棉花种植机械化关键技术与装备研究进展
2023-05-15苑严伟白圣贺周利明伟利国刘立晶
苑严伟,白圣贺,牛 康,周利明,赵 博,伟利国,刘立晶
·专论与综述·
棉花种植机械化关键技术与装备研究进展
苑严伟1,2,白圣贺1,2,牛 康2,周利明2,赵 博2,伟利国2,刘立晶1,2※
(1. 中国农业大学工学院,北京 100083;2. 中国农业机械化科学研究院集团有限公司农业装备技术全国重点实验室,北京 100083)
作为棉花产业发展的基础环节,棉花种植机械化是制约棉花产业发展的重要瓶颈。实现棉花种植机械化是棉花产业发展方式转变、提质增效、提升国际市场竞争力的重要途径之一,也是棉花产业全程机械化和规模化的研究重点。该文总结了中国棉花种植现状和特点,阐述了国内外典型棉花种植机械化关键技术与装备的研究现状,重点剖析了棉花育苗移栽和直播2种主要种植技术与装备发展动态。在此基础上,结合精准农业背景和棉花产业生产发展要求,归纳了现有棉花种植机械化技术与装备面临的机会和挑战,提出未来的研究方向和发展建议,以期为棉花种植机械化技术研究与装备创新设计提供参考。
农作物;农业机械;种植;棉花;机械化;育苗移栽;直播
0 引 言
作为国家重要战略物资和经济作物,棉花种植面积和产量均位于全球前列,其产业是中国乡村振兴的基础配套产业,占有重要地位[1-2]。随着棉花产业发展方式转变、结构调整以及比较效益降低,现如今中国棉花生产正面临着以单纯追求高产向高产优质高效的方向发展[3-4]。中国作为世界棉花生产和消费大国,增强棉花话语权和国际市场竞争力,确保棉花产业高质量发展刻不容缓。这已得到政府、生产企业、科研院所等各方的广泛关注和重视[1,5-6]。
棉花种植是棉花全程生产的基础环节,更是促进棉花生产提质增效和提升棉花生产竞争优势的重要途径。农业生产经营朝以机械化为支撑的适度规模化方向转变[7],我国棉花种植范围广,存在种植模式多、栽培自然条件差异较大、农艺工序繁杂、劳动强度大和效率低等诸多问题。因此,发展棉花机械化种植技术与装备是对我国棉花生产发展的有力支撑,更是提高棉花综合机械化水平、推进农业现代化的重要举措[8]。
目前国内棉花机械化种植分为棉花直播和育苗移栽[9]。育苗移栽是在营养钵上育苗,再将培育合格的棉苗移栽到棉田。育苗移栽属于劳动密集型作业,具有典型的旱田作物移栽的特点,但易产生伤苗与漏播现象[10]。棉花直播可将棉种直接播入棉田,工序简单,劳动强度低且作业效率高,适合于大田种植作业,应用广泛[11-12]。现有研究主要集中在装备结构设计及优化、流场模拟仿真分析、作业性能试验研究等方面,已初步形成了棉花种植机械化技术与装备体系[13-20]。棉花种植机械化需符合精准农业发展方向,追求高产优质高效的发展目标。这是棉花产业发展的重大现实需求,更是棉花全程机械化和规模化的研究重点[21]。
本文阐述中国棉花种植概括,归纳分析国内外典型棉花种植机械化关键技术与装备的研究现状。围绕棉花育苗移栽与直播技术及装备的研究动态,基于精准农业背景,结合棉花产业生产发展要求,以高效率、高精度、高效益为目标,提出棉花种植机械化面临的问题,并展望未来发展方向。
1 棉花种植概况
棉花种植范围集中在全球北纬40°至南纬30°之间,主要分为亚洲东南部、北美洲、沙丁美洲和非洲产棉区。其中,亚洲东南属于最大的棉花生产和消费地区,主要是中国、印度、巴基斯坦;北美洲属于第二产棉区,也是出口第一大区,主要是美国;拉丁美洲属于第三产棉区,以巴西、墨西哥、阿根廷为主;非洲属于第四产棉区,也是世界高品级长绒棉的主要产地[22]。
国内棉花产区主要分为黄河流域棉区(以冀豫鲁陕为主)、长江流域棉区(以皖鄂湘苏赣川浙为主)、西北内陆棉区(以甘肃、新疆为主)三大区域[23-24],1991、2000、2010、2020年各省棉花生产情况[24-25]如表1所示。由表1可知,国内棉花种植呈现西移态势,长江流域、黄河流域棉区面积大幅减少,逐渐由西北内陆棉区变为主体,尤其是新疆棉花播种面积增幅最快,比重逐步增大。棉花种植主体正向新疆集中,已成为中国棉花生产的中坚力量和新主产区。

表1 不同省区棉花播种面积和总产量的比较
注:“*”表示无数据或该数值<0.01。
Note: “*” indicates that there is no data or that the value is less than 0.01.
