Anti-drilling ability of Ziliujing conglomerate formation in Western Sichuan Basin of China
2023-08-30NinPengTinshouGongshengZhuQingSu
Nin Peng ,Tinshou M ,* ,Gongsheng Zhu ,Qing Su
a State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation,Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu,610500,China
b Drilling & Production Engineering Technology Research Institute,CNPC Chuanqing Drilling Engineering Co.,Ltd.,Guanghan,618300,China
c Engineering Technology Research Institute,PetroChina Southwest Oil & Gas Field Company,Chengdu,610052,China
Keywords:Conglomerate rock Ziliujing formation Mechanical properties Drillability Drill bit selection
ABSTRACT The conglomerate rock is usually featured by strong heterogeneity,high abrasiveness,and poor drillability due to its complex composition and texture,which brought a huge challenge for drilling efficiency.In order to guide the drill bit selection and high-efficiency drilling,the physical,mechanical,and drillability characteristics were investigated for conglomerate rock that collected from the lower Jurassic Ziliujing formation in the Western Sichuan Basin of China.The mineral composition,SEM microstructure,P-and S-wave velocities,uniaxial and triaxial compressive testing,drillability,abrasiveness were systematically tested and analyzed.The mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability of Ziliujing formation were proposed for a typical deep well of S-07,and the distribution characteristics were analyzed.The results indicated that the Ziliujing rock is rich-in quartz and clay minerals,due to the coexisting of strong quartz gravel and weak argillaceous cement,the Ziliujing rock shows strong heterogeneity.The relationships are roughly linear among UCS,drillability,and grinding weight loss with Pwave velocity.The Young's modulus,UCS,internal friction angle,drillability,and abrasiveness meet the Weibull distribution pattern,while only the Poisson's ratio meets the Kernel Smooth distribution pattern.Logging interpretation results reval that the Ziliujing formation has the Young's modulus of 38.61 ± 17.08 GPa,the Poisson's ratio of 0.327 ± 0.006,the internal friction angle of 49.21 ± 11.00°,the drillability of 8.04±1.54,and the abrasiveness grade of 4.32±1.94.The mechanical properties and antidrilling ability of logging interpretation are in good agreement with the experimental data.The Ziliujing formation is a kind of hard rock with strong heterogeneity,high strength,poor drillability,and medium abrasiveness.Based on the characteristics of Ziliujing formations,the SV516TAUL PDC bit with nonplanar cutters was selected for the field application due to the good abrasion resistance,impact resistance,self-sharpening and thermal stability of the non-planar cutters.The field application shows that the average ROP of the new type drill bit in Ziliujing formation is 2.93 m/h,and the average footage is 225.9 m.Comparing with the traditional PDC bit,the ROP of the new drill bit with non-planar cutters has increased by 67.4%,and the footage has increased by 92.1%.The results of this paper can be utilized to guide the drill bit selection and high-efficiency drilling in conglomerate formation.
1.Introduction
The Western Sichuan Basin of China is rich in oil and gas resources,especially for the deep and ultra-deep formations.Currently,the depth of petroleum exploration and development increase by years in the Western Sichuan Basin,and the deepest well had exceeded 8000 m and reached 8600 m [1].There are a series of difficulties and challenges during drilling in the Sichuan Basin,such as complicated geological conditions,deep burial depth,high-temperature/high-pressure (HTHP),low rate of penetration(ROP),high drilling risk,long drilling period,and high operation cost [1-4].Thereinto,the low ROP is a very difficult problem encountered during drilling in the Sichuan Basin.There are several difficult formations featuring with strong heterogeneity,high abrasiveness,and poor drillability in the Western Sichuan Basin,and the Ziliujing conglomerate formation is one of the typical difficult formations,resulting in low ROP,long drilling period,and high operation cost.The Ziliujing conglomerate formation is a graywhite massive conglomerate rock,and it is usually featured by strong heterogeneity,high abrasiveness,and poor drillability due to its complex composition and texture.In fact,the ROP is mainly dependent on both formation properties and drilling technologies.The formation properties,including the mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability,are the objective factors affecting ROP [5-7].Thus,understanding the mechanical and anti-drilling ability characteristics of deep formation is the premise of drill-bit design,drillbit selection,drilling plan optimization,and drilling parameter optimization [7,8].
The drillability is a comprehensive metric for evaluating the rock broken by the drill bit,which is significant in investigating the formation characteristics in petroleum engineering [9,10].In general,the poorer the drillability,the lower the ROP and the higher the drilling difficulty is.In order to understand the anti-drilling ability of deep formation,the experimental methods,logging prediction methods,and seismic prediction methods were proposed and applied to characterize the anti-drilling ability [11-30].Currently,there are five typical kinds of methods used to characterize the anti-drilling ability: the micro-drilling test [11],the NTNU/SINTEF drillability test[20],the hardness index grading[27],the uniaxial compressive strength grading[27],and the mechanical specific energy method [31].The micro-drilling test is the most commonly used method in petroleum engineering [11,27].The mechanical and drillability characteristics of most common sedimentary rocks had been widely investigated using the abovementioned methods [7,11,15,16,24].Regarding the drillability of conglomerate type of formation,Yang et al.[29] investigated the drillability of gravel formation by using a single-tooth PDC composite chip test bench and the mechanical specific energy method,the results indicated that the gravel particle size has a decisive impact on the average cutting speed.Currently,there are a few studies on the drillability of conglomerate rock.Thus,the physical,mechanical,and drillability characteristics were tested and analyzed for the lower Jurassic Ziliujing conglomerate rock.The mechanical properties and drillability profiles were proposed for a typical deep well of S-07,and the longitudinal distribution characteristics were analyzed.The results can be utilized to guide drillbit design,drill-bit selection,drilling plan optimization,and drilling parameter optimization.
2.Experiments
2.1.Specimen preparation
The conglomerate rock was collected for the lower Jurassic Ziliujing formation(hereinafter referred as“Ziliujing conglomerate formation”) in the Western Sichuan Basin of China.The Ziliujing conglomerate formation is a kind of gray-white massive conglomerate rock,containing lots of gravel,and the size of gravel ranges from 3 mm to 25 mm.In order to meet the requirement of physical-mechanical and drillability testing,according to the suggested method of the International Society of Rock Mechanics(ISRM)and the Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries Standards of the People's Republic of China(SY/T 5426-2000),the specimen was cored as a standard cylinder with a diameter of 50 mm and height of 100 mm,as shown in Fig.1.The two ends of the specimen were ground to ensure parallel and smooth ends using a face grinder,the parallel error of two ends must be less than 0.5 mm,the roughness of two ends must be less than ±0.05 mm,and the perpendicular error among two ends and specimen axis must be less than±0.25°.

