妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症孕妇血清及胎盘中IL-8、IL-31水平及其临床意义
2023-11-05张姝丽钱丽华陈璐孙婧卢丹孔祥
张姝丽 钱丽华 陈璐 孙婧 卢丹 孔祥


[摘 要] 目的:研究妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症(intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy,ICP)孕妇血清及胎盘中白介素-8(IL-8)、白介素-31(IL-31)表达水平及其临床意义。方法:选择妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症孕妇22例作为ICP组,健康孕妇20例作为对照组,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测血清中IL-8、IL-31水平,免疫组织化学法检测胎盘组织中IL-8、IL-31的表达。结果:ICP组血清中IL-8和IL-31水平分别为1 404.81±278.53 pg/mL和619.75±20.13 pg/mL,显著高于对照组的648.68±91.44 pg/mL和515.21±10.66 pg/mL,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。ICP组胎盘组织中IL-8、IL-31表达强度明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:ICP组患者血清和胎盘组织中IL-8和IL-31表达明显升高,提示炎症参与ICP的发生,IL-31可能与ICP瘙痒症状的发生有关。
[关键词] 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症;血清;胎盘;白介素-8;白介素-31
[中图分类号] R714.25 [文献标志码] A [DOI] 10.19767/j.cnki.32-1412.2023.04.002
IL-8 and IL-31 levels in serum and placenta of pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and their clinical significance
ZHANG Shuli1, QIAN Lihua2, CHEN Lu2, SUN Jing2, LU Dan2, KONG Xiang2
(1Yangzhou University, Jiangsu 225001; 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Clinical Shcool of Medicine, Yangzhou University)
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the expression levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-31 in serum and placenta of pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) and their clinical significance. Methods: A total of 22 pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy were selected as ICP group. Another 20 healthy pregnant women were selected as the control group. The serum level of IL-8 and IL-31 was detected by enzymed-linked immunosorbent assay, and the expression of IL-8 and IL-31 in the placenta tissues of each group was detected by immunohistochemistry. Results: The serum levels of IL-8 and IL-31 in ICP group were 1 404.81±278.53 pg/mL and 619.75±20.13 pg/mL, which were significantly higher than those of 648.68±91.44 pg/mL and 515.21±10.66 pg/mL in the control group (P<0.05). The expressions of IL-8 and IL-31 in the placenta tissue in ICP group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: The expressions of IL-8 and IL-31 in serum and placenta tissue in ICP patients significantly increased, implying that inflammation was involved in the occurrence of ICP. IL-31 may be associated with itchiness symptoms of ICP.
