Recent Progress on Fabrication of Thermal Conductive Aluminum Nitride Fibers
2023-12-28SHENZhuoer沈卓尔RENSongGECanZHAOHaoyue赵浩阅HANMengyao韩梦瑶FANGJian
SHEN Zhuoer(沈卓尔), REN Song(任 松), GE Can(葛 灿), ZHAO Haoyue(赵浩阅),HAN Mengyao(韩梦瑶), FANG Jian(方 剑)
College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215021, China
Abstract:Among nitride fibers, aluminum nitride (AlN) fibers have been developed for various advanced applications due to their mechanical flexibility, high thermal conductivity, and excellent electrical insulation and chemical stability. This article presents an overview on the recent progress of AlN fibers. The properties of AlN, particularly the thermal conductivity of AlN in polymer matrix composites are introduced. Afterward, two major approaches, carbothermal reduction and nitriding polycrystalline alumina fiber, for the preparation of AlN fibers are discussed. The carbothermal reduction includes electrospinning, solution blow spinning, and chemical vapor deposition. Furthermore, some perspectives on the future directions for the preparation and application of fibrous AlN are highlighted. This review is expected to provide readers with valuable guidance on the preparation of AlN fibers and inspire researchers to explore more potential applications.
Key words:aluminum nitride fiber; thermal conductivity; carbothermal reduction; nitriding polycrystalline alumina fiber
0 Introduction
As a group of thermal stable materials, flexible ceramic fibers not only have the advantages of high-temperature oxidation resistance, excellent corrosion resistance, high strength and stiffness, and high specific modulus but also overcome the problems of the fragility of traditional ceramic materials[1]. Ceramic fibers normally have high strength retention in oxidizing or other harmful gas atmospheres and can meet the requirements of processing and application[2-3]. Due to the remarkable properties of ceramic fibers, they have been widely used in the fields of thermal insulation[4-6], air filtration[7-8], water treatment[9-11], sound absorption[12],etc.
He examined them all, lifted them up and smelled them, and said at last: This jam seems good, weigh me four ounces of it, my good woman; and even if it s a quarter of a pound I won t stick at it
Ceramic fibers can be divided into oxide fibers, carbide fibers, nitride fibers, and other ceramic fibers according to their chemical composition. Oxide fibers such as silica (SiO2) fibers, alumina (Al2O3) fibers, zirconia (ZrO2) fibers, titania (TiO2) fibers and zinc oxide (ZnO) fibers have been extensively studied for their high mechanical strength, low thermal conductivity, good electrical insulation and chemical stability. For carbide fibers, silicon carbide (SiC) fiber is one of the most widely used fibers. Nitride fibers usually refer to silicon nitride (Si3N4), aluminum nitride (AlN) and boron nitride (BN) fibers.
But what was still more curious, whoever held his finger in the smoke of thekitchen-pot, immediately smelt all the dishes that were cooking on everyhearth in the city--this, you see, was something quite different from therose.
Benefiting from the high thermal conductivity (about 320 W/(m·K))[13], AlN particles are commonly used to form thermal conductive paths within composite structures. However, compared with AlN particles, AlN fibers have significantly reduced amounts of material interfaces under the same volume[14], which effectively overcomes the thermal barrier between different materials, resulting in better thermal conductivity in power electrical and electronic applications. Besides, due to high electrical resistance (>1014Ω·cm)[15-16], large energy bandgap (about 6.2 eV), and low thermal expansion coefficient (3.2×10-6/K), AlN fibers are expected to be used in the field of heat dissipation in flexible electronic packaging materials for communication, military, and energy storage systems[17-22], fabrication of piezoelectric energy harvesters in micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS)[23],etc.
SBS is an effective fiber fabrication process using two concentric needles. The center needle is loaded with the spinning solution extruded at a constant speed, and the outer needle delivers the pressurized gas flowing around the polymer solution, carries and drafts the droplets. Before reaching the collector, the solvent evaporates, and the fibers are formed[49]. Figure 3 shows the methods related to the SBS process. The detailed process is divided into two steps: spinning the solution into Al-precursor fibers through SBS and nitridation at high temperature to obtain inorganic AlN nanofibers (Fig.3(a))[50]. In comparison with the electrospinning technique, fibers fabricated from the SBS process can be deposited onto both planar and nonplanar substrates without using high-voltage power. Meanwhile, SBS is an efficient technique, and its deposition rate is approximately ten times faster than that of electrospinning[51]. SBS has a similar working mechanism to industrial methods, such as melt spinning or dry spinning. Hence, it is possible to adapt this technique in high throughput fiber production.