Fig.1.Experimental specimen photos.
2.2.Experimental methods
2.2.1.Mineral composition testing
The X'Pert PRO type of X-ray diffraction (XRD) instrument was adopted to test the mineral composition of Ziliujing conglomerate rock.The testing operations followed the Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries Standard of the People's Republic of China (SY/T 5163-2010),and the testing parameters are listed as follows:ambient temperature of 25°C-30°C,environment humidity of<70% RH,scanning voltage of 40 kV,scanning current of 30 mA,scanning speed of 6°/min,and the scanning range of 2.6°-45°.
2.2.2.Scanning electron microscope (SEM) testing
The EVO MA15 type of SEM instrument was adopted to test the micro-structure of Ziliujing conglomerate rock.The testing operations followed the Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries Standard of the People's Republic of China(SY/T 5162-2014),and the testing parameters are listed as follows:ambient temperature of 25-30°C,environment humidity of <70% RH,scanning voltage of 20 kV,scanning magnification of 100-3000 X.
2.2.3.Ultrasonic wave velocity testing
The RIGOL-DS1052E type of ultrasonic wave velocity instrument was adopted to test the P-and S-wave velocity of Ziliujing conglomerate rock.This ultrasonic wave velocity instrument is a co-axial measuring instrument for both P-and S-wave velocity.The testing operations followed the Geology and Mineral Industries Standard of the People's Republic of China (DZ/T 0276.24-2015),and the testing ambient temperature was 25-30°C,testing environment humidity was <70%RH.
2.2.4.Mechanical properties testing
The rock triaxial testing system was adopted to test the mechanical properties,and the YSSZ-600 type of electro-hydraulic servo system was used.The testing operations followed the suggested method of ISRM,and the testing ambient temperature is 25°C-30°C,testing environment humidity is<70%RH,the loading mode was set as displacement control,and the axial displacement rate is 0.01 mm/min.The testing confining pressure was 0 MPa,30 MPa,and 60 MPa for uniaxial and triaxial compression testing.
2.2.5.Micro-drilling testing of drillability
The drillability is a comprehensive metric for evaluating the rock broken by the drill bit [9,10].According to the Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries Standard of the People's Republic of China(SY/T 5426-2000),the drillability is usually tested by the microdrilling method.Micro-drilling testing was conducted using the rock drillability testing instrument,as shown in Fig.2(a),and it is composed of the rock sample holder,the micro-bit,the rotational sub-system,the loading sub-system,the measuring and data acquisition sub-system,and the power sub-system.The micro-bit can be selected from micro roller cone bit and micro polycrystalline diamond compact(PDC)bit,the micro PDC bit was used in the present paper.The micro PDC bit is shown in Fig.2(b)-(c),it consists of a steel body and two PDC cutters,the micro PDC bit has an outer diameter of 32 mm,the PDC cutter has a diameter of 13.3 mm,a back dip angle of 20°,and roll angle of 5°.

Fig.2.Photos of rock drillability testing instrument and micro-bit.
The rock samples are drilled perpendicularly to their crosssections with a weight on bit (WOB) of 500 N and a revolution speed of 55 rpm,a hole with a total depth of 4 mm is drilled in each micro-drilling testing,the drilling depth versus time is used to determine the drillability [25,27,28].In general,the first 1 mm depth is regarded as a predrilled depth to avoid the impact of the sample surface,then the time of the next 3 mm depth is regarded as the drilling time for drillability grade calculation.The drillability can be expressed as [28],
whereTis the drilling time when drilling a hole with a depth of 3 mm using micro PDC bit,s;Kdis the rock drillability,dimensionless.

Table 1 Formation drillability grades[27,28].
According to the rock drillability grade,the formation drillability can be classified into 10 grades,as shown in Table 1.In general,the poorer the drillability,the lower the ROP and the higher the drilling difficulty is.
2.2.6.Abrasiveness testing
The abrasiveness is a metric for evaluating the ability of the rock to wear the drill bit during drilling.The drilling machine and electronic scale were used to test the rock abrasiveness.A standardsteel tube with an outer diameter of 12 mm and an inner diameter of 8 mm is made of A3 annealed steel with a hardness of HRB70-75.The standard steel tube is installed on the drilling machine,and the standard steel tube is ground by rock sample with the axial loading of 300 N,the revolution speed of 500 rpm,and grinding 5 min under water cooling.The weight loss of the standard steel tube is measured by an electronic scale to determine the grinding weight loss,and the abrasiveness can also be classified into 10 grades,as shown in Table 2.In general,the higher the abrasiveness grade,the higher the bit wears and the higher the drilling difficulty is.
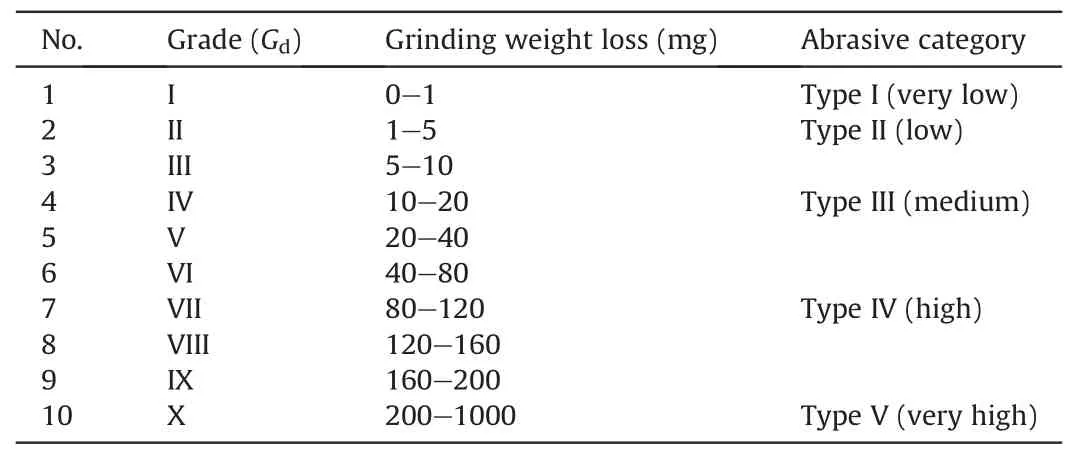
Table 2 Formation abrasiveness grades[30,32].
