基于F-Score特征选择的癫痫脑电信号识别方法
2023-11-09凌宇杜玉晓李向欢
凌宇 杜玉晓 李向欢


摘要:隨着癫痫脑电信号自动检测算法研究地不断深入,需要处理的特征维度也不断增加,且冗余特征增大了算法的复杂度,导致算法性能下降。为此,提出一种基于F-Score特征选择的癫痫脑电信号识别方法。首先,从原始癫痫脑电信号数据集中提取特征,并计算每个特征的F-Score统计值;然后,根据分类模型的分类准确率,通过序列前向搜索方法,选择最优特征集;最后,利用支持向量机和逻辑回归分类模型进行实验,并与传统的特征降维方法PCA进行对比。实验结果表明,本文方法可有效降低特征矩阵的维数,提高算法运算效率。
关键词:F-Score;PCA;特征提取;特征选择;癫痫脑电信号识别
中图分类号:R742.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1674-2605(2023)05-0009-06
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-2605.2023.05.009
Epileptic EEG Signal Recognition Method Based on F-Score Feature Selection
LING Yu DU Yuxiao LI Xianghuan
(Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China)
Abstract:With the continuous deepening of research on automatic detection algorithms for epileptic EEG signals, the number of feature dimensions to be processed continues to increase, and redundant features increase the complexity of the algorithm, leading to a decrease in algorithm performance. To this end, a method for epileptic EEG signal recognition based on F-Score feature selection is proposed. Firstly, extract features from the original epileptic EEG signal dataset and calculate the F-Score statistical value for each feature; Then, based on the classification accuracy of the classification model, the optimal feature set is selected through a sequence forward search method; Finally, experiments were conducted using support vector machines and logistic regression classification models, and compared with the traditional feature dimensionality reduction method PCA. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively reduce the dimensionality of the feature matrix and improve the computational efficiency of the algorithm.
Keywords:F-Score; PCA; feature extraction; feature selection; epileptic EEG signal recognition
0 引言
目前,癫痫的临床诊断主要以脑电图(electro-encephalogram, EEG)为依据。随着计算机技术的飞速发展,人们开始利用计算机处理癫痫脑电信号。计算机处理癫痫脑电信号的基本原理是提取癫痫脑电信号的特征并进行分类[1],应用较多的分类方法是机器学习算法。在机器学习算法中,理论上认为特征越多,
分类性能就越好。然而,大量特征可能存在冗余,降低分类模型的准确率。机器学习算法的基础是特征选择,从原始数据特征集中筛选出最优特征子集,可降低特征矩阵的维度[2],提高算法的运算效率。目前,常用的特征选择方法可分为过滤式和封装式[3]。其中,过滤式方法通过设置阈值对特征评价进行筛选;封装式方法通过机器学习算法来寻找特征评价。常用的特
