一种进境抗药性杂草
2023-11-20左然玲冯黎霞虞赟李盼畔牟桂萍印丽萍
左然玲 冯黎霞 虞赟 李盼畔 牟桂萍 印丽萍

左然玲,冯黎霞,虞 赟,等. 一种进境抗药性杂草——东方大蒜芥(Sisymbrium orientale L.)[J]. 杂草学报,2023,41(2):1-5.
doi:10.19588/j.issn.1003-935X.2023.02.0001
摘要:東方大蒜芥(Sisymbrium orientale L.)是十字花科大蒜芥属杂草,与作物争夺资源,影响作物产量,其植株影响作物收割,种子可影响小麦的等级评定;对磺酰脲、咪唑酮和三唑吡啶类除草剂具有抗药性,且具有交叉抗性,大大增加了防治成本。2019年至今,我国多次在进境粮谷中检出该种杂草种子,表明东方大蒜芥可随粮谷贸易长距离传播。应加强粮谷的过筛及筛下物的挑拣,提升检疫鉴定能力,增加相关进口粮谷加工企业周边的环境监测和后续监管工作。
关键词:东方大蒜芥;抗药性;检疫;杂草防治
中图分类号:S451 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1003-935X(2023)02-0001-05
An Invasive Herbicide-Resistant Weed—Sisymbrium orientale L.
ZUO Ran-ling1,FEN Li-xia2,YU yun3,LI Pan-pan2,MOU Gui-ping1,YIN Li-ping4
(1.Technology Center of Huangpu Customs,Guangzhou 510535,China;
2.Technology Center of Guangzhou Customs,Guangzhou 510623,China;
3.Technology Center of Fuzhou Customs,Fuzhou 350003,China;
4.Technology Center of Shanghai Customs,Shanghai 200137,China)
Abstract:Sisymbrium orientale L.,belongs to Sisymbrium in Bricaceae,competes with crops for resources,and affects crop yield. Its plant also affects the harvest of crops,and its seed affects the grade estimation of wheat. It is resistant to sulfonylurea,imidazolone and triazopyridine herbicides,and has cross-resistance,which greatly increases the control cost. Since 2019,the seed of S. orientale were often detected in imported grains. It indicated that S. orientale could spread long distances with grains trade. It is necessary to strengthen the selection of grain screening,improve the quarantine identification capacity,and increase the environmental monitoring and follow-up supervision.
Key words:Sisymbrium orientale L.;herbicide-resistant;quarantine;weed control
