Study on the mechanism of action of Feng-Liao-Chang-Wei-Kang combined with 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of colitis-associated colon cancer
2023-12-29WANGQianruZHONGLifanHUANGLing
WANG Qian-ru, ZHONG Li-fan, HUANG Ling
1.Hainan Province Key Laboratory for Drug Preclinical Study of Pharmacology and Toxicology Research, Haikou 570100, China
2.Key Laboratory of Hainan Trauma and Disaster Rescue, Haikou 570100, China
3.Hainan Research Center for Drug Safety Evaluation, Hainan Medical College, Haikou 57119, China
4.School of Pharmaceutical Sciences Hainan Medical University, Haikou 57119, China
Keywords:Colitis-associated colon cancer Feng-Liao-Chang-Wei-Kang 5-fluorouracil IL-6/STAT3
ABSTRACT
1.Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer in the world, and its incidence and mortality rate are increasing year by year[1].Colitis-associated colorectal cancer develops from active colitis, and the incidence of colitis-associated colon cancer increases with the severity of colitis, the duration of disease, and the extent of colonic damage[2, 3].
5-Fluorouracil is a chemotherapy drug used clinically to treat colorectal cancer, breast cancer, stomach cancer and other cancers[4,5].However, 5-fluorouracil is prone to adverse reactions and drug resistance due to its obvious first pass effect[6, 7].Therefore,5-fluorouracil is often given in combination with other drugs to enhance the therapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer.FLCWK is composed of bullwort and horsetail, and contains many chemical components such as flavonoids and alkaloids, which have anti-ulcerative colitis, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects [8, 9].In clinical practice, it is mainly used for the treatment of colitis and irritable bowel syndrome, etc[9, 10].
The group found that FLCWK can inhibit the proliferation of colon cancer cells and promote apoptosis by inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 pathway potentiated by 5-fluorouracil.In this study, we used a mouse model of colitis-associated colon cancer to observe the lesions of colon tissue in mice with colitis-associated colon cancer after drug administration and to investigate the effect of coadministration on the IL-6/STAT3 pathway.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Main reagents
FLCWK granules purchased from Haikou Pharmaceutical Factory Co.5-Fluorouracil injection purchased from Shanghai Xudong Haipu Pharmaceutical Co.IL-6, IL-1β, STAT3, P-STAT3 antibodies purchased from Cell Signaling Technology.Cyclin D1, CDK4,Bax, Bcl-2, β-actin antibodies purchased from Abcam.Protein concentration assay kit and ECL luminescence kit were purchased from Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.
2.2 Experimental animals
100 4-6 weeks old BALB/c mice, male, purchased from Haislake Laboratory Animal Co.License No.SCXK(Shanghai)2017-0005.
2.3 Grouping and drug administration
One hundred mice were randomly divided into five groups: 10 mice in the blank control group, 30 mice in the AOM/DSS model group, and 20 mice in the FLCWK (4 g/kg), 5-FU (24 mg/kg) and 5-FU (24 mg/kg) + FLCWK (4 g/kg) combination administration groups.The FLCWK group and the co-administration group started gavage injection of FLCWK solution from the 1st day of modeling;the 5-FU group and the co-administration group started tail vein injection of 5-FU one week before the 1st day of modeling, with 1 injection on 1 for a total of 7 times.
2.4 Establishment of an animal model of colitis-associated colon cancer
At the beginning of modeling, saline was injected intraperitoneally into the blank control group, and 12.5 mg/kg AOM was injected intraperitoneally into the AOM/DSS model group, FLCWK group,5-FU group, and 5-FU+FLCWK combination administration group.One week later, in addition to the blank control group, the other groups of mice consumed drinking water containing 2.5% DSS for one week and normal drinking water for two weeks, and this was repeated for three cycles to establish a mouse model of colitis-related colon cancer(see Figure 1).At the end of modeling, the mice were executed, the cecum was taken to the anal area, and the colonic tissue was cut along the longitudinal direction, and the feces was cleaned with saline to observe the intestinal lining tumor lesions.Then part of the colon was taken and fixed in 4% neutral formaldehyde, and the rest of the tissue was stored at -80 ℃ for subsequent protein detection tests.
2.5 General observation of mice
During the feeding period, we observed and recorded the diet,mental, hair and activity status of each group of mice every 2 d,and observed the disease activity index (DAI), colon length, tumor formation rate, and tumor size changes of mice.Disease activity index (DAI) in mice = (weight loss fraction + stool trait fraction +blood in stool fraction)/3.

