Protective Effect and Molecular Mechanism of Shui People’s Classic Prescription Jipei Dilong Ointment on Osteoarthritis in Rats
2023-10-31LailaiLIBaoyingHUAShiyunYEYihuiCHAIHaotianWANGJinghuaRUANXiangPULiyanZHANGSibuMA
Lailai LI,Baoying HUA, Shiyun YE, Yihui CHAI, Haotian WANG, Jinghua RUAN, Xiang PU, Liyan ZHANG, Sibu MA*
1. Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550025, China; 2. The First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, China
Abstract [Objectives] To explore the protective effect and molecular mechanism of Shui People’s Classic Prescription Jipei Dilong Ointment on knee osteoarthritis in rats. [Methods] 72 SPF male SD rats were divided into control group, model group, Jipei Dilong Ointment high, medium and low dose groups, and positive drug Diclofenac group, with 12 rats in each group. Except the control group, all other groups were injected with 0.2 mL of 2% papain and 0.3% L-cysteine mixture into knee joint cavity to establish osteoarthritis model, while the control group was injected with the same amount of normal saline. The Lequesne MG score was used to determine the success of the model. After successful modeling, external administration was given for 4 weeks. The histopathological changes in articular cartilage and synovium were observed by HE staining; the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and COX-2 in serum were detected by ELISA, and the relative expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 mRNA in cartilage was detected by qRT-PCR; the relative expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in rat cartilage was detected by Western-blot. [Results] Compared with the model group, Jipei Dilong Ointment could significantly reduce the Lequesne MG score and Mankin’s score of arthritic rats (P<0.01); significantly improve the pathological changes in articular cartilage and synovium, reduce tissue edema, necrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrous tissue proliferation; reduce the expression of MMP-9 mRNA (P<0.01) in different degrees and increase the expression of TIMP-1 mRNA (P<0.01); reduce the relative expression of MMP-9, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB protein in different degrees (P<0.01), and significantly increase the relative expression of TIMP-1 protein in cartilage (P<0.01). [Conclusions] Jipei Dilong Ointment can improve the joint injury of osteoarthritis rats, and the mechanism may be related to the regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and the ratio of MMP-9/TIMP-1.
Key words Jipei Dilong Ointment, Osteoarthritis (OA), Traditional Chinese medicine application
1 Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative disease characterized by synovial inflammation and cartilage degeneration, and it is most common in the knee joint[1]. OA is more common in middle-aged and elderly people, and women are more than men. OA is often accompanied by joint swelling and pain, morning stiffness, adverse flexion and extension, and can cause deformity or even disability in severe cases[2]. The injury of articular cartilage is irreversible, resulting in a longer course of OA, which affects the life, work and family of patients, thus OA has gradually attracted wide attention of the whole society[3]. The pathogenesis of OA is very complex[4], and there is no effective method to prevent the occurrence and development of the disease and to cure it. Therefore, it is urgent to explore the etiology and pathogenesis of OA and find an effective prevention and treatment method.