3.Experimental results and analysis
3.1.Mineral composition and micro-structure
The XRD testing results in Fig.3 showed that the Ziliujing conglomerate rock was rich in quartz and clay minerals,with a relative content of 87.24-88.79% (mean of 88.02%) and 11.21-12.76% (mean of 11.99%),respectively.The SEM testing results in Fig.4 also showed that the gravel is made of quartz,while the cement is mainly composed of clay mineral,and the clay mineral is mainly cemented among the pores of gravel,thus,the Ziliujing conglomerate rock is a typical kind of argillaceous cemented gravel rock.Due to the difference in strength,hardness,drillability,and abrasiveness between quartz gravel and clay cement,and there is a wide distribution range of gravel size(3-25 mm,as shown in Fig.1),the Ziliujing conglomerate rock may display a strong heterogeneity in physical-mechanical and drillability characteristics,and it may affect the performance of drill bit.

Fig.3.XRD testing results of Ziliujing conglomerate rock.
Fig.4.SEM testing results of Ziliujing conglomerate rock.
3.2.P-and S-wave velocities
The relationship between P-and S-wave velocities of the Ziliujing conglomerate rock was shown in Fig.5,it is clearly found that the 5-95% confidence intervals of P-wave velocity were 4169-5439 m/s,the 25-75% confidence intervals of P-wave velocity were 4649-5072 m/s,and the mean of P-wave velocity was 4842 m/s.The 5-95%confidence intervals of S-wave velocity were 2330-4583 m/s,the 25-75%confidence intervals of S-wave velocity were 2643-4097 m/s,and the mean of S-wave velocity was 3479 m/s.On the whole,the S-wave velocity is proportional to P-wave velocity,and the wave velocity ratio of P-wave to S-wave ranged from 1.10 to 1.76,and the average was 1.37.This also reflects the heterogeneity characteristics of the Ziliujing conglomerate rock.
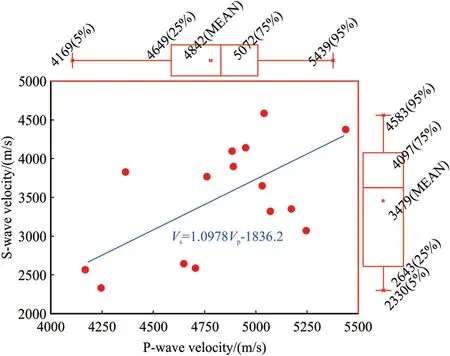
Fig.5.Relationship between P-and S-wave velocities.
3.3.Mechanical properties
The uniaxial and triaxial compression tests were conducted for Ziliujing conglomerate rock,and the complete stress-strain curves were shown in Fig.6(a),the variation of rock strength,Young's modulus,and Poisson's ratio versus confining pressure were shown in Fig.6(b)-(d),and the testing results were listed in Table 3.It is clearly found that the Ziliujing conglomerate rock has a UCS of 80.54 ± 22.17 MPa,cohesive strength of 15.07 ± 2.63 MPa,and internal friction angle of 50.12 ± 4.45°.The rock mechanical parameters are closely related to the gravel size,gravel amount,gravel texture,and argillaceous cement property.As the Ziliujing conglomerate specimens featured by the strong heterogeneity,the differences in compression testing results were larger even though the same experimental condition was adopted.On the whole,the rock strength,Young's modulus,and Poisson's ratio linearly increased with increasing confining pressure,while their variable coefficient also increased with increasing confining pressure.In addition,the typical failure modes of uniaxial and triaxial compression tests were shown in Fig.7,it has obviously been noticed that there were four typical kinds of failure modes: axial splitting failure,single shear failure,double shear failure,and combined failure.The gravel plays a controlling role in the failure modes of Ziliujing conglomerate rock,especially for the conditions of uniaxial compression and low confining pressure.Due to the low strength of argillaceous cement and high strength of gravel particles,the Ziliujing rock is much more prone to crack in the argillaceous cement,thus,there are a large number of cement cracks,inter-granular cracks,and trans-granular cracks,as shown in Fig.7.Under the conditions of uniaxial compression and low confining pressure,the rock specimens mainly occur the axial splitting failure.As confining pressure increasing,the rock specimens mainly occur single shear failure,double shear failure,and combined failure.Therefore,the Ziliujing rock displays a strong heterogeneity in rock mechanical behaviors.

Table 3 Statistical results of uniaxial and triaxial compression tests.

Fig.6.Experimental results of uniaxial and triaxial compression tests.(a) Complete stress-strain curves;(b) Strength versus confining pressure;(c) Young’s modulus versus confining pressure;(d) Poisson’s ratio versus confining pressure.
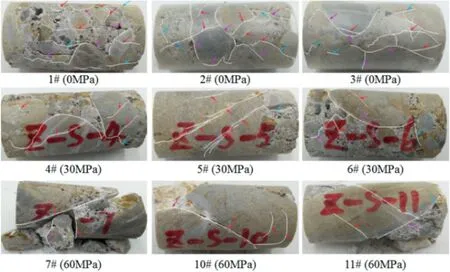
Fig.7.Specimen failure modes of uniaxial and triaxial compression tests.
3.4.Drillability
The micro-drilling testing of drillability was conducted for Ziliujing conglomerate rock,and the drilling depth versus time was shown in Fig.8 and the specimenphotos after drilling were alsogiven.Asshown in Fig.8,due to the strong heterogeneity of Ziliujing conglomerate rock,the curve noise of drilling depth versus time is significant,and it may cause incorrect testing results for the determination of drilling time.Thus,the smoothing filter method was utilized to filter the original curve of drilling depth versus time,and the filtered curve of drilling depth versus time was also shown in Fig.8.On the basis of the smoothing filter,the statistical results of micro-drilling testing were collected inTable 4.It has obviously been noticed that the drilling time ranges from 350 s to 440 s,the Ziliujing conglomerate rock has a poor drillability of 8.58±0.20 and a poor drillability grade of 9(IX).Due to the large size of gravel in the Ziliujing conglomerate rock,the breaking parts of the specimen in micro-drilling testing were mainly the gravel particle,thus,the drillability is very poor.On the whole,the Ziliujing conglomerate rock is the type III of hard rock.

Fig.8.Drilling depth versus time and sample photo after drilling.(a) Z-D-1;(b) Z-D-2;(c)Z-D-3.
3.5.Abrasiveness
The abrasiveness testing was conducted for Ziliujing conglomerate rock,and the testing results were shown in Table 5 and Fig.9.It has obviously been noticed that the grinding weight loss ranges from 26.8 mg to 38.7 mg,and the Ziliujing conglomerate rock has a medium abrasiveness of grade 5 (V).Due to the strong heterogeneity of Ziliujing conglomerate rock,there is a high grinding weight loss when the standard steel tube is grinding on the gravel particle,while there is a relatively low grinding weight loss when the standard steel tube is grinding on the boundary of gravel particle and cement,as shown in Fig.9.On the whole,the Ziliujing conglomerate rock is the type III of medium abrasive rock.