Tab1 DAI scoring criteria
2.6 Western blot detection of IL-6/STAT3 pathway-related protein expression in mouse colon tissue
The protein was extracted and the BCA protein was quantified and then sampled.The concentrated gel is at a constant pressure of 90 V and the separated gel is at a constant pressure of 120 V.When the sample migrates to the bottom, the target protein region gel is cut off and the filter paper, gel and PVDF are sandwiched to form a sandwich for membrane transfer.After rotating the membrane at a constant flow of 200 mA for 1 hour, the PVDF membrane was removed and placed in 5% skim milk powder or BSA for 2 h to close the membrane.After washing the membrane 3 times with TBST, the primary antibody was added and incubated overnight at 4°C.The film was washed 3 times with TBST, the secondary antibody was added and incubated for 1.5 h.The film was washed 3 times with TBST and then developed.
2.7 Histopathological changes in the colon observed by HE staining
The fixed colonic tissues were dehydrated, embedded and sectioned, and the slides were baked overnight in a 60 ℃ oven for staining: xylene dewaxing, ethanol immersion, hematoxylin staining, hydrochloric acid fractionation, eosin staining, dehydration,transparency, and neutral gum sealing.
2.8 Statistical Methods
The experimental data were analyzed using the statistical analysis software SPSS 26.0 and Graph Pad Prism 8.0, and the results were expressed as mean ± standard error (Means ± SEM), and the experimental data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (Oneway ANOVA), and P < 0.05 indicated that the differences were statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Effect of FLCWK combined with 5-FU on the status of mice
As shown in Figure 1, during the period of drinking DSS, the mice lost weight significantly, reduced activity, and serious blood in stool and diarrhea; when the DSS was replaced with normal drinking water, these symptoms gradually subsided, and the weight gradually returned to normal.In the third drinking water stage, the body weight of mice increased, and after the tail vein injection of 5-FU, the body weight of mice in both the 5-FU group and the co-administered group decreased, while the mice in the FLCWK group showed good mental status and less symptoms.The disease activity index (DAI)increased significantly in all groups of mice except the blank group during DSS consumption, and the DAI decreased gradually after replacing DSS with normal drinking water.
After modeling with AOM/DSS, the mice were executed on day 70, the cecum was taken to the anal area, the colonic tissue was cut along the longitudinal direction, the feces was washed with saline,the length of the colon was measured and the size of the tumor was observed.As shown in Figure 2, the colon wall of mice in the blank group was permeable and no tumor was observed; in the model group, all mice were tumor-bearing, the intestinal wall was thickened, multiple tumors were clearly observed and the length of the colon was significantly shortened (P < 0.01); compared with the model group, the colon length of mice in the FLCWK, 5-FU and co-administered groups increased significantly (P < 0.01), and all tumors were formed but a significant decrease in the number of tumors and smaller tumor size was observed compared with the model group.