Shui people culture has a long history. After a long period of historical changes, Shui people mainly live in Shui People autonomous counties, Sandu in Guizhou Province and Fuyuan County in Yunnan Province[5]. Shui people’s ancestors lived in the rugged mountain environment for a long time. Coupled with the cold and humid climate, rheumatism and arthralgia occurr frequently. Shui people’s medicine believes that OA belongs to the category of "impediment syndrome", "rheumatic bone pain" and "wind paralysis". The diagnosis and treatment of OA adopts the strategy of adapting measures to local conditions and taking effect as the basis, and Shui people have accumulated a large number of effective prescriptions in long-term clinical practice[6]. Among them, sheep offal therapy and Jipei Dilong Ointment external application therapy were used to treat knee osteoarthritis with excessive wind and dampness, and the curative effect was definite, which was favored by the local people. Jipei Dilong Ointment consists of chicken embryo, Dipsaci Radix, Pheretima, Drynariae Rhizoma, Herba Gaultheria, Benincasae Exocarpium, Strychni Semen, Gardeniae Fructus, Polygoni Cuspidati Rhizoma Et Radix, and Borneolum Syntheticum[7]. The chicken embryo is sweet, salty and fishy in taste, warm in nature, enters the spleen and stomach meridians, is used for treating weakness, emaciation, fracture, muscle injury and pain, and has the effects of warming the middle, benefiting qi, and replenishing essence and marrow. The chicken embryo has been used as a folk medicine in Shui people for more than 100 years. According to the medicine theory of Shui people, the chicken embryo is used to tonify muscles and bones with flesh and blood products. It is recorded inShuiPeople’sOrthopedicMedicinethat chick has the effect of healing wounds and promoting granulation, and is a commonly used bone-setting drug in Shui people’s orthopedic drugs[8]. Pheretima is cold in nature, salty in taste, good at scurrying and running, and often passing through meridians and collaterals. Drynariae Rhizoma and Dipsaci Radix can nourish liver and kidney, strengthen bones and muscles, promote blood circulation, remove blood stasis, and heal wounds; Herba Gaultheria and Strychni Semen open channels and collaterals, reach joints, dissipate stagnation and reduce swelling; Gardeniae Fructus and Polygoni Cuspidati Rhizoma Et Radix can clear away heat and toxic materials, dissipate blood stasis and relieve pain; Benincasae Exocarpium can improve subcutaneous hemorrhage and blood stasis; Borneolum Syntheticum can induce resuscitation, clear away heat, and relieve pain; and all the herbs have the effects of relieving arthralgia, dredging collaterals, and promoting blood circulation by removing blood stasis. Modern studies have reported that Jipei Dilong Ointment has a significant effect in the treatment of bone injuries[9-10], but its mechanism is not yet clear.
Through the papain-induced rat OA model[11], we observed the histopathological changes in Jipei Dilong Ointment on rat cartilage and synovium, explored the effects of Jipei Dilong Ointment on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and the ratio of MMP-9/TIMP-1 in OA rats, and studied the possible mechanism of Jipei Dilong Ointment in protecting cartilage, so as to provide a theoretical support for the clinical treatment of OA.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1Laboratory animals and drugs. We selected 72 male SD rats, weighing (180-220) g, which were purchased from Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Animal License No.:SCXK (Xiang) 2014-0011). The rats were raised in natural conditions, the animal room was regularly disinfected, the animal room was well ventilated, the temperature was kept at 20 ℃, the relative humidity was 50%-70%, and the rats were fed and drunk freely in each cage of 6 rats. This experiment was approved by the examination of the ethics committee of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (20210088). The Jipei Dilong Ointment (batch No.:20200901) was provided by the First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
2.1.2Reagents. Papain (Solarbio, batch No.:716M022); L-CYSTEINE (Solarbio, batch No.:820N029); Ultrapure RNA Kit (Beijing CoWin Biotech Co., Ltd., batch No.:50250); One-Step Rapid WB (HRP) Kit (Rabbit) (Beijing CoWin Biotech Co., Ltd., batch No.:20330); One-Step Rapid WB (HRP) Kit (Mouse) (Beijing CoWin Biotech Co., Ltd., batch No.:30324); TLR4 antibody (Proteintech, part No.:66350-1-lg); TIMP-1 antibody (Boorsen, batch No.:BA03267022); MMP-9 antibody (abcam, batch No.:GR3399016-12); MyD88 antibody (Abcam, batch No.:GR3356289-12); NF-κB antibody (Abcam, batch No.:GR3275776-13).
2.1.3Instruments. Mini PROTEAN Tetra Electrophoresis System (BIO-RAD), ZS-2 plate microplate reader (Beijing Xinfeng Mechanical and Electrical Co., Ltd.); QuantStudio type 1 real-time fluorescence quantitative (qRT-PCR) instrument (Applied Biosystems).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1Establishment and grouping of animal models. First, 72 male SPF SD rats were weighed and labeled, and then they were randomly divided into control group (Control), model group (Model), Jipei Dilong Ointment high, medium and low dose groups (JP-H, JP-M, JP-L) and positive drug (Diclofenac) group, 12 rats for each group. The control group was injected with 0.2 mL 0.9% sodium chloride injection into the knee joint cavity of rats, and other groups were injected with 0.2 mL 2% papain solution (containing L-CYSTEINE 0.03 mol/L) into the knee joint cavity of rats, once on the 1st, 3rdand 7thdays. The Lequesne MG score was performed after 2 weeks to investigate the establishment of the model.
