Risk assessment of oil and gas pipelines hot work based on AHP-FCE
2023-08-30SnHeHuilnXuJinxiongZhngPeiqingXue
Sn He ,Huiln Xu ,Jinxiong Zhng ,Peiqing Xue
a Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu,610500,China
b Sinopec Southwest Oil & Gas Company,Chengdu,610095,China
c PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gas Field Company Shunan Gas Mine,Luzhou,64600,China
d PetroChina Qinghai Oilfield Downhole Operation Company,Haixi Mongolian and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture,816100,Qinghai,China
Keywords:Oil and gas pipelines Hot work Risk assessment Analytic hierarchy process (AHP)Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation (FCE)
ABSTRACT A new quantitative risk assessment method for hot work is proposed based on the analytic hierarchy process(AHP)and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation(FCE).It can help pipeline companies realize the risk management of hot work and further ensure the safe operation of oil and gas pipelines.Taking one natural gas pipeline in China as an example,this paper evaluates the risk of a single hot work in the spring of one natural gas pipeline in a high consequence region.First of all,the risk factors are determined with reference to the job safety analysis (JSA),and then experts were invited to fill out a questionnaire to collect their opinions.According to the results of the questionnaire,AHP is used to calculate the weight coefficients of the evaluation indicators,and FCE is used to evaluate the risk level of hot work.After calculation,the comprehensive risk score of hot work is 40.888.It belongs to a "general risk".This method can not only quantitatively evaluate the risk levels of hot work,but also reasonably sort the importance of various risk factors.It is helpful for the effective management of hot work and provides suggestions for implementing control measures.
1.Introduction
In oil and gas field,the production process involves equipment maintenance and repair,technical transformation,and project construction.Hot work is inevitable [1].Hot work refers to any work that requires using open flames,applying heat or friction,or may generate sparks or heat.Oil and gas are flammable and explosive materials.In the construction of oil depots,oil pump areas,and oil and gas pipelines,fire sources such as electric shock sparks,mechanical friction,welding,torches,and open flames may cause fires and explosions.Such dangerous accidents will lead to irreparable economic losses and personal injury[2].In 2013,due to improper hot work,a miscellaneous material tank exploded in the triphenyl tank area of a petrochemical company in Dalian,China.After the spilled material caught fire,the three adjacent storage tanks were also ignited one after another.The explosion caused four deaths and an economic loss of 0.99 million dollars.In 2019,a refined oil storage tank of a logistics company in Qingdao,China accidently caught fire during the hot work for inspection and maintenance,resulting in one death and one injury [3].
In the field of work safety,the analytic hierarchy process(AHP)is widely used.It is simple and practical.Saman Aminbakhsh et al.[4] proposed a security risk assessment framework based on AHP.The aim is to prioritize safety risks in construction projects and identify potential hazards.Abel Pinto et al.[5]studied the impact of the occupational injury on safety,health,and economy.P.K.Marhavilas et al.[6] classified a variety of risk analysis and evaluation methods.The results show that the usage rate of the quantitative method is 65.63%,the usage rate of the qualitative method is 27.68%,and the usage rate of the hybrid method is only 6.70%.I.A.Papazoglou et al.[7]established a worker occupational risk model.It can link working conditions,worker behavior,and the possibility of accidents.Yas¸ar Kasap et al.[8]analyzed the operational risks of open-cut mining to prevent industrial accidents.The fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (FAHP) is improved based on the traditional analytic hierarchy process.It improves the reliability of decisionmaking and is conducive to quantifying evaluation indicators.Metin Da deviren et al.[9] used the fuzzy analytical hierarchy process(FAHP)to determine the risk level of wrong behavior in the workplace.Shi-yu Li et al.[10] established a fire evaluation index model for high-rise buildings based on FAHP and analyzed the influencing factors of fire.Besides,the application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation (FCE) is also relatively wide.Its results are clear and systematic.It can solve vague and difficult to quantify problems.Jun Hu et al.[11] quantitatively evaluated earthquake risk based on FCE.Weijun Li et al.[12] improved the conventional health,safety,and environment (HSE) performance evaluation method.The new HSE performance evaluation method combines expert weights with FCE.The application of the above methods is relatively mature,but all have certain limitations.It is necessary to consider a reasonable combination of them to improve the accuracy of the evaluation results.
