Effect of naringin on despair behavior and neuroprotective mechanisms in mouse model of menopausal depression
2023-12-13SUTingWANGLihongYUHaoCUIYueZHANGNingZHAODepingXUHongdanLEIXia
SU Ting, WANG Li-hong, YU Hao, CUI Yue, ZHANG Ning, ZHAO De-ping, XU Hong-dan, LEI Xia,2✉
1.School of Pharmacy, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, China
2.Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Wuxi, Wuxi 214071, China
3.Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, China
4.Wuxi Health Higher Vocational and Technical School, Wuxi 214071, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the effect of naringin on hippocampus estrogen receptor and neuronal cell apoptosis in a mouse model of menopausal depression.Methods: The menopausal depression model was replicated by bilateral ovariectomy (OVX) combined with chronic unpredictable mild stimulation (CUMS), 54 female Kunming mice were randomly divided into Blank group, Model group (OVX+CUMS group), Sham operation group (SHAM group), Estradiol group (E2 group 20.090 mg·Kg-1·d-1), Naringin group (100 mg·Kg-1·d-1),Naringin+ICI182780 group (100 mg·Kg-1·d-1+0.075 mg·Kg-1·d-1), each group of 9 mice were administered for 21 consecutive days.The depression-like behaviour changes of each group of mice were observed by tail suspension and forced swimming experiments; The morphological changes of hippocampal neurons were observed by HE staining; Immunohistochemical method was used to detect the expression of ER and ERβ positive cells in the hippocampus of mice;The expression of ERβ, GluR2, CAMKⅡ, NMDAR1, Bad, Bcl-2 and Caspase3 proteins in the hippocampus of the mice was detected by western blot.Results: Compared with the Blank group, the immobility time of the mice in the OVX+CUMS group was significantly increased (P<0.01), mice hippocampal neurons with a sparsely organized cell arrangement,nuclear fixation, the expressions of ERβ, GluR2, and Bcl-2 were decreased (P<0.01,P<0.001), and the expressions of NMDAR1, CAMKⅡ, Bad, and Caspase3 were increased(P<0.05, P<0.01); Compared with the OVX+CUMS group, the immobility time of the mice in the SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group was significantly reduced (P<0.01), mice hippocampal neuronal cells are relatively intact and tightly packed, the expressions of ERβ,GluR2 and Bcl-2 were increased (P<0.01, P<0.05), and the expressions of NMDAR1, CAMKⅡ, Bad and Caspase3 were decreased (P<0.05, P<0.01); Compared with the Naringin group,the quiescent time of the mice in the Naringin+ICI182780 group was increased (P<0.05), the smaller cell body of mouse hippocampal neurons, the expressions of ERβ, GluR2, and Bcl-2 were decreased (P<0.01, P>0.05, P<0.05), and the expressions of NMDAR1, CAMKⅡ, Bad,and Caspase3 were increased (P<0.01, P<0.05).Conclusions: Naringin may reduce neuronal cell excitotoxicity caused by glutamate receptor activation, reduce neuronal cell apoptosis and improve depression-like behavior by activating ERβ receptors in the hippocampus in a mouse model of menopause depression.
1.Introduction
Menopause depression is a mental disorder with low mood, despair and anxiety as the main clinical features, and hippocampal neuronal damage is one of its main pathological features[1].The hippocampal neuronal cells in the brain of postmenopausal women lack the protective effect of estrogen and make it more difficult to cope with stressful events, which is an important cause of susceptibility to depression in postmenopausal women[2].Studies have shown that stress stimulation can cause massive release of glutamate in the prefrontal cortex, causing neuronal excitatory toxic damage,resulting in excessive apoptosis and reduced cell number[3].
Naringin (4,5,7-trihydroxyflavanone-7-rhamnoside) is a widely distributed flavonoids with a high content in bone fragmentation and a phytoestrogen-like structure[4].Jung U J et al.[5] showed that naringin easily crosses the blood-brain barrier and has a strong antiapoptotic effect.Further studies revealed that the anti-apoptotic effect of naringin on neuronal cells was dependent on the activation of the estrogen receptor (Estrogen receptor, ER)[6, 7].So, does naringin act against apoptosis by promoting the expression of ER receptors in the brain of menopausal depression (OVX+CUMS) model? This paper mainly investigated the effects of naringin on the apoptosis of estrogen receptor and neurons in the hippocampus of OVX+CUMS model mice.