Fig.9.Specimen photos after abrasiveness testing.(a)Z-A-1;(b) Z-A-2;(c) Z-A-3.
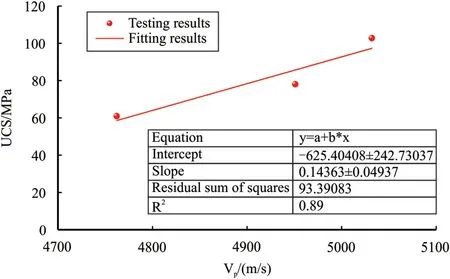
Fig.10.UCS versus P-wave velocity.
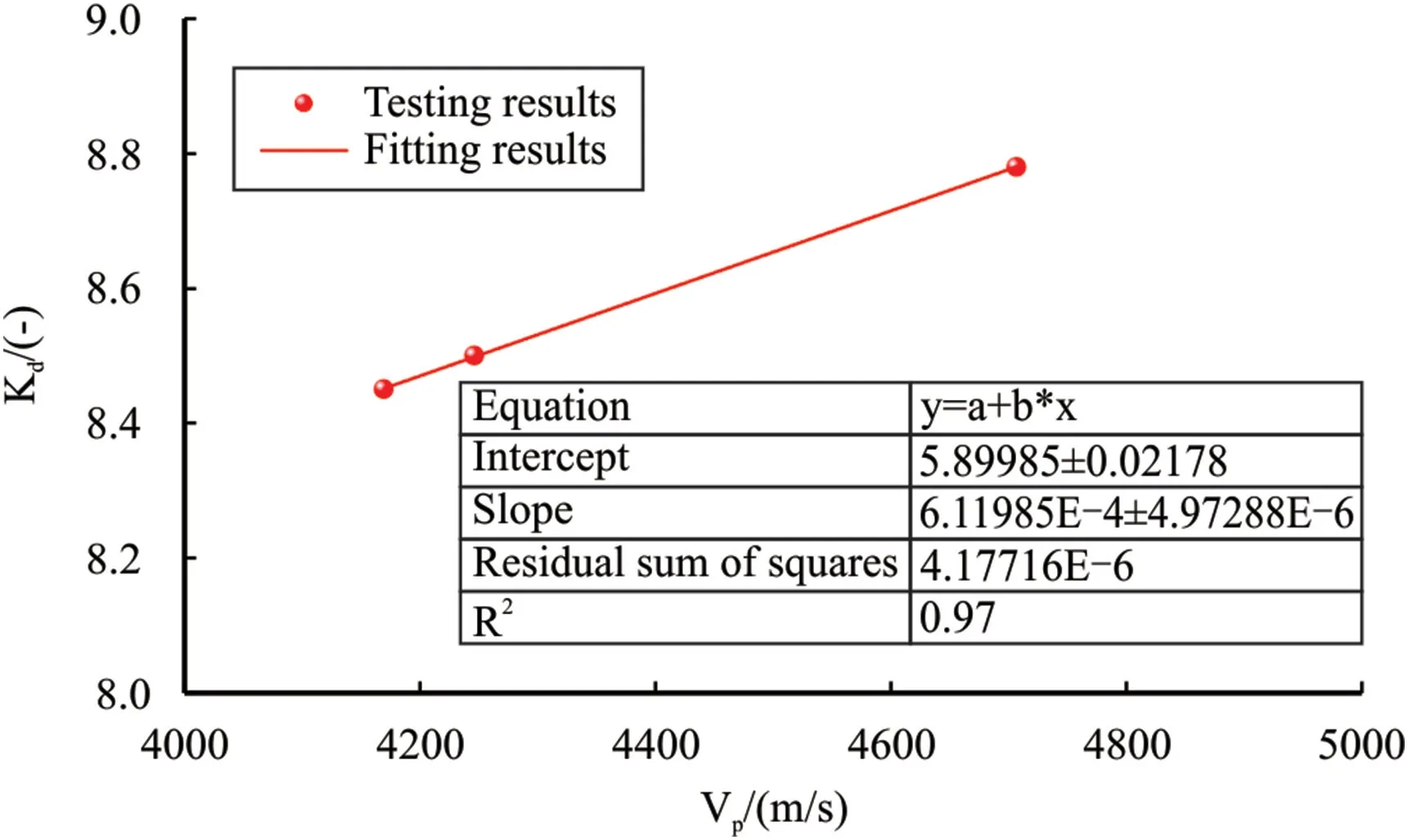
Fig.11.Drillability versus P-wave velocity.
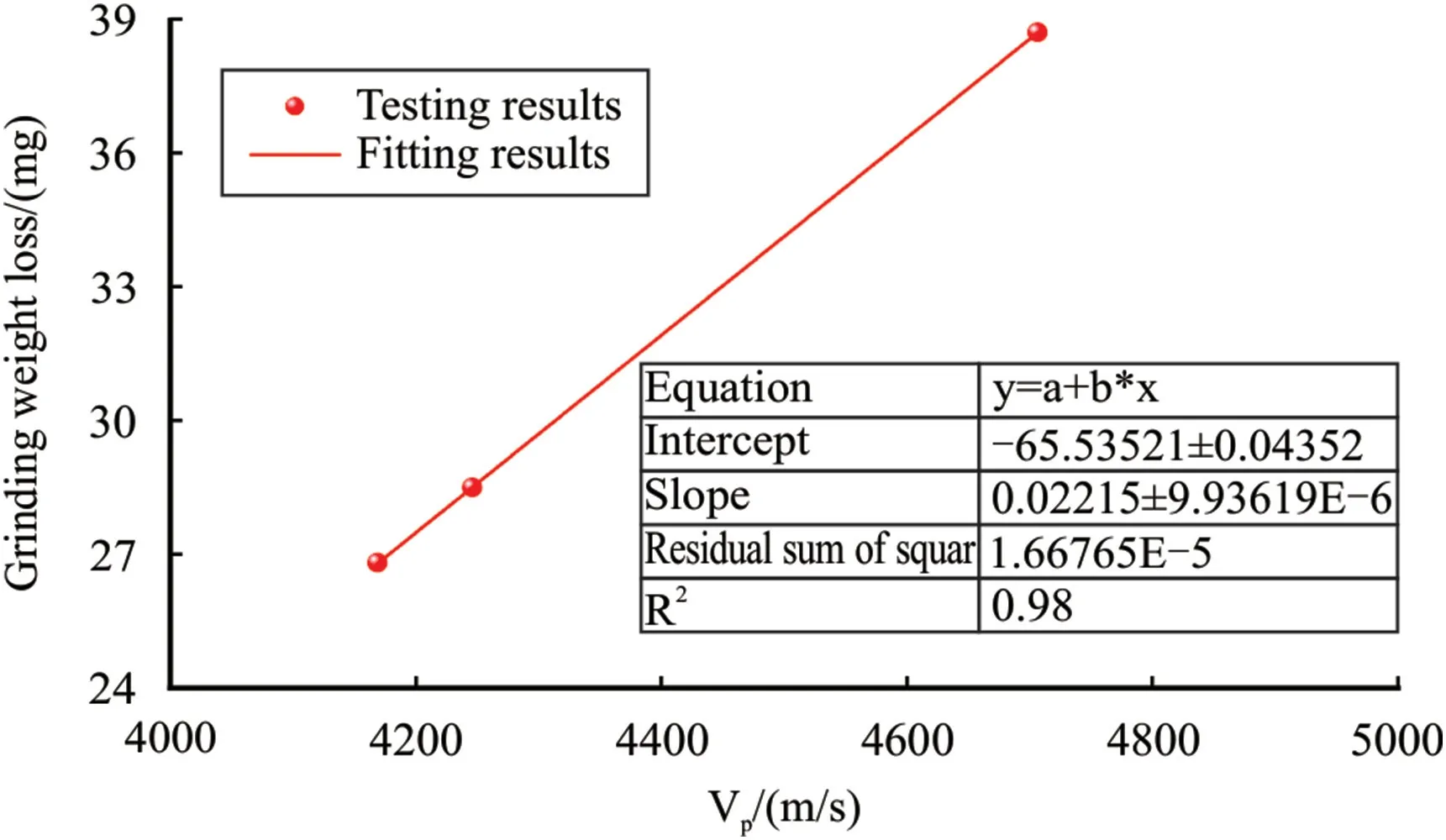
Fig.12.Grinding weight loss versus P-wave velocity.