At present,there are few studies on the risk assessment of hot work.Oil and gas companies often use job safety analysis (JSA) to identify risk factors for hot work in advance and take control measures to reduce operational risks [12].However,JSA's subjective influence is large,and it can only judge the operational risk qualitatively rather than quantitatively[13].Based on the combined method of AHP-FCE,a new quantitative risk assessment method for hot work is proposed.This method can be applied to the fields of oil and gas.It aims to evaluate the risk level of hot work of oil and gas pipelines and to reasonably sort the importance of various risk factors.
2.AHP-FCE-based risk assessment method
Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation(FCE)is a method based on the membership degree theory of fuzzy mathematics.It can solve multivariate problems in complex decision-making processes[14].In this process,it is often necessary to consider multiple related factors to obtain vague evaluation results [15].One of the prerequisites of FCE is to determine the weight of each evaluation index.It is generally specified directly by the decision-maker.However,for complex issues,for example,there are many evaluation indicators and they have an influence relationship with each other.It is difficult to directly give the weight of each evaluation index,and this problem is exactly what AHP is good at.The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is a combination of qualitative and quantitative decision-making methods.It can be applied to different evaluation layers,namely the target layer,the criterion layer,and the scheme layer [16].In AHP,through the decomposition of the problem,the complex problem is decomposed into multiple subproblems.Then,the weight of the evaluation index can be obtained through the pairwise comparison of the evaluation index.The combination of the two methods makes up for their shortcomings.
The combined AHP-FCE can be used to evaluate the risk of hot work.The main steps are as follows:
Step 1 Determination of risk factors.
By referring to existing evaluation standards or expert experience,analyze the target problem to determine the set of influencing factors[17].The factor setUcan be described as:ui(i=1,2,…,m)is called the influencing factor of the evaluation object.
Step 2 Calculation of weight coefficient of risk factors
Based on the analysis of the research object,the paper establishes a hierarchical analysis model for risk assessment of hot work.A certain factor in the upper layer is the evaluation criterion.Through the pairwise comparison of the factors of this layer,the relative weight value of each factor of this layer relative to the factors of the previous layer can be determined.The two factors are denoted as i and j,the relative weight value is denoted ascij,and the judgment matrix is denoted as C=(cij)n*n.The judgment matrix is obtained from the questionnaire results of the evaluation team members.
The three scale method and the nine scale method are often used to characterize the relative importance of various factors.However,in practical applications,when the evaluation team members use the nine scale method,it is difficult to make a rigorous distinction between the importance of evaluation indicators.It may cause blurred judgment boundaries.The judgment boundary of the three scale method is too simple,and the degree of discrimination between the factors is not high [18].Therefore,in this paper,the five scale method is used to construct the judgment matrix.It is simple in form and conforms to the thinking logic of the human brain.
According to the judgment matrix,the largest eigenvalue λmaxand the corresponding eigenvector Wiare obtained (see Table 1)[18].After normalizing Wi,the value (W1,W2,…,Wn)of the eigenvector W0i is obtained.This is the weight coefficient of the evaluation indicators.According to formulasCR=CI/RIandCI=(λmax-n)/(n-1),the consistency test of the judgment matrix is carried out to judge whether the weight distribution is reasonable[19].CIis the consistency index;nis the order of the judgment matrix;RIis the average random consistency index.As shown in Table 2.WhenCR<0.1,the consistency check of the judgment matrix passes.Otherwise,it is necessary to adjust the judgment matrix to ensure that the value ofCRis less than 0.1.