收稿日期:2023-03-02
作者简介:左然玲(1979—),男,安徽蚌埠人,硕士,高级农艺师,主要从事进出境植物检疫。E-mail:zrlspace@163.com。
东方大蒜芥是一种对多种除草剂有抗性的杂草,自2019年在我国口岸首次截获以来,多次在进境粮谷中被检出。本文对东方大蒜芥的形态、生物学特性、抗除草剂种类及防治措施方面进行综述,以期为检疫鉴定、监测、防控提供关键信息。
1 分类地位
东方大蒜芥(Sisymbrium orientale L.)是十字花科大蒜芥属杂草[1-2],也称西亚大蒜芥、戟叶播娘蒿等。 其英文名为Indian hedge mustard,异名为Brassica subhastata Willd.、Hesperis columnae (Jacq.) Kuntze、H. orientalis (L.) Kuntze、Pachypodium columnae (Jacq.) Webb、Sisymbrium columnae Jacq.、S. costei Foucaud & Rouy、S. daghestanicum Vassilcz.、S. fujianense L.K. Ling、S. irio var. longicarpum Albo、S. orientale var. leiocarpum (DC.) Halácsy、S. orientale var. orientale、Sisymbrium orientale subsp. orientale、S. subhastatum (Willd.) Hornem[3]。
2 分布区域
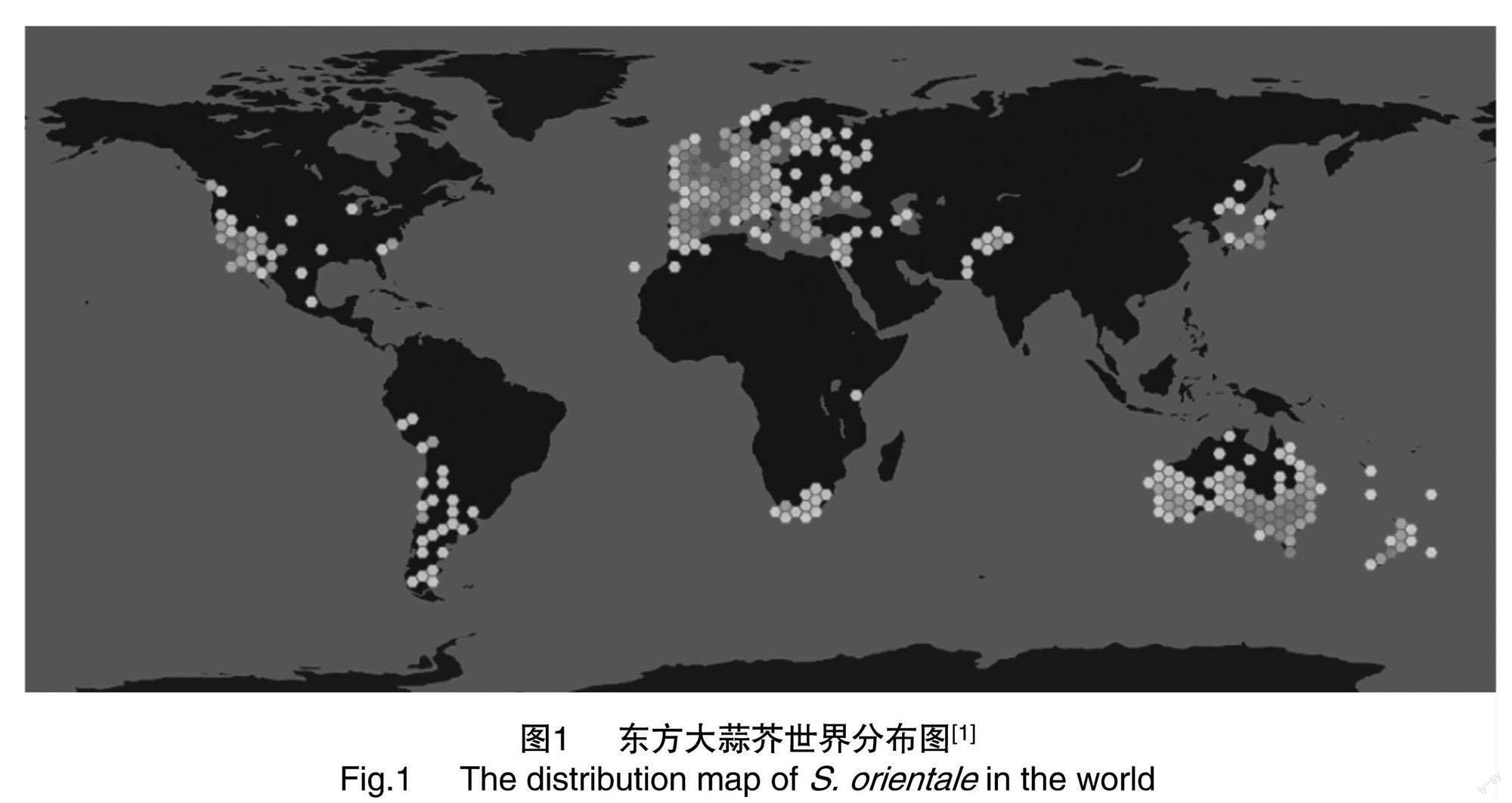
东方大蒜芥原产于地中海地区,现在欧洲、亚洲、非洲、美洲均有分布[4-5]。我国对该物种仅在《Flora of China》福建和山西省分布中有简单的描述[2],最近的一次报道是2005年在云南发现该种[6];近年来,多次在小麦等粮谷中发现(图1)。
3 形态特征
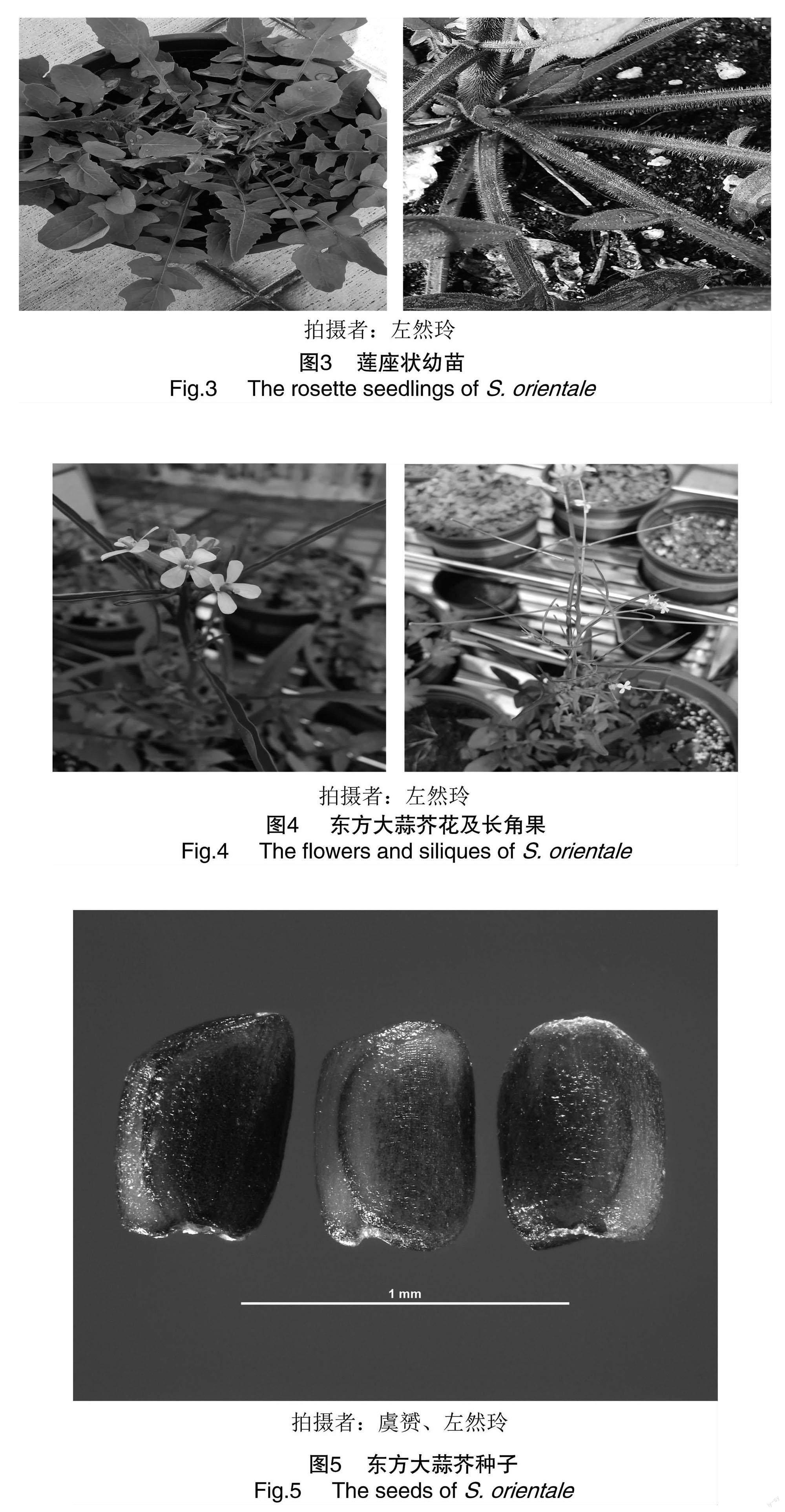
植株高15~50 cm,茎有毛。单叶互生,初生幼苗叶片卵形;叶片羽状裂,叶片上部披针形,全缘,中部裂片呈戟状。花两性,簇生于茎端,总状花序;萼片4片,分离;花瓣4枚,浅黄色;四强雄蕊;子房上位,2室。角果线形,长3~10 cm[6]。幼苗呈莲座状,叶深裂(图2~图4)。
种子形态多变,方形、长圆形至多边形,稍有压缩。一个面纵向凸出,另一个面平坦,橫向凸出。长1~1.5 mm,宽0.7~0.9 mm,厚0.5~ 0.6 mm,两面均有明显的纵向凹槽。表面无毛,纹理多变,粗糙,有光泽,棕黄色,常具深绿色或紫色斑点。种脐线性,位于凹陷处,常具白色珠柄。胚弯曲,子叶内曲至斜内曲状,胚乳缺乏(图5)。
4 生物学特性
东方大蒜芥是十字花科二倍体植物(2N=14)[7],两性,自花授粉。常出现在路边荒地、牧场及农田,草地偶然会有发现,受土壤类型的影响小。花果期4—8月,长角果8 cm左右,结实量大且种子较细小[6],可产生种子约 10 000 粒/株[8]。东方大蒜芥种子的种子库可维持3~5年[9],种子能够在土壤水分充足光线良好的情况下萌发,并可在短时间内完成其生活史。
高盐胁迫和渗透胁迫可抑制东方大蒜芥的萌发,当pH值在4~10的范围内,种子萌发率大于50%。在土壤表层的种子萌发率最高,可达70%。萌发率随土层深度的增加而下降,当土层深度在10 mm时,则难出苗[10]。
5 危害情况
东方大蒜芥常出现在燕麦(Avena sativa)、大麦(Hordeum vulgare)、小麦(Triticum aestivum)、鹰嘴豆(Cicer arietinum)、油菜 (Brassica napus)等作物田中[10],且与这些作物的生育期一致,在作物的整个生育期间与其竞争,降低作物的产量[11]。