4.Logging interpretation of drillability characteristics
4.1.Logging interpretation methods
The geophysical well logging is used to interpret the mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability of formation rocks.In general,the sonic logging data is the most commonly used method,and the mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability of formation rock usually include Young's modulus,UCS,internal friction angle,drillability,and abrasiveness.In the present paper,the experimental results were utilized to propose the corresponding relationships.
Based on the testing results of Ziliujing conglomerate rock,the relationships among mechanical properties,drillability,and abrasiveness with ultrasonic wave velocity clarified,and we found that the UCS,drillability,and abrasiveness are proportional to ultrasonic wave velocity,especially for the P-wave velocity.The relationships among UCS,drillability,and grinding weight loss with P-wave velocity were shown in Figs.10-12.On the whole,the relationships are roughly linear among UCS,drillability,and grinding weight loss with P-wave velocity,and the fitting equations are listed as follows:whereUCSis the UCS,MPa;Vpis the P-wave velocity,m/s;Kdis the drillability,dimensionless;GWLis the grinding weight loss,mg.

Table 4 Statistical results of micro-drilling testing.
The above mentioned equations can be utilized to determine theUCS,drillability,and abrasiveness.In order to determine Young's modulus and internal friction angle of the rock,the following equations can be used [33,34],
whereEis the Young's modulus,GPa;ρ is the rock density,g/cm3;Vsis the S-wave velocity,m/s;φ is the internal friction angle,(°).
4.2.Logging interpretation results
In order to determine the mechanical properties and antidrilling ability of Ziliujing conglomerate formation in the Western Sichuan Basin of China,the logging interpretation methods were used to interpret the longitudinal distribution characteristics of mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability,the rock mechanical and drillability profiles were proposed for a typical deep well of S-07,and the results were shown in Fig.13,the statistical analysis results were shown in Fig.14 and Table 6.The interpretation results of acoustic logging indicated that the Ziliujing conglomerate formation displays a strong heterogeneity in rock mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability,the Ziliujing conglomerate formation has the Young's modulus of 38.61±17.08 GPa,the Poisson's ratio of 0.327 ± 0.006,the UCS of 93.02 ± 40.89 MPa,the internal friction angle of 49.21 ± 11.00°,the drillability of 8.04 ± 1.54,and the abrasiveness grade of 4.32 ± 1.94.The Young's modulus,UCS,internal friction angle,drillability,and abrasiveness meet the Weibull distribution pattern,while only the Poisson's ratio meets the Kernel Smooth distribution pattern.On the whole,the Ziliujing conglomerate formation is a kind of hard rock with strong heterogeneity,high strength,poor drillability,and medium abrasiveness.The physical-mechanical and drillability results can be utilized to guide the drill bit selection and high-efficiency drilling.
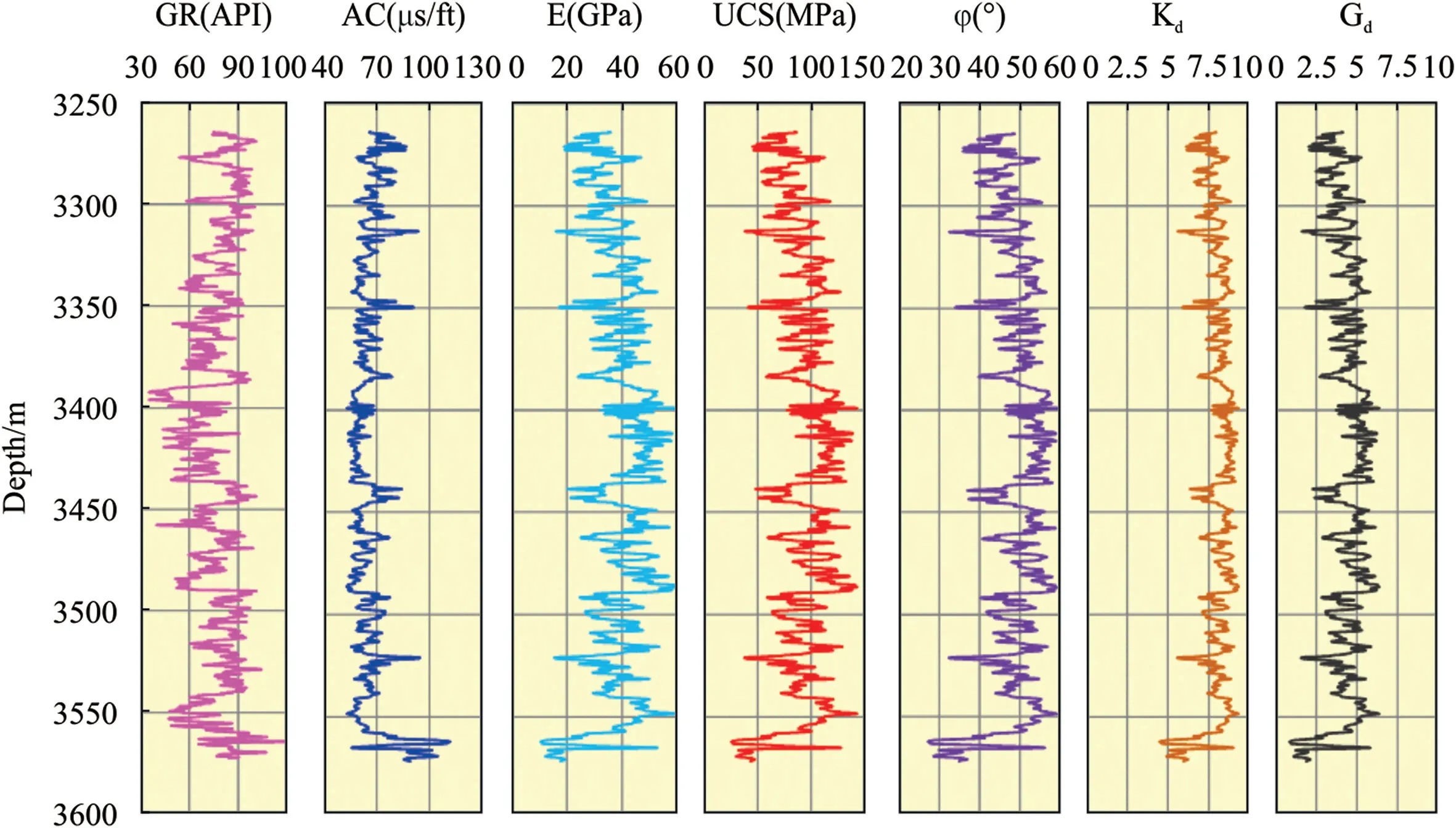
Fig.13.Logging interpretation results.