2.2.2Administration. Control group: 70% ethanol (containing 5% glycerol); Model group: 70% ethanol (containing 5% glycerol); JP-H group: 4.5 g crude drug/kg (according to the proportion of 4 mL wetting agent/kg and 2 g drug core content/kg); JP-M group: 1.5 g crude drug/kg (according to the proportion of 1.34 mL wetting agent/kg and 0.67 g drug core content/kg); JP-L group: 0.5 g crude drug/kg (according to the proportion of 0.44 mL wetting agent/kg, 0.22 g drug core content/kg); Diclofenac group: Diclofenac cream 3 g (1.0 g/kg). After administration, the knee joint was fixed with cotton wool and bandage for 6 h and lasted for 4 weeks.
2.2.3Lequesne MG score of knee joint. According to the scoring criteria, three experimental participants scored before administration and 4 weeks after administration, to observe and compare the establishment of models in each group before administration and the improvement of osteoarthritis symptoms in rats after administration. The total score was 15 points, and the model was successfully established if the average score was greater than 8 points. Table 1 lists the scoring criteria.
To this end one of you who is bold and artful must go into the city dressed as a traveller, and discover whom we have killed, and whether men talk of the strange manner of his death
2.2.4Observation of general condition of rats. During the experiment, the general changes of rats in each group were closely observed, including mental state, hair state, diet state, feces state,etc., and after 4 weeks of administration, the appearance of knee joints of rats in each group was observed and photographed at the time of sample collection, and the pathological changes of rats in each group were analyzed and compared.
2.2.5Indicator detection. (i) Detection of the histopathological changes in cartilage and synovium by the HE staining. Synovium and decalcified cartilage (decalcified with 10% EDTA) were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for more than 24 h, and then dehydrated, waxed, embedded and sectioned. Tissue sections were dewaxed, hematoxylin stained nuclei, eosin stained cytoplasm, dehydrated and sealed, and examined under microscope for professional description and analysis. Designated experimenters randomly selected 3 visual fields from each picture under the microscope, scored and graded the morphology of cartilage tissue slices in each group by Mankin’s, and the scoring criteria are shown in Table 2.
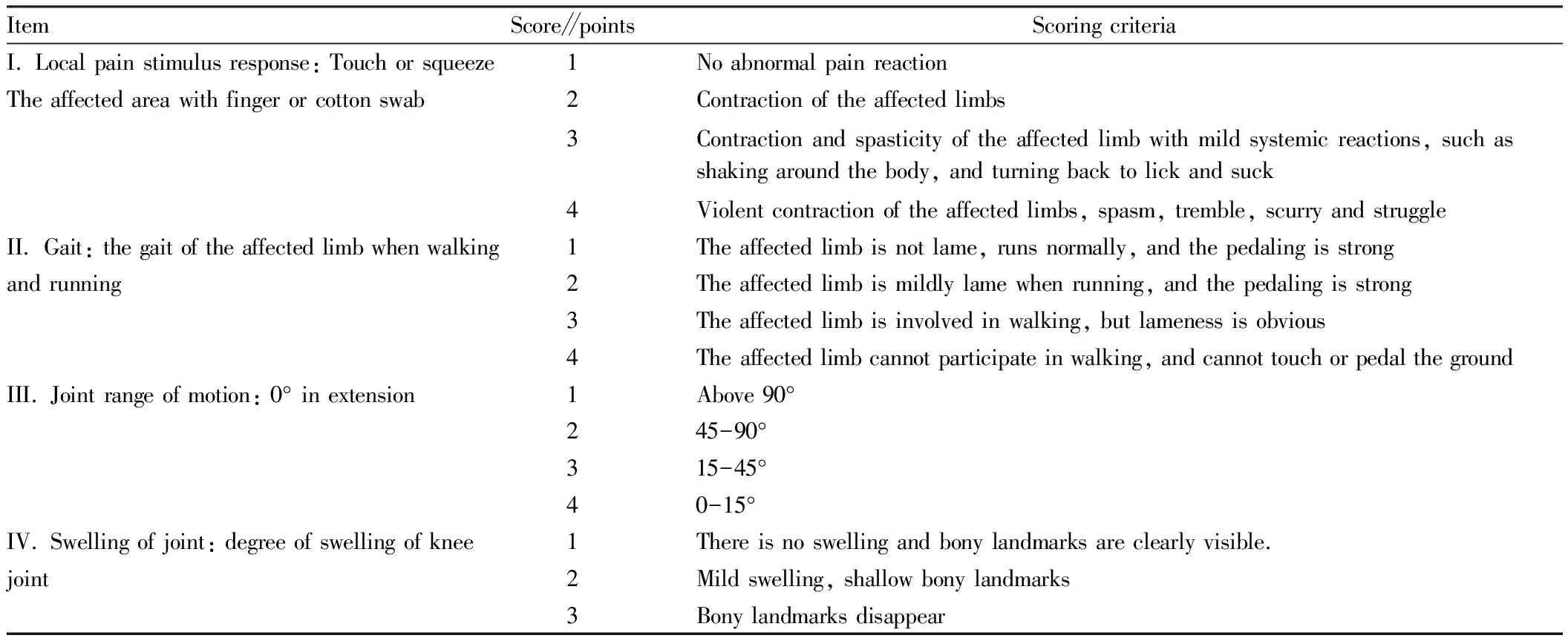
Table 1 Lequesne MG scoring criteria for knee joint[12]

