Effect of glycyrrhetinic acid on Th1/Th2 balance in cough variant asthma mice
2023-12-13CHENQiulingZHOUBeiLIYanlingLINHuiWUYanchunLIUHan
CHEN Qiu-ling, ZHOU Bei, LI Yan-ling, LIN Hui, WU Yan-chun, LIU Han
Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530020, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of Glycyrrhetinic Acid on cough variant asthma(CVA) mice and to investigate the possible mechanism in reducing lung inflammation.Methods: 48 young female Balb/c mice were divided into Control, CVA, Prednisone Acetate,Glycyrrhetinic Acid high-dose, Glycyrrhetinic Acid middle-dose and Glycyrrhetinic Acid lowdose groups randomly, with 8 mice in each group.The CVA mice model was established by ovalbumin (OVA) sensitization and OVA challenge, the animal asthma behavior was observed after drug administration, and the index of the lung of mice were recorded.The level of OVAsIgE in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was tested by ELISA.The pathological changes of the lung tissue were observed by Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining.The protein expressions of T-bet, IFN-γ, Gata3, IL-4 and IL-13 in the lung tissue were determined by Western blot.Results: Compared with the CVA group, the index of lung of mice, the OVA-sIgE level in BALF and expression levels of Th2-related factor in the lung tissue of mice in Prednisone Acetate and Glycyrrhetinic Acid groups were significantly decreased (P<0.05 or P< 0.01), the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lung tissue was reduced, while expressions of Th1-related factor in the lung tissue was significantly increased (P< 0.05 or P<0.01).Conclusion: Glycyrrhetinic acid has therapeutic effect on CVA mice, the underlying mechanism of Glycyrrhetinic acid alleviating lung impairment and airway inflammation may be associated with mediating the Th1/Th2 imbalance in the lung tissue.
1.Introduction
Cough Variant Asthma (CVA) is a special asthma characterized by irritating dry cough, but with no signs and symptoms of typical asthma such as wheezing, shortness of breath and dyspnea[1].It is one of the most common causes of chronic cough in Chinese children[2].CVA is difficult to heal but easy to relapse, and children with CVA have a high probability of developing typical asthma[3].The specific pathogenesis of CVA has not been fully elucidated.Most scholars believe that CVA has abnormal contraction of airway smooth muscle, bronchospasm, and hypersecretion of mucus glands, and its pathological changes are characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness, continuous airway inflammatory and airway remodeling[4], involving a variety of inflammatory cells,inflammatory mediators and cytokines to participate and interact together, mainly with activation and production of T helper cell 2(Th2), Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and eosinophil (Eos)[5-6].In terms of treatment, existing guidelines at home and abroad emphasize that after diagnosis, long-term standardized treatment of classic asthma is followed[7-8].At present, the clinical treatment of CVA is mainly based on glucocorticoids combined with β2 receptor agonists,which can achieve the expected therapeutic effect, but there are also side effects and limitations with long-term use.
Liquorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) is one of the oldest and most commonly used medicines in the world[9], it not only had been recorded in ancient Chinese books, but also recorded in other countries’ ancient books.In China, the use of liquorice as a medicine was first recorded in the “The Sheng Nong’s classic on roots and herbs” of Han Dynasty and was listed as top grade.Liquorice has a good reputation, it had been widely used in treatment of diseases in nervous system, digestive system, respiratory system and cardiovascular system in traditional Chinese medicine.Studies have shown that licorice is the most frequently medicine in TCM prescription in the treatment of CVA[10], there may be indispensable pharmacological effects involved.
Glycyrrhetinic acid (GA, Cas No.471-53-4, Molecular Formula C30H46O4, Fig.1), the key active ingredient of licorice, believed to have anti-inflammation, improved airway remodeling and antitussive effects[11-13].In this study, we established a CVA immature mouse model to evaluate the efficacy of GA and hypothesized the mechanism of GA in treating CVA is related to the regulation of the balance of Th1/Th2, which provided an experimental basis for its further use in CVA.