2 棉花育苗移栽技术与装备
我国棉花育苗移栽方式主要有2种:基质裸苗移栽和钵苗移栽[26]。基质裸苗移栽育苗费用高,容易引起棉苗根系损伤;钵苗移栽省种省时,具有补偿气候、提前作物发育期的综合效益,即提高作物复种指数,该模式逐渐得以推广。棉花钵苗移栽多通过半自动移栽机进行作业,人工辅助喂苗,需在旁照看机器以防漏投棉苗,作业效率较低。长期以来,棉花钵苗移栽技术深受农艺专家和农户的青睐,但由于缺少性能可靠的移栽装备,致使难以大面积推广应用。
国外棉花种植均是直播,对棉花钵苗移栽研究较少,但旱地自动钵苗移栽技术相对成熟[27-31]。棉花钵苗移栽装备技术研究在国内起步较晚,进展缓慢,大多是借鉴国外成熟旱田钵苗移栽机型。山东青州火绒机械制造的半自动棉花钵苗移栽机,每台机器配置2~3人工投苗至鸭嘴式栽植器,利用行星轮式控制鸭嘴栽植器开合并带动附带的覆土镇压装置。该机用于棉花钵苗栽植效果较好,裸根苗直立度差[32]。半自动吊篮式棉花钵苗移栽机由山东理工大学和石河子大学联合设计,采用偏心圆盘式驱动吊篮实现开穴栽植,再由覆土镇压器覆土压实。该类机型结构简单,价格低廉,以小田作物为主,比如2YZ-40型吊篮式钵苗移栽机[33-34]。
为进一步提高棉花钵苗移栽机工作效率,学者开展了全自动棉花钵苗移栽机构研究。华中农业大学研制了棉花钵苗移栽系统总成,利用液压缸和曲柄滑块机构分别控制分钵装置和投钵装置完成对应的分钵和投钵动作,但结构复杂、机构庞大,尚处于研究阶段[35]。浙江理工大学设计了旋转式棉花钵苗取苗机构,利用双向螺旋轴驱动秧箱横向往复运动,纵向间歇机构控制秧箱纵向间歇送秧动作。该机首次将回转式移栽机构应用于棉花钵苗移栽,结构简单、效率高、成本低,但需与栽植机构紧密配合[36-37]。
由于种植农艺区别,国外几乎不采用棉花移栽方式,致使学者研究较少。但国外旱地自动移栽机技术先进,性能可靠,已有一定规模推广使用,可为国内开展棉花移栽研究提供经验和思路[38]。国内棉花移栽基本采用人工投苗的半自动移栽方式(鸭嘴式与吊杯式),均缺乏可靠的自动送苗装置,长期作业故障率高,致使移栽作业劳动强度增大、作业速度降低、综合效益不明显;针对全自动棉花钵移栽机研究不够系统,多处于试验阶段,无性能稳定可靠的产品。后续围绕移栽质量与效率为目的,加强移栽机构创新。通过现代设计软件仿真、试验等手段对其进行不断优化,为研发高效、精准、低损取苗机构提供有力理论支撑。引入信息化、智能化技术,加强机电一体化融合,助于实现移栽机的全自动化作业,并促使移栽机械向智能化方向发展,提升作业质量。
3 棉花直播技术与装备
3.1 种植农艺
棉花直播根据种植模式可分为露地直播和地膜覆盖直播[39]。露地直播工序简单,省力省本,但播后受环境影响程度大,风险高;地膜覆盖直播具有增温保墒、改善品质效应等特点,有利于获得高产、优质棉,广泛应用于国内棉花主产区[40-42]。其中地膜覆盖直播又称地膜覆盖穴播,根据铺膜与播种程序不同分为膜上打孔穴播和膜下开沟穴播。膜上打孔穴播可省放苗、封土工序,播种均匀,但若遇雨水,致使土面易板结,出苗难,且对土壤质地及整地质量要求高[43-44];膜下开沟穴播具有适应性强(粘土、沙壤土均能作业)、作业速度快、劳动效率高等特点,能够保持土壤结构与墒情,利于实现一播全苗,但劳动力消耗大[45-46]。地膜覆盖穴播集中于新疆地区,主要有3种:传统模式、机采模式与超宽膜模式[47-48],特点如表2所示。
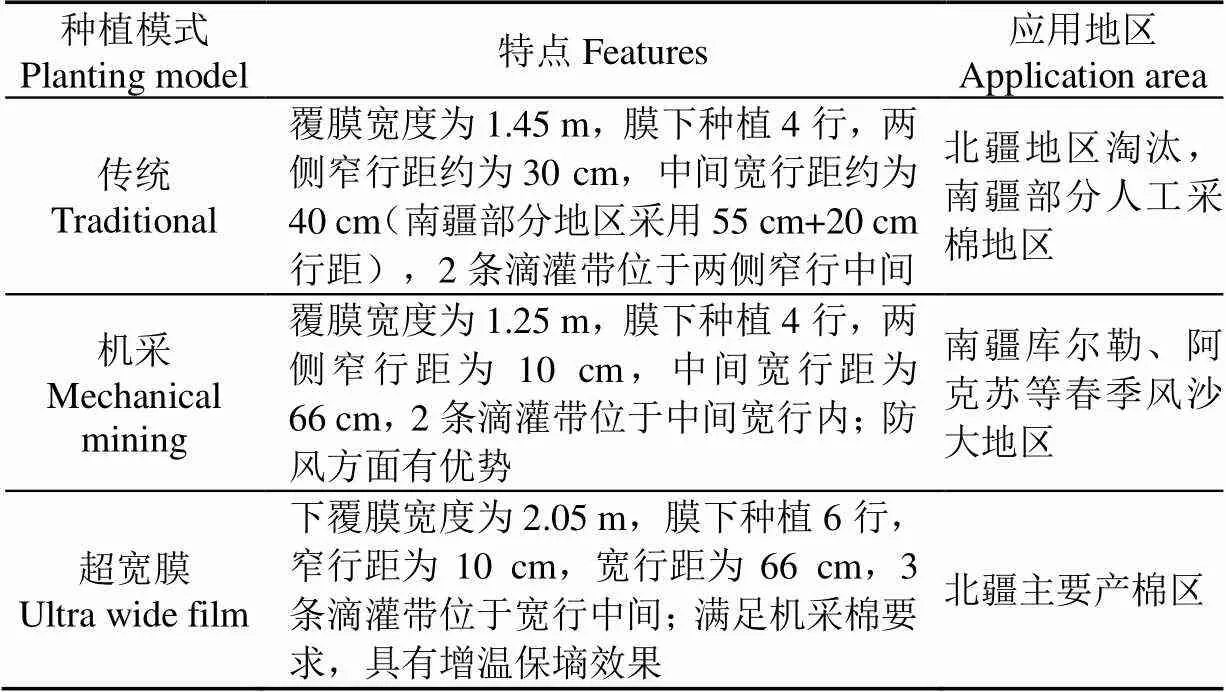
表2 新疆棉花主要种植模式特点
3.2 棉花机械化穴播技术
穴播器是地膜覆盖直播机的核心部件,是决定播种机工作性能的关键要素。根据工作原理不同,棉花穴播器分为气力式和机械式[49],其中气力式基于真空吸力原理,形成气流作为载体确保完成囊肿和排种工作;机械式有多种方法实现排种,比如水平圆盘式、勺式、指夹式等[50]。
3.2.1 气力式
气力式穴播器分为2种:负压式(气流清种)和正压式(气压差携种),通过改变吸孔大小和数量,以适应不同尺寸规格的种子。1950年,国外开始研究气力式排种器,因具有适应性强、稳定性好、高速播种等特点逐渐发展成为主流[51]。1970年,HUDSPETHA等[52]研制出气吸式棉花精密播种机。结果表明:该机种子间距合理,与传统的条播机相比具有良好的生长环境。PARISH等[53-54]以玉米和棉花种子为研究对象,构建气吸式排种器投种过程的数学模型。结果表明:在保证排种性能的条件下,最大排种频率为16粒/s,排种盘充种极限线速度为0.34 m/s。YAZGI等[55]以棉花和玉米种子为研究对象,开展垂直圆盘气吸式排种器不同吸孔数量及作业速度对排种性能的影响。结果表明排种器在播种作业速度为1~1.5 m/s时,具有良好的适应性,直至作业速度提高到2 m/s时,排种性能将急剧下降;SINGH[56]为优化棉花播种机的结构与工作参数,探究排种盘转速、真空度和吸种孔形状对播种质量影响。
