Clinical study of electroacupuncture combined with exercise therapy in improving the balance function of patients with knee osteoarthritis
2024-02-27XUEKun薛堃WUJi吴佶BAOJie暴洁ZHAOHaiyin赵海音ZHAOYun赵芸LUYusun陆虞荪XUQiong许琼HUANGChunshui黄春水
XUE Kun (薛堃), WU Ji (吴佶), BAO Jie (暴洁), ZHAO Haiyin (赵海音), ZHAO Yun (赵芸), LU Yusun (陆虞荪),XU Qiong (许琼), HUANG Chunshui (黄春水)
1 Longhua Hospital Tianshan Branch, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Shanghai Changning Tianshan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital), Shanghai 200051, China
2 Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
Abstract Objective: To observe the clinical effect of electroacupuncture (EA) combined with exercise therapy on balance function in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA).
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Exercise Therapy; Osteoarthritis, Knee; Balance Function; Visual Analog Scale; Pain Measurement
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a chronic and progressive disease with a high incidence in middle-aged and elderly people.At present, the aging trend of the population in China is aggravating year by year, and the incidence of KOA remains high and shows an upward trend with the increase in age[1].The main clinical manifestations of KOA are joint pain and limited motion[2], and the balance function of patients decreases, resulting in an increased risk of falls.Therefore, relieving pain and improving joint function are the main goals of KOA rehabilitation treatment.In terms of treatment, except for severe KOA requiring joint replacement surgery, conservative treatments of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Western medicine are used in clinical practice, including various external treatment methods and rehabilitation therapy.Among them, electroacupuncture (EA), an external therapy with TCM characteristics and definite curative effect, has significant advantages in anti-inflammation,reducing swelling, and pain relief when applied to the treatment of KOA[3].Exercise therapy is to train muscle strength and joint range of motion through active or passive movements of patients.It can effectively improve joint function.At present, it has been recommended by many guidelines at home and abroad as the first-line treatment for KOA[4].EA combined with exercise therapy in the treatment of KOA can inhibit inflammation, relieve pain, and improve joint function.Studies have shown that the degree of pain, joint mobility, and balance function of KOA patients are closely related[5].The balance function of KOA patients can objectively reflect the pain and joint function of patients.This study was to explore the clinical effect of EA combined with exercise therapy on the balance function in patients with KOA through a randomized controlled clinical trial.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
1.1.1 Diagnostic criteria in Western medicine
The diagnostic criteria for KOA in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) were adopted[6]:① knee pain for most of the time in the past month;② knee joint osteophyte formation; ③ age ≥40 years old; ④ morning stiffness ≤30 min; ⑤ bone friction sound during joint movement.KOA can be diagnosed if① + ② or ① + ③ + ④ + ⑤ are satisfied.
1.1.2 Diagnostic criteria in TCM
The diagnostic criteria in theDiagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicinewere adopted[7]: at the initial onset, vague pain in the knee joints, accompanied by stiffness or unfavorable flexion and extension, which can be relieved by light activities and aggravated by climatic changes, or recurrently prolonged and unresolved; insidious onset with slow development,mostly seen in the middle-aged and senior patients;joints may be accompanied by topical swelling, and the friction sensation is obvious when the joints are moving,and a popping or clicking sound can be heard in joints.In severe cases, muscle atrophy of the lower limbs and deformity of the knee joints can be seen; imaging tests such as X-ray or MRI often indicate osteoporosis, may be accompanied by irregular joint surfaces, narrow joint spaces, sclerosis of the subchondral bone of the joints,marginal labial changes, or bony encumbrances;detection of anti-“O” blood sedimentation, C-reactive protein, and rheumatoid factor in the peripheral venous blood to exclude rheumatoid, rheumatism, and other diseases.
1.2 Inclusion criteria[8]
Met the above Chinese and Western medicine diagnostic criteria for KOA; aged 40-75 years; agreed and signed the informed consent form; had not used Chinese or Western medicines and other therapies related to the treatment of KOA in the last 1 month;with early-to-mid-stage KOA, i.e., joint function gradeⅡ or Ⅲ (ACR criterion), or osteoarthritic radiological condition grades 1-3 (Kellgren-Lawrence grading).
1.3 Exclusion criteria
People with acute knee injuries, knee tuberculosis, or knee tumor; those with obvious knee deformity; those with a history of vascular and nerve damage to the affected limb; those with serious diseases of the heart,liver, brain, kidney, or blood system; those with psychiatric disorders; pregnant or breastfeeding women.