2.Materials and methods
2.1Materials
2.1.1 Animals
The SPF class of Kunming mice (female, weight 23±2 g) were purchased from Changsheng Biotechnology Co.LTD, SCXK (Liao)2019-0001.All protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Permit N0.2019-002).Mice were housed and acclimatized five per plastic cage (42×30×27 cm) in standard environmental conditions with a 12:12-h light/dark cycle at (21±1) ℃, 62±2%humidity.They were allowed to have standard rodent pellet food and water ad libitum during the experimental period.
2.1.2 Drugs and primary reagents
Naringin (purity 98%, lot number: B21594), purchased from Shanghai Jinye Biotechnology Co.Ltd.; ICI182780, (lot number:531042), bought from Sigma; Estradiol (purity=98%, lot number:S30633), purchased from source leaf organisms; The BCA protein quantification kit (lot number: 20201ES76), purchased from Yisheng Biotechnology (Shanghai) Co.Ltd.; PVDF membrane and Immobilon Western HRP substrate (lot number: 10600023,WBKLS0100), purchased from Whatman Company; ER , ERβ,GluR2, CAMKⅡ, NMDAR1, β-actin, Goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) (lot number: ab22595, ab22595, ab52180, ab181052,ab17345, ab8227, ab6721), purchased from Abcam Corporation;Bad, Bcl-2, Caspase3 (lot number: BM4241, BA0412, BA2142),purchased from Dr.De Bio; Antibody dilutions (lot number: E-IRR106), purchased from Elabscience.
2.1.3 Primary instrument
Light microscope (model number: BX41, Olympus); Chemical imaging system (model number: A44116, Thermo); Microplate reader (model number: 5187149, Thermo); Horizontal shaking bed (model number: WD9405B, Beijing Liuyi Instrument Factory); Electrophoresis apparatus trophoresis (model number:Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell, The BIO-RAD Corp); Semi-dry transmembrane instrument (model number: Trans-Blot SD Cell,The BIO-RAD Corp); Ultrapure water preparation system (model number: Rsearch UV UF, Shanghai Hetai Company).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Animals grouping
54 mice were randomly divided into 6 groups (n=9), namely Blank group, Model (OVX+CUMS) group, Sham group (SHAM group),Estradiol group (E2 group), Naringin group, and Naringin+ER Blocker (ICI182780) group.
2.2.2 OVX+CUMS model replication and drugs administration
After 7 d of adaptive feeding, mice outside the Blank group were removed for bilateral ovaries according to Yu Feng[8] surgical method.After using 2% isoflurane, an incision was made in the dorsal area to locate the fat around the ovary, pulled out the ovaries, removed the ovary and cut the remaining line, and then sent the uterine horn back in place.Sham surgery was performed as described above, but only equal volume fat masses were cut off.
14 d after the operation, mice from all groups except the Blank group and SHAM group were stimulated according to the stress mode of Yi Wu et al.[9].One stress stimulus was randomly performed each day, but discontinuously using the same stress mode, with continuous stimulation for 21 d.
At the end of 21 d stimulation, the Blank, SHAM and OVX+CUMS groups were infused and received 0.2 mL of distilled water per day, and the E2 group and the Naringin group were intragastrically administered equal volumes of E2 (20.090 mg·Kg-1·d-1) and naringin(100 mg·Kg-1·d-1) every day.In the Naringin+ICI182780 group,ICI182780 (0.075 mg·Kg-1·d-1) was intraperitoneally injected first, and an equal volume of naringin (100 mg·Kg-1·d-1) was intragastrically administered 15 min later.The dose of naringin determined the optimal dose based on the results of previous laboratory studies[10].After 21 d continuous administration, tail suspension was performed on day 22 and forced swimming on day 23.
2.2.3 Behavioral experiments
2.2.3.1 Suspension tail experiment
Each mouse was taped to suspension on the edge of the shelf 58 cm above the table top.Placed approximately 1 cm from the tip of the tail, the suspension was maintained for 6 min, and the rest time was recorded during the last 4 min of the test.The stationary time criterion is that when the mouse is passively and completely stationary, it is regarded as stationary.
