鲁棒截断L1-L2全变分稀疏恢复模型
2023-06-30韩乐江怡华
韩乐 江怡华
鲁棒截断1-2全变分稀疏恢复模型
韩乐 江怡华
(华南理工大学 数学学院,广东 广州 510640)
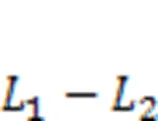
鲁棒压缩感知;截断全变分;非凸非光滑优化;稀疏噪声;结构稀疏
随着计算机科学与技术的高速发展,越来越多的大规模数据库的出现,推动着信号处理领域的变革。然而,仍然存在着小规模数据领域,如医学图像领域,由于受辐射剂量限制,只能采集到少量的CT图像和MRI图像等[1]。
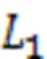
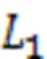
受硬件条件的限制,信号在获取的过程中不可避免地会被噪声污染。除了常见的高斯噪声外,还有非高斯噪声,如脉冲噪声、柯西噪声、泊松噪声等,其中脉冲噪声和柯西噪声均具有稀疏属性。鲁棒稀疏信号恢复[11]就是处理稀疏噪声影响下的稀疏信号恢复问题。相关的优化模型通常是用向量零范数的各种近似来表示原始信号和噪声的稀疏性[12]。
1 预备知识
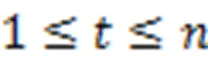
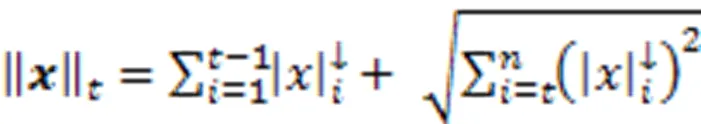
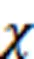
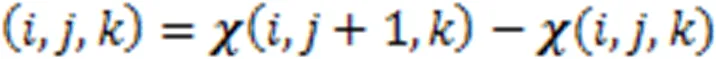
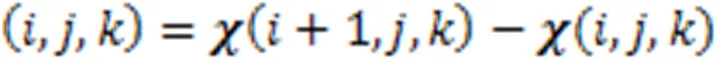
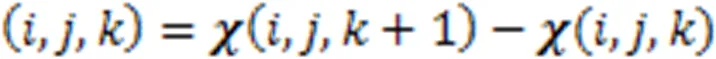

2 全变分稀疏恢复模型
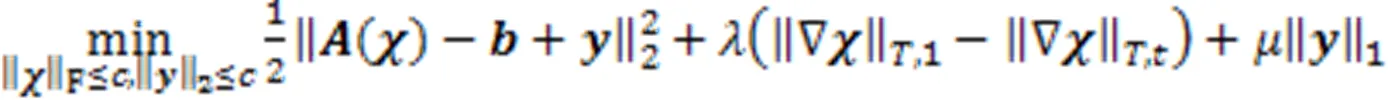
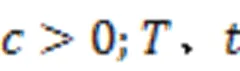
注意到,可以利用指示函数将问题(1)等价转化为无约束问题
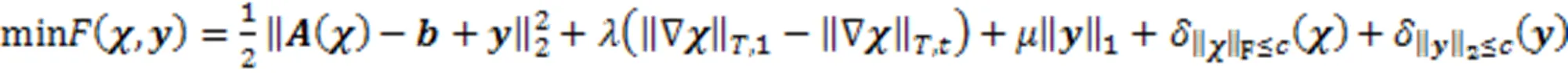
式中,指示函数定义为
虽然优化问题(2)是非凸非光滑的,但可以采用邻近交替线性化算法求解。文中采用有加速的邻近交替线性化算法GiPALM[13]求解问题(2)。
Do
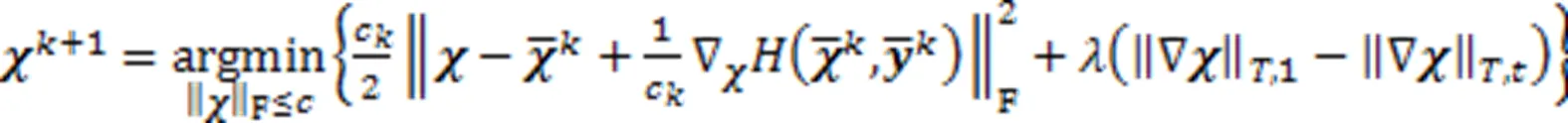
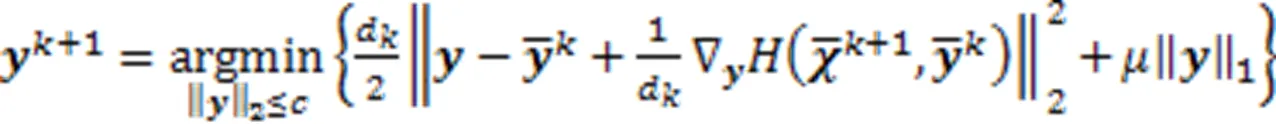
定义3 称满足
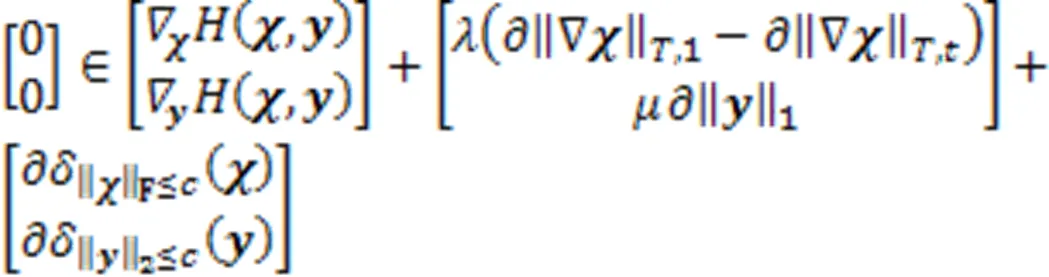
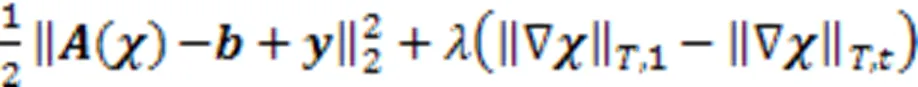
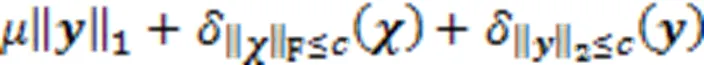
证毕。
3 子问题求解
GiPALM算法中的子问题(3)可写为
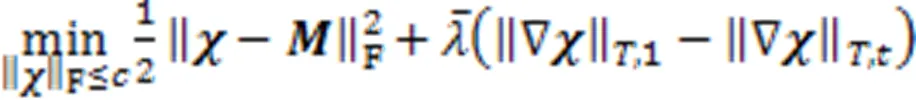