1.4 Criteria for dropout and elimination[9]
Those who did not complete the full treatment sessions for various reasons; those who consumed calcium-containing agents during the treatment period;those who did not follow the clinical trial’s regulations or did not follow the doctor’s instructions on daily life,which prevented an accurate judgment of the efficacy of the treatment; and those who underwent other treatments during the treatment period.
1.5 Statistical methods
Data were put into SPSS version 26.0 software for analysis.Measurement data conforming to normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), andt-test was used for comparisons between groups; those not conforming were expressed as median (lower quartile, upper quartile) [M (QL, QU)],and rank-sum test was used for comparisons between groups.Count data were expressed as the number of cases or percentages, and the Chi-square test was used for comparisons between groups.Two-factor repeatedmeasures analysis of variance was used when the repeated-measures data conformed to normal distribution and fulfilled the assumption of spherical symmetry; if the data did not conform to normal distribution, the Scheirer-Ray-Hare test was used; if the assumption of spherical symmetry was not fulfilled, the Greenhouse-Geisser corrected test was used.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
1.6 General data
This clinical trial was conducted by randomized grouping and blinded evaluation of the results.The enrolled cases were derived from inpatients and outpatients of the Department of Rehabilitation of Longhua Hospital Tianshan Branch, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Shanghai Changning Tianshan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital)between August 2020 and August 2022.A total of 70 patients who met the inclusion criteria were collected and randomly divided into a treatment group and a control group according to the order of consultation,with 35 cases in each group.Two cases in the control group withdrew during the study, and 68 cases were finally included in the statistics, including 35 cases in the treatment group and 33 cases in the control group.The trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Changning Tianshan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Approval No.2020TSKY05, Approval Date: 23 July 2020).The trial procedure is shown in Figure 1.