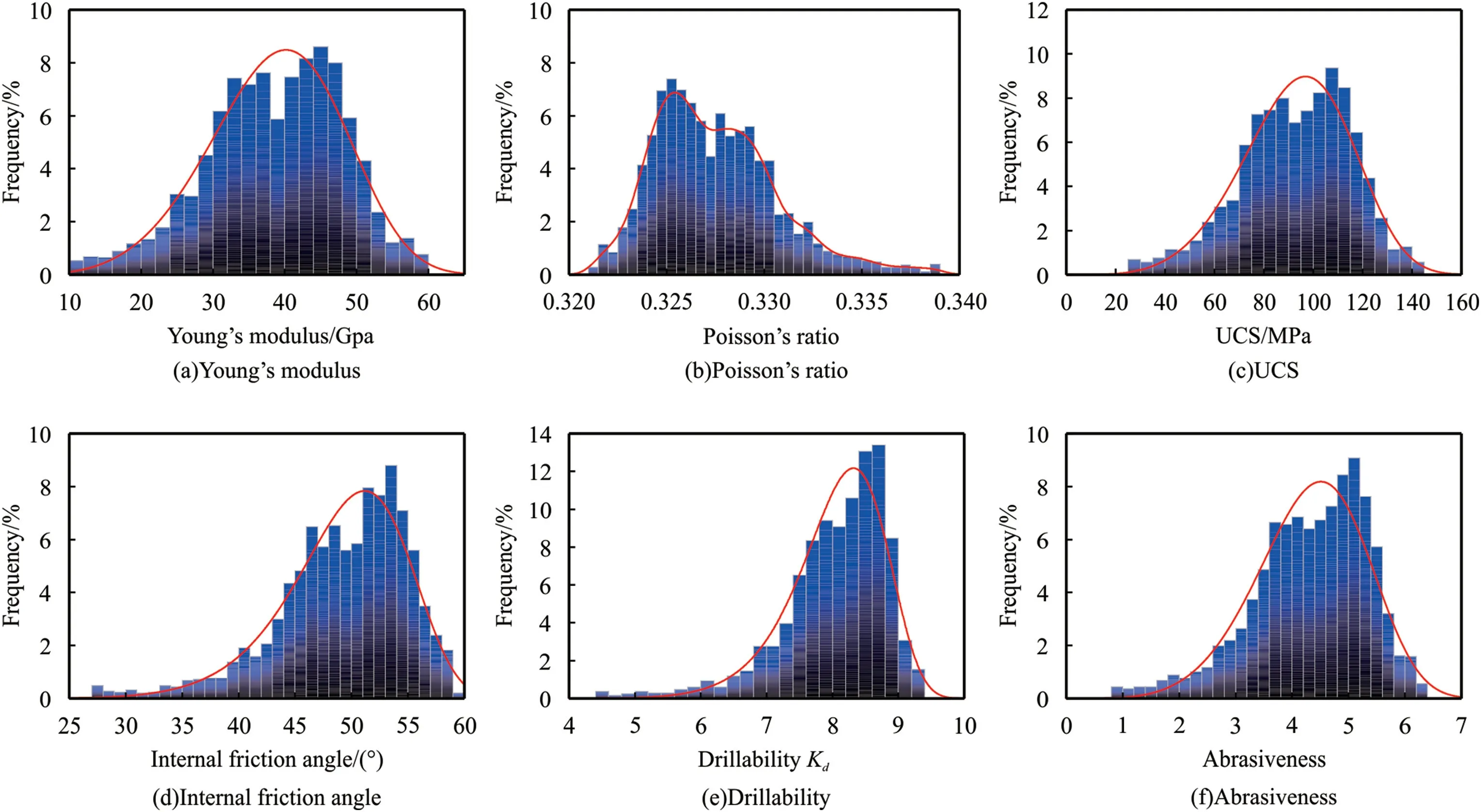
Fig.14.Statistical histogram of Logging interpretation results.
5.Drill bit selection and application
The Ziliujing formation is approximately 600 m thick,and the lithology of the formation includes mudstone,shale,sandstone,and contains quartz and gravel at the bottom layers.It was found from the experimental results and the logging interpretation results that the conglomerate formation of Ziliujing featured by strong heterogeneity,high rock strength and large proportion of quartz in mineral composition makes the rock of this formation having the poor drillability,high abrasiveness,serious bit wear and low ROP.The field statistical results in Table 7 suggest that it takes an average of 5 times to cross the formation,the average footage of a single bit is 117.60 m,and the average ROP is 1.75 m/h.The formation was mainly drilled by the PDC bit with planar cutters and the morphology of the used drill bit after pulled out of hole as shown in Fig.15.It was found that the PDC teeth,shoulder and crown of the bit are worn to varying degrees.For highly heterogeneous formations,the drill bit is susceptible to axial impact,causing the teeth of the drill bit chipping and losing.The main reason is that the conventional PDC drill bits are planar polycrystalline diamond compact,using a circular arc surface to break the rock.When the drill bit hits unevenly distributed gravel under high-speed cutting condition,it will produce a frontal impact,causing the drill bit's outer cone teeth to break or the polycrystalline diamond compact to damage.On the other hand,due to the higher abrasive characteristics of the formation rock,the drill bit is severely worn,the cutting ability is reduced,and the life of the drill bit is shortened.The shortened bit life will not only increase the cost of the bit,but also cause a lot of non-productive time due to the frequent bit replacement,which reduces the drilling efficiency.