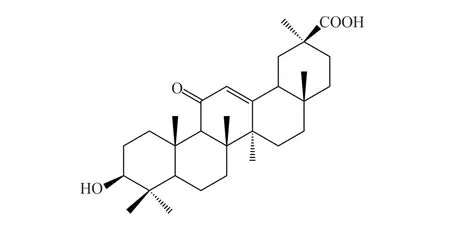
Fig 1 Glycyrrhetinic acid
2.Materials
2.1 Animal
48 BALB/c female mice (4~6 weeks, 14~16 g) were purchased(SJA, Changsha, China) and bred in individually ventilated cages(IVC) at 20~26 ℃ with an humidity of 40~70% under specific pathogen free (SPF) conditions, free access to feed and water on a circadian rhythm of 12 h.The mice were divided into Control, CVA,Prednisone Acetate (P-A), GA high-dose (GA-H), GA middle-dose(GA-M) and GA low-dose (GA-L) groups, with 8 mice in each group.The protocol was approved by Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Institutional Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee(Animal experiment ethics No.DW20220422-160).
2.2 Drug and reagents
GA is purchased from China National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (purity 99.6%, Batch No.110723-201715, Beijing, China).OVA is obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Batch No.SLCB8249;Aluminum hydroxide is obtained from Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, Batch No.20170523; Prednisone acetate tablets is purchased from Zhejiang Xianju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Batch No 201215; OVA-sIgE ELISA kit is purchased from Shanghai Jianglai industrial Limited By Share Ltd., Cat No.: 032210ZF234050324;T-bet (Proteintech, Cat No.: 13700-1-AP); IFN-γ (Abcam, Cat No.: ab171081); Gata3 (Proteintech, Cat No.: 66400-1-Ig); IL-4(Proteintech, Cat No.: 66142-1-Ig); IL-13 (Beyotime Biotech.Inc.,Cat No.: AF7254); β-actin (Bioworld, Cat No.: BS6007M); Goat anti-mouse HRP secondary antibody (Bioworld, Cat No.: BS12478);Goat anti-rabbit HRP secondary antibody (Bioworld, Cat No.:BS13278)
2.3 Instrument
Compression atomizer (Bairui, BRM-085Ⅱ); Bio-rad Powerpac Universal (Bio-rad, PowerPac); Imager (GE, Amersham Imager 800 Fluor system); Microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Biotek Epoch 2); Microscope (Olympus Corporation, BX53).
3.Methods
3.1 Cough Variant Asthma Model Establishment
The CVA mice model was established according to the previous study[14-16].Mice were divided into Control, CVA,Prednisone Acetate (P-A), Glycyrrhetinic Acid high-dose (GA-H),Glycyrrhetinic Acid middle-dose (GA-M) and Glycyrrhetinic Acid low-dose (GA-L) groups randomly, with 8 mice in each group.Aluminum hydroxide gel was prepared by adding aluminum hydroxide to normal saline (NS); OVA was added into the above mentioned gel to obtain the sensitizing agent (OVA: 1 mg/mL,aluminum hydroxide: 20 mg/mL).
After adaptive feeding, except for the Control group, 0.2 mL sensitizing agent were intraperitoneally injected on days 1, 8 and 15 of rhythmic feeding, and the Control group was sensitized with 0.2 mL NS instead.After 22 d, the OVA-sensitized mice were placed in a sealed acrylic container and stimulated to compressed air nebulization of NS containing 3% OVA at a maximum inhalation volume, and this procedure was performed once a day lasting 30 min for 14 d.
3.2 Drug Administration
P-A group were given intragastric administration with 0.2 mL/10 g of P-A tablets (5 mg/kg), GA groups were given intragastric administration with 0.2 mL/10 g of GA (20 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg), the Control group and CVA group were given NS, all administrations were 30 minutes before stimulation and lasting for14 d.
3.3 Asthmatic behavior of mice
30 min after the last challenge, asthmatic behavior of mice in each group were observed and scored[17,18].Asthma behavior in mice can be manifested as: insanity (easily startled, irritable or unresponsiveness, lethargy), shortness of breath, cyanosis of lips,abdominal muscle convulsion, dyspnea (arched back, abdominal breathing), scratching nose, etc.The rating table is shown in Table 1.