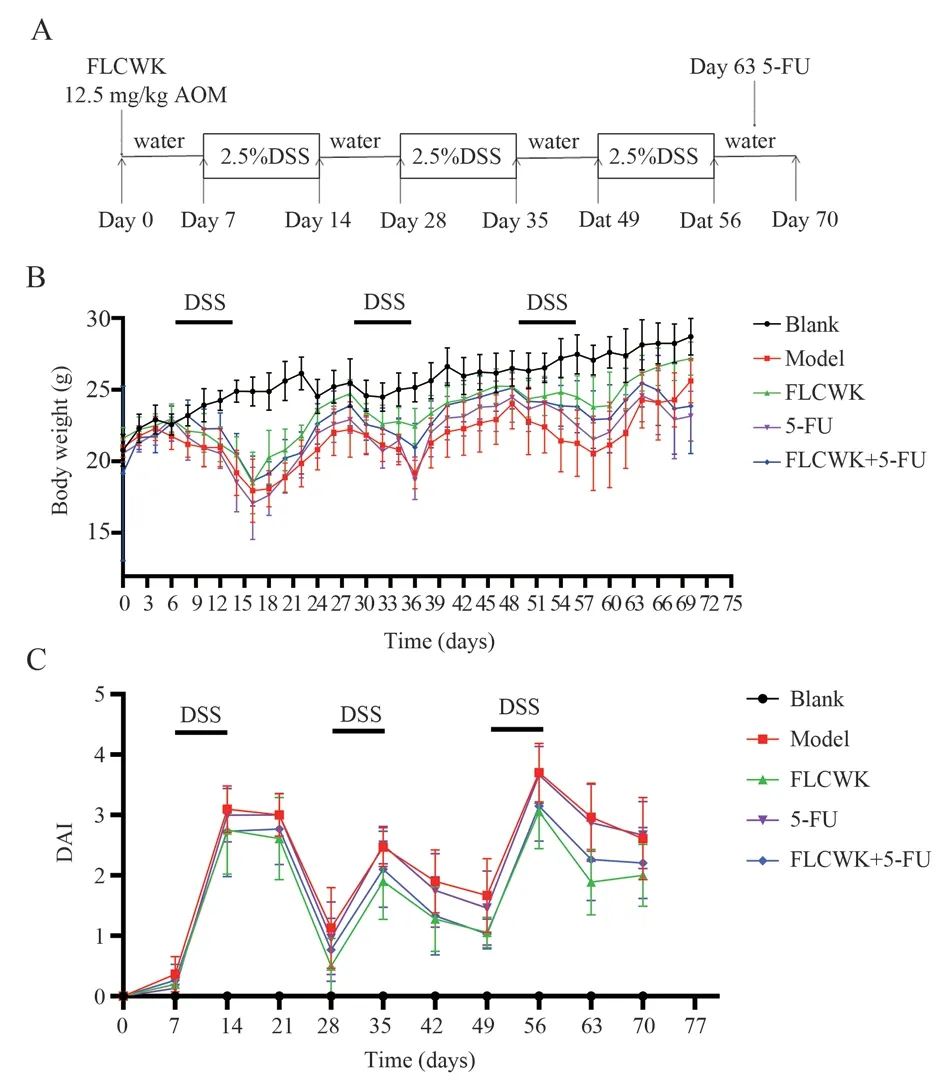
Fig 1 Changes in body weight and DAI of mice in each group after modeling

Fig 2 Colonic length of mice in each group after modeling
3.2 Effect of FLCWK combined with 5-FU on the survival rate of mice
As shown in Figure 3, the highest mortality rate was observed in the model group during the first DSS drinking period, with nearly 1/3 of the mice dying; during the second DSS drinking period, there was no mortality in all groups; and during the third DSS drinking period, there was mortality in all groups.The survival rate of mice in the FLCWK and 5-FU groups was significantly higher than that in the model group, and the survival rate of mice in the co-administered group was higher than that in the FLCWK and 5-FU groups.
3.3 Effect of FLCWK combined with 5-FU on IL-6/STAT3 pathway-related proteins
As shown in Figure 4, the expression of P-STAT3, IL-6, and IL-1β protein was significantly increased in the model group of mice after modeling with AOM/DSS; the expression of P-STAT3, IL-6,and IL-1β was significantly and significantly decreased after coadministration of FLCWK and 5-FU compared with the model group (P < 0.01).STAT3 expression was not significantly different after modeling and drug administration.The experimental results showed that FLCWK combined with 5-FU administration could more effectively inhibit the expression of P-STAT3, IL-6 and IL-1β.
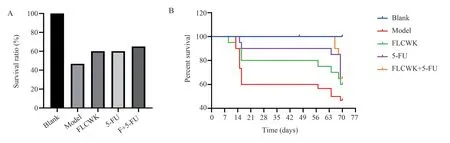
Fig 3 Survival rate of mice in each group
As shown in Figure 5, the expression of Cyclin D1, CDK4, and Bcl-2 increased and the expression of Bax decreased significantly after modeling with AOM/DSS.FLCWK combined with 5-FU administration significantly decreased the expression of Cyclin D1 and CDK4 (P < 0.01) and upregulated the expression of Bax (P <0.01).
3.4 Effect of FLCWK combined with 5-FU on colon pathology in mice
As shown in Figure 6, the cells in the blank control group were neatly arranged without inflammatory cell infiltration.The model group could observe multiple polyp-like and nodular masses on the surface of the colon, irregular arrangement of cup-shaped cells,altered crypt structure, enlarged nuclei, common nuclear divisions,large aggregation of basal lymphocytes, and thickening of the intestinal wall, which met the diagnostic criteria of colitis-associated colon cancer.In the FLCWK and 5-FU administration groups alone,the cell arrangement was neater and the inflammatory cell infiltration was reduced compared with the model group; in the combined administration group, the cell arrangement was significantly neater and the inflammatory infiltration was significantly reduced.