Fig.15.The morphology of the used drill bit after pulled out of hole.

Table 6 Statistical results of Logging interpretation data.
Through the above analysis,it can be known that the main reason for the low ROP in conglomerate formations is the bit wear and the planar polycrystalline diamond compact damage caused by the strong heterogeneity and high abrasiveness of the formation.Therefore,the key to increasing the speed and efficiency of drilling in conglomerate formations is to select a drill bit with high wear resistance and strong impact resistance [7,35,36].Studies have shown that the PDC bit with non-planar cutters has high impact resistance and wear resistance [37-40].The PDC bit with nonplanar cutters as shown in Fig.16,the angle between the three ridges of the tooth is 120°,and the surface is treated with cobalt removal.When the drill bit is working,the protruding edge of the non-planar polycrystalline diamond compact first contacts the formation,which produces a large point load to pre-crack the rock,and then produces a ploughing action to achieve the purpose of composite crushing the formation rock.Through the indoor impact experiments,it was found that the non-planar cutters are basically intact after more than 12,000 impacts,while the plane cutters fail after more than 950 impacts.Compared with conventional planar cutters,the impact resistance of non-planar cutters is increased by more than 10 times.

Fig.16.The PDC bit with non-planar cutters.
In view of the good abrasion resistance,impact resistance,selfsharpening and thermal stability of the PDC bit with non-planar cutters,the SV516TAUL PDC bit was selected for the field application in Ziliujing formations,and the actual drilling comparison between the new type drill bit and traditional drill bit as shown in Fig.17.The results show that the average ROP of the new type drill bit in Ziliujing formation is 2.93 m/h,and the average footage is 225.9 m.Comparing with the traditional PDC bit with planar cutters,the ROP of the new type drill bit has increased by 67.4%,and the footage has increased by 92.1%.The morphologies of the SV516TAUL drill bit before and after drilling are shown in Fig.18.It was found that there are no teeth chipping or teeth broken after the drill bit pulled out of hole,and the wear degree of the drill bit was significantly lower than that of the drill bit with planar cutters.The field application further confirmed the high wear resistance,strong impact resistance and high rock breaking efficiency of the PDC bit with non-planar cutters,which significantly reduced the risk of impact failure and wear failure of the cutting teeth,and provided the necessary support and guarantee for the safe and efficient drilling in conglomerate formation.
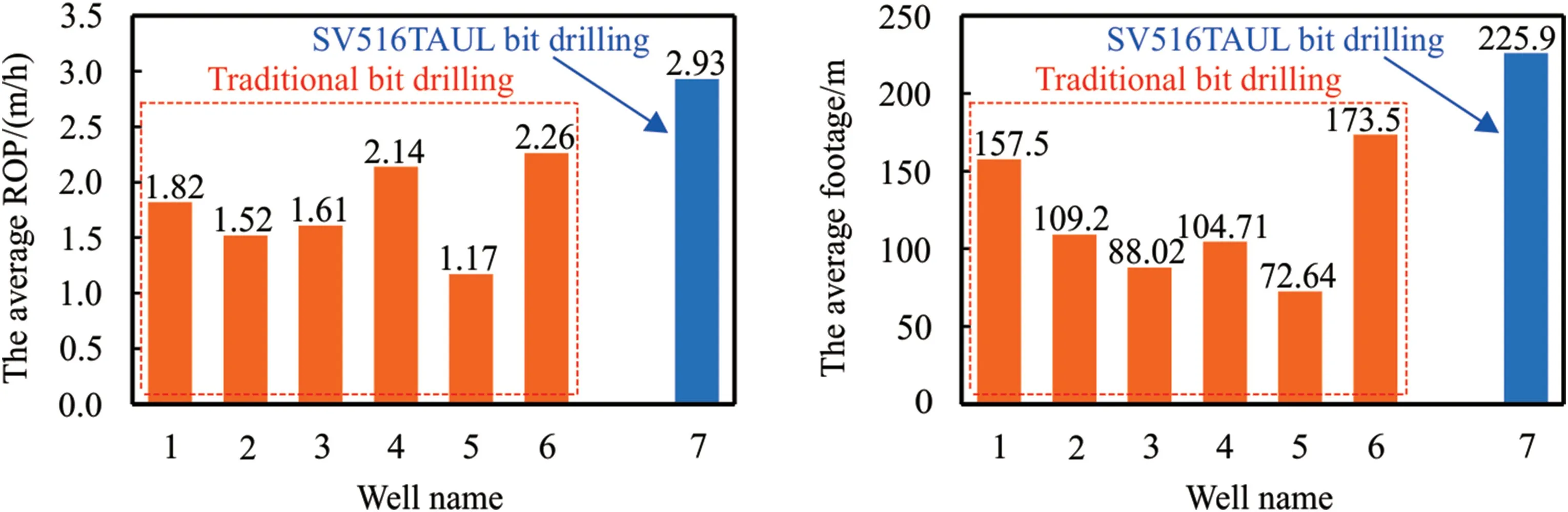
Fig.17.Comparison of the ROP and footage between traditional and SV516TAUL drill bit.