东方大蒜芥对磺酰脲、咪唑酮和三唑吡啶类除草剂有抗性[4],也有研究表明东方大蒜芥对咪唑啉酮(IMI)类除草剂产生抗性[12]。在澳大利亚昆士兰州等地区,发现不少东方大蒜芥的抗除草剂生物型种群[13]。大多东方大蒜芥种群对乙酰乳酸合酶(ALS)抑制剂具有抗性,而一些东方大蒜芥种群已进化出对光系统Ⅱ(PSⅡ)抑制剂、八氢番茄红素脱氢酶(phytoene desaturase,简称PDS)抑制剂[14]的抗性,以及对ALS和合成生长素抑制剂的多重耐药性[15],对不同除草剂的抗性,使得防除成本大大增加。
东方大蒜芥茎纤维粗大,可缠绕机械影响作物收割。其种子细小且量大,易混杂在作物种子里造成污染,影响小麦等种子的等级评定。
6 防治措施
因抗性使用传统的除草剂防治东方大蒜芥的效果大大降低,因此,可在不影响生态环境情况下,使用灭生性除草剂草甘膦等进行防除,若发现零星发生,建议人工拔除。因土壤深度可直接影响东方大蒜芥的萌发,在农事耕作上,可采取深耕及轮作的方式,降低东方大蒜芥土壤种子库的密度。
要加强对进境粮谷储存地、运输路线及加工厂周边环境的监测和下脚料的管控,有植株或种群出现应及时处理。
7 小结
东方大蒜芥可随粮谷贸易进行长距离传播进入我国,其种子细小,在取检疫样品时,需注重粮谷筛下物的获取和挑拣,取样点尽量多,最大可能获取样本和相关信息。
东方大蒜芥现广泛分布在澳大利亚、美国等我国的主要粮谷贸易国,应根据相应情况制定检疫措施、鉴定规程、处理方法,加强监测和防控,防患于未然。
采用除草剂进行化学防除一直是控制杂草的有效方式。东方大蒜芥有不同的抗除草剂生物种群,使得传统除草剂如磺酰脲类除草剂的防除效果大大降低。因此,须加强新型除草剂筛选和东方大蒜芥抗性机制的相关研究,以精确防除,延缓其抗性。
参考文献:
[1]Sisymbrium orientale L.[EB/OL]. (2021-01-19)[2023-01-01]. https://www.gbif.org/species/3046812.
[2]Sisymbrium orientale L.[EB/OL][2023-01-01]. http://www.iplant.cn/info/Sisymbrium%20orientale?t=foc.
[3]Sisymbrium orientale L.[EB/OL][2023-01-01]. https://www.catalogueoflife.org/data/taxon/6YSJS.
[4]Boutsalis P. Resistance to acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicides in Sonchus oleraceus,Sisymbrium orientale and Brassica tournefortii[D]. Adelaide:The University of Adelaide,1996.
[5]Rollins R C. Weeds of the cruciferae (Brassicaceae) in north america[J]. Journal of the Arnold Arboretum,1981,62(4):17-540.
[6]周虹霞,刘恩德,刘振稳,等. 外来植物西亚大蒜芥在云南出现并定居[J]. 云南植物研究,2007,29(3):333-336.
[7]Erogˇlu H E,Sefali A,nal M,et al. Cytogenetical analyses of some species of the genus Sisymbrium (Brassicaceae) in Turkey[J]. Anatolian Journal of Botany,2019,3(1):21-24 .