The gender, age, height, body mass, and disease duration of the two groups of cases were statistically analyzed, and the differences between the groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05).There was no statistically significant difference in the joint function grading and radiological condition grading of osteoarthritis between the two groups before treatment.The above results indicated that the two groups were comparable.See Table 1-Table 3 for details.
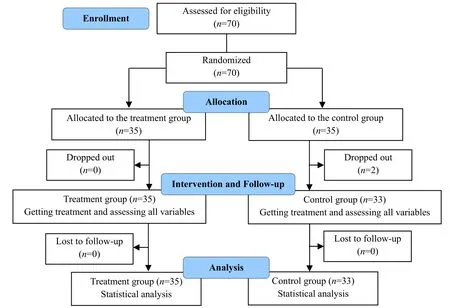
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study
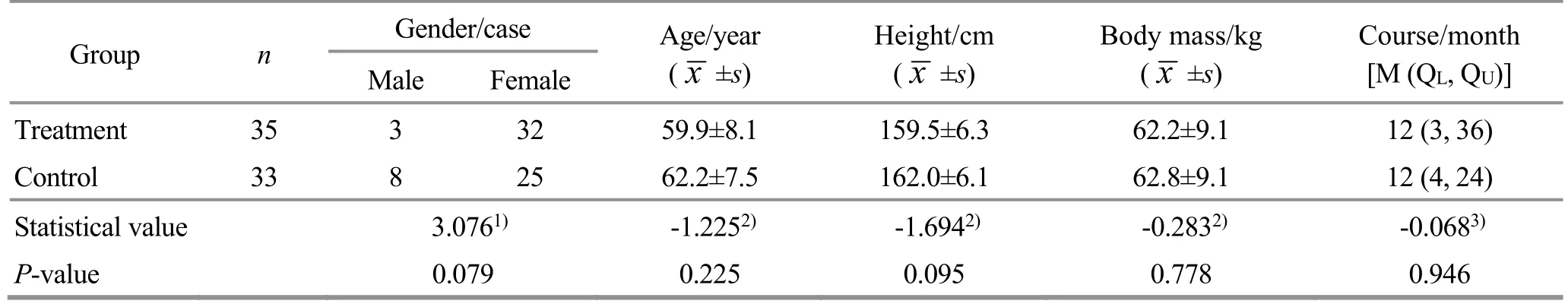
Table 1 Comparison of the general data of patients between the two groups
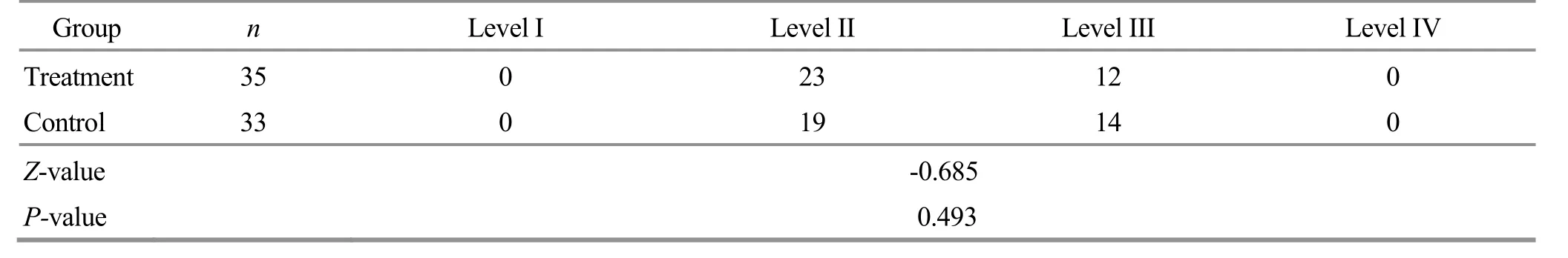
Table 2 Comparison of the joint function grading between the two groups before treatment Unit: case
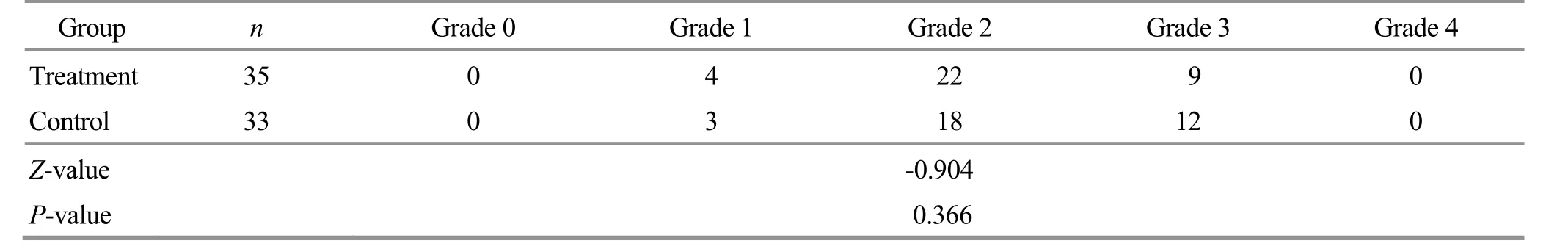
Table 3 Comparison of the radiographic condition grading of osteoarthritis between the two groups before treatment Unit: case
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Treatment group
2.1.1 EA therapy
Points: Dubi (ST35) on the affected side, Neixiyan(EX-LE4), Xuehai (SP10), Liangqiu (ST34), Yanglingquan(GB34), and Zusanli (ST36).
Methods: The positioning of the points consulted theNames and Positioning of Acupoints(GB12346-2006)[10].The patient took the supine position.After routine local disinfection of the acupuncture points, according to the operation method ofScience of Acupuncture and Moxibustion[11], acupuncture needles of 0.25 mm in diameter and 50 mm in length were selected and inserted perpendicularly for 15-40 mm.After the arrival of the needling sensation (Deqi), the G6805-2 EA instrument was connected to Dubi (ST35) and Neixiyan(EX-LE4) as a pair, and Xuehai (SP10) and Liangqiu (ST34)as a pair.The continuous wave was selected, with a frequency of 2 Hz and width of 0.5 ms, and the current intensity was the maximum intensity that the patient could tolerate.The needles were removed after 20 min of treatment.The treatment was carried out 3 times a week (an interval of 1-2 d between two sessions),continuously for 4 weeks for a total of 12 sessions.
2.1.2 Exercise therapy
The therapeutic exercise focused on muscle strength training and joint range of motion training[12-14].
Muscle strength training included quadriceps femoris muscle strength training and adductor muscle strength training.