国内陈学庚等[57]研制出气吸式棉花精密穴播器,可实现精量取种、清种、精准投种和精确点种,单粒穴播量合格率达到95%以上。为解决气吸式精量穴播器易漏气、能耗大等难题,该团队卢勇涛又设计了一种新型穴播器[58],优化其关键部件参数。试验表明单粒率超过95.5%,重播率低于2.9%,漏播率低于1.6%。徐国杰[59]采用阵列吸孔吸种与侧向气吹清种相结合的方式,设计出一种气吸滚筒阵列式棉花精密排种器,对3种棉花种子进行试验。结果表明:合格指数均在92%以上,漏播指数均在3%以下,重播指数均在5%以下。为解决气吸滚筒式排种器能耗大、吸孔易堵塞等问题,康施为等[60]采用气流清种、减小负压气室空间及清理吸孔等方法,以气流吸种为基础设计了一种滚筒式精密排种器。结果表明:播种合格率为93.2%,漏播率为2.1%,重播率为4.7%。姜有忠等[61]设计了一种基于有序充种的集排滚筒式排种器,解决了结构复杂、振动大、动力消耗大等问题。
3.2.2 机械式
机械式总体分为两种:一是通过机械方式直接从种群中精确攫取种子来确定排种量,如指夹式,严格要求种子形状与尺寸。因此需精选种子,必要时需进行丸粒化处理,应用较少;二是通过控制种子体积以确定排种量,如圆盘式、勺轮式、窝眼式等,利用排种元件上的容腔从种子群精确分离单粒种子,但种子形状和大小、型孔形式对排种性能产生直接影响[49,62]。
YAZGI等[55]研究排种盘在不同型孔数量条件下精密播种装置的排种均匀性。结果表明:在种子间距为100 mm的条件下,棉花在排种盘型孔数为26孔时具有最好的排种效果。王吉奎等[63-64]设计了一种夹持自锁式棉花精量穴播器,可实现精量播种。为降低地面振动引起的种子脱落问题,王吉奎等[65]优化了取种器结构,增设护种装置,改善整机播种稳定性。陈学庚等[66]以新疆地区土壤与气候状况为依据,研制出棉花双膜覆盖精量播种机。结果表明:该机空穴率低于3%,穴粒数合格率高于85%。张学军等[16]设计了双仓转盘式棉花竖直圆盘穴播排种器,结果表明单粒率为94.3%,破损率0.09%。肖旭等[67]以南方棉种“一穴两粒”的农艺要求为基础,设计了一种机械式精量穴播棉花排种器。结果表明穴粒数合格指数为93.62%,重播指数3.87%,漏播指数2.51%。王龙等[68]模拟分析窝眼式穴播器转速对排种性能的作用关系。为解决排种器在充种过程中由于型孔未囊取种子而造成漏播问题,李娟娟等[69]建立棉种充填过程的运动学模型对相互抢位棉种进行力学分析,研究取种轮运动参数与排种器转速对充种性能的影响。应用离散元仿真软件分析落入型孔的棉种速度的变化趋势,并分析取种轮振动频率对种群扰动的影响。表3为典型棉花播种装置[70-75]。表4为典型棉花机械化穴播技术特点。
气力式播种具有不伤种子、通用性好、作业速度快等特点,可更换排种盘适用于不同尺寸种子。这既提高作业效率,又确保排种作业质量。但由于种子群在高速旋转作用下易造成运动规律不合理,影响排种性能,需严格要求气密性,并存在结构复杂、动力消耗大、价格高昂、不耐用易磨损等问题。今后在研究气力式播种技术时,在排种过程中应构建棉种的运动学和动力学模型,对排种器气流场动力学特性进行仿真分析,明确棉种运动规律和工作机理,优化穴播器空间结构,开发低能耗、低成本、高耐用的产品。机械式排种器因其结构简单、成本低得到广泛使用,按照作业形式主要分为指夹式、圆盘式、勺轮式、窝眼式等。其中指夹式利用机械力夹持种子进行排种;圆盘式通过更换排种盘来保证运转,单粒点播或穴播种子;勺轮式采用型孔大小取种,实现单粒穴播和点播;窝眼式利用取种轮实现取种,但存在易伤种、对种子外形尺寸要求较高及播种作业速度不高等问题。后续应针对国内不同区域种植模式与技术需求的差异,完善棉花播种相关基础理论,优化改进关键部件与结构,集成先进技术,提高机械式排种器的适应性和高效性。

表3 典型棉花播种装置
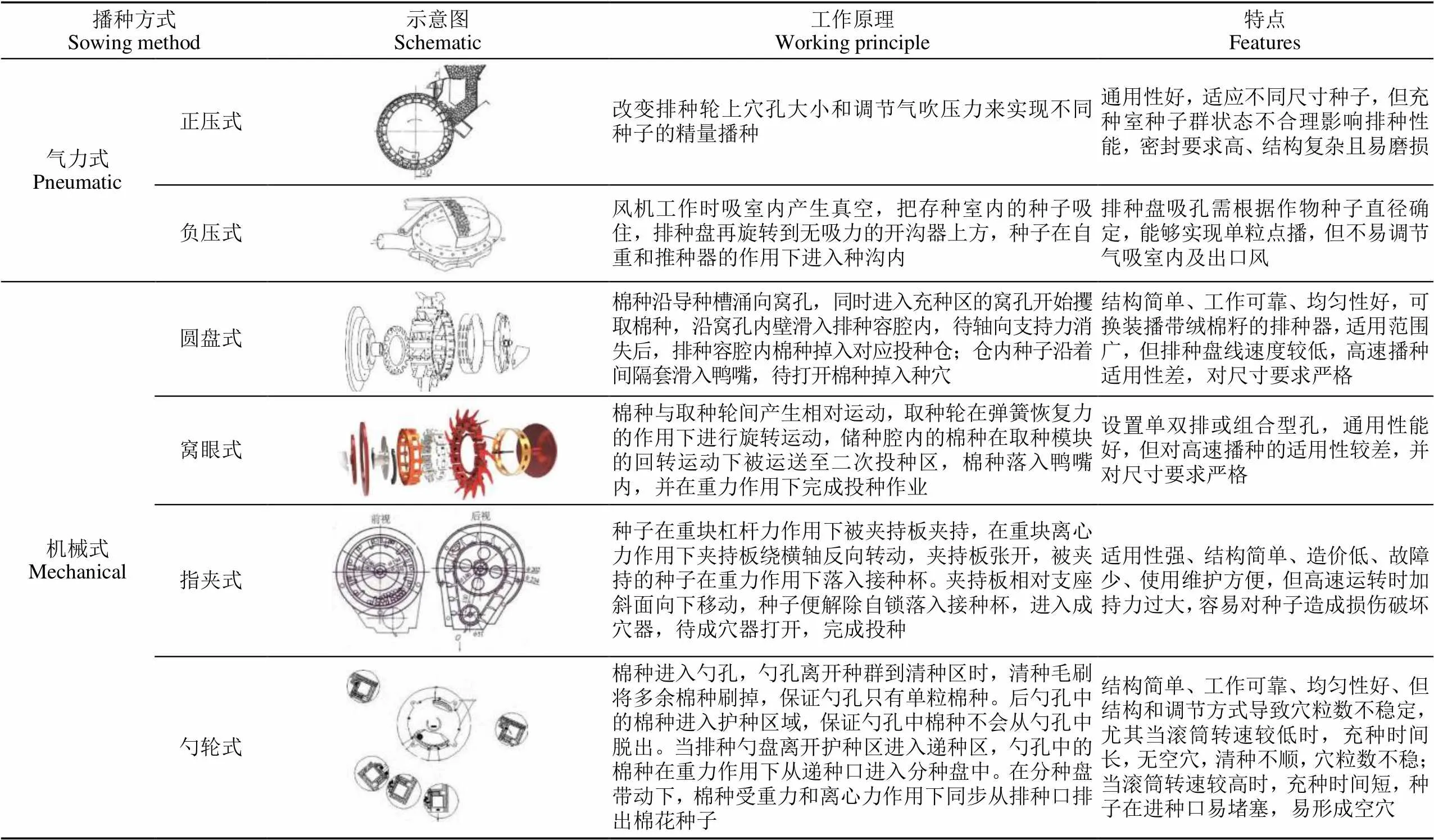
表4 典型棉花机械化穴播技术特点
3.3 棉花机械化播种智能化技术
采用精量播种技术省种省工,作业效率高、播种均匀性好、出苗整齐,利于后续田间管理和机械化收获,成为棉花机械化播种的技术重点和研究热点[66,76]。国外精量播种技术成熟,智能化水平较高,其中气力式应用较多[56]。国内棉花种植普遍采用地膜覆盖穴播,与国外农艺相差较大,难以直接应用。目前棉花机械化播种智能化技术发展缓慢,研究集中在自动导航和播种作业参数实时监控等[3,77-79]。
北斗卫星导航自动驾驶有效保障作业后的条田接行准确、播行端直,为后续棉花打药、施肥、收获等提供了标准化作业环境[80-82]。KAIVOSOJA等[83]开发了GNSS错误模拟器提高拖拉机导航和定位精度。ERKAN等[84]使用分布式非线性预测控制方法解决拖拉机轨迹追踪问题,可提高控制精度和对环境干扰的鲁棒性。2013年,罗锡文院士团队研发国内首套“基于GPS的轮式农业机械导航及自动作业系统”棉花铺膜播种机在新疆兵团第八师121团33连棉田进行现场播种演示[85]。张超[86]利用卫星导航自动技术搭载田间性能检测设备,与传统机械播种的误差比对。结果表明,卫星自动驾驶技术播种精度更高,棉花更易采净,且降低了劳动强度。王晨[87]研究了视觉导航试验控制平台,通过LabVIEW建立了视觉导航控制测控系统。