Table 2 Mankin’s scoring criteria[13]
(ii) Detection of TNF-α, IL-1β, COX-2 and PGE2in serum by ELISA. The frozen serum samples were centrifuged and the supernatant was detected according to the instructions of TNF-α, IL-1β, COX-2 and PGE2kits.
(iii) The relative expression levels of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 mRNA in rat cartilage were detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). Took the frozen rat cartilage tissue, weighed an appropriate amount of each tissue, ground it into powder, added Trizol, extracted the total RNA of the injured soft tissue by centrifugal column method, reversely transcribed into cDNA, and carried out RT-PCR reaction. ABI real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument was used to monitor and record the data. Using β-actin as internal control gene, the primer sequence was β-actin upstream primer sequence 5′-TTGCTGACAGGATGCAGAAG-3′ and downstream primer sequence 5′-TAGAGCCACCAATCCACACA-3′, and the length of amplified product was 108 bp; the upstream primer sequence of MMP-9 was 5′-AGCCTGTGGTTGGTCAGAAG-3′, and the reverse primer sequence of MMP-9 was 5′-GTCCGGTTTCAGCATGTTTT-3′; the sequence of TIMP-1 upstream primer was 5′-GCCATGGAGAGCCTCTGTGG-3′, and the sequence of downstream primer was 5′-GCAGGCAGGCAAAGTGATCG-3′, and the length of the amplified product was 310 bp. According to theCtvalue of qRT-PCR original data, the relative expression of each mRNA was analyzed by 2-ΔΔCtmethod.
(iv) Detection of expressions of MMP-9, TIMP-1, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB by Western Blot. The frozen rat cartilage tissue was taken, 20 mg of each tissue was weighed and placed in a 2 mL EP tube, and 200 μL of the lysate was added, the homogenizer was used to homogenize for 5 min, and centrifuged at 4 ℃ and 13 000 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was aspirated, and the protein concentration was determined by BCA method to prepare protein samples; Loaded samples, performed SDS-Page electrophoresis, blocked added TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 primary antibodies, incubated overnight at 4 deg C, and washed with PBS-T for 3 times; added the goat anti-rabbit IgG labeled with horseradish peroxidase to incubate for 2 h, and then washed with PBS-T for 3 times; ECL luminescent solution was used for development, and automatic gel imaging system was used for observation and photography, and GAPDH was used as internal reference, and Image J software was used to calculate the protein gray value.