The weight coefficients of evaluation indicators can explain the relative importance of various risk factors.Their rationality directly affects the accuracy of risk assessment results [20].The index weight setAcan be described as:
Step 3 Determination of evaluation set
Evaluation set refers to various possible evaluation results.It is usually expressed in vague language.For example,the assessment results are divided into four categories: (1) low risk;(2) general risk;(3) high risk;and (4) significant risk.Then the evaluation set can be described as:
where vi(i=1,2,3,4)represents four possible assessment categories.
Step 4 Determination of the evaluation matrix
Assuming that the membership degree of factorui(i=1,2,…,m)to each evaluation result is vi(i=1,2,…,n),then the evaluation result set ofuican be expressed as:
rijis determined by the evaluation team members.For example,if 40%of the total members of the evaluation team classifyuias theevaluation result vi,the value ofrijis 0.4.Whenrijhas more than 4 significant digits,four significant digits are reserved.After calculating the evaluation result set of all factors in factor setUby the above method,the evaluation matrix can be determined.As follows:

Table 1 Assignment principles of the five scale method.
Step 5 Fuzzy composition
After the fuzzy composition of the index weight setAand evaluation matrixR,the membership degree of the evaluation subject can be obtained.The calculation formula is as follows:
where,birepresents the degree of membership of the evaluation object to each evaluation result,and the symbol"◦"represents the fuzzy composition method.
There are many fuzzy composition methods,includingM(∧,∨),M(∙,∨),M(∧,⊙),M(∙,⊙),etc.“∧”and“∨”indicate the selection of smaller value and larger value,respectively,“∙” indicates multiplication,and “⊙” indicates addition.MethodM(∧,∨)belongs to the prominent main factor type,with simple and practical characteristics.It is suitable for the risk assessment and analysis of hot work.The specific method is as follows:
3.Case study
Take a natural gas pipeline of one oil and gas company as an example.The pipeline has a total length of 130 km,a pipe diameter of 1016 mm,and a design pressure of 10 MPa.There are 4 sections of the pipeline within 100 m from the established school.They are all high-consequence regions.Take one of the pipeline sections in the high consequence region as an example.The total length of the pipeline in this block is 596 meters,and its district level is a secondary district.According to the classification rules for highconsequence regions,this section should be a level II highconsequence region.The paper evaluated the risk of a single hot work of the natural gas pipeline in this block in spring.The basic data comes from the HSE evaluation department.
The five main steps of the above-mentioned combined AHP-FCE are summarized into four specific application steps,including: (1)determine the risk factors of hot work;(2)invite experts to fill out the questionnaire;(3)AHP-based calculate the weight coefficient of the evaluation index;and(4)FCE-based quantitatively evaluate the risk level.
3.1.Risk factors and evaluation indicators
With reference to JSA,the process of hot work is divided into three parts,namely,preliminary preparation,during construction,and end of construction [21].The various risk factors in the construction process are the evaluation indicators[22].The evaluation indicators of hot work are listed in Table 3.
3.2.Questionnaire survey process and results
To collect relevant information on hot work,we conducted a questionnaire survey.Participants included 27 company employees and 13 university scientific researchers,a total of 40 people formed the evaluation team.The members of the assessment team shall be engaged in pipeline safety assessment and technical supervision for 3 years or more.Among them,the company's employees include 5 technical experts(3 doctors and 2 masters)who have been engaged in the safety field for more than 10 years,as well as 4 safety managers and 18 safety engineers with 5 years of work experience.University researchers include 5 professors and 8 associate professors.The evaluation team members need to compare each subindicator of the main indicator in turn.According to their experience,the importance scale is given to obtain the judgment matrix.In addition,they also need to evaluate the risk levels of various risk factors in the process of hot work.Table 4 shows the evaluation results of the risk levels of various risk factors of hot work.