Isometric training for the quadriceps femoris: Took a supine position.Started with straight leg raises.Extended the knee joint, lifted the affected limb,maintaining an angle of approximately 30° with the bed surface, continued to raise the affected limb by 30-40 cm with the toes pointing upward, and contracted the posterior quadriceps femoris,maintaining the position, holding for over 5 s, and relaxing for 5 s.Then, proceeded to leg extension training.Extended the knee joint, dorsiflexed the ankle joint, and tightened the quadriceps femoris with the patella keeping stable, holding for over 5 s and relaxing for 5 s.
Isotonic training for the quadriceps femoris in a sitting position: Took a sitting position.Bent the knee joint of the affected limb and dorsiflexed the ankle joint rapidly, holding for over 5 s, and then relaxed the knee joint and slowly retracted.Bent the knee by 90°, let the lower leg hang down, and gradually increased the weight on the dorsum of the foot from 5 kg to 10 kg,and lifted the weight while extending, holding for over 5 s and relaxing for 5 s.
Adductor muscle training: Took a supine position.Instructed the patient to flex the knee by 20° and placed a soft pillow about 20 cm thick under the popliteal fossa.Let the patient gradually extend the knee joint and exert maximum force to press down on the soft pillow, holding for over 5 s each time and relaxing for 5 s.
Knee joint range of motion training: The patient lay supine and practiced the movement as if pedalling a stationary bicycle within a pain-free and tolerable range,30 s each time, with a rest for 10 s.
The above exercises were performed 3 times a week,approximately 20 min each time (20 repetitions for each movement), continuously for 4 weeks for a total of 12 sessions.
2.2 Control group
The control group used the same exercise therapy as the treatment group, and the frequency and course of exercise were the same as in the treatment group.
3 Observation of the Therapeutic Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
3.1.1 Balance test[15-17]
The balance feedback training instrument (Pro-Kin254P balance testing system, Tecnobody Company,Italy) was used to measure the balance at 4 time points:before the first treatment, after 1 session of treatment,after 12 sessions of treatment, and at the 1-month follow-up[4].
The 4 lock blocks of the system were placed under the balance plate and fixed.The static and dynamic balance assessment module was selected for standing static stability test.The patient stood on the balance board with their shoes off and on the center of the force table symmetrically.The second toes of both feet were directly opposite lines A2 and A8 of the balance board, the heels together and close to lines A1 and A5,and the highest point of bilateral arches was located on axes A3 and A7.The patient’s upper limbs naturally hung down, and they looked straight ahead with the chest straight up.Patients should try their best to maintain an upright and stable posture.Tests with open and closed eyes were conducted 3 times each, and the balance indexes were recorded accordingly.It included the mean center of pressure in the X-axis [C.O.P(x)], the mean center of pressure in the Y-axis [C.O.P(y)], the standard deviation in the anteroposterior direction(SDofap), the standard deviation in the transverse direction (SDofla), the mean velocity in the anteroposterior direction (ASofap), the mean velocity in the transverse direction (ASofla), the area of the movement ellipse (Area), motor length, Romberg area(Romberg area = Area of eye-closing ellipse ÷ Area of eye-opening ellipse × 100), and Romberg length(Romberg length = Length of eye-closing ellipse ÷Length of eye-opening ellipse × 100).The above test results were averaged over 3 times.Romberg area and Romberg length are the main indicators to comprehensively evaluate the balance function changes.
3.1.2 Assessment of pain level
Visual analog scale (VAS) was used to evaluate the degree of pain[18].Patients rated their pain on a 10-cm scale from 0 to 10, with 0 as no pain and 10 as extreme pain, with higher scores indicating more severe pain.The VAS score was observed and recorded before treatment, after 1 session of treatment, after 12 sessions of treatment, and 1 month after treatment.
3.1.3 Evaluation of knee joint function
With the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis index (WOMAC), the knee joint function was comprehensively evaluated from the aspects of pain, stiffness, and joint function[19-20].There are 24 WOMAC items, with a total score of 96.The higher the score, the worse the function of the knee joint.The score of each item was observed and recorded before treatment, after 1 session of treatment, after 12 sessions of treatment, and 1 month after treatment.
3.2 Criteria for efficacy evaluation
The Nimodipine method was used to calculate the VAS-weighted value[21].VAS-weighted value = (VAS score before treatment - VAS score after treatment) ÷VAS score before treatment × 100%.
Markedly effective: VAS-weighted value ≥50%.
Effective: VAS-weighted value ≥25% but <50%.