2.2.3.2 Forced swimming experiment
The mice were individually placed in a glass-polycarbonate cylinder (height: 25 cm; diameter: 10 cm) filled to a depth of 10 cm with water maintained at 24 ℃ and they were allowed to swim for 6 min, and the durations of immobility were recorded during the last 4 min of the test.Static time judgment standard such as “1.2.3.1”.
2.2.4 Collection of brain tissues
After the behavioral experiment was over, the mice in each group were anesthetized with pentobarbital (80 mg·Kg-1), and an appropriate amount of normal saline was perfused through the heart,and 3 mice in each group continue to perfuse 4% paraformaldehyde through the heart, brain tissue was removed immediately after completion of the perfusion, and divided it into hemibrains along the midline, then washed the surface with normal saline, blotted surface water moisture with filter paper, and weighed.Finally, the brain tissues of 3 mice infused with paraformaldehyde was fixed in 4%paraformaldehyde for 24 h.After isolating the hippocampus of the remaining mice, it was kept at -80 ℃.
2.2.5 Morphological changes in mice hippocampal neurons were visualized by HE staining
After dehydration, embedding, sectioning (thickness: 4 μm) and drying of the mice brain tissue under “1.2.4”, the sections were stained with HE and observed under a microscope.
2.2.6 Positive cell expression of ERα and ERβ in the hippocampus was determined by IHC
Performed immunohistochemical experiments according to the steps of Yun Hailong et al.[11], and incubated after diluting the primary antibody ER (1:200), ERβ (1:200) and secondary antibody HRP (1:500) with antibody diluent in corresponding proportions,and finally used Image J software to analyze and calculate the positive cells in 5 different fields of view for each section.
2.2.7 The protein expression of ERβ, GluR2, CAMKⅡ,NMDAR1, Bad, Bcl-2, and Caspase3 was detected by protein immunoblotting (WB) in the hippocampus
The hippocampus was taken out, and the operations of protein extraction, sample loading, and protein content detection were carried out according to the method of Na Geng[12].After sample loading, electrophoresis, membrane transfer, and antibody incubation, the imaging system was used to develop and image the signal through ECL chemiluminescence detection.Finally, the clear bands were analyzed by Image J software.Used antibody diluent for each antibody according to ERβ (1:200), GluR2 (1:500), CAMKⅡ(1:200), NMDAR1 (1:500), Bad (1:500), Bcl-2 (1:500), Caspase3(1:500), β-actin (1:1000) ratio to dilute the antibody.
2.2.8 Statistical analysis
Data were presented as mean±standard deviation (±s).Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using GraphPad Prism 8.0 and a post hoc test (Bonferroni test) for multiple comparisons.The level of P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Results of the behavioral experiments
3.1.1 Results of suspension tail experiment
Compared with the Blank group, OVX+CUMS mice increased significantly (P<0.01); Compared with OVX+CUMS group,the immobility time of mice in SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group was significantly reduced (P<0.01); Compared with the Naringin group, the immobility time of the mice in the Naringin+ICI182780 group was significantly increased (P<0.05).The results are shown in Fig.1.
3.1.2 Results of the forced swimming experiment
Compared with the Blank group, OVX+CUMS mice increased significantly (P<0.01); Compared with OVX+CUMS group,the immobility time of mice in SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group was significantly reduced (P<0.01); Compared with the Naringin group, the resting time of the mice in the Naringin+ICI182780 group was significantly increased (P<0.05).The results are shown in Fig.2.
3.2 The morphology changes of hippocampal neurons in each group were observed by HE staining
As shown in Fig.3, the hippocampal neuronal cells in the Blank group were normal and closely arranged; In the OVX+CUMS group,the hippocampal neurons had sparsely arranged cells, with cell pyknosis and reduced cell bodies; Compared with the OVX+CUMS group, the hippocampal neuronal cells of SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group mice were intact and relatively closely arranged;The changes of neuron cells in the Naringin+ICI182780 group were similar to those in the OVX+CUMS group, with smaller cell bodies and looser cell arrangements.