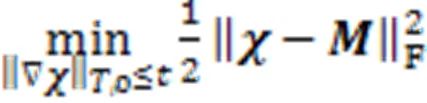
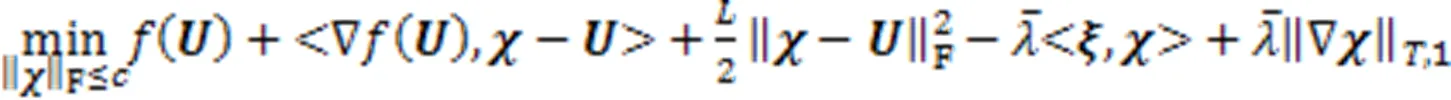
Do
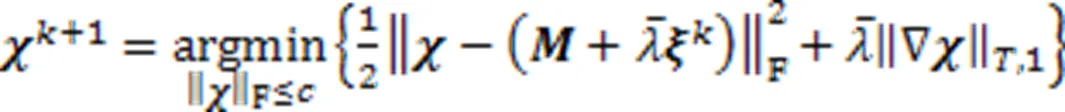
证毕。
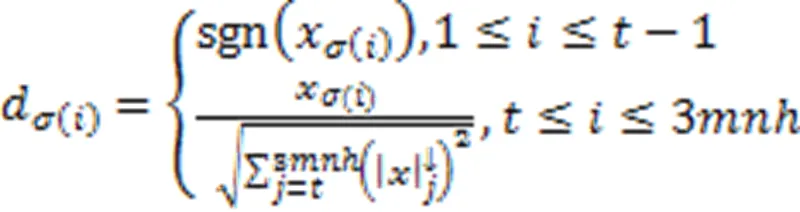
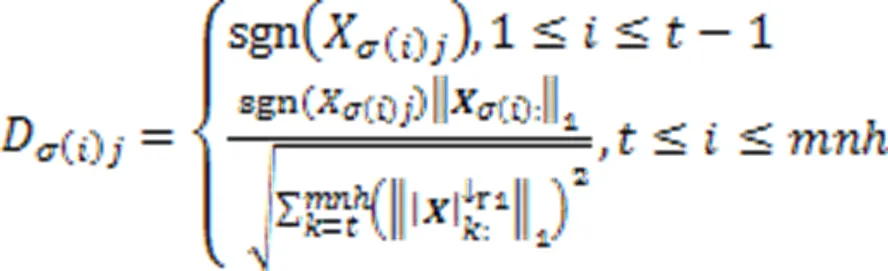
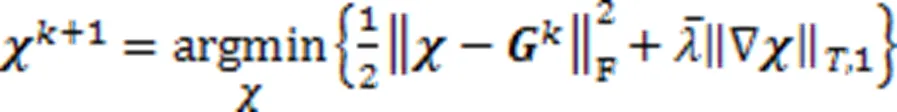
最优解可以由软阈值算子[22]给出,即
4 数值实验及结果分析
文中使用峰值信噪比(PSNR,PSN)和结构相似度(SSIM,SIM)作为噪声图像复原评价标准,
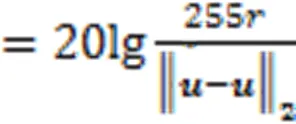
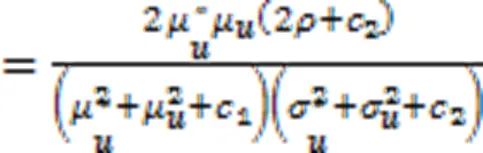
4.1 高斯噪声灰度图像恢复
实验采用的原始无噪声灰度图像见图1,其中灰度图像1-4的大小为256×256,灰度图像5和6的大小为512×512。在原始灰度图像上叠加高斯噪声,生成含噪声的观测数据,其中高斯噪声由Matlab中Imnoise函数按照均值为0、标准差为0.01生成。

图1 原始灰度图像
表1 恢复含高斯噪声灰度图像的PSNR、SIMM与运行时间
Table 1 PSNR, SSIM and running time of recovering grey images with Gaussian noise
图像序号PSNR/dBSSIM/dB运行时间/s TVT0TVT1TVT0TVT1TVT0TVT1 126.8225.6227.160.760 00.506 90.802 80.020.0145.25 228.1026.7230.190.760 00.438 40.818 00.020.0143.30 326.8426.9629.080.800 00.508 90.880 70.020.0144.01 428.9027.6831.210.820 00.692 10.896 10.020.0146.86 526.9226.5129.380.860 00.807 30.910 00.100.05282.85 623.9824.9024.900.860 00.806 70.834 00.100.05733.15
4.2 混合噪声彩色图像恢复

图2 原始彩色图像
文中分别测试了在原始彩色图像中添加稀疏噪声和混合噪声两种情形。稀疏噪声的添加是在每幅图像中随机选取30%的像素,将其设置为0~255中的随机数(将图像每个通道对应位置的值都进行破坏),形成噪声图像。混合噪声的添加则是在稀疏噪声的基础上,用Imnoise函数叠加均值为0、标准差为0.02的高斯噪声。
表2 恢复含噪彩色图像的PSNR
Table 2 PSNR of recovering color images with noises