Suppose the risk level is set as:
V={V1,V2,V3,V4}={“Low risk”,“General risk”,“High risk”,“Significant risk”}
3.3.AHP-based index weight determination
The highest layer is the decision-making goal,the lowest layer is the decision-making plan,and the middle layer is the decisionmaking criterion [23].The hierarchical analysis model is shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1.Hierarchical analysis model.
The judgment matrix obtained from the questionnaire is shown in Table 5.
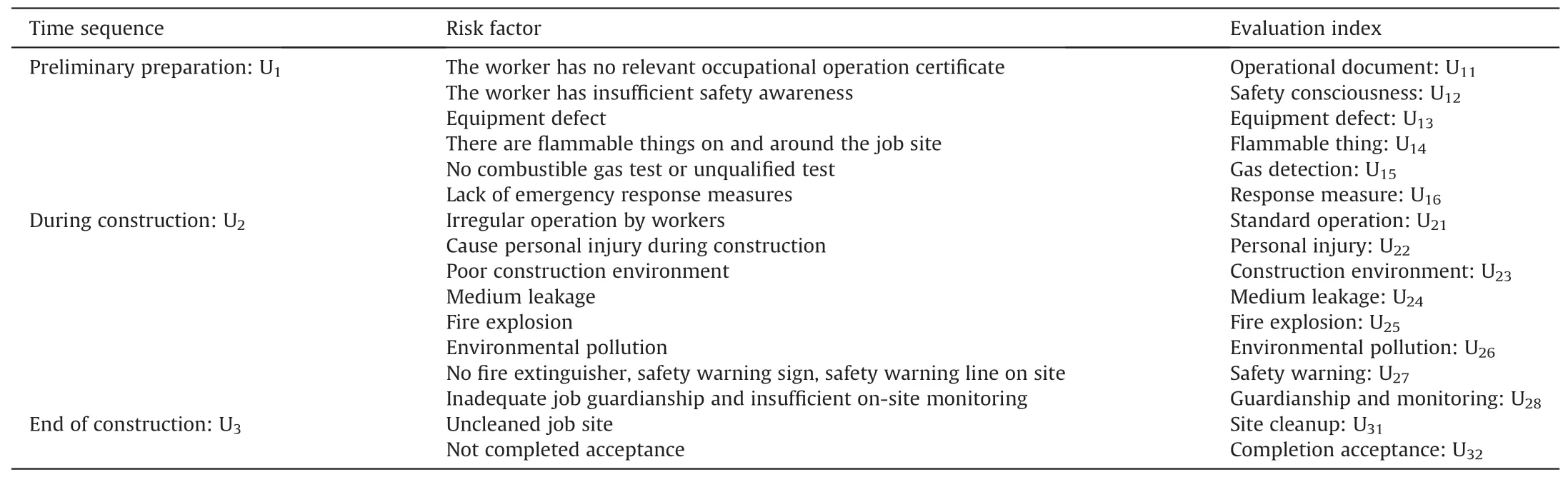
Table 3 Evaluation index of hot work.
3.4.FCE-based risk level evaluation
According to the risk level evaluation results of hot work from Table 4,the sub-indicator evaluation results set are obtained:

Table 5 Judgment matrix and consistency test results.
The main index evaluation matrix is determined as follows:
The main index weight setA=[0.2255 0.6738 0.1007] can be obtained from Table 6.
The comprehensive evaluation result is calculated:
3.5.Analysis of evaluation results
To quantitatively evaluate the risk of hot work,the exact score can be used to represent the risk level.The risk of hot work is divided into 4 levels,and the full score is set to 100 points.“Low risk”means a score below 25,“General risk”means a score between 25 and 50,“High risk” means a score between 50 and 75,and“Significant risk” means a score over 75.