Clemente played an important part in the Pirate s sweep of the double header that day and helped lead his team to a World Series victory over my Yankees that October
1 Properties of AlN
AlN has a hexagonal wurtzite structure and two kinds of cubic structure[24]. Hexagonal AlN is the most common and stable one[25]. Pure AlN is bluish-white, usually gray or off-white, and a typical group III-Ⅴ wideband gap semiconductor material. AlN has attracted an increasing amount of interest in the electronic industry in recent years, especially as an electronic packaging material.
The specific parameters and various properties of AlN and other ceramic materials are listed in Table 1[26-29]. Compared with other ceramic materials, AlN has outstanding comprehensive performance and is very suitable as semiconductor substrates and structural packaging materials, with great potential for application in the electronic industry.

Table 1 Comparison of properties for several ceramics
1.1 Thermal conductivity of AlN in polymer matrix composites
PMCs with combined properties can be produced by adding fillers that are intrinsically thermally conductive. The thermal conductivityKof the formed PMCs depends on many factors as schematically shown in Fig.1, such as polymer conductivity, filler conductivity, distribution of filler, filler shape and size, and interfacial bonding between filler and matrix[30-34]. Heterogeneous fillers or hybrid fillers have also been employed to achieve highK[35]. It has been demonstrated that there is a positive synergic effect on the thermal conductivityKof composites when different fillers are combined[36]. Forming a better thermally conductive pathway through the synergistic effect of multiple fillers, much more heat can be transferred between the fillers and the matrix, enhancing theKvalue. Leeetal.[37]found that theKvalue of the composites filled with spherical particles or fibrous fillers was higher than that of the matrix at low or intermediate filler content. Xuetal.[38]also found that using hybrid fillers at a volume ratio of 1∶6 achieved higher thermal conductivity compared to the use of individual filler. The fillers with fibrous shapes are more effective in comparison to spherical and cylindrical fillers, which can be attributed to the reduction of interfacial thermal resistance.