Tab 1 Asthmatic behavior rating table
3.4 Calculation of the index of lung
Mice were sacrificed and the weight of body were recorded.The right lung of mice were separated and the weight of the right lung were recorded.The index of lung was calculated.Mouse lung index= weight of right lung (mg)/weight of body (g).
3.5 ELISA
Ligature the right main bronchus, 0.1 mL NS was infused into the left lung and the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was collected for twice.The supernatant were taken for further testing after centrifuging at 4 ℃/2 000 rpm for 5 min.The level of OVA special immunoglobulin (OVA-sIgE) in the BALF was tested in strict accordance with an ELISA kit.The optical density (OD) values were tested with Biotek Epoch 2 reader (BioTek, USA).
3.6 H&E staining
The lower lobe of the right lung were removed and fixed in 4%paraformaldehyde solution.Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining were conducted to observe the pathological changes in lung tissue.
3.7 Western Blot Analysis
The upper lobe of the right lung tissues were homogenized and lysed with RIPA Buffer containing phosphatase inhibitor cocktail and protease inhibitor cocktail.The centrifuged supernatant were then collected and degenerated in loading buffer and boiled for 10 minutes at 100 ℃.About 10 μg degenerated samples were taken for gel electrophoresis.Membranes were blocked with Blocking Buffer for 10 min and incubated for 8-10 h at 4 ℃ with primary Ab against total T-bet (1:500 v/v), IFN-γ (1:2,000 v/v), Gata3 (1:5,000 v/v), IL-4 (1:1,000 v/v), IL-13 (1:1,000 v/v) or β-actin (1:10,000 v/v).Membranes were incubated for 1 hour with secondary Ab (antirabbit or anti-mouse, 1:20,000 v/v).Protein bands were visualized using a super ECL Chemiluminescence plus kit and detected by chemiluminescence using Amersham Imager 800 Fluor system.Densitometry was performed using ImageJ software.
3.8 Statistical analysis
The One-way ANOVA or nonparametric test were performed using Prism 8.0 (GraphPad, San Diego, USA).Data are presented asor median(IQR) obtained from at least three independent tests.P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.P < 0.01 was considered very statistically significant.
4.Results
4.1 Asthma behavioral
30 min after the last challenge, the control group showed almost no asthmatic behavior, the hair of mice was smooth and glossy, the mental state was good, the respiratory rhythm was uniform and stable.
The CVA group showed listlessness, shortness of breath, frequent nose grabbing, impatience, and abnormal behavior such as lethargy and unresponsiveness, the asthmatic behavior score was significantly increased compared with the control group (P< 0.01).
The asthma behavior of mice in the P-A group was alleviated, the mental state is slightly better, the degree of hair disorder is eased, the activity is more frequent, the frequency of nose grabbing is reduced,and the breathing rhythm is eased.Compared with the CVA group,the asthma behavioral scores were significantly decreased (P< 0.01).Compared with the CVA group, the asthma behavior in GA groups were relieved.The mental state was slightly better, the frequency of nose grabbing was reduced, and the respiratory rhythm was eased.Compared with the CVA group, the asthma behavioral scores in GA-H group was significantly decreased (P< 0.05, Table 2).