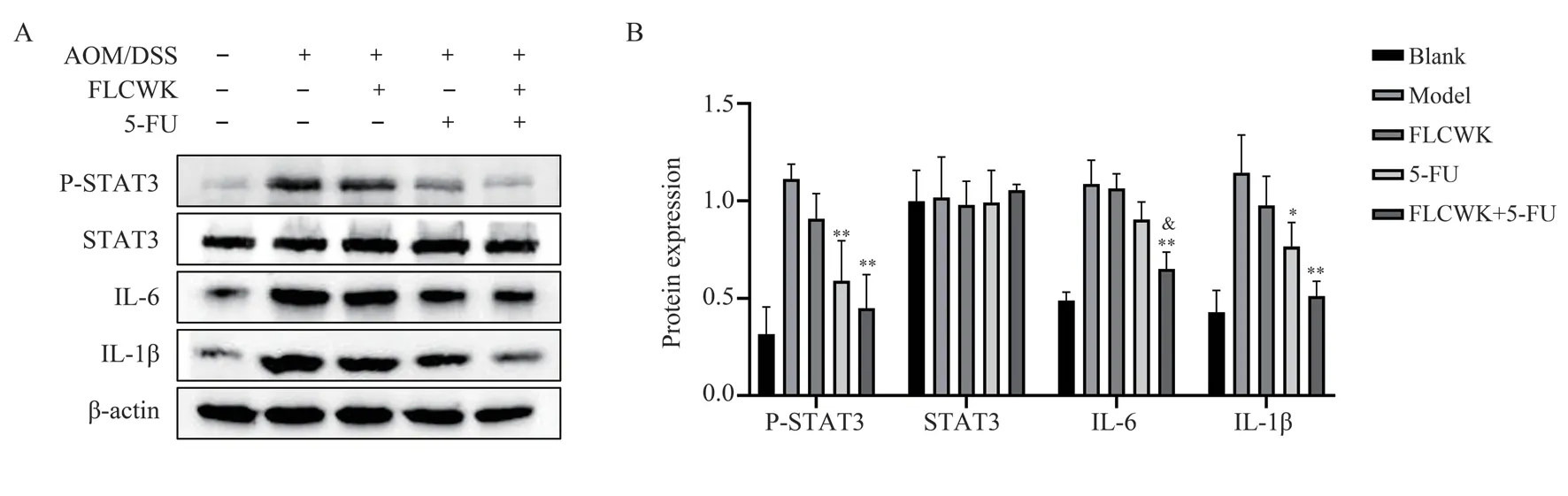
Fig 4 Western blot detection of colonic P-STAT3, STAT3, IL-6, IL-1β expression in CACC mice
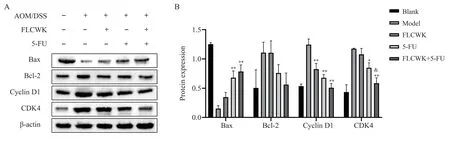
Fig 5 Western blot detection of colonic Bax, Bcl-2, Cyclin D1, CDK4 expression in CACC mice
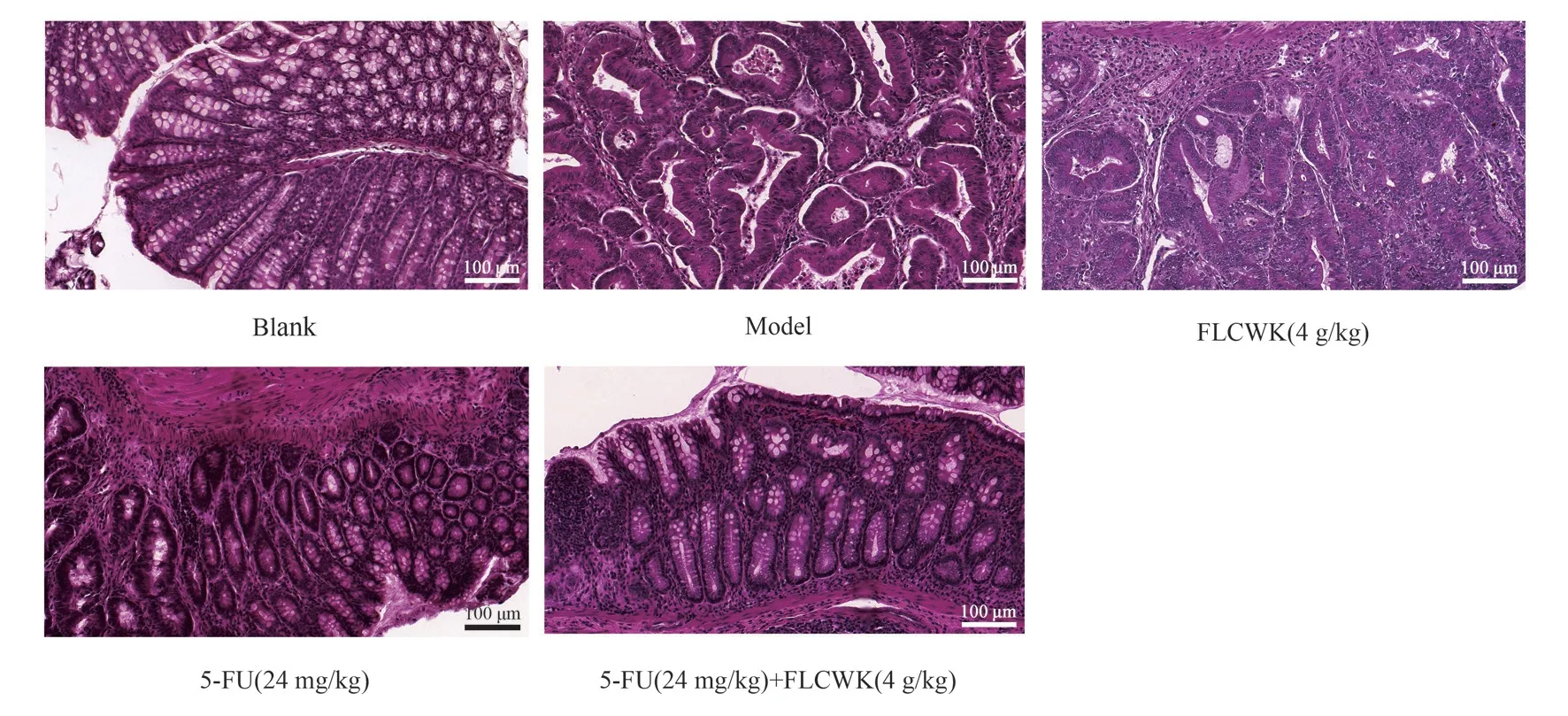
Fig 6 Schematic diagram of HE staining in each group of mice(×200) (Scale bar 100 μm)
4.Discussion
The incidence of colon cancer is high and the mortality rate is high,and the probability of colon cancer in young people is increasing year by year, so the search for effective drugs and targets to treat colon cancer has become a hot topic of current research[11].The development of colon cancer is associated with multiple signal transduction pathways, among which IL-6/STAT3 is a classical one.Activation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway will lead to the development of cell proliferation and promote the development of cancer[12].
It has been shown that abnormal activation of the IL-6/STAT3 pathway is associated with overexpression of CyclinD1, Bcl-2,etc., leading to excessive proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis in tumor cells[13].Bcl-2 and Bax cells play an important role in apoptosis[14].Bax forms a heterodimer with Bcl-2 and inhibits apoptosis when the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio decreases[15-17].Cyclin D1 and CDK4 are involved in tumor cell genesis and development, and abnormal cell proliferation caused by dysregulation of cytokinesis is one of the hallmark features of tumors.The progression from one step of the cell cycle to the next is controlled by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)[18].When stimulated, cell cycle protein D interacts with CDK4[19].In tumor cells, activation of CDK4 and Cyclin D1 causes cells to divide all the time and promotes tumor growth[20].