Invalid: VAS-weighted value <25%.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
The markedly effective rate of the treatment group was 62.9%, and the total effective rate was 94.3%.The markedly effective rate of the control group was 21.2%,and the total effective rate was 84.9%.There were significant differences in the markedly effective rate and total effective rate between the two groups (P<0.05).See Table 4 for details.
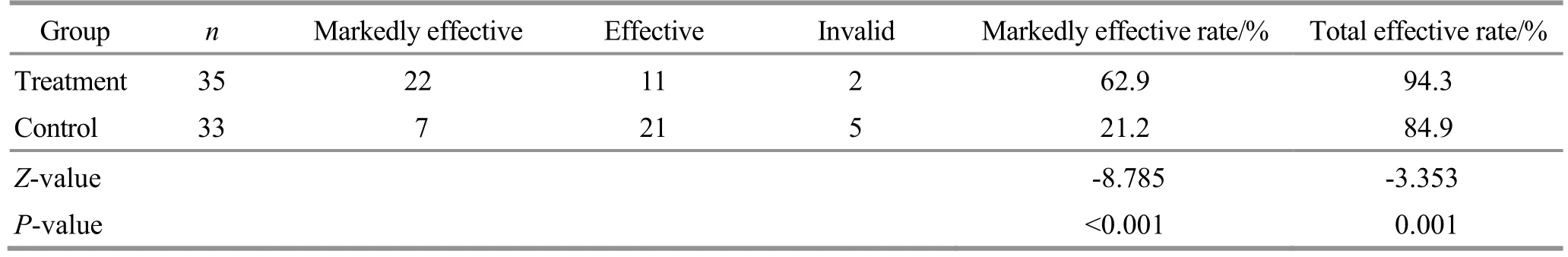
Table 4 Comparison of the clinical efficacy between the two groups Unit: case
3.3.2 Comparison of the balance function parameters
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in the Romberg area and Romberg length between the two groups (P>0.05).The data met spherical symmetry,and the two-factor repeated measurement data analysis of variance was used.There were significant differences in both groups between different time points (P<0.05).After 1 session of treatment, 12 sessions of treatment, and 1 month after treatment, the differences between the two groups were statistically significant (P<0.05).The interaction between intervention and time was statistically significant(P<0.05).See Table 5 and Table 6 for details.
The above results showed that the balance function of the two groups of KOA patients was improved, and the improvement of balance function was more significant by EA combined with exercise therapy.The increase in the number of treatments was positively correlated with the improvement of balance function;that is, the balance function was gradually improved with the increase in the treatment sessions.
3.3.3 Comparison of the VAS score
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in the VAS score between the two groups (P>0.05).The data met spherical symmetry, and the two-factor repeated measurement data analysis of variance was used.There were significant differences in the VAS score in both groups between different time points(P<0.05).There were statistically significant differences in the VAS score between the two groups after 1 session of treatment, 12 sessions of treatment, and 1 month after treatment (P<0.05).The interaction between intervention and time was statistically significant(P<0.05).See Table 7 for details.
The above results showed that the pain of the two groups of KOA patients was reduced, and the effect of EA combined with exercise therapy was more significant.The increase in the number of treatments was positively correlated with the degree of pain relief; that is, the pain was gradually relieved with the increase in the treatment sessions.
Table 5 Comparison of the Romberg area between the two groups ( ±s)
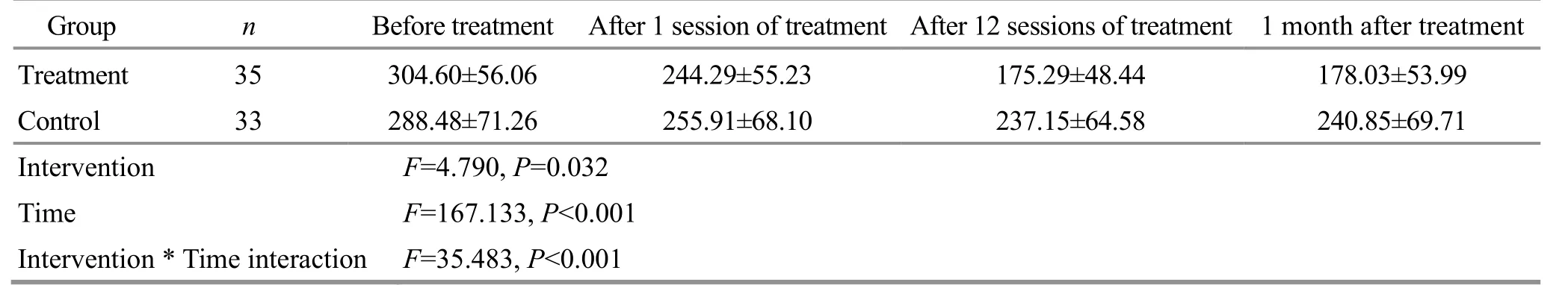
Table 5 Comparison of the Romberg area between the two groups ( ±s)
?