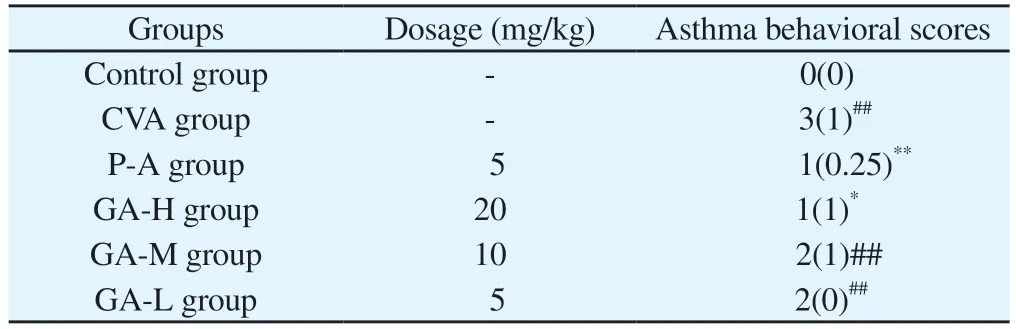
Tab 2 Asthma behavioral scores in mice [n = 8, median(IQR)]
4.2 The index of lung of mice
Compared with the Control group, the index of lung in the CVA group were obviously increased (P < 0.01).After treatment, the levels were declined, and GA-H and GA-M group decreased obviously (P < 0.01) (Table.3).Tab 3 Index of lung (n = 8,±s)
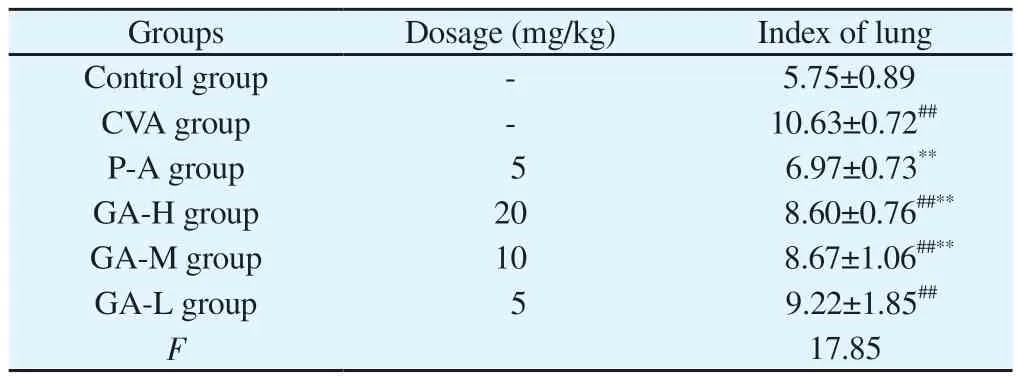
Note: # P<0.05 VS Control group; ## P<0.01 VS Control group; * P<0.05 VS CVA group; ** P<0.01 VS CVA group.
4.3 Level of OVA-sIgE in BALF
The OD value of OVA-sIgE in the CVA group were obviously increased after sensitization by OVA (P < 0.01).After treatment, the expression levels of OVA-sIgE declined, among which GA-H group decreased obviously (P < 0.01) (Table.4).
Tab 4 OVA-sIgE level in BALF, (n = 8, ±s )
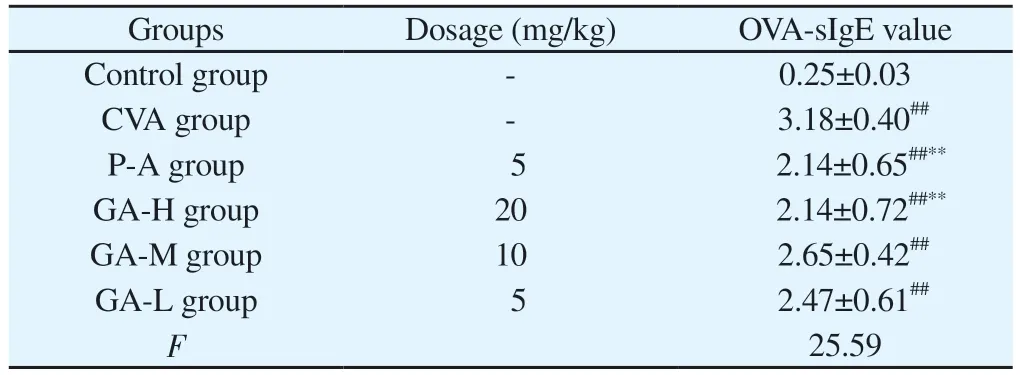
Tab 4 OVA-sIgE level in BALF, (n = 8, ±s )
Note: # P<0.05 VS Control group; ## P<0.01 VS Control group; *, P<0.05 VS CVA group; **, P<0.01 VS CVA group.