3.3 Results of positive cell expression of ERɑ and ERβ in the hippocampus
Compared with the Blank group, OVX+CUMS group mice had decreased expression of ERɑ positive cells, but not statistically significant (P>0.05), and the expression of ERβ positive cells was significantly decreased (P<0.01); Compared with the OVX+CUMS group, the expression of ERɑ positive cells was increased in SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group, but there was no statistical significance (P>0.05), and the expression of ERβ positive cells was significantly increased (P<0.01); Compared with the Naringin group,the expression of ERɑ and ERβ positive cells in the Naringin+ICI182780 group were significantly decreased (P<0.01).The results are shown in Fig.4.
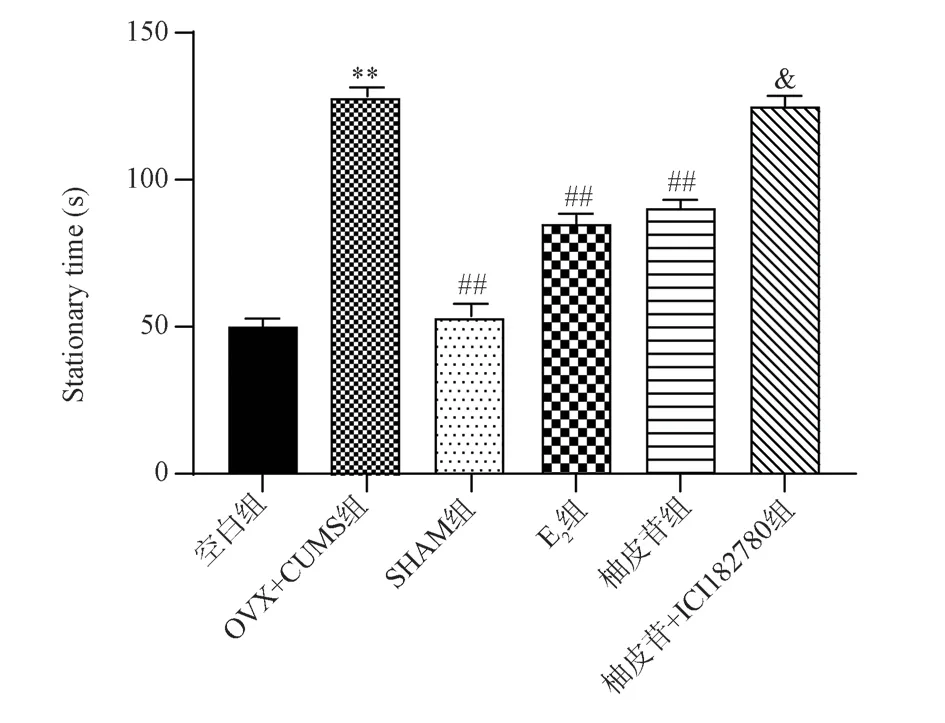
Fig 1 Effect of each group of mice on the suspended tail experiment (±s,n=9)
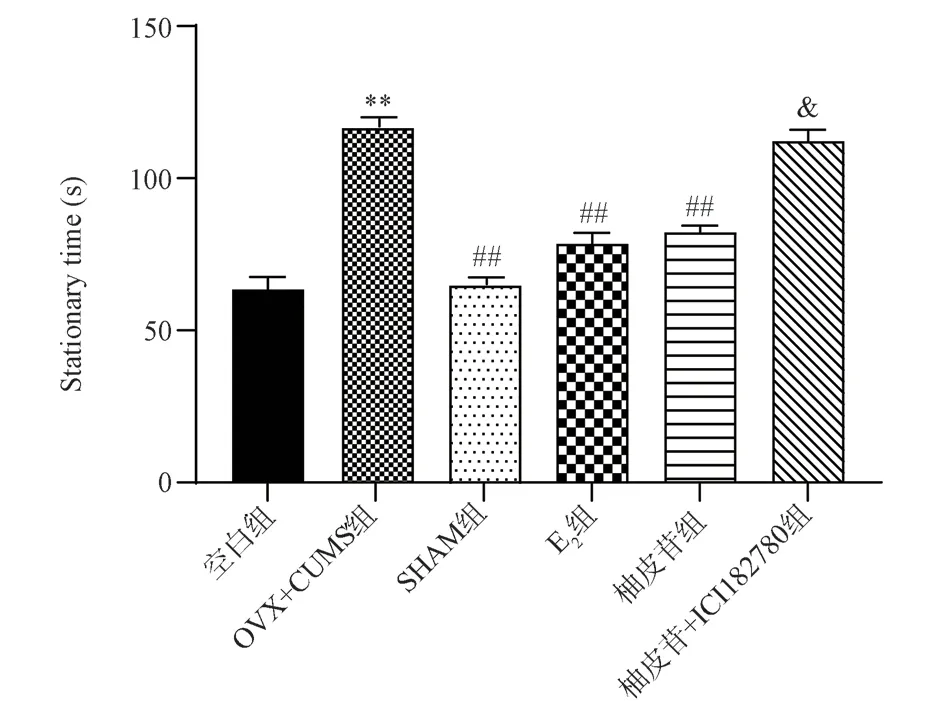
Fig 2 Effect of each group of mice on the forced swim experiment (±s, n=9)

Fig 3 Cell morphological changes of hippocampal neurons in each mouse group (HE, ×100)
As shown in Fig.5, the expression of ERɑ positive cells in the hippocampus of the Blank group of mice were closely arranged;In the OVX+CUMS group, expression of ERɑ positive cells in the hippocampus area decreased, and the nucleus pyknosis; The mice in the SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group had more positive cells in the hippocampus than those in the OVX+CUMS group, and the positive cells were arranged in a slightly orderly manner; The Naringin+ICI182780 group had fewer positive cells in the hippocampus than the Naringin group, and the positive cell morphology was similar to that of the OVX+CUMS group.
3.4 The expression results of ERβ, GluR2, NMDAR1, CAMKⅡ and apoptosis factors Bad, Bcl-2 and Caspase3 in the hippocampus detected by WB