图像序号含稀疏噪声的PSNR/dB含混合噪声的PSNR/dB TRPCATVT0TVT1TRPCATVT0 TVT1 123.2824.3824.7119.1821.4821.74 224.4924.6724.9819.2121.4021.40 327.7028.0027.5020.6823.2222.71 424.4324.6224.4019.5221.3621.08 529.7330.1129.8721.7921.7923.73 631.5231.8929.8320.6321.1220.75
表3 恢复含噪彩色图像的平均运行时间与迭代次数
Table 3 Running time and iteration number of recovering color images with noises
图像序号噪声每次迭代的平均运行时间/s总迭代次数 TRPCATVT0TVT1TRPCATVT0TVT1 1稀疏噪声0.0020.9934.95643150150 20.0010.9603.81542150150 30.0011.0253.9624384113 40.0021.0433.90943127150 50.0010.9704.0294489143 60.0011.0203.72043116101 1混合噪声0.0011.1493.474401501 20.0021.1273.087401501 30.0011.0993.071401501 40.0021.0563.140401501 50.0011.1193.092411501 60.0011.1083.25740150150
表4 含混合噪声彩色图像的恢复效果
Table 4 Recovering results of color images with mixed noise
图像序号混合噪声图像恢复结果 TRPCATVT0TVT1 1 2 4
4.3 混合噪声视频恢复
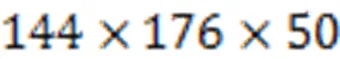
表5 含高斯噪声视频恢复结果的PSNR
Table 5 PSNR of recovering video with Gaussian noise
帧数PSNR/dB TRPCA中值滤波TVT0TVT1 123.3824.8525.6725.64 721.0322.5223.4423.48 1320.7721.9322.9222.92 1820.6521.7422.5322.45 2420.4721.5122.3422.26 3020.6021.4422.1022.10 3620.6121.3222.0922.12 4219.3120.5520.8620.84 4821.2922.8823.9323.86
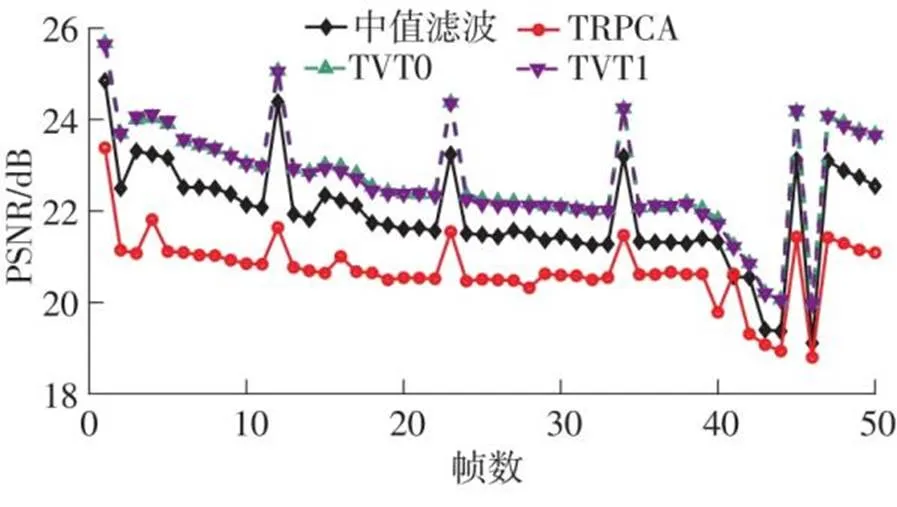
图4 混合噪声下视频恢复的帧数-PSNR曲线
5 结语
[1] WANG C,TAO M,NAGY J G,et al.Limited-angle CT reconstruction via the1/2minimization [J].SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences,2021,14(2):749-777.
[2] FANNJIANG A,LIAO W.Coherence pattern-guided compressive sensing with unresolved grids [J].SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences,2012,5(1):179-202.
[4] BIAN W,CHEN X J.A smoothing proximal gradient algorithm for nonsmooth convex regression with cardinality penalty[J].SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,2020,58(1):858-883.
[5] YOU J,JIAO Y,LU X,et al.A nonconvex model with minimax concave penalty for image restoration [J].Journal of Scientific Computing,2019,78(2):1063-1086.
[6] THI H A L,PHAMDINH T.DC programming and DCA:thirty years of developments [J].Mathematical Programming,2018,169:5-68.
[7] ARAGÓN ARTACHO F J,VUONG P T.The boosted difference of convex functions algorithm for nonsmooth functions [J].SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization,2020,30(1):980-1006.
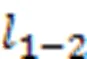
[10] LIU T X,PONG T K,TAKED A.A refined convergence analysis of pDCAwith applications to simultaneous sparse recovery and outlier detection [J].Computational Optimization and Applications,2019,73:69-100.
[11] CARRILLO R E,RAMIREZ A B,ARCE G R,et al.Robust compressive sensing of sparse signals:a review [J].EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing,2016,2016:108/1-17.