[Key words] intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy; serum; placenta; IL-8; IL-31
妊娠期肝內胆汁淤积症(intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy,ICP)主要出现在妊娠30周后,表现为血清中总胆汁酸(total bile acid,TBA)和(或)转氨酶浓度升高以及皮肤瘙痒,分娩后能自行缓解[1]。ICP病因复杂,可能与遗传易感女性的生殖激素的胆汁淤积有关[2]。近年来有研究发现,某些细胞因子可能参与ICP的发生[3]。白介素-8(IL-8)是一种促炎细胞因子,在肝脏疾病发生中具有一定作用[4-5]。白介素-31(IL-31)是IL-6家族成员,在慢性炎症的诱导中发挥重要作用[6]。IL-31主要由活化Th2细胞产生[7],与IL-31受体A(IL-31 RA)及抑癌素M受体(OSMR)组成的异二聚体相互作用,这些受体在感觉神经元的背根神经节、脊髓、真皮的初级传入纤维中高表达,参与瘙痒感觉的发生[8]。本研究选择2021年5月—2022年2月于扬州大学临床医学院就诊的ICP孕妇22例,分析ICP孕妇血清及胎盘中IL-8、IL-31表达水平变化及其临床意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 ICP孕妇22例(ICP组),均符合中华医学会妇产科学分会2015年发布的《妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症诊疗指南(2015)》相关诊断标准[9],年龄24~34岁,平均27.95±2.19岁;孕周32~37周,初产妇12例,经产妇10例;体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)25.72±3.30 kg/m2,白细胞计数(9.03±2.27)×109/L,新生儿体重3.17±0.64 kg。另选择同期于本院进行常规产检的健康孕妇20例作为对照组,年龄21~34岁,平均27.1±3.89岁;孕周32~37周,初产妇11例,经产妇9例;BMI 26.29±2.21 kg/m2,白细胞计数(9.12±2.69)×109/L,新生儿体重3.42±0.33 kg。两组一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。排除标准:(1)胎位异常、多胎妊娠、头盆不称、免疫系统疾病、肝胆疾病;(2)合并妊娠期高血压、心脏病及糖尿病等;(3)既往有复发性自然流产、死胎、畸胎等不良孕产史;(4)有长期服用药物及吸烟史。本研究经过医院伦理审查委员会批准,获得所有参与者知情同意。
1.2 检测方法
1.2.1 血清中IL-8、IL-31水平:采集孕妇晨间空腹外周静脉血5 mL,室温静置30 min,凝固后离心取上清,-80 ℃保存备测。采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)测定血清中IL-8、IL-31水平,严格按照试剂盒(上海恒远生物科技有限公司)说明书进行操作。
1.2.2 胎盘组织中IL-8、IL-31表达:采用免疫组织化学法(immunohistochemical method,IHC)检测胎盘组织中IL-8、IL-31表达。胎盘娩出后10 min内,避开胎盘钙化灶、梗死区,取胎盘母体面约1 cm×1 cm×1 cm大小组织2块,用磷酸盐缓冲液(phosphate buffered saline,PBS)漂洗后放入10%甲醛中固定。酒精梯度脱水、二甲苯透明后常规石蜡包埋,切成5 μm厚薄片。石蜡包埋标本免疫标记IL-8,IL-31。操作严格按照免疫组化法试剂盒程序进行,使用兔抗IL-8抗体试剂盒(Proteintech公司)和兔抗IL-31抗体试剂盒(Origene公司),阳性对照取已知阳性片,阴性对照用PBS代替一抗,二氨基聯苯胺染色。
免疫组化结果判定:由两名不知情的研究人员在光学显微镜下观察石蜡切片染色情况并进行评分。染色强度:无染色计0分,同时存在阴性和微量阳性细胞计1分,阳性细胞中等染色计2分,阳性细胞强染色计3分。阳性细胞<5%计0分,阳性细胞5%~30%计1分,阳性细胞31%~60%计2分,阳性细胞>60%计3分。两项评分相乘为最终评分,最终评分0分为阴性(-),1~2分为弱阳性(+),3~4分为阳性(++),6~9分为强阳性(+++)。