Groups Dosage (mg/kg) OVA-sIgE value Control group - 0.25±0.03 CVA group - 3.18±0.40##P-A group 5 2.14±0.65##**GA-H group 20 2.14±0.72##**GA-M group 10 2.65±0.42##GA-L group 5 2.47±0.61##F 25.59
4.4 Histopathological Changes in Lung Tissues
The results of H&E staining showed that in the Control group,the structure of lung tissue were clear, the alveolar epithelium were smooth, almost no inflammatory cell infiltration were found in the lung of the mice.After OVA sensitization, the lung tissue had irregular structure, inflammatory secretions were seen in the alveolar cavity, and the inflammatory foci in some areas merged into pieces in the CVA group.After administration, the inflammatory response were less severe in comparison with the CVA group (Fig.2.).
4.5 Protein Expressions of T-bet, IFN-γ, Gata3, IL-4 and IL-13 in Lung Tissue
After OVA sensitization, the Th2 related protein expressions of Gata3, IL-4 and IL-13 in the CVA group were all significantly increased (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01).After treatment, the protein expressions of Th2 related cytokines were all decreased, among which Gata3 in GA-L group was significantly decreased (P < 0.01),IL-4 in GA-H group was significantly decreased (P < 0.05).IL-13 in GA-M and GA-L group were significantly decreased (P < 0.05).
After OVA sensitization, the expression of IFN-γ, the Th1 related protein, was decreased in the CVA group compare with the Control group (P < 0.01).After treatment, the IFN-γ protein expressions in GA groups were all increased, and GA-H group was increased significantly (P < 0.05).
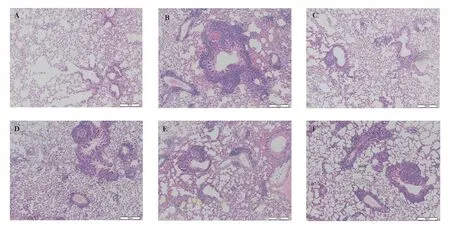
Fig 2 H&E staining results in each group ( 100 × )
Tab 5 Protein expressions of Th1/Th2 related factors (n = 3-5, ±s)
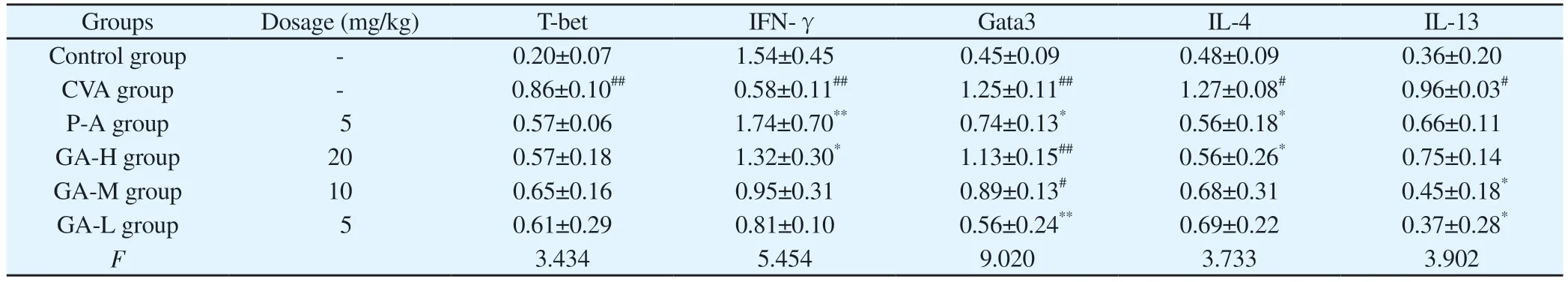
Tab 5 Protein expressions of Th1/Th2 related factors (n = 3-5, ±s)
Note: # P<0.05 VS Control group; ## P<0.01 VS Control group; * P<0.05 VS CVA group; ** P<0.01 VS CVA group.