In this experiment, we used a mouse model of colitis-associated colon cancer to observe the therapeutic effects of FLCWK combined with 5-FU administration on mice.The results showed that FLCWK combined with 5-FU administration significantly increased the survival rate and reduced the intestinal wall thickening and interstitial inflammation in mice.FLCWK combined with 5-FU can inhibit the phosphorylation of STAT3, inhibit the expression of IL-6 and IL-1β; meanwhile, it can inhibit the expression of Cyclin D1,CDK4, Bcl-2 and up-regulate the expression of Bax.
In conclusion, a mouse model of colitis-associated colon cancer was established using oxazomethane/dextran sodium sulfate (AOM/DSS), HE staining was used to observe the changes in mouse colon cases, and Western blot was used to detect the expression of IL-6/STAT3 pathway-related proteins.It was found that FLCWK combined with 5-FU could inhibit the IL-6/STAT3 pathway to exert an inhibitory effect on colitis-associated colon cancer
Statement of Interest
All authors of this article declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Authors’ contributions
Wang Qianru: design experiments, conduct experiments, analyze data, write papers; Zhong Lifan: design experiments, revise papers;Huang Ling: provide research ideas, guide paper writing and revision.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Isoliquiritigenin regulated ox-LDL through activating the PPAR-γ signaling pathway to stabilize atherosclerosis plaques
- Inhibitory effect of water soluble propolis on oxidative damage in rats with ulcerative colitis
- Effect of hepatocyte growth factor on inflammatory factors associated with CCL4-induced hepatocyte injury
- The expression of TUSC3 in Preeclampsia and the function in trophoblast cell
- Effects of intravenous infusion of esketamine on analgesia and postpartum antidepressant after cesarean section
- Expression and significance of ADAM12 in bladder cancer