1.3 统计学处理 应用SPSS 26.0统计学软件对数据进行分析。计数资料以频数和率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验;正态分布的计量资料以±s表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验;IL-8、IL-31表达强度的比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H秩和检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 两组孕妇血清中IL-8、IL-31水平比较 ICP组患者血清中IL-8和IL-31水平分别为1 404.81±278.53 pg/mL和619.75±20.13 pg/mL,显著高于对照组的648.68±91.44 pg/mL和515.21±10.66 pg/mL,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
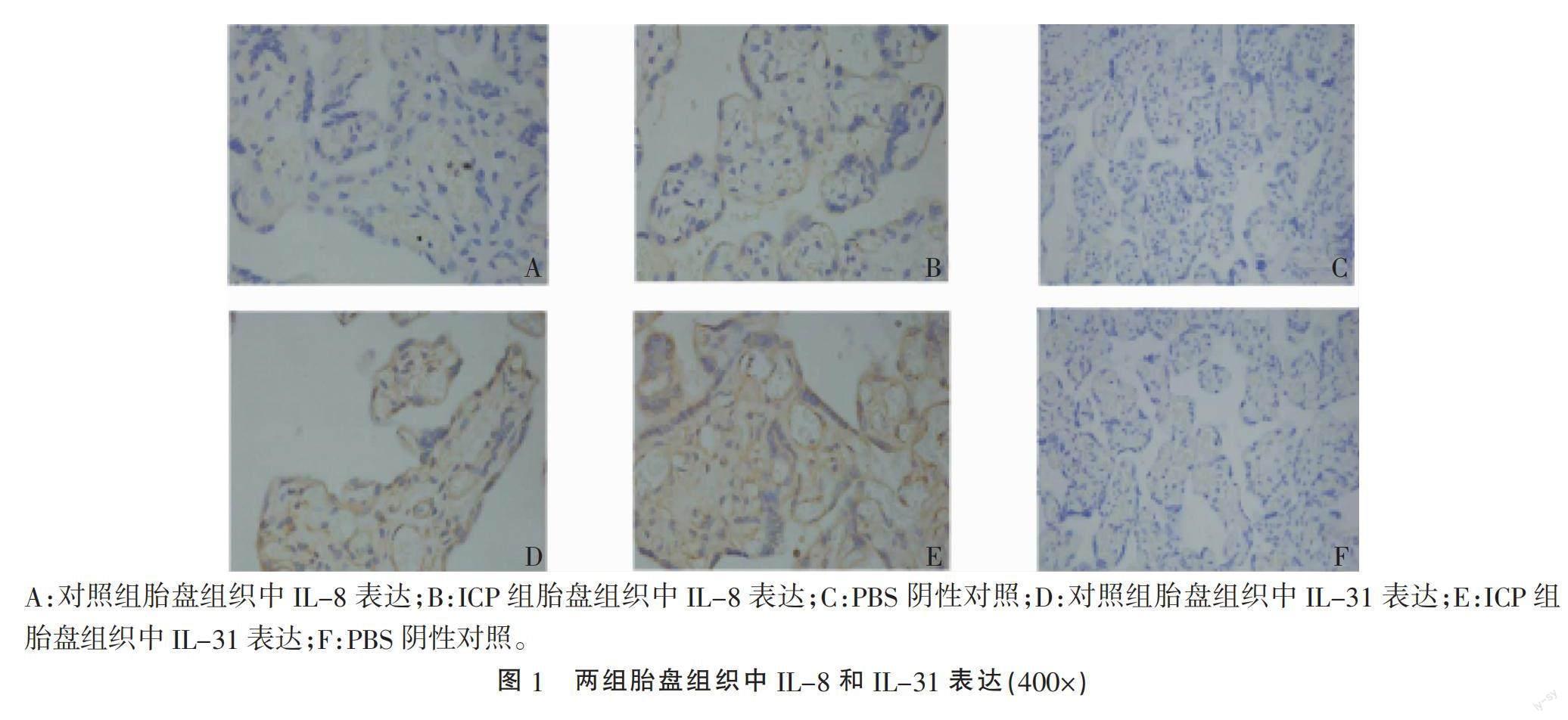
2.2 两组产妇胎盘组织中IL-8、IL-31表达强度比较 ICP组胎盘组织中IL-8表达强度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图1(A-C)、表1。ICP组胎盘组织中IL-31表达强度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图1(D-F)、表2。
3 讨 论
ICP是一种妊娠特异性肝病,遗传、激素、环境和饮食因素与其发病机制有关[10]。近年来开始关注ICP孕妇炎症反应的研究,强调炎症在ICP发生中的作用[11-13]。大量研究表明,ICP患者血清中炎症细胞因子发生改变,促炎1型细胞因子的产生增加,而抗炎2型细胞因子的产生减少[14-18]。本研究结果显示,与对照组比较,ICP组孕产妇血清及胎盘组织中IL-8、IL-31水平显著升高。提示IL-8和IL-31可能是辅助诊断ICP的潜在标志物,同时需要进一步研究ICP发病前几周内这两种炎症因子水平的变化,为预测ICP的发生提供线索,从而尽早采取干预措施。
IL-8由单核细胞、上皮细胞、表皮细胞、成纤维细胞和T淋巴细胞受IL-1、肿瘤坏死因子和外源性细菌多糖刺激产生,它不仅是促炎细胞因子,还是中性粒细胞趋化激活因子,介导多形核白细胞迁移到炎症或损伤部位[19]。IL-8与许多炎症疾病有关,促进炎症发生和诱导免疫反应[20]。有研究报告溃疡性结肠炎患者中IL-8水平显著升高,认为TNF-α、IL-1和IL-6引起的炎症反应主要由IL-8所代表的趋化因子介导[20-21]。本研究中ICP孕产妇血清及胎盘组织中IL-8表达水平明显高于对照组,提示炎症参与该疾病的发生。ZHANG等[22]研究表明,胆汁酸通过受体1激活磷酸肌醇3-激酶/核因子-κB通路引起胎盘炎症,ICP患者IL-2、IL-4、IL-8、IL-10、TNF-α和干扰素-γ基因表达显著上调。
瘙痒是ICP的典型症状,严重影响孕妇的生活质量。角质形成细胞、肥大细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞、T细胞和瘙痒特异性神经元等都可以诱导、加重或抑制瘙痒症状[23]。研究表明,IL-31可能在瘙痒性炎症性皮肤病的发生中发挥作用。小鼠IL-31过度表达可导致皮炎和瘙痒,这类似于人类的特应性皮炎[24]。研究显示,重复应用IL-31后,小鼠背根神经节中IL-31受体(IL-31 RA)和oncostatin M受体β(OSMRβ)表达增加,提示IL-31可能上调背根神经节中IL-31受体的表达,增强皮肤注射IL-31引起的瘙痒感觉[25],推测IL-31可能激活介导瘙痒的神经纤维。本研究结果显示,ICP组血清及胎盘组织中IL-31水平显著高于对照组,提示IL-31可能作为瘙痒的中介物参与ICP的发生。
综上所述,ICP孕产妇血清及胎盘组织中IL-8和IL-31表达水平明显升高,提示炎症参与ICP的发生,IL-31可能与ICP瘙痒症状的发生有关,检测血清IL-8、IL-31水平对ICP具有一定的辅助诊断价值。
[参考文献]
[1] FLOREANI A,GERVASI M T. New insights on intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Clin Liver Dis,2016,20(1):177-189.
[2] JACQUEMIN E,CRESTEIL D,MANOUVRIER S,et al. Heterozygous non-sense mutation of the MDR3 gene in familial intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Lancet,1999,353(9148):210-211.