[8]McGillion T,Storrie A. Integrated weed management in Australian cropping systems-a training resource for farm advisors[M]. Adelaide:CRC for Australian Weed Management,2006.
[9]Boutsalis P,Powles S B. Seedbank characteristics of herbicideresistant and susceptible Sisymbrium orientale[J]. Weed Resesrch,1998,38(5):389-395.
[10]Chauhan B S,Gill G. Influence of environmental factors on seed germination and seedling emergence of oriental mustard (Sisymbrium orientale)[J]. Weed Science,2006,54(6):1025-1031.
[11]Dang H,Malone J M,Boutsalis P,et al. Identification of a target-site mutation conferring resistance to triazine herbicides in oriental mustard (Sisymbrium orientale L.) from Australia[J]. Weed Biology and Management,2017,17(4),153-160.
[12]Long W H,Maloneb J,Boutsalisb P,et al. Diversity and extent of mutations endowing resistance to the acetolactate synthase (AHAS)-inhibiting herbicides in Indian hedge mustard (Sisymbrium orientale) populations in Australia[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,2019,157:53-59.
[13]Dang H T. Investigation of herbicide resistance in oriental mustard (Sisymbrium orientale L.) in Australia[D]. Adelaide:The University of Adelaide,2018.
[14]Dayan F E,Owens D K,Tranel P J,et al. Evolution of resistance to phytoene desaturase and protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors state of knowledge[J]. Pest Management Science,2014,70(9):1358-1366.
[15]Preston C,Dolman F C,Boutsalis P. Multiple resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting and auxinic herbicides in a population of oriental mustard (Sisymbrium orientale)[J]. Weed Science,2013,61:185-192.