3.4.1 Detection of ERβ expression results in the hippocampus by WB
Fig 4 Effect of positive cell expression of ER and ERβ in the hippocampus of each mouse group (±s, n=3)

Fig 5 Expression of ER protein in each group of mice (immunohistochemical, ×200)
Compared with the Blank group, mice with OVX+CUMS group had significantly lower ERβ expression (P<0.01); Compared with OVX+CUMS group, the expressions of ERβ in SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group were significantly increased (P<0.01);Compared with the Naringin group, the expression of ERβ in the Naringin+ICI182780 group was significantly decreased (P<0.01).The results are shown in Fig.7.
3.4.2 The results of NMDAR1, GluR2, and CAMKⅡexpression in the hippocampus by WB
Compared with the Blank group, the expression of CAMKⅡ in the OVX+CUMS group was significantly increased (P<0.01), the expression of NMDAR1 was significantly increased (P<0.05), and the expression of GluR2 was significantly decreased (P<0.01);Compared with the OVX+CUMS group, the expressions of GluR2 and CAMKⅡ in the SHAM group were significantly increased(P<0.05), the expression of CAMKⅡ in mice in E2 group decreased significantly (P<0.01), the expression of NMDAR1 decreased significantly (P<0.05), and the expression of GluR2 increased significantly (P<0.01), and in the Naringin group, the expression of CAMKⅡ was significantly decreased (P<0.05), the expression of NMDAR1 was significantly decreased (P<0.01), and the expression of GluR2 was significantly increased (P<0.01).Compared with the Naringin group, the expressions of CAMKⅡ and NMDAR1 in the Naringin+ICI182780 group were significantly increased (P<0.05),and the expression of GluR2 was decreased (P>0.05).The results are shown in Fig.8.