3 Results and analysis
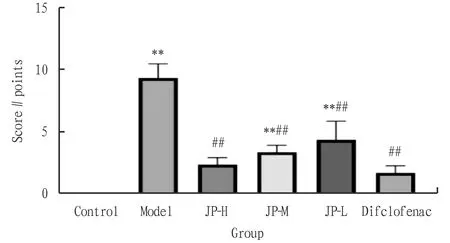
3.1 Effects on Lequesne MG score of rat knee jointThrough observing and comparing the Lequesne MG scores of each group before administration and 4 weeks after administration, it can be seen from Fig.1 that before administration, compared with the control group, other groups had extremely significant differences (P<0.01), but there was no difference between groups, which showed that the rat osteoarthritis model of other groups was successfully established; after 4 weeks of administration, there was still a significant difference between the other groups and the control group (P<0.01), and compared with the model group, there was a significant difference between other administration groups (P<0.01).
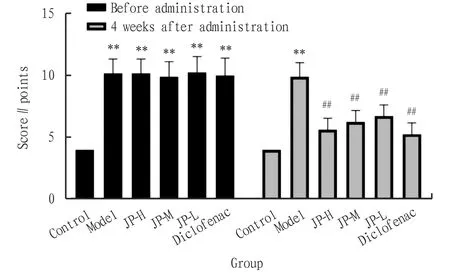
Note: **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with the control group; ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 compared with the model group.
3.2 Effects on behavior and appearance of knee joint in rats
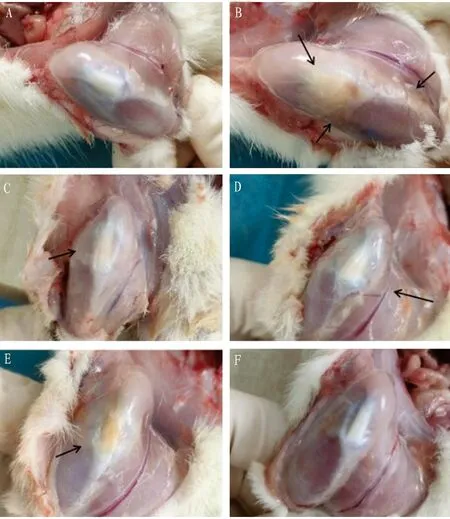
Through observing and comparing the appearance of the knee joints of the rats in each group after 4 weeks of administration, that is, at the time of sample collection, it can be found that the knee muscles of the rats in the control group were not injured, and the patella and patellar ligament were intact without inflammation. By contrast, the patella and surrounding tissues of rats in the model group were seriously fibrosed, the synovium was thickened, the synovial fluid was yellow and thick, the tissues were mostly edematous and necrotic, the pannus was obvious, and the inflammatory symptoms were prominent. Compared with the model group, the Diclofenac group had the most prominent curative effect, and the symptoms of the JP-H and JP-M groups were significantly improved. Although the appearance of the JP-L group still showed severe patellar inflammation, the pannus and tissue fibrosis were significantly improved (Fig.2).
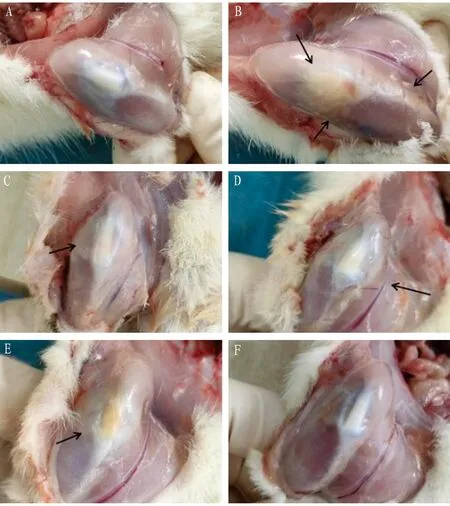
Note: A is control group, B is model group, C is JP-H group, D is JP-M group, E is JP-L group, and F is Diclofenac group.