征评价标准有相关系数[4]和互信息[5]。文献[6]先利用极限学习机对非线性特征进行评价,再利用多目标演化算法来筛选最优子集。
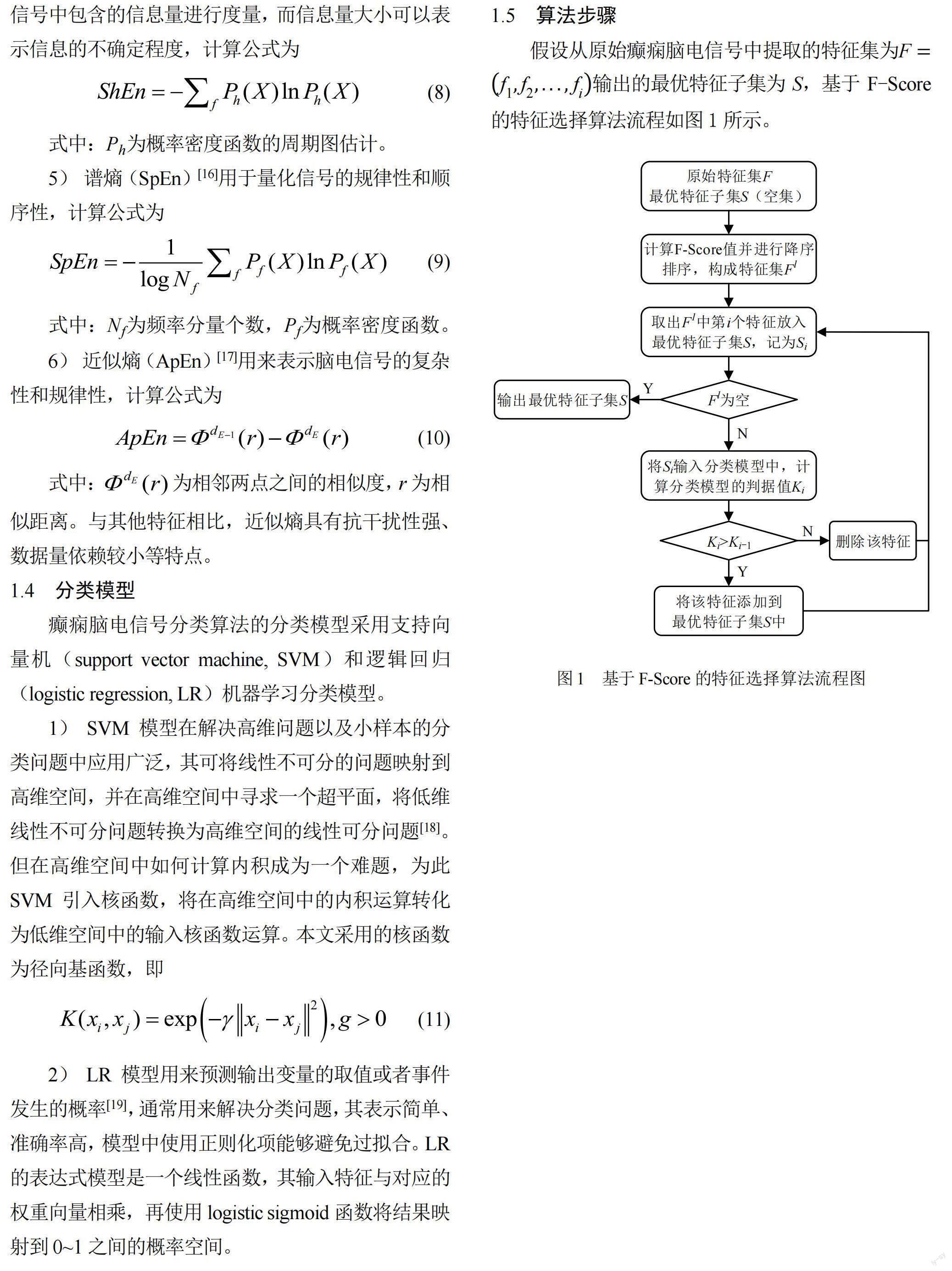
为全面反映癫痫脑电信号,需要从原始脑电信号中提取多个维度的特征,包括时域、频域、时频域和非线性特征[7],导致原始癫痫脑电信号特征集中有许多冗余特征。为此,本文提出一种基于F-Score特征选择的癫痫脑电信号识别方法。首先,利用F-Score对原始脑电信号的特征进行评价;然后,采用序列前向搜索方法,以分类模型的分类准确率为反馈来寻找最优的特征子集。
1 特征提取与特征选择算法
1.1 PCA特征降维
主分量分析(principal component analysis, PCA)是一种常用的数据降维方法[8],它将原始数据集中的多维特征映射到低维空间,从而减少数据的维度。PCA可以减少计算量,提高算法的运算效率,消除噪声,提高模型的泛化能力;但可能丢失重要的特征信息,影响算法的准确率。
1.基于F-Score的特征选择算法具体步骤为:
1) 对特征集F中的每个特征进行基于F-Score算法的特性评价,计算每个特征的F-Score值;
2) 将每个特征的F-Score值降序排序,重新构建特征集F1;
3) 每次从特征集F1中取出F-Score值最大的特征放入最优特征子集S,如果特征集F1为空,算法结束,否则继续执行下一步;
4) 将特征子集S输入到分类模型中进行分类,以分类模型的K为判据;假设当前的特征集为Si,分类模型的判据值为Ki,从F1中取出当前F-Score值最大的特征加入Si中,记为Si+1,同样计算Si+1的判据值Ki+1;
5) 比较Ki与Ki+1,如果Ki+1 ≤Ki,表示这个特征对分类效果起不到正向促进作用,将这个特征从S中去除,并返回步骤3);如果Ki+1 >Ki,表示这个特征可以提高分类效果,将这个特征保留在S中,并返回步骤3);
6) 直到遍历特征集F1的所有特征,生成的特征集S即为最优特征子集。
2 实验结果及分析
本文实验仿真采用MATLAB实现。实验对比PCA和F-Score 2种特征选择算法在SVM和LR 2种分类模型上的性能。
2.1 实验数据
本文采用的EEG数据集来自伯恩大学的Bonn数据集。Bonn数据集中包含Set A、Set B、Set C、Set D、Set E 5组数据,选取Set A(正常脑电信号)和Set E(癫痫脑电信号)2组进行分类实验。Set A和Set E脑电信号波形图如图2所示。
实验前,将每个EEG信号分成4个相等的部分,获得400个标准的EEG样本和400個癫痫发作样本,每个样本长度为1 024。
2.2 实验结果分析
本文对比经过PCA和F-Score特征选择后的特征集,分别在SVM模型和LR模型的分类效果,实验流程如图3所示,特征选择的结果如表1所示。
本文选取准确率(Accuracy)、精确率(Precision)、特异性(Specificity)和敏感度(Sensitivity)4个指标对分类模型进行评估。其中,准确率是模型正确预测的样本数量与总样本数量之比;精确率衡量模型在预测为正类的样本中的准确性;特异性衡量模型对于实际为负类的样本的预测能力;敏感度衡量模型对于实际为正类的样本的预测能力。分类效果如表2和表3所示。
由表2和表3可以看出:原始特征经过特征选择后,分类模型的分类效果有一定提升,且F-Score特征选择算法的分类效果比PCA特征降维的效果更好。
原始癫痫脑电信号特征集为31维,经F-Score特征选择算法得到的最优特征子集为15维;经PCA特征降维后特征为18维,表明经过F-Score特征选择算法处理过后可有效降低特征集维度,减少分类模型计算的复杂度。
3 结论
本文提出基于F-Score特征选择的癫痫脑电信号识别方法,首先,采用原始EEG数据集中的F-Score统计特性对特征进行评价,并结合序列前向搜索方法搜寻最优特征子集,在搜索过程中采用分类性能评价所选择的特征子集。该特征选择方法能够选择出优化的特征子集,降低数据维数和计算复杂度,进一步提高分类器的性能。
参考文献
[1] YILDIZ A, ZAN H, SAID S. Classification and analysis of epileptic EEG recordings using convolutional neural network and class activation mapping[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 68:102720.