Fig 6 Expression of ERβ protein in each group of mice (immunohistochemical, ×200)
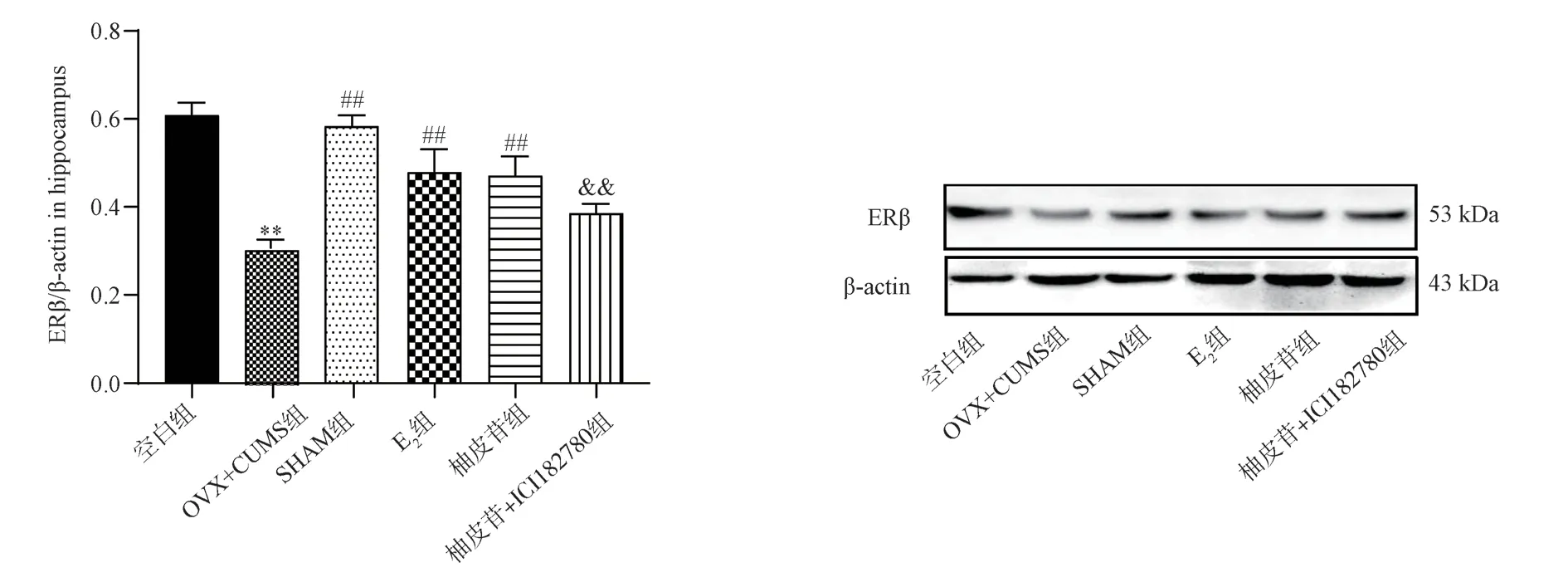
Fig 7 Results of ERβ expression in the hippocampus of each mouse group (±s, n=3)
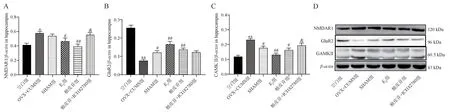
Fig 8 Results of NMDAR1, GluR2, and CAMKⅡ expression in the hippocampus of each mouse group (±s, n=3)
3.4.3 The expression results of the apoptotic factors Bad,Bcl-2 and Caspase3 in the hippocampus by WB
Compared with the Blank group, the expression of Bad and Caspase3 in the OVX+CUMS group was significantly increased(P<0.01), and the expression of Bcl-2 was extremely significantly decreased (P<0.001); Compared with OVX+CUMS group, the expressions of Bad and Caspase3 in SHAM group, E2 group and Naringin group were significantly decreased (P<0.01), and the expression of Bcl-2 was significantly increased (P<0.01); Compared with the Naringin group, the expression of Bad and Caspase3 in the mice in the Naringin+ICI182780 group increased (P<0.01, P<0.05),and the expression of Bcl-2 decreased significantly (P<0.05).The results are shown in Fig.9.