3.3 Effects on pathological damage of cartilage in rats and Mankin’s score of cartilage tissueUnder the microscope, it can be observed that the joint surface of control group was covered with a thin layer of hyaline cartilage, without obvious tissue hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration and other pathological changes. In the model group, most of the joints were fibrotic, with a large number of inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrous proliferation. In JP-H group, infiltration of inflammatory cells was occasionally seen, and no obvious tissue hyperplasia was found. In the JP-M group, the articular cartilage was destroyed, and occasionally there was infiltration of fibrous connective tissue and inflammatory cells. In the JP-L group, fibroplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration were occasionally observed in the articular cartilage. In Diclofenac group, fibrous tissue hyperplasia was occasionally seen in articular cartilage, and a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration could be seen (Fig.3-4).
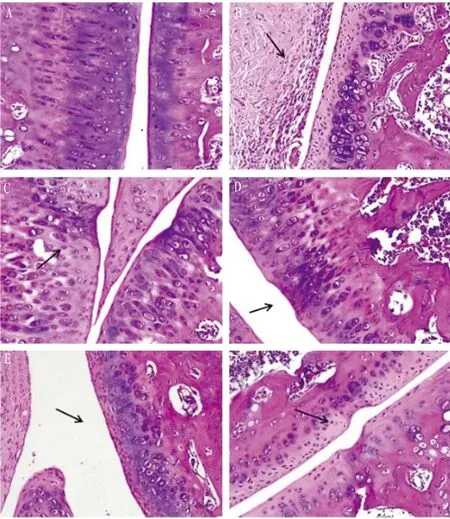
Note: A is control group, B is model group, C is JP-H group, D is JP-M group, E is JP-L group, and F is Diclofenac group.
Note: **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with the control group; ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 compared with the model group.
3.4 Effects on pathological injury of synovium in ratsUnder the microscope, it can be observed that there were no obvious pathological changes such as cell proliferation, interstitial congestion and inflammatory cell infiltration in the synovium of control group. In model group, synovial cells proliferated, layers increased, synovial tissue hyperemia, edema, infiltration of a large number of inflammatory cells, granulation tissue formation and severe fibrosis were observed. In JP-H group, there was no obvious cell proliferation and interstitial congestion in synovium, and inflammatory cell infiltration was occasionally seen. In the JP-M group, the synovial cells proliferated and scattered inflammatory cells infiltrated. In JP-L group, there were synovial cell proliferation, interstitial congestion, edema and inflammatory cell infiltration. In Diclofenac group, there was no obvious cell proliferation and interstitial congestion in the synovium, and sporadic inflammatory cell infiltration was occasionally seen (Fig.5).
Note: A is control group, B is model group, C is JP-H group, D is JP-M group, E is JP-L group, and F is Diclofenac group.
3.5 Effects on TNF-α, IL-1β and COX-2 in serum of ratsFrom Fig.6, it can be seen that compared with the control group, the contents of TNF-α, IL-1β and COX-2 in the model group were significantly increased (P<0.01); compared with model group, the contents of TNF-α, IL-1β and COX-2 in JP-H and JP-M groups were significantly lower (P<0.01), and the contents of TNF-α and COX-2 in JP-L and Diclofenac groups were significantly lower (P<0.01).
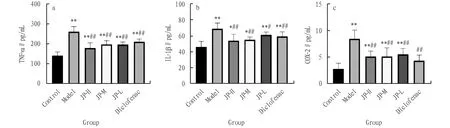
Note: **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with the control group; ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 compared with the model group.
3.6 Effects on the relative expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 mRNA in rat cartilageThe results of qRT-PCR showed that the relative expression of MMP-9 mRNA in model group was significantly higher than that in Control group (P<0.01), and the relative expression of TIMP-1 mRNA in model group was significantly lower than that in Control group (P<0.01). Compared with model group, the relative expression of MMP-9 mRNA in JP-H group was significantly increased (P<0.01), the relative expression of TIMP-1 mRNA was significantly decreased (P<0.05), and the relative expression of MMP-9 mRNA in JP-M group was significantly increased (P<0.01), the relative expression of MMP-9 mRNA in Diclofenac group was significantly increased (P<0.01), while the relative expression of TIMP-1 mRNA was significantly decreased (P<0.01), as shown in Fig.7.