Table 6 Comparison of the Romberg length between the two groups ( ±s)
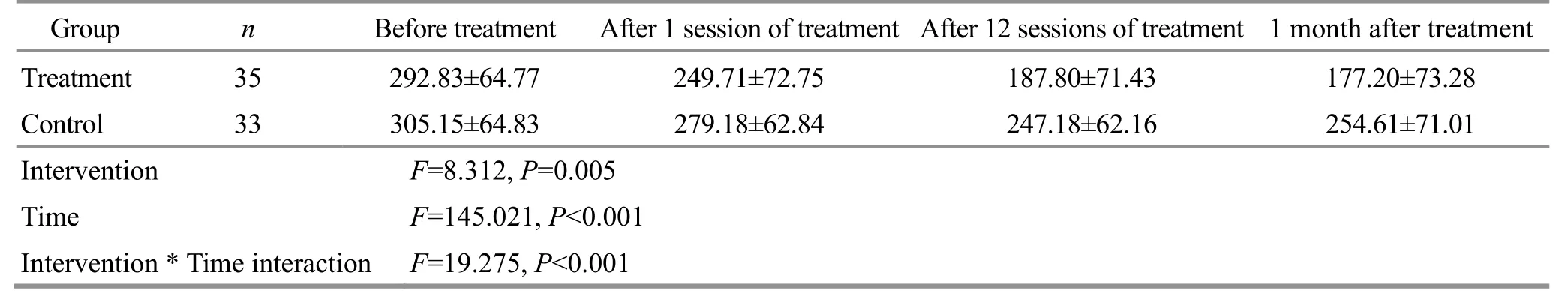
Table 6 Comparison of the Romberg length between the two groups ( ±s)
Group n Before treatment After 1 session of treatment After 12 sessions of treatment 1 month after treatment Treatment 35 292.83±64.77 249.71±72.75 187.80±71.43 177.20±73.28 Control 33 305.15±64.83 279.18±62.84 247.18±62.16 254.61±71.01 Intervention F=8.312, P=0.005 Time F=145.021, P<0.001 Intervention * Time interaction F=19.275, P<0.001
Table 7 Comparison of the VAS score between the two groups ( ±s) Unit: point
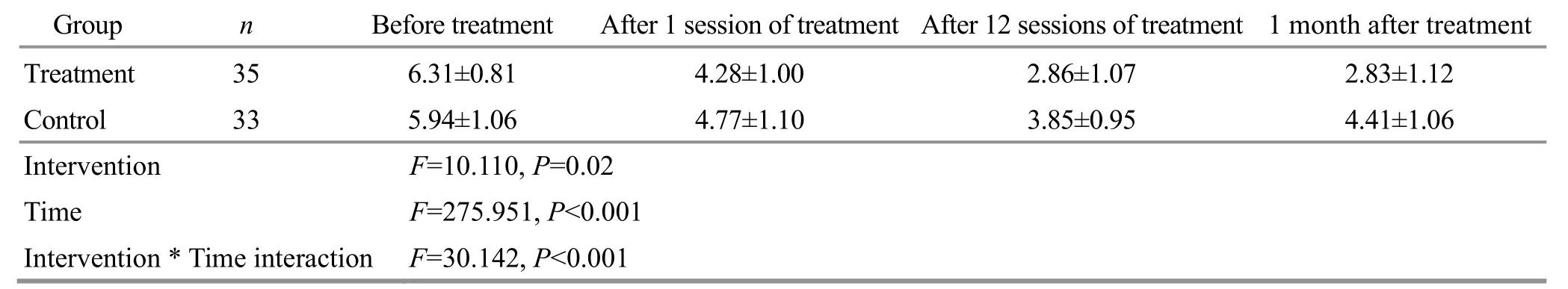
Table 7 Comparison of the VAS score between the two groups ( ±s) Unit: point
Note: VAS=Visual analog scale.