播种作业参数实时监测是目前研究最多和最为成熟的领域。穴播器自身转动及前进时易振动,工作环境恶劣,易出现取种、排种不畅造成空穴;再者穴播器内部完全封闭,不易及时发现空穴问题。张学军等[88]以齿盘式穴播器为对象,基于激光对射型和霍尔传感器开发了一种棉花精量穴播器取种状态监测系统。结果表明:光照对监测系统无影响,合格穴数监测精度最低为96.17%,空穴数监测精度最低为93.11%。曹叶等[89-90]利用CCD高速摄像头,开发了棉花穴播器排种性能自动监测系统。周利明等[91-92]研制了螺旋型电容籽粒传感器,实现了棉花精密播种机播种量的检测。结果表明,播种量监测精度为94.6%,漏播量监测精度为93.5%,重播量监测精度为88.1%。
播种作业中应用北斗卫星导航自动驾驶技术,有效解决了“播不直、接不上茬”难题。自动导航技术已逐步应用于棉花规模化的农业生产,但针对棉花播种过程智能化作业的实用性、适应性、可靠性仍需进一步研究。目前棉花精密播种机普遍采用穴播的方式,与常见排种器结构和排种方式不同,属于“点播式投种”,现有监测技术难以运用。播种作业参数实时监控虽取得一定成果,但无推广应用,后续需提高测控设备精度,降低设备成本。另外,变量播种核心是变量播种处方图和变量播种机,其中变量播种处方图获取是难点,需要依赖于各方面技术发展与进步。
3.4 点播式全约束导种技术
棉花地膜覆盖直播则以点播式导种为主,利用与地面垂直的往复式投种机构将种子直接送进种沟,属于全约束的种子运移[93]。杨徐飞等[19]设计一种气吸式棉花精量穴播器,惯性和刮种器的共同推动使种子顺利滚落到穴播器滚筒内圈,优化鸭嘴结构尺寸,减少种子碰撞嘴壁情况,确保种子准确落入穴中,不会造成太大位置偏移。卢勇涛等[58]优化设计鸭嘴结构,确保滚筒工作平稳,作业过程中不易挂膜,滑移率低。康建明等[94]利用负压气吸取种与强制断气投种组合的排种原理,实现精量取种和精确投种。王顺利[95]设计一种机械钳夹式棉花精量排种器,利用凸轮导轨和弹簧强制控制动钳和定钳间的张开角度,提高取种可靠度,并依靠弹簧弹力强制取种,确保了取种稳定性和可靠性。
点播式投种实质是用点播方式让土壤包围种子,在土壤摩擦力和回流作用下消除种子落入种床土壤的弹跳滑移现象,能够保证种距一致性,适用于穴播、铺膜播种等低速作业,但无法实现高速作业[76]。零速投种[96]一直都是机械化播种中的技术难点和研究重点,现有技术仍做不到绝对的零速投种。后续应继续深入研究和应用“零速投种”理论,如通过虚拟仿真技术和高速摄影等技术研究种子与土壤的碰撞过程,以播种机“零速投种”为目标创新设计穴播器与配套导种装置,合理优化导种装置结构曲线[97-98]。
4 棉花种植机械化面临问题与发展建议
棉花种植技术经历了快速的发展,在精准农业发展的大背景下,追求高产优质高效的发展目标。结合棉花产业生产发展要求与现有棉花种植机械化技术与装备现状,在以后研究中需重点关注和解决[1,66,99-100]:
4.1 棉花种植机械化面临的主要问题
1)地区发展不均衡,忽略农机作业适应性。我国棉花生产布局随国家农业布局和结构调整而发生重大变化,承担国家棉花产业发展的重任。新疆棉区作为全国最主要的棉花产区,但由于长期的产量优势和扎实的农业生产基础,忽视了区域布局和长远发展规划。其中,南疆传统棉区发展缓慢,缺乏适宜小规模机采的种植模式,限制机器使用,且技术应用到位率不足,难以发挥区域特色;北疆棉区土地流转快,新技术应用快,机械化程度高,生产效益提升。
2)基础性研究薄弱,科技创新不足。棉花种植机械的综合基础系统理论和共性技术综合分析比较欠缺,企业技术创新机制有待完善。另外缺乏多层次、多途径的创新探索,生产实践中存在问题研究不够深入,尤其棉花移栽机构创新过程中依然难以摆脱对经验和灵感的依赖,其创新设计的系统理论和方法仍未完成形成。由此造成棉花种植机械产品技术水平不高,影响机具作业的适应性和可靠性
3)智能化作业装备缺乏,农业环境日益恶化。重要农艺活动更多依赖于传统作业设备或人工操作,缺乏智能化精准作业装备,且绝大多数设备在作业过程中存在作业质量差、精准度低、操作不方便等多种问题。另外我国大部分棉花种植以直播为主,采用覆膜种植方式,产量明显高于传统直播方式,但造成了农田白色污染,连续多年种植导致土壤质量下降,加剧了农业生态环境恶化,给农业生产增加了不确定性。
4.2 棉花种植机械化发展建议
现代化农业背景下,高效率、高精度、高效益成为棉花种植机械化发展方向。结合国内实际情况,因地制宜地开展棉花种植机械化技术研究,主要朝以下方向发展:
1)优化棉花产区布局,增强农机与农艺配合。坚持棉区合理布局“三足鼎立”,兼顾三大棉区均衡发展。根据棉区比较优势,重点布局新疆棉区,确定扶持重点,实行规模化和专业化生产,弥补效率(单产)和效益(收益)优势不足,持续提高新疆棉花生产效率竞争力。适当发展长江和黄河流域棉区,稳定和巩固棉花生产。出台政策文件,整合相关资源,充分调动各相关涉棉部门的积极性,加强棉花种植扶持力度,确保种植结构保持合理水平。
研究农艺技术与农机技术融合发展模式,采用先进农艺技术,发展节本、高产的种植技术体系。构建规模化、轻简化种植体系改善棉田种植条件,投入智能化机械生产,实现棉花高效播种作业。针对不同地区棉花种植实际要求,研究不同作业要求机械装备,配套相应的农艺要求。明确标准,灵活形式,以规模化、标准化棉田为基础,配套建设高效节水、精准施肥设施,提高棉花生产管理水平、棉田产出水平和水肥资源利用效率,促进棉花产业模式规范化。
2)加强基础理论研究,提升自主创新能力。探究土壤和作物与作业机具及关键部件的相互作用关系理论技术研究,集成作物物理特性、机构创新设计以及互作机理的一体化研究体系。加强生产工艺与生产机械的联动性,形成土壤-作物-机具有效的三元一体发展模式。优化改进机具关键部件与结构,集成先进技术,确保机具及关键部件的适用性和可靠性。
应加大研发和引进核心技术,进行二次创新,研制适用性强的农机装备并不断加以改进。不断突破新技术、新方法、新材料、新装备,加速学科间融合与渗透,提高播种质量。重点加大对穴播机的研究力度,提高其作业效率和耐久性,延长穴播机使用寿命。在满足农艺要求、提高自动化程度的前提下,兼顾装备的经济型和适应性,加快开发多功能、多元化自动种植装备,提高棉花种植业生产发展水平。
3)加快智能化技术应用,绿色优质发展。加大信息化和智能化利用力度,突破关键工况参数及作业质量参数采集传感器的研究与开发,精准采集机具作业信息与播种质量指标。研发智能精准化装备,将使棉花种植机械向智能化、无人化方向发展,降低作业成本和劳动强度,提高生产效率和作业质量,提升资源利用率,从而推进传统棉区升级改造,加快产业模式与生产方式创新。
加大研发棉花种植生物降解地膜力度,逐步替代聚乙烯地膜,依靠科技创新来突破资源环境瓶颈制约,推动形成产业布局合理、资源高效利用、生态系统稳定、产地环境良好的农业发展格局。突破生物降解地膜、农业污染控制与修复等关键技术,依靠科技支撑棉花生产走向优质高效、绿色安全、资源节约、环境友好的现代化道路。
棉花种植机械化是棉花产业转变发展方式、提质增效、增强国际市场竞争力的重要途径之一。目前棉花种植机械化已形成了比较完备机械化播种技术与装备体系,但自动化、智能化程度仍需提高。智能化精量播种装备成为发展趋势,必将向信息智能化、高效大型化的方向发展。精准农业是我国传统农业粗放化生产经营向现代化、精量化生产经营转型的必然要求。棉花精量播种技术的推广应用则是棉花全程机械化技术推广应用技术重点和基础,最终目标是实现棉花精准化、智能化、无人化播种。优化棉花产区布局,确保种植结构保持合理水平,提高新疆棉花生产效率与竞争力。加强加大自主研发力度,提高自主创新能力和技术储备是确保棉花产业发展的保障。推进棉花机械化种植模式下农机农艺农信深度融合,形成科学合理的棉花机械化播种体系。突破资源环境瓶颈制约,优化资源配置,全面推动中国棉花生产的绿色优质可持续发展。
[1] 刘文静,范永胜,董彦琪,等. 我国棉花生产现状分析及建议[J]. 中国种业,2022(1):21-25.
[2] 全国优势农产品区域布局规划(2008-2015年)[Z]. 农业部,2008-08-22
[3] 赵岩,陈学庚,温浩军. 新疆兵团精准农业发展与北斗卫星导航技术的应用[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2018,36(4):397-404.
ZHAO Yan, CHEN Xuegeng, WEN Haojun. Application of the development of precision agriculture and the China's Beidou satellite navigation system in agricultural production in the xinjiang production and construction corps[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2018, 36(4): 397-404. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 杨丽,颜丙新,张东兴,等. 玉米精密播种技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(11):38-48.