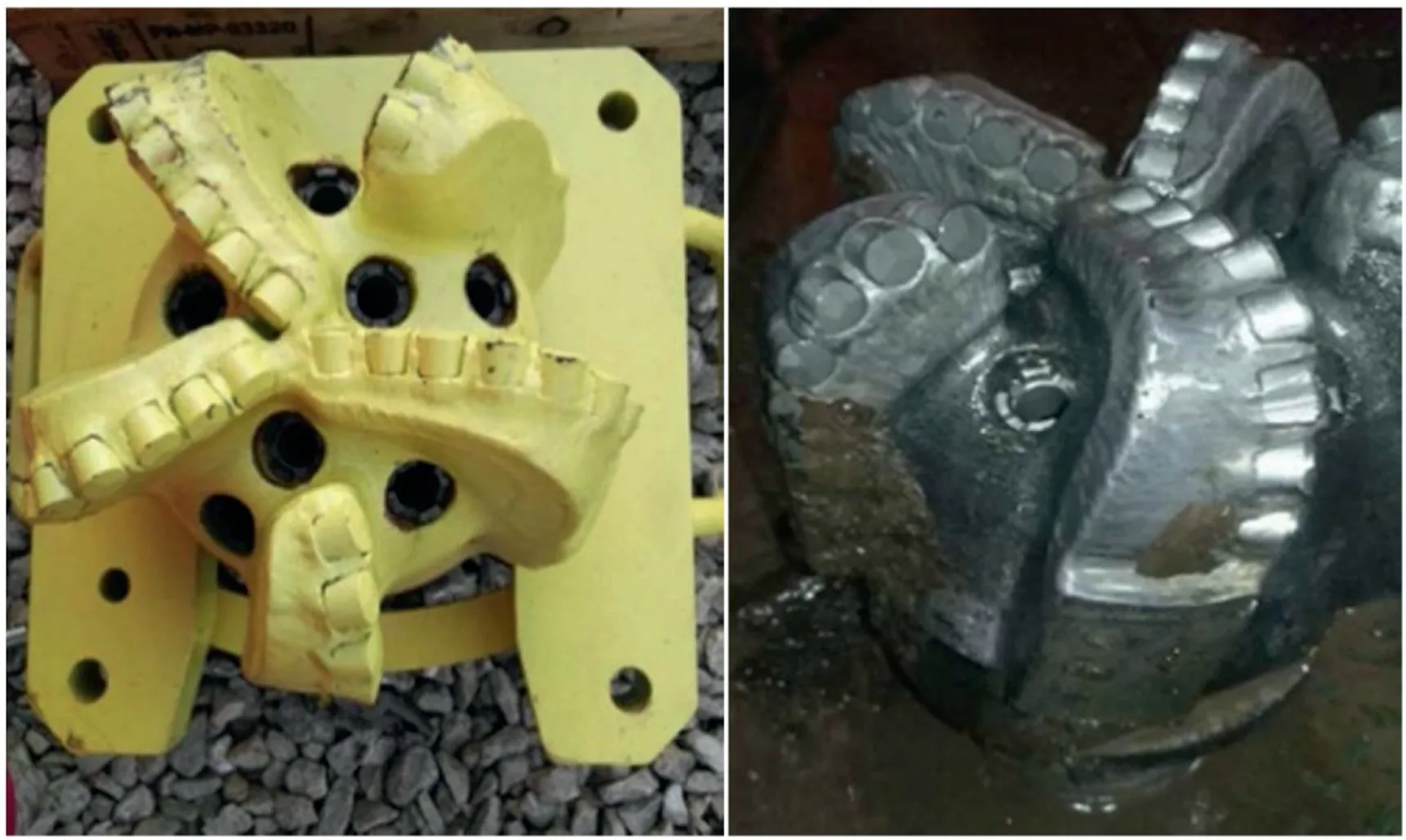

Fig.18.The morphologies of the SV516TAUL drill bit before and after drilling.
6.Conclusions
In order to guide the drill bit selection and high-efficiency drilling,the physical,mechanical,and drillability characteristics were investigated for Ziliujing conglomerate rock in the Western Sichuan Basin of China.The rock mechanical and drillability profiles were proposed for a typical deep well of S-07,the longitudinal distribution characteristics were analyzed,and drill bit selection and field application were conducted.Based on the experiments,logging interpretation,and field applications,the following conclusions can be drawn:
(1) The Ziliujing conglomerate rock is rich in quartz and clay minerals,with the relative content of 87.24-88.79%(mean of 88.02%)and 11.21-12.76%(mean of 11.99%),respectively.The Ziliujing conglomerate rock is a typical kind of argillaceous cemented gravel rock,and the gravel is made of quartz,while the cement is mainly composed of clay minerals.
(2) The Ziliujing conglomerate rock has a P-wave velocity of 4842 ±673 m/s and an S-wave velocity of 3479±1149 m/s,the S-wave velocity is proportional to P-wave velocity,and the wave velocity ratio of P-wave to S-wave ranges from 1.10 to 1.76 (average of 1.37).
(3) The experimental results indicated that the Ziliujing conglomerate rock has a UCS of 80.54±22.17 MPa,cohesive strength of 15.07 ± 2.63 MPa,and internal friction angle of 50.12 ± 4.45°.There are four typical kinds of failure modes:axial splitting failure,single shear failure,double shear failure,and combined failure.The gravel plays a controlling role in the failure modes of Ziliujing conglomerate rock,especially for the conditions of uniaxial compression and low confining pressure.
(4) The experimental results indicated that the Ziliujing conglomerate rock has a poor drillability of 8.58 ± 0.20,a poor drillability grade of 9 (IX),and a medium abrasiveness of grade 5(V).Thus,the Ziliujing conglomerate rock is a kind of hard rock with poor drillability and medium abrasiveness.
(5) The logging interpretation results indicated that Young's modulus,UCS,internal friction angle,drillability,and abrasiveness meet the Weibull distribution pattern,while only Poisson's ratio meets the Kernel Smooth distribution pattern.The Ziliujing conglomerate formation has the Young's modulus of 38.61 ± 17.08 GPa,the Poisson's ratio of 0.327 ± 0.006,the UCS of 93.02 ± 40.89 MPa,the internal friction angle of 49.21±11.00°,the drillability of 8.04±1.54,and the abrasiveness grade of 4.32±1.94.On the whole,the mechanical properties and anti-drilling ability of logging interpretation are in good agreement with the experimental data.The Ziliujing conglomerate formation is a kind of hard rock with strong heterogeneity,high strength,poor drillability,and medium abrasiveness.
(6) Based on the characteristics of Ziliujing formations,the SV516TAUL PDC bit with non-planar cutters was selected for the field application.The field result shows that the average ROP of the SV516TAUL PDC bit in Ziliujing formation is 2.93 m/h,and the average footage is 225.9 m.Comparing with the traditional PDC bit with planar cutters,the ROP of the new type drill bit has increased by 67.4%,and the footage has increased by 92.1%,which shows a great potential for the ROP increasing in conglomerate formations drilling.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No.2020JDJQ0055),and the Youth Scientific and Technological Innovation Team Foundation of Southwest Petroleum University (Grant No.2019CXTD09).
杂志排行
Petroleum的其它文章
- Super gas wet and gas wet rock surface: State of the art evaluation through contact angle analysis
- Petroleum system analysis-conjoined 3D-static reservoir modeling in a 3-way and 4-way dip closure setting: Insights into petroleum geology of fluvio-marine deposits at BED-2 Field (Western Desert,Egypt)
- Development and performance evaluation of a high temperature resistant,internal rigid,and external flexible plugging agent for waterbased drilling fluids
- Production optimization under waterflooding with long short-term memory and metaheuristic algorithm
- Investigation of replacing tracer flooding analysis by capacitance resistance model to estimate interwell connectivity
- Experimental study on sand production and coupling response of silty hydrate reservoir with different contents of fine clay during depressurization