Group n Before treatment After 1 session of treatment After 12 sessions of treatment 1 month after treatment Treatment 35 6.31±0.81 4.28±1.00 2.86±1.07 2.83±1.12 Control 33 5.94±1.06 4.77±1.10 3.85±0.95 4.41±1.06 Intervention F=10.110, P=0.02 Time F=275.951, P<0.001 Intervention * Time interaction F=30.142, P<0.001
3.3.4 Comparison of the WOMAC score
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in the total WOMAC score between the two groups(P>0.05).The data met spherical symmetry, and the two-factor repeated measurement data analysis of variance was used.There were significant differences in the WOMAC total score in both groups between different time points (P<0.05).After 1 session of treatment, 12 sessions of treatment, and 1 month after treatment, there was no significant difference in WOMAC total score between the two groups (P>0.05).The interaction between intervention and time was statistically significant (P<0.05).See Table 8 for details.
The above results showed that the joint function of the two groups of KOA patients was improved, and the increase in the number of treatments was positively correlated with the improvement of joint function; that is, the joint function gradually improved with the increase in the treatment sessions.However, the improvement of joint function was similar between the two treatment protocols.
Table 8 Comparison of the WOMAC total score between the two groups ( ±s) Unit: point
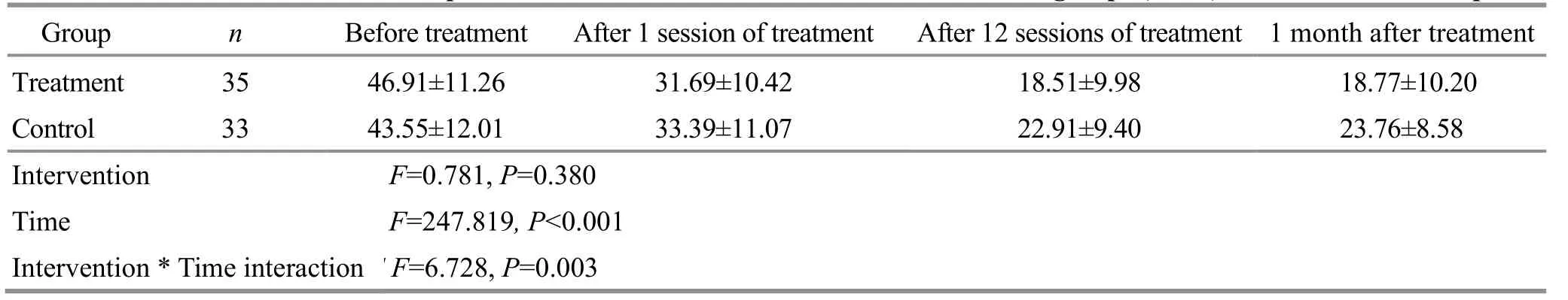
Table 8 Comparison of the WOMAC total score between the two groups ( ±s) Unit: point
Note: WOMAC=Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis index.
Group n Before treatment After 1 session of treatment After 12 sessions of treatment 1 month after treatment Treatment 35 46.91±11.26 31.69±10.42 18.51±9.98 18.77±10.20 Control 33 43.55±12.01 33.39±11.07 22.91±9.40 23.76±8.58 Intervention F=0.781, P=0.380 Time F=247.819, P<0.001 Intervention * Time interaction F=6.728, P=0.003
4 Discussion
KOA belongs to the category of “Bi-impediment syndrome”, “bone Bi-impediment”, and “knee Biimpediment” in TCM.In the later stage, the joint function is limited, muscle atrophy and weakness occur,and the manifestations are more like Wei-flaccidity syndrome.Therefore, the clinical manifestations of KOA involve both Bi-impediment and Wei-flaccidity, mainly pain and joint function limitation[22].Therefore, relieving pain and improving joint function have become the main goals of rehabilitation treatment for KOA.
In this study, points near the diseased site of the knee joint were selected to stimulate directly the diseased area.The knee is the house of sinew.Yanglingquan(GB34) is the tendon influential point of the eight influential points and can treat various diseases of the knee joint.Zusanli (ST36) and Liangqiu (ST34) are the He-sea point and Xi-cleft point of the Stomach Meridian of Foot Yangming, respectively.The use of both has the function of tonifying Qi and nourishing blood, and the Stomach Meridian of Foot Yangming is used to moisten the tendon, regulate the bone, and lubricate the joint.Dubi (ST35) and Neixiyan (EX-LE4) have the effect of dispersing wind and cold.Xuehai (SP10) has both tendon-relaxing and pain-relieving functions.The combination of all points can unblock meridians,promote blood circulation, and relieve pain.