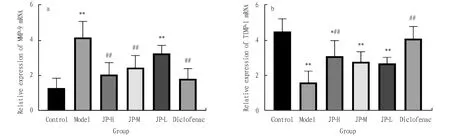
Note: **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with the control group; ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 compared with the model group.
3.7 Effects on the expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in rat cartilageBy collecting the cartilage tissue of rat knee joint, we extracted the protein and detected it by Western-blot. The results showed that the relative protein expression of MMP-9, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in Model group was significantly higher than that in control group (P<0.01), while the relative protein expression of TIMP-1 was significantly lower than that in control group (P<0.01). Compared with model group, the relative expression of MMP-9 was significantly increased (P<0.01), and the relative expression of TIMP-1 was significantly decreased (P<0.01); the relative protein expression of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in JP-H group was significantly increased (P<0.01,P<0.05), the relative protein expression of MyD88 and NF-κB in JP-M and JP-L group was significantly increased (P<0.01,P<0.05), and the relative protein expression of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in Diclofenac group was significantly increased (P<0.05). The relative protein expression of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB was significantly increased (P<0.01), as shown in Fig.8 and 9.
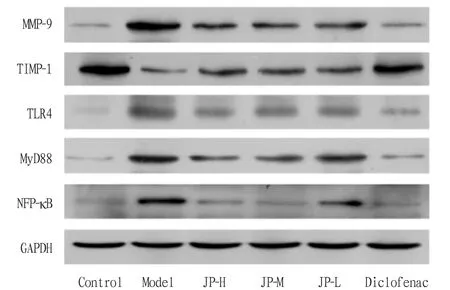
Fig.8 Effects of Jipei Dilong Ointment on the expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in rat cartilage
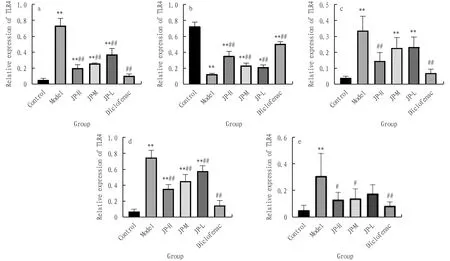
Note: **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with the control group; ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 compared with the model group.
4 Discussion
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that OA belongs to the category of "bone impediment". Wang Heming[14], a famous contemporary orthopedist, combined with previous experience, believed that deficiency of liver and kidney and deficiency of qi and blood are the root causes of OA[15]. At present, conservative treatment such as patient education and self-conditioning is often used for patients with early OA[16]. If the effect is not obvious, priority should be given to oral analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate symptoms and restore knee joint function, but such drugs can also increase the prevalence of gastrointestinal and cardiovascular diseases. For advanced patients with ineffective drug treatment and loss of joint function, surgical treatment such as joint replacement is common, but such methods are not only expensive, but also increase the risk of complications such as deep vein thrombosis and infection of lower limbs[17]. In recent years, external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine has been widely used in clinical practice based on its characteristics of high quality,low price, remarkable curative effect and rapid action, which provides new ideas and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of OA, including external application of traditional Chinese medicine, body acupuncture, small needle knife, massage, acupoint catgut embedding, acupoint injection, moxibustion and so on. Among them, external application of traditional Chinese medicine is an enduring treatment method, whose mechanism is to directly act on the lesion site and play a therapeutic role through the conduction of the corresponding meridians[18].
