduced.Moreover,a large amount of ROS is produced in cell because the reduction reaction catalyzed by GPX4 cannot metabolize lipid peroxides,and Fe2+oxidizes lipids [31].In our study,the levels of GSH and GPX4 were reduced and the levels of Fe2+and ROS were increased in TAA-induced mice and L02 cells.
SIRT2 is one of the members of the sirtuins family which widely exist in various tissues such as kidney,liver and brain.A previous study has verified that SIRT2 is associated with inflammatory responses [32].Inhibiting SIRT2 activity can result in a prominent decrease in the LPS-induced neuroinflammation [33].In addition,in passive cutaneous anaphylaxis and acute lung injury animal models,AGK2 pre-treatment inhibits the expression of proinflammatory cytokines via regulation of NF-κB and NRF2 [34].In our present study,the results indicated that AGK2 pre-treatment showed a hepatoprotective effect in ALF.AGK2 pre-treatment improved the liver histology and function in TAA-induced mice.In addition,the TAA-induced hepatocellular apoptosis in mice and L02 cells was reduced by AGK2 pre-treatment as well.AGK2 pretreatment could enhance the expressions of MFN2 and level of MAMs and inhibit the expressions of PERK/ATF6β/IRE and ferroptosis in ALF.Moreover,MFN2-siRNA could weaken the protective effect of AGK2 pre-treatment in ALF.This effect may be associated with the increased apoptosis rate.PERK/ATF6β/IRE axis may be involved in ferroptosis.The possible mechanisms were showed in Fig.8.

Fig.8. Summary diagram.AGK2 promoted the expression of MFN2 and inhibited the level of PERK signaling pathway in ALF mice and L02 cells stimulated by TAA.AGK2 can inhibit ferroptosis pathway.In addition,upregulated MFN2 level by AGK2 can block the ferroptosis level.MFN2: mitofusin 2;PERK: protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase;TAA: thioacetamide;ALF: acute liver failure.
In this study,there were some limitations.The role of AGK2 has not been widely applied in the clinic.There are some literatures(including our previous studies) with regard to pre-treated mice and cells with AGK2 [21,34-36],and other literatures about pretreated L02 cells with drugs [37–39].Therefore,the pre-treatment of AGK2 in L02 cells was performed in our study.Moreover,AGK2 pre-treatment increases the drug concentration of AGK2 before TAA treatment in L02 cells,which can better inhibit the expression of SIRT2 during TAA induction.Further studies on the co-and post-treatment of AGK2 are necessary for the application of AGK2 in patients with ALF.
In conclusion,our data verified that TAA contributed to severe liver damageinvitroandinvivo.SIRT2 inhibitor AGK2 had a protective effect on ALF.AGK2 improved liver pathological structure and liver function,and reduced the hepatocellular apoptosis rate in TAA-induced mice and L02 cell.Furthermore,AGK2 could upregulate the level of MFN2 and MAMs in ALF and downregulate the level of PERK/ATF6β/IRE and ferroptosis pathway.Therefore,we propose that SIRT2 inhibitor AGK2 could be a novel potential candidate for the treatment of ALF.
Acknowledgments
None.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Qing-Qi Zhang:Formal analysis,Methodology,Visualization,Writing– original draft.Qian Chen:Formal analysis,Methodology,Resources.Pan Cao:Methodology,Visualization.Chun-Xia Shi:Formal analysis,Methodology,Resources.Lu-Yi Zhang:Formal analysis,Methodology.Lu-Wen Wang:Resources,Validation.Zuo-Jiong Gong:Conceptualization,Project administration,Supervision,Writing– review &editing.
Funding
This study was supported by the grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82070609).
Ethical approval
This study was approved by Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University [WDRM (F) 20181018].
Competing interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
杂志排行
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- Recent advances in promising drugs for primary prevention of gastroesophageal variceal bleeding with cirrhotic portal hypertension
- Stereotactic body radiotherapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Application of ultrasonography-elastography score to suspect porto-sinusoidal vascular disease in patients with portal vein thrombosis
- Polydatin ameliorates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating macrophage polarization
- Hypomethylation of glycine dehydrogenase promoter in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is a new diagnostic marker of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
- Circulating RNA ZFR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition process through miR-624–3p/WEE1 axis