YANG Li, YAN Bingxin, ZHANG Dongxing, et al. Research progress on precision planting technology of maize[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(11): 38-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 崔涛,樊晨龙,张东兴,等. 玉米机械化收获技术研究进展分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2019,50(12):1-13.
CUI Tao, FAN Chenlong, ZHANG Dongxing, et al. Research progress of maize mechanized harvesting technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(12): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张淑荣,刘朝敏. 我国棉花主产区区域竞争力及生产趋势分析[J]. 中国棉花,2011,38(11):2-6.
ZHANG Shurong, LIU Zhaomin. Regional competitiveness and tendency of production in main producing areas of cotton in China[J]. China Cotton, 2011, 38(11): 2-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 信桂新,杨朝现,邵景安,等. 基于农地流转的山地丘陵区土地整治技术体系优化及实证[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(6):246-256.
XIN Guixin, YANG Chaoxian, SHAO Jing’an, et al. Optimization and demonstration of land consolidation technical system in mountainous and hilly region based on farmland transfer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(6): 246-256. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 杨欣,王建合,杨淑华,等. 京津冀棉花种植机械化发展建议与配套机具研发[J]. 农业工程,2015,5(6):1-5,9.
YANG Xin, WANG Jianhe, YANG Shuhua, et al. Development proposals and supporting equipment development of cotton planting mechanization in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 5(6): 1-5, 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 伍彩虹. 棉花压缩营养钵播种机的研制[D]. 武汉:湖北工业大学,2016.
WU Caihong. Development of Seeding-Machine for Cotton Compression Nutrition Bowl[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 于晓旭,赵匀,陈宝成,等. 移栽机械发展现状与展望[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(8):44-53.
YU Xiaoxu, ZHAO Yun, CHEN Baocheng, et al. Current situation and prospect of transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(8): 44-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 裴新民,张友腾,刘晨,等. 我国棉花生产机械化发展状况研究[J]. 农机科技推广,2011(1):19-22.
[12] 张国强,周勇. 棉麦套作棉花种植机械化现状与思考[J]. 安徽农业科学,2014,42(32):11597-11598.