[12] BABAHREINIAN M,TRON R.A computational theory of robust localization verifiability in the presence of pure outlier measurements [EB/OL].(2019-10-12)[2021-05-03].https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.05509.
[13] GAO X,CAI X,HAN D.A Gauss-Seidel type inertial proximal alternating linearized minimization for a class of nonconvex optimization problems [J].Journal of Global Optimization,2020,76:863-887.
[14] BOLTE J,DANIILIDIS A,LEWIS A S,et al.Clark subgradients of stratifiable functions [J].SIAM Journal on Optimization,2007,18(2):556-572.
[15] CHAMBOLLE A.An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications [J].Journal of Mathematical Imaging & Vision,2004,20:89-97.
[16] XU Y,HUANG T Z,LIU J,et al.Split Bregman iteration algorithm for image deblurring using fourth-order total bounded variation regularization model [J].Journal of Applied Mathematics,2013,2013:238561/1-11.
[17] CHAMBOLLE A,EHRHARDT M J,RICHTÀRIK P,et al.Stochastic primal-dual hybrid gradient algorithm with arbitrary sampling and imaging applications [J].SIAM Journal on Optimization,2018,28(4):2783-2808.
[18] HINTERRMULLER M,STADLER G.An infeasible primal-dual algorithm for total bounded variation-based inf-convolution-type image restoration [J].SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing,2006,28(1):1-23.
[19] CHEN C,MICHAEL K N,ZHAO X.Alternating direction method of multipliers for nonlinear image restoration problems [J].IEEE Transaction on Image Processing,2015,24(1):32-43.
[20] GOLDFARB D,YIN W.Parametric maximum flow algorithms for fast total variation minimization [J].SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing,2009,31(5):3712-3743.
[21] BARBERO L,SRA S.Modular proximal optimization for multidimensional total-variation regularization [J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2018,19(1):1-82.
[22] NOCEDAL J,WRIGHT S T.Numerical optimization[M].New York:Springer,1999:510.
[23] MARTIN D,FOWLKES C,TAL D,et al.A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics[C]∥ Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Vancouver:IEEE,2001:416-423.
[24] LU C,FENG J,CHEN Y,et al.Tensor robust principal component analysis with a new tensor nuclear norm [J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2020,42(4):925-938.
[25] BIOUCAS-DIAS J M,FIGUEIREDO M,OLIVEIRA J P.Total variation-based image deconvolution:a majorization minimization approach[C]∥ Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing.Toulouse:IEEE,2006:861-864.
(School of Mathematics,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China)
In addition to Gaussian noise, there is sparse noise with impulsive properties in the signal acquisition process. The common robust sparse signal recovery models can recover the original sparse signal under sparse noise environment. However, in many practical applications, the structural sparsity of the original signal, for example, gradient sparsity needs to be considered. In order to recover the sparse structure of the original high-dimensional signal from the coexistence of sparse noise and Gaussian noise, this paper proposed two nonconvex and nonsmooth optimization models based on truncated1-2total variation (TV) and 3D truncated1-2TV, respectively. These optimization models were solved by the proximal alternating linearized minimization algorithm with extrapolation, and the sub-problems involved were solved by the proximal convex difference algorithm with extrapolation. Under the assumption that the potential function has Kurdyka-Lojasiewicz (KL) property, the convergence analysis of these algorithms was given. The numerical experiments test grey images with Gaussian noise, color images with mixed noise, grey video with mixed noise and so on. The peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) was used as the evaluation criterion for recovered quality. The experimental results show that the new models can correctly recover the original structured sparse signal, and have better PSNR values in the same noisy environment.
robust compressed sensing;truncated total variation;nonconvex and nonsmooth optimization;sparse noise;structural sparse
Supported by the General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11971177),the Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (2021A1515010210) and the Degree and Graduate Education Reform Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (2022JGXM011)
10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220485
2022⁃08⁃01
国家自然科学基金面上项目(11971177);广东省基础与应用基础研究基金资助项目(2021A1515010210);广东省学位与研究生教育改革研究项目(2022JGXM011)
韩乐(1977-),女,副教授,主要从事矩阵优化、图像处理研究。E-mail:hanle@scut.edu.cn
TP391.41
1000-565X(2023)05-0045-09