Groups Dosage (mg/kg) T-bet IFN-γ Gata3 IL-4 IL-13 Control group - 0.20±0.07 1.54±0.45 0.45±0.09 0.48±0.09 0.36±0.20 CVA group - 0.86±0.10## 0.58±0.11## 1.25±0.11## 1.27±0.08# 0.96±0.03#P-A group 5 0.57±0.06 1.74±0.70** 0.74±0.13* 0.56±0.18* 0.66±0.11 GA-H group 20 0.57±0.18 1.32±0.30* 1.13±0.15## 0.56±0.26* 0.75±0.14 GA-M group 10 0.65±0.16 0.95±0.31 0.89±0.13# 0.68±0.31 0.45±0.18*GA-L group 5 0.61±0.29 0.81±0.10 0.56±0.24** 0.69±0.22 0.37±0.28*F 3.434 5.454 9.020 3.733 3.902

Fig 3 WB bands of lung tissue
5.Discussion
CVA is a specific type of asthma in which irritating dry cough is the sole or primary clinical manifestation.At present, the pathogenesis of CVA is still unclear.Since the pathological changes are similar to those of classic asthma, CVA is considered to be one of the varying stages or progression of asthma and is suggested to have a longterm standardized treatment following the classic asthma method.Since CVA patients are mostly children and adolescents who are in a golden stage of physical growth and development, their unique physiological and pathological features bring challenges to the diagnosis, treatment, medication safety, and the maintenance of normal lung function and development.At present, many mature chemical drugs have good curative effect in the treatment of asthma,but there are still some disadvantages such as excessive systemic side effects and high cost.
In traditional medicine system, natural medicines and natural ingredients play important roles in prevention and treatment of diseases, some of which may have good anti-asthma effects with few side effects.In this study, the therapeutic effects of glycyrrhetinic acid on CVA mice and the mechanism of Th1/Th2 balance were studied.
The OVA-induced model is characterized by a Th2 response[19],which can provide a Th2 cell effector functions to explore possible Th1 and Th2 imbalance mechanisms.To this end, we established an OVA-sensitized mice and studied the expressions of Th1 and Th2 in lung tissue to explore the mechanism.Our results show that after OVA stimulation, the asthma behavioral scores, the index of the lung,the inflammatory cells, the OVA-sIgE level in BALF and protein expression level of Th2-related factors GATA-3, IL-4 and IL-13 significantly increased in lung tissue, and Th1-related factors IFN-γ significantly decreased in lung tissue.After treatment, GA relieved the asthma behavioral, decreased the index of the lung, reduced inflammatory cell infiltration, reduced bronchial mucus secretion caused by CVA, and reduced the level of OVA-sIgE in BALF.The protein expression of Th2-related factors in lung were significantly decreased and Th1-related factors was increased.Studies has shown that Th1/Th2 imbalance exists in children with asthma, and the level of IFN-γ in patients is decreased while the level of IL-4 is increased[20], and the ratio of Th1/Th2 cell in peripheral blood was decreased[21].Studies has shown that once the Th1/Th2 immune response is unbalanced, a large number of cytokines can be secreted,causing abnormal immune responses.The low function of Th1 cells and the dominant differentiation of Th2 cells in respiratory system can lead to asthma.The characteristic cytokine IL-4 secreted by Th2 cells can induce IgE to produce eosinophils and aggregate in the tracheal, leading to chronic airway inflammation[22].The another cytokine IL-13 secreted by Th2 cells can aggravate asthma by promoting mucus secretion and exacerbating airway hyperreactivity[23].As a characteristic cytokine of Th1, IFN-γ can enhance the response of Th1 cells and reduce chronic inflammation.When Th2 is hyperactive, the function of Th1 is down-regulated[23].In conclusion, GA might have some therapeutic effects on CVA,the mechanism might be associated with the regulation of Th1 and Th2 immune imbalance in lung tissue.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effect of naringin on despair behavior and neuroprotective mechanisms in mouse model of menopausal depression
- Maternal stress exposure during pregnancy impairs ultrastructural changes in the white matter and reduces cognitive function in offspring mice
- Prognostic model and treatment plan analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma based on genes related to glutamine metabolism
- Efficacy and safety of oral Chinese patent medicine combined with sacubitril/valsartan in the treatment of chronic heart failure: A Metaanalysis
- Study on pharmacodynamics and mechanism of nano-Kuiyangye in treating radiation esophagitis in rats
- Construction and validation of prognostic model of Cuproptosis-related LncRNA in osteosarcoma