The research result shows that after the Jipei Dilong Ointment treatment for 4 weeks, compared with the model group, the Lequesne MG score and the cartilage tissue Mankin’s score of each administration group of the Jipei Dilong Ointment can be significantly reduced. The results of HE staining of cartilage and synovium suggested that Jipei Dilong Ointment could improve the infiltration of inflammatory cells, tissue fibrosis and hyperplasia of cartilage and synovium in different degrees. Western-blot results showed that Jipei Dilong Ointment could effectively reduce the protein expression of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB in articular cartilage of OA rats, inhibit the occurrence of inflammation, and play a protective role in articular cartilage to a certain extent. Yang Yiyunetal.[19]taking spontaneously hypertensive rats as the research object, concluded that Pheretima can reduce early renal damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats, which may be related to the regulation of Ang II-TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. The research results of Li Zhongetal.[20]suggest that the combination of Polygoni Cus pidati Rhizoma Et Radix and cassia twig can relieve the symptoms of rats with acute gouty arthritis induced by sodium urate, which may be related to the inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway expression. Lai Genxiangetal.[21]confirmed that Gardeniae Fructus glycoside alleviated hippocampal inflammation and improved cognitive function in sleep-deprived rats, which may be related to the inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Based on this, the protective mechanism of Jipei Dilong Ointment on arthritis rats may be related to the inhibition of abnormal activation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.
The secretion of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors (TIMPs) in healthy cartilage remains in equilibrium. Some scholars stated that MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-9 are highly expressed in cartilage and synovial cells of early OA patients, while the expression of TIMP-1 has no upward trend, so the balance of MMPs/TIMPs is broken at this time, which further accelerates the course of OA[22]. In this study, the changes in mRNA and protein expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the cartilage of arthritic rats also showed that the imbalance of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 was an important factor leading to OA. Findings of Fu Yuanfengetal.[23]showed that Drynariae Rhizoma decoction combined with alendronate sodium tablets had significant clinical efficacy in elderly patients with osteoporosis, and could effectively reduce the content of MMP-9 in serum. The research results of Wang Songetal.[24]indicated that the effect of Polygoni Cus Pidati Rhizoma Et Radix glycoside on delaying the process of renal fibrosis in rats may be related to the up-regulation of MMP-9 protein expression and the down-regulation of TIMP-1 protein expression, and the increase in the MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio. Based on this, there is evidence that Jipei Dilong Ointment can protect the cartilage of OA rats by regulating the ratio of MMP-9/TIMP-1, and the study of the relationship between the ratio of MMPs and TIMPs has important value for the treatment and prognosis of OA.
Ethnic minority medicine is mostly spread and used in the areas inhabited by ethnic minorities in Southwest China. Due to the influence of historical culture, cultural customs and traffic congestion, the resources of ethnic minority medicine are scarce, and the development and promotion of ethnic minority medicine are limited because of people’s limited understanding of ethnic medicine. In this study, we explored the protective effect and mechanism of Shui People’s Classic Prescription Jipei Dilong Ointment on OA in rats byinvivoexperiments. The results suggest that Jipei Dilong Ointment may play a protective role in OA by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. The imbalance of MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio also plays an important role in the intervention of OA by Jipei Dilong Ointment, which can regulate osteoarthritis in multiple pathways and directions. However, the results still lack the effect of advanced Jipei Dilong Ointment of osteoarthritis on the ratio of MMP-9/TIMP-1 in articular cartilage. In the future, our team will further inherit and carry forward ethnic medicine on this basis, and provide a scientific basis for expanding the clinical use of Jipei Dilong Ointment, in order to promote rural revitalization and serve the social and economic development of Guizhou Province.
杂志排行
Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Quality Control of Zhuang Medicine Xiaoyan Zhiyang Lotion
- Research Progress and Ideas on the Anti-liver Fibrosis Effect of Ethnic Medicine Plumbagin Based on microRNAs/TLR4/NF-κB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- Gastroprotective Effect of Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) Burttet Smith on Ethanol-induced Gastric Ulcers in vivo and vitro
- Exploring the Mechanism of Blumea balsamifera (L.) DC in Preventing and Treating Alzheimer’s Disease Based on HPLC-ESI-HRMS and Network Pharmacology
- Observation on Therapeutic Effect of Erxian Decoction on Relieving Low Back Pain after PVP of PMOP-derived Vertebral Fracture
- Effects of Early-stage Phased Rehabilitation Training on Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