ZHANG Guoqiang, ZHOU Yong. The development status and thinking for wheat-cotton interplanting mechanization[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(32): 11597-11598. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 倪向东,徐国杰,王琦,等. 气吸滚筒阵列式棉花精密排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(12):58-67.
NI Xiangdong, XU Guojie, WANG Qi, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic cylinder array precision seed-metering device for cotton[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(12): 58-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李海潮,王爽,陈永,等. 基于EDEM的双腔式棉花精量排种器排种性能仿真研究[J]. 新疆农机化,2022(1):10-14.
LI Haichao, WANG Shuang, CHEN Yong, et al. Simulation study on performance of double-chamber cotton precision seed metering device based on EDEM[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Mechanization, 2022(1): 10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王龙,贺小伟,胡灿,等. 基于离散元法的棉花窝眼式穴播器排种性能模拟与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2021,43(1):151-156.
WANG Long, HE Xiaowei, HU Can, et al. Simulation and experiment for seeding performance of socket cotton dibbler based on discrete element method[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2021, 43(1): 151-156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张学军,陈勇,史增录,等. 双仓转盘式棉花竖直圆盘穴播排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(19):27-36.
ZHANG Xuejun, CHEN Yong, SHI Zenglu, et al. Design and experiment of double-storage turntable cotton vertical disc hole seeding and metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(19): 27-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 王方艳. 棉花覆膜播种机主要部件的设计[J]. 农机化研究,2010,32(7):142-145.
WANG Fangyan. Design of cotton mem brane seeder’s major part[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(7): 142-145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 冯洋洋,纪超,陈金成,等. 棉花气吸式排种机构的优化[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2021,26(8):140-149.
FENG Yangyang, JI Chao, CHEN Jincheng, et al. Optimization of cotton air suction seed metering device[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2021, 26(8): 140-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 杨徐飞,杨继芳. 气吸式棉花精量穴播器的设计与试验[J]. 湖北农机化,2020(18):16-17.
[20] 安军鹏,王永振,张晓辉,等. 多功能棉花覆膜播种机的设计与试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2017,38(11):1-4.
AN Junpeng, WANG Yongzhen, ZHANG Xiaohui, et al. Design and experiment of multifunetional cotton film mulching planter[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2017, 38(11): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 朱德文,陈永生,徐立华. 我国棉花生产机械化技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 农机化研究,2008(4):224-227.
ZHU Dewen, CHEN Yongsheng, XU Lihua. Cotton production mechanization technology present situation and development discussion in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008(4): 224-227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 仇半农. 中国棉花种植及联合收获机需求预测[J]. 农机科技推广,2019(4):23-25.
[23] 黄滋康,崔读昌. 中国棉花生态区划[J]. 棉花学报,2002(3):185-190.
HUANG Zikang, CUI Duchang. Ecological regionalization of cotton production in China[J]. Cotton Science, 2002(3): 185-190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 张泓,郭刚. 中国棉花生产区域格局变动及影响分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2022,50(7):214-218.
ZHANG Hong, GUO Gang. Analysis on the change and impact of china’s cotton production regional pattern[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(7): 214-218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[J]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2021.
[26] 孔卓. 棉花移栽机的虚拟样机设计[D]. 淄博:山东理工大学,2006.
KONG Zhuo. Design of Cotton Transplanter Based on Virtual Prototype[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 赵春龙. 全自动蔬菜移栽机设计[D]. 佳木斯:佳木斯大学,2017.
ZHAO Chunlong. Automatic Vegetable Transplanting Machine Design[D]. Jiamusi: Jiamusi University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] TSUGA K. Development of fully automatic vegetable transplanter[J]. Jarq-japan Agricultural Research Quarterly, 2000, 34(1): 21-28.
[29] 张智超. 非圆齿轮行星轮系全自动玉米钵苗移栽机构优化设计[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2014.
ZHANG Zhichao. The Optimization Design of Non-Circular Gear Planetary Gear Train Corn Automatic Transplanting Machine[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 尹大庆. 玉米钵苗移栽有序顶出式分秧机构的机理与试验研究[D]. 大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学,2014.
YIN Daqing. Experiment and Theory Studies on the Mechanism of Orderly Push-Out Separating Seedling for Corn Transplanter[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 李明勇. 全自动移栽机关键作业质量监测系统的研究[D]. 洛阳:河南科技大学,2019.
LI Mingyong. Research on Key Operation Quality Monitoring System of Automatic Transplanter[D]. Luoyang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 薛向磊. 取栽一体式棉花钵苗移栽机关键部件优化设计与试验研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2020.
XUE Xianglei. Optimized Design and Experimental Research on Critical Components of Integrated Transplanter with Picking and Planting for Cotton Bowl Seedling[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 李其昀,鲁善文,杨宪武. 吊篮式棉花移栽机的研究[J]. 农机化研究,2006(4):164-166.
LI Qiyun, LU Shanwen, YANG Xianwu. Research of the cotton transplanting machine with the nacelle[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2006(4): 164-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 武科. 吊篮式棉花移栽机栽植器的研究与分析[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2010.
WU Ke. The Study and Analysis of Nacelle of Dibble-Type Transplanter[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 王会丽. 棉花移栽机关键部件的研究与试验[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学,2017.
WANG Huili. Design and Experiment Study on Key Component of Cotton Transplanter[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 陈建能,黄前泽,王英,等. 钵苗移栽机椭圆齿轮行星系植苗机构运动学建模与分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(5):6-12.
CHEN Jianneng, HUANG Qianze, WANG Ying, et al. Kinematics modeling and analysis of transplanting mechanism with planetary elliptic gears for pot seedling transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(5): 6-12. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[37] 赵雄,沈明,陈建能,等. 棉花移栽机旋转式取苗机构的运动学分析及虚拟试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(8):13-20.