[2] CAI J, LUO J, WANG S, et al. Feature selection in machine learning: A new perspective[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018,300: 70-79.
[3] 计智伟,胡珉,尹建新.特征选择算法综述[J].电子设计工程, 2011,19(9):6.
[4] 周金治,唐肖芳.基于相关系数分析的脑电信号特征选择[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2015,32(4):5.
[5] PENG H, LONG F, DING C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005,27(8):1226-1238.
[6] WANG X, HU T, TANG L. A multiobjective evolutionary nonlinear ensemble learning with evolutionary feature selection for silicon prediction in blast furnace[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021,(99):1-14.
[7] WU M, SUN Y B, WEI Z H, et al. Automatic detection of epileptiform transients in EEG by a two-stage algorithm based on sparse representation[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2009,60:101966.
[8] KE Xi, CHENG Cai. Feature selected based on PCA and optimized LMC[C]//2020 2nd International Conference on Computer Science Communication and Network Security (CSCNS2020)(2020年第二届计算机科学, 通信和网络安全国际学术会议)论文集, 2020:1-6.
[9] HUANG WEI, YAN HONGMEI, LIU RAN, et al. F-score feature selection based Bayesian reconstruction of visual image from human brain activity[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018,316(17): 202-209.
[10] HYDE, CHARLES E. The Piotroski F-score: evidence from Australia[J]. Accounting and finance,2018,58(2):423-444.
[11] MIROWSKI P, MADHAVAN D, LECUN Y, et al. Classifica-tion of patterns of EEG synchronization for seizure prediction [J]. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2009,120(11):1927-1940.
[12] ISLAM K A, TCHESLAVSKI G V. Independent Component Analysis for EOG artifacts minimization of EEG signals using kurtosis as a threshold[C]// International Conference on Electri- cal Information & Communication Technology. IEEE, 2016.
[13] BO H. EEG analysis based on time domain properties[J]. Electroencephalography & Clinical Neurophysiology, 1970, 29(3):306-310.
[14] BOYLAN G B, RENNIE J M. Automated neonatal seizure detection[J]. Clinical Neurophysiology Official Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 2006, 117(7):1412-1413.
[15] GAO W W. Entropy measures for biological signal analyses[J]. Nonlinear dynamics, 2012, 68(3).
[16] MIRZAEI A, AYATOLLAHI A, GIFANI P, et al. Spectral Entropy for Epileptic Seizures Detection[C]// Second Interna-tional Conference on Computational Intelligence. IEEE, 2010.
[17] KUMAR Y, DEWAL M L, ANAND R S. Epileptic seizure detection using DWT based fuzzy approximate entropy and support vector machine[J]. Neurocomputing, 2014,133(8): 271-279.
[18] CHEN S, ZHANG X, CHEN L, et al. Automatic Diagnosis of Epileptic Seizure in Electroencephalography Signals Using Nonlinear Dynamics Features[J]. IEEE Access, 2019(99):1.
[19] ROY S, KIRAL-KORNEK I, HARRER S. Deep learning enabled automatic abnormal EEG identification[C]//2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2018:2756-2759.
作者簡介:
凌宇,男,1999年生,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:脑机接口、癫痫脑电信号的特征提取与分类。E-mail: 3467255048@qq.com
杜玉晓(通信作者),男,1973年生,副教授,硕士生导师,主要研究方向:医疗器械设备及脑机接口(BCI)技术、数字图像处理、自动化装备与集成。E-mail: yuxiaodu@gdut.edu.cn
李向欢,男,1997年生,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:脑电信号检测、智能信号处理以及脑机接口。