[3] BIBEROGLU E,KIRBAS A,DAGLAR K,et al. Role of inflammation in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. J Obstet Gynaecol Res,2016,42(3):252-257.
[4] LANGHANS B,KR?MER B,LOUIS M,et al. Intrahepatic IL-8 producing Foxp3+ CD4+ regulatory T cells and fibrogenesis in chronic hepatitis C[J]. J Hepatol,2013,59(2):229-235.
[5] ZIMMERMANN H W,SEIDLER S,GASSLER N,et al. Interleukin-8 is activated in patients with chronic liver diseases and associated with hepatic macrophage accumulation in human liver fibrosis[J]. PLoS One,2011,6(6):e21381.
[6] DILLON S R,SPRECHER C,HAMMOND A,et al. Interleukin 31,a cytokine produced by activated T cells,induces dermatitis in mice[J]. Nat Immunol,2004,5(7):752-760.
[7] CORNELISSEN C,L?SCHER-FIRZLAFF J,BARON J M,et al. Signaling by IL-31 and functional consequences[J]. Eur J Cell Biol,2012,91(6/7):552-566.
[8] BANDO T,MORIKAWA Y,KOMORI T,et al. Complete overlap of interleukin-31 receptor A and oncostatin M receptor beta in the adult dorsal root Ganglia with distinct developmental expression patterns[J]. Neuroscience,2006,142(4):1263-1271.
[9] 中華医学会妇产科学分会产科学组. 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症诊疗指南(2015)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志,2015,50(7):481-485.
[10] MULLALLY B A,HANSEN W F. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: review of the literature[J]. Obstet Gynecol Surv,2002,57(1):47-52.
[11] BAKHSH H A,ELAWAD M M,ALQAHTANI R S,et al. Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy: A Case Report of Third-Trimester Onset of the Disease[J]. Cureus,2022,14(11):e31926.
[12] KIRBAS A,BIBEROGLU E,DAGLAR K,et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a diagnostic marker of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol,2014,180:12-15.
[13] LUO M J,WANG L,YAO H B,et al. Publisher Correction: diagnostic and prognostic value of blood inflammation and biochemical indicators for intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in Chinese pregnant women[J]. Sci Rep,2022,12(1):21916.
[14] WANG L P,LU Z K,ZHOU X W,et al. Effects of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy on hepatic function,changes of inflammatory cytokines and fetal outcomes[J]. Exp Ther Med,2019,17(4):2979-2984.
[15] KONG W C,LI X Y,ZOU M Z,et al. iNKT17 cells play a pathogenic role in ethinylestradiol-induced cholestatic hepatotoxicity[J]. Arch Toxicol,2023,97(2):561-580.
[16] BASILE F,SANTAMARIA A,MANNUCCI C,et al. Interleukin 31 is involved in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med,2017,30(9):1124-1127.
[17] SHAO Y,CHEN J,ZHENG J,et al. Effect of histone deacetylase HDAC3 on cytokines IL-18,IL-12 and TNF-α in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2017,42(4):1294-1302.
[18] YAYI H,DANQING W,SHUYUN L,et al. Immunologic abnormality of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Am J Reprod Immunol,2010 ,63(4):267-273.
[19] MATSUSHIMA K,OPPENHEIM J J. Interleukin 8 and MCAF: novel inflammatory cytokines inducible by IL 1 and TNF[J]. Cytokine,1989,1(1):2-13.
[20] MIN M,YANG J,YANG Y S,et al. Expression of transcription factor FOXO3a is decreased in patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Chin Med J,2015,128(20):2759-2763.
[21] REDDY K P,MARKOWITZ J E,RUCHELLI E D,et al. Lamina propria and circulating interleukin-8 in newly and previously diagnosed pediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients[J]. Dig Dis Sci,2007,52(2):365-372.
[22] ZHANG Y H,PAN Y D,LIN C D,et al. Bile acids evoke placental inflammation by activating Gpbar1/NF-κB pathway in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. J Mol Cell Biol,2016,8(6):530-541.
[23] OZLER A,UCMAK D,EVSEN M S,et al. Immune mechanisms and the role of oxidative stress in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Cent Eur J Immunol,2014,39(2):198-202.
[24] WILLIAMSON C,MIRAGOLI M,SITI S A K,et al. Bile acid signaling in fetal tissues: implications for intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Dig Dis Basel Switz,2011,29(1):58-61.
[25] ARAI I,TSUJI M,MIYAGAWA K,et al. Repeated administration of IL-31 upregulates IL-31 receptor A (IL-31RA) in dorsal root ganglia and causes severe itch-associated scratching behaviour in mice[J]. Exp Dermatol,2015,24(1):75-78.
[收稿日期] 2023-02-05
(本文編辑 赵喜)