Fig 9 Results of expression of apoptotic factors Bad, Bcl-2 and Caspase3 in the hippocampus of mice in each group (±s, n=3)
4.Discussion
The depression model using OVX combined with CUMS can reasonably simulate the dual pathogenic factors of estrogen withdrawal and stressful stimuli[13].Moreover, the OVX+CUMS model can induce depression-like behavior and typical excessive apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, which is an ideal model in the study of the mechanism of menopausal depression[14, 15].The results of this experiment show that the tail suspension time and swimming still time of the model mice are significantly increased, and the mice develop desperate behavior, which shows that the menopausal depression model mice replicated by the OVX+CUMS method can express the core symptoms of human depression, with states such as decreased willpower or low mood[1, 9].After the intervention of E2 or naringin, the resting time of mice was reduced to varying degrees,indicating that naringin can reduce the despair behavior of mice.Under the action of ER blockers, the recovery effect of naringin on the behavior of model mice was reversed, indicating that ER may be an important target that mediates the effects of naringin.
Glutamate receptors are divided into ionotropic receptors(NMDARs) and metabotropic receptors (mGLuRs)[16].In the depressed state, studies have shown that NMDA receptors mainly regulate the calmodulin/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM/CaMKⅡ) pathway, and the high expression of GluR2 subunit will promote Ca2+influx, and a large amount of influx of Ca2+ will be in the mitochondria rapid deposition in the body, resulting in the loss of mitochondrial function, further increasing the activity of nitric oxide synthase, thereby increasing the synthesis of NO[17-19].Therefore, when neurons contain a large number of ionotropic NMDA receptors, intracellular Ca2+overload will lead to excessive apoptosis of a large number of neurons due to excitotoxicity[20].The loss of synaptic structure, quantity and function of hippocampal neurons is an important reason for depressive-like behavior.This study found that the hippocampal neuron cells of model mice will have changes such as cell body reduction and nuclear pyknosis,and naringin administration can improve the pathological changes in the hippocampus, up-regulate the expression of GluR2 protein,and inhibit the expression of NMDA receptor protein in the hippocampus, down-regulate the expression of CAMKⅡ, thereby reducing cell death due to excitotoxicity.Under the intervention of ER blockers, it was also reversely verified that naringin’s inhibition of glutamate receptor-mediated calcium overload was dependent on ER receptors.
In this paper, by performing a semiquantification of ER and ERβ proteins expression in the hippocampus, and the results found that naringin up-regulated the expression of ERβ protein in the hippocampus of model mice, but had no significant effect on ER , which was consistent with the conclusions reported in the literature[21], suggesting that Naringin mainly activates ERβ in the hippocampus, but not ER (mainly regulates the secretion level of peripheral hormones).Yang Zhang et al.[22] confirmed that ERβ has a protective effect on hippocampal neurons.ERβ activates downstream signals, mainly exerts genomic effects by regulating nuclear translocation, and promotes the synthesis of anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2[7].The continuous activation of the Bcl-2 family and the Caspase3 family can play an anti-apoptotic effect[6], but after animals are repeatedly stimulated, the ratio of Bcl-2/Bad often decreases significantly, which indicates that the cells in the corresponding areas of the brain are excessive apoptosis.However, naringin has anti-apoptotic effect, but its anti-apoptotic effect is significantly reduced under the action of ICI182780, indicating that naringin may reduce excessive apoptosis of neurons by activating ERβ in the hippocampus.
In conclusion, naringin may inhibit neuronal excitotoxicity induced by glutamate receptor activation by activating ERβ in the hippocampus of menopausal depression model mice, reduce apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, and improve despair behavior.
Authors’ Contributions
Ting Su, Hao Yu, Yue Cui, Deping Zhao: Established the model,index detection, Collated and analyzed the data, wrote the paper;Lihong Wang, Ning Zhang, Hongdan Xu: Guided the experiments and revised the paper; Xia Lei: Fund support and reviewed the paper.All authors have no conflict of interest relationship.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Maternal stress exposure during pregnancy impairs ultrastructural changes in the white matter and reduces cognitive function in offspring mice
- Prognostic model and treatment plan analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma based on genes related to glutamine metabolism
- Efficacy and safety of oral Chinese patent medicine combined with sacubitril/valsartan in the treatment of chronic heart failure: A Metaanalysis
- Effect of glycyrrhetinic acid on Th1/Th2 balance in cough variant asthma mice
- Study on pharmacodynamics and mechanism of nano-Kuiyangye in treating radiation esophagitis in rats
- Construction and validation of prognostic model of Cuproptosis-related LncRNA in osteosarcoma