EA stimulates points with micro-current close to human bioelectricity.EA has the effects of unblocking meridians, harmonizing Yin and Yang, and reinforcing healthy Qi to eliminate pathogenic factors, and can remove inflammation, improve circulation, and relieve pain[23-24].For pain caused by Qi and blood deficiency and meridian blockage, EA has a definite curative effect,fast onset, and few adverse reactions[23-24].The research of CHEN W,et al[25]has shown that acupuncturemoxibustion combined with isokinetic muscle strength training has a better effect on cold-dampness KOA patients.The exercise therapy used is recommended by theGuidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoarthritis(2018 Edition)[26]to maintain and improve the knee joint function of KOA patients.Therefore, the treatment group in this trial was treated with EA plus exercise therapy.
Studies[27-28]have shown that KOA can impair proprioception and cause a decline in the patients’balance function, thereby increasing the risk of falls.The proprioception of the knee joint is formed by the integration of afferent signals from muscles, tendons,joint capsules, ligaments, menisci, articular cartilage,and skin receptors located around the knee joint.After being processed in different centers, the signals are efferent through reflex responses and muscle tension regulation circuits.The decreased proprioceptive afferent ability of the knee joint will lead to decreased joint stability, loss of joint movement control, and abnormal gait[29].The balance function of the human body depends on the control of the central nervous system and is coordinated by the sensory system and the motor system.Problems in any of these links can cause a decline in balance.Patients with KOA have balance disorders due to lower limb pain, muscle weakness, decreased proprioception, and reduced range of motion of the joint[27-28].
Previous studies on balance function have shown that changes in balance function can objectively reflect changes in pain and joint function in KOA patients[5,30].Studies on balance ability at home and abroad have suggested that evaluating postural stability through dynamic and static balance posture maps can effectively evaluate balance ability[30-31].The measurement of dynamic and static balance posturography is simple and reliable to provide a basis for the quantitative study of clinical balance ability.Therefore, the Pro-Kin254P balance test system was used in this study to accurately evaluate the static balance function of KOA patients.The results show that EA combined with exercise therapy can effectively improve the balance function of KOA patients, relieve pain, and improve joint function,and the total effect is better than that of exercise therapy alone.Pain and joint function can affect the patients’ balance function.After pain relief and joint function improvement, the balance function will be improved accordingly.Analysis of the reasons shows that EA has advantages in eliminating inflammation,improving circulation, and relieving pain.Exercise therapy is good at improving joint motor function.Therefore, the combination of the two can improve the pain and joint movement limitation in KOA patients to the greatest extent, improve muscle strength and muscle activity coordination around the knee joint,improve the body control ability and trunk stability, and finally regulate the balance function.In conclusion, EA combined with exercise therapy can effectively improve balance function in the treatment of KOA and thus can be used as a rehabilitation program for KOA.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (上海市卫生健康委员会中医药科研项目,No.2020LP012); Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Changning District Health Commission (上海市长宁区卫生健康委员会科研课题, No.20194Z006); Cultivation Project of TCM Dominant Diseases of Shanghai [上海市中医优势病种培育项目, No.ZY(2018-2020)-ZYBZ-24];Project of Shanghai Changning District Science and Technology Commission (上海市长宁区科学技术委员会科研项目, No.CNKW2020Y25).
Statement of Informed Consent
This trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Changning Tianshan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Approval No.2020TSKY05).Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 3 March 2023/Accepted: 28 July 2023
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Study on the mechanism of herb cake-partitioned moxibustion inhibiting tumor growth in colitis-associated colorectal cancer based on KDM4D receptor
- Effects of electroacupuncture on gut microbiota and related inflammatory factors in rats with Crohn disease
- Effects of Tuina static training on vascular endothelial cell dysfunction and adiponectin in obese rats
- Effects of warming triple needling plus Chinese medication on inflammatory responses and daily functioning ability in knee osteoarthritis patients
- Clinical observation of kidney-tonifying and mindcalming acupuncture therapy in the treatment of perimenopausal insomnia
- Clinical study of electroacupuncture improving sleep electroencephalogram and event-related potential in patients with somatoform disorders