The evaluation result value setNcan be expressed as:
It is necessary to consider the worker's sensitivity to the risks of hot work.If the risk level value is too high,the workload of workers and managers will increase.If it is too low,the risk will not get enough attention and dangerous accidents will easily occur.Therefore,the risk level value should be moderate to meet theactual construction conditions.The risk level value set should be set toN=(13 38 63 88).
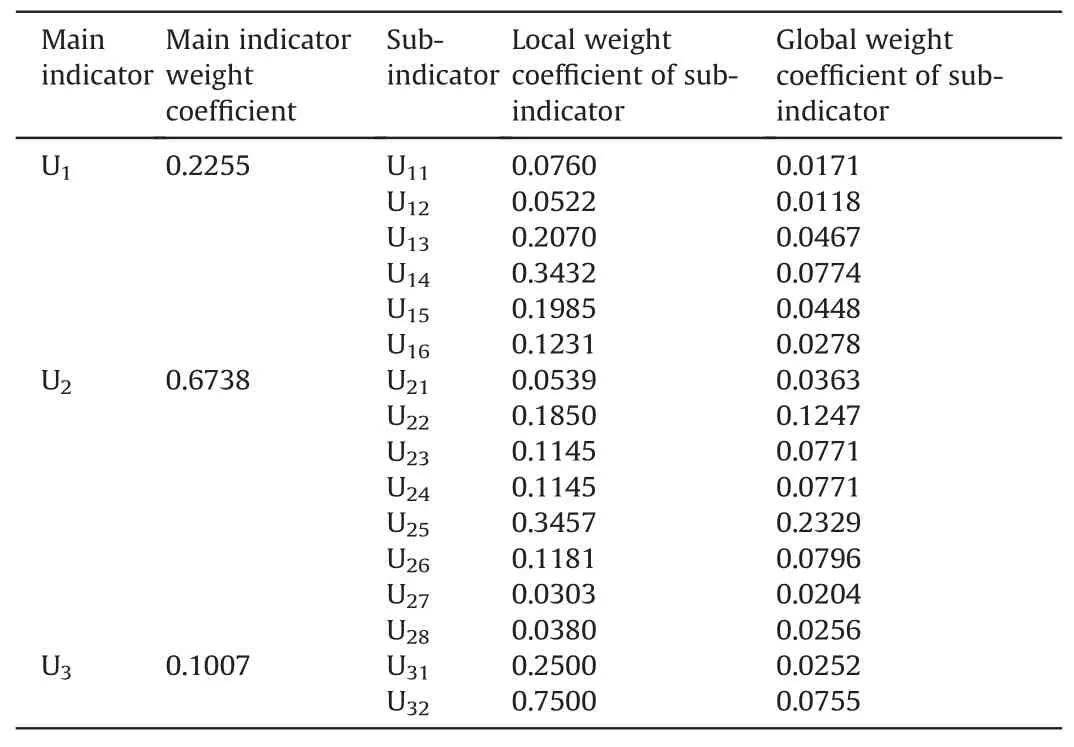
Table 6 Weight coefficient of the evaluation index.
After calculation,the comprehensive risk assessment score of hot work is:
Therefore,the comprehensive risk assessment score of this hot work is 40.888.It belongs to a "General risk".
4.Discussion
The steps of risk assessment for hot work of oil and gas pipelines include identification of risk factors,questionnaire surveys and data collection,calculation of the weight coefficient of evaluation indicators based on AHP,and evaluation of risk levels based on FCE.It can be seen from Table 6 that the weight coefficient of During construction (U2) is the highest among the three main indicators,followed by Preliminary preparation (U1) and End of construction(U3).When Preliminary preparation (U1) is used as the evaluation standard,among the sub-indicators,flammable thing(U14)has the highest weight coefficient,and safety consciousness (U12) has the lowest weight coefficient.Similarly,when During construction(U2)is used as the evaluation standard,among the sub-indicators,fire explosion (U25) has the highest weight coefficient,followed by personal injury(U22)and environmental pollution(U26),and safety warning(U27)has the lowest weight coefficient.Finally,when End of construction (U3) is used as the evaluation criterion,the weight coefficient of completion acceptance (U32) is greater than site cleanup (U31) in the sub-indicators.During the construction process,managers should focus on risk indicators with high weight coefficients,and take targeted control measures to reduce the risk of hot work.The results of the questionnaire show that the evaluation team members have different judgments on the risk levels of various risk factors.But the scope of the difference is not large and it is acceptable.Most of the evaluation team members believe that fire explosion (U25),personal injury (U22),and flammable thing(U14) have high-risk levels,while site cleanup (U31) has low-risk levels.