I have always remembered those moments when my father would be spontaneously inspired to write a poem. He would just walk off and lock in, pen to paper. He could turn his already phenomenal vocabulary into music. When I found out that he started writing poetry at age 7, I was amazed. Outside of the original collection of poetry I have, he left behind two books he published on his own.
Among other things, this poor child was forced twice a day to draw water above a mile and a-half off the house, and bring home a pitcher3 full of it.10 One day, as she was at this fountain,11 there came to her a poor woman,12 who begged of her to let her drink.13
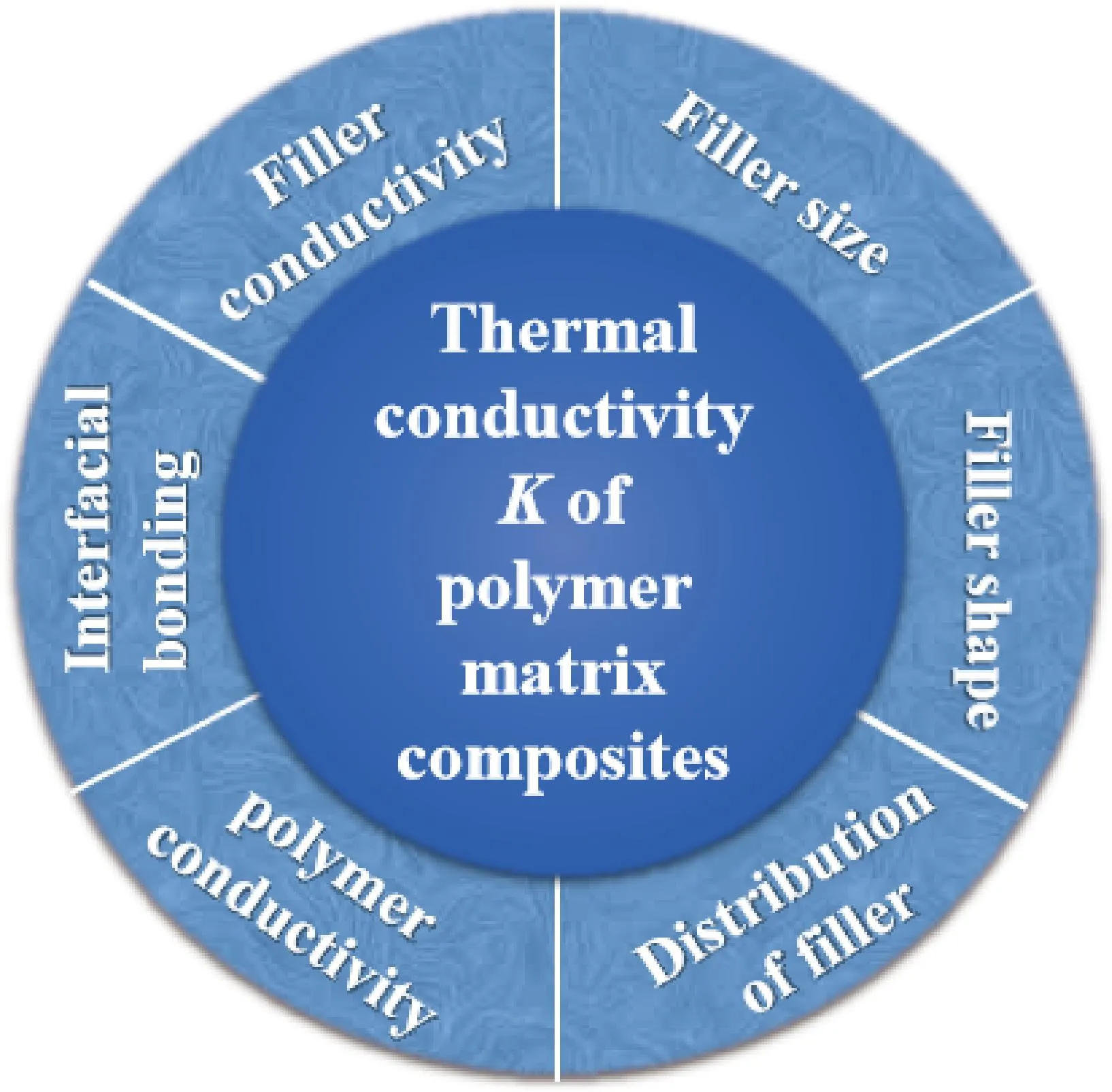
Fig.1 Schematic representation of factors that influence the thermal conductivity of PMCs
SBS is a simple procedure that uses high-speed gas flow as the driving force and does not need a high-voltage electrostatic field, so it has a higher spinning efficiency[5]. In addition, blow-spun fibers can be collected by any type of collector, such as plastic or metal meshes or nonwoven fabrics. Also, SBS can produce both two-dimensional films and webs[6], as well as three-dimensional sponges.
Even though AlN has a goodKvalue, its cost is higher than many other filler materials, so designing and developing composite materials with lower AIN content (<30%), and forming a thermally conductive pathway is the key to obtaining good thermally conductive composites.
1.2 The significance of high thermal conductivity of AlN fibers
I always waited for Jennifer and Amy after classes, so we could walk together to our next class. Amy and Jennifer chatted by Jennifer s desk as Jennifer packed her books up and I waited by the door. Sometimes when they left, they d walk right past me. No Thanks for waiting. No S
杂志排行
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Cleaning of Multi-Source Uncertain Time Series Data Based on PageRank
- Deep Multi-Module Based Language Priors Mitigation Model for Visual Question Answering
- Detection of Residual Yarn in Bobbin Based on Odd Partial Gabor Filter and Multi-Color Space Hierarchical Clustering
- Electromagnetic and Thermal Characteristics of Molybdenite Concentrate in Microwave Field
- Path Planning of UAV by Combing Improved Ant Colony System and Dynamic Window Algorithm
- Robot Positioning Based on Multiple Quick Response Code Landmarks