To reduce the overall risk level of hot work,managers should consider properly controlling the three risk factors with the highest weight coefficients,namely fire explosion (U25),personal injury(U22),and environmental pollution(U26).The fire source should be strictly controlled during the construction period.The equipment should be placed on the upwind.At the same time,it is economical and effective to use soil,dry powder,and water mist to isolate flammable things.Besides,it is strictly forbidden to throw working tools and materials during the construction process.It is necessary to strictly abide by the operating procedures and ensure that the electric pick and the power cord are not damaged.After the completion of construction,all kinds of garbage in the construction site should be recycled to protect the environment.
Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is a multi-objective decision analysis method that combines qualitative and quantitative analysis.It has been widely used in resource allocation,enterprise management,project evaluation,and planning consultation.Through this method,the weight coefficient of the evaluation index of the research object can be calculated so that the importance of each index can be ranked,which is convenient for management.However,the AHP method cannot make an overall quantitative evaluation of the research object,and it is greatly influenced by human beings.The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method (FCE)can better solve the fuzzy and difficult to quantify problems,reduce the human influence,and is suitable for solving various nondeterministic problems.In recent years,applying the FCE method in medicine,construction industry,environmental quality supervision,water conservancy,and other fields has achieved initial results.But the calculation process of FCE is more complicated.The AHP-FCE evaluation method combining the systematicness of the AHP and the fuzzy problem-handling ability of the FCE method is introduced to evaluate the risk of hot work.It can quantitatively assess the risk of hot work and reasonably sort the weight coefficients of various risk factors.It is conducive to optimizing resource allocation and helping to improve the level of operational risk management.
The hot work case in the paper is representative,but different hot work may have different risk factors.It is necessary to determine the evaluation index according to actual working conditions.When the evaluation index changes,the weight coefficient of the evaluation index and the comprehensive risk assessment score will also change.The risk assessment method of hot work in the paper is also applicable to the risk assessment of other types of work.The use of this method requires specific analyses of specific circumstances.It is necessary for real-time analysis and accurate replacement of evaluation indicators.
5.Conclusions
(1) Based on the AHP-FCE combination method,this paper establishes a risk assessment method for hot work that can be applied to the oil and gas field.This method can quantitatively evaluate the risk of hot work.At the same time,it can sort the importance of various risk factors of hot work,help managers better understand the operation risks,and provide appropriate management and control suggestions.
(2) This method is also applicable to other types of operational risk assessment,and the assessment indicators need to be replaced according to the actual situation.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
杂志排行
Petroleum的其它文章
- Super gas wet and gas wet rock surface: State of the art evaluation through contact angle analysis
- Petroleum system analysis-conjoined 3D-static reservoir modeling in a 3-way and 4-way dip closure setting: Insights into petroleum geology of fluvio-marine deposits at BED-2 Field (Western Desert,Egypt)
- Development and performance evaluation of a high temperature resistant,internal rigid,and external flexible plugging agent for waterbased drilling fluids
- Anti-drilling ability of Ziliujing conglomerate formation in Western Sichuan Basin of China
- Production optimization under waterflooding with long short-term memory and metaheuristic algorithm
- Investigation of replacing tracer flooding analysis by capacitance resistance model to estimate interwell connectivity