ZHAO Xiong, SHEN Ming, CHEN Jianneng, et al. Kinematic analysis and virtual experiment of rotary pick-up mechanism on cotton transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(8): 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 俞高红,王磊,孙良,等. 大田机械化移栽技术与装备研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2022,53(9):1-20.
YU Gaohong, WANG Lei, SUN Liang, et al. Advancement of mechanized transplanting technology and equipments for field crops[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(9): 1-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 徐照耀. 棉麦套作棉花铺膜直播机的设计与试验[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学,2020.
XU Zhaoyao. Design and Experiment of Cotton Film Mulching Direct Seeder in Cotton and Wheat Intercropping[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] 戴新俊. 棉花双膜覆盖播种技术的应用[J]. 农村科技,2007(6):12.
[41] 田立文,崔建平,徐海江,等. 新疆棉花生产技术现状与存在的问题[J]. 安徽农业科学,2013,41(34):13164-13167,13193.
TIAN Liwen, CUI Jianping, XU Haijiang, et al. Status of cotton production technologies in Xinjiang and its existing problems[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(34): 13164-13167, 13193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] BARBARA I, GABRIELLA S, GIULIANO V. Preparation, characterisation and field-testing of a biodegradable sodium alginate-based spray mulch[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2009, 102: 461-472.
[43] 赵鑫,何同庆. 我国棉花种植发展初探[J]. 北京农业,2015(30):128-129.
[44] 刘飞. 膜下播种机参数化造型及排种装置性能试验研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2009.
LIU Fei. The Parametric Modeling of Planting under Plastic Film and Capability Test of Discharging Seed Equipment[D]. Huhehaote: Inner MongoliaAgricultural University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[45] 温浩军,颜利民,王士国. 棉花双膜覆盖精量播种技术研究应用[J]. 农业机械,2010(7):131-133.
[46] 温浩军. 新疆兵团棉花精量铺膜播种技术的研究与推广[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2008.
WEN Haojun. Xinjiang Cotton Planting Filming Precision Technology Research and Promotion[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[47] 董万城,张立新,李文春,等. 新疆棉花播种机械应用现状及发展趋势[J]. 新疆农机化,2021(2):11-15.
DONG Wancheng, ZHANG Lixin, LI Wenchun, et al. Application status and developing trend of cotton planting machinery in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Mechanization, 2021(2): 11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[48] 孙冬霞,李明军,石磊,等. 机采棉精播机关键部件运动仿真及有限元分析[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(2):46-55.
SUN Dongxia, LI Mingjun, SHI Lei, et al. Motion simulation and mechanical analysis of key components of machine-picking cotton[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(2): 46-55. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[49] 黄鸿浩. 精量排种器现状及发展分析[J]. 时代农机,2019,46(5):34-35.
[50] 侯攀登. 棉花排种器的发展趋势[J]. 时代农机,2018,45(6):76.
[51] 许剑平,谢宇峰,陈宝昌. 国外气力式精密播种机技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 农机化研究,2008(12):203-206.
XU Jianping, XIE Yufeng, CHEN Baochang. The present technic status and developing tendency of abroad pneumatic precision drill[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008(12): 203-206. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[52] HUDSPETH E B, WANJURA D F. A planter for precision depth and placement of cottonseed[J].Transaction of the ASAE, 1970, 13(2): 153-155.
[53] PARISH R L. Development of a narrow-row vertical-plate planter[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1979, 15(4): 636-637.
[54] ÖNAL İ, DEGIRMENCIOGLU A, YAZGI A. An evaluation of seed spacing accuracy of a vacuum type precision metering unit based on theoretical considerations and experiments[J]. Turkish Journal of Agriculture Forestry, 2012, 36(2): 133-144.
[55] YAZGI A, DEGIRMENCIOGLU A. Measurement of seed spacing uniformity performance of a precision metering unit as function of the number of holes on vacuum plate[J]. Measurement, 2014, 56(10): 128-135.
[56] SINGH R C, SINGH G, SARASWAT D C. Optimization of design and operational parameters of a pneumatic seed metering device for planting cottonseeds[J]. Biosystems Engineering,2005, 92(4): 429-438.
[57] 陈学庚,卢勇涛. 气吸滚筒式棉花精量穴播器排种性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(8):35-38.
CHEN Xuegeng, LU Yongtao. Sowing perfomance of air-suction cylindrical cotton precision dibbler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(8): 35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[58] 卢勇涛,李亚雄,陈学庚. 气吸式棉花精量穴播器的设计与试验[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2012,47(3):129-133.
LU Yongtao, LI Yaxiong, CHEN Xuegeng. Design and experiment on air-suction cotton precision dibbler[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2012, 47(3): 129-133. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[59] 徐国杰. 气吸滚筒阵列式棉花精密排种器的设计与试验研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2018.
XU Guojie. Design and Experiment of Pneumatic Cylinder Array Precision Seed-metering Device for Cotton[J]. Shihezi:Shihezi University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[60] 康施为,倪向东,齐庆征,等. 气吸滚筒式棉花精密排种器的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2020,42(6):136-141.
KANG Shiwei, NI Xiangdong, QI Qingzheng, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic cylinder precision seed-metering device for cotton[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2020, 42(6): 136-141. (in Chinese with English abstract with English abstract)
[61] 姜有忠,李继霞,陈永,等. 基于有序充种的集排滚筒式排种器性能试验研究[J]. 农机化研究,2022,44(5):140-146.
JIANG Youzhong, LI Jixia, CHEN Yong, et al. Experimental research on the performance of collecting and arranging drum seed metering device based on ordered seed filling[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2022, 44(5): 140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[62] 李国林,宋炜,毛俐,等. 国内外几种主要排种器的特点[J]. 农业科技与装备,2011(8):70-73.
LI Guolin, SONG Wei, MAO Li, et al. Characteristics of several major seed dispensers at home and abroad[J]. Agricultural Technology and Equipment, 2011(8): 70-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[63] 王吉奎,坎杂,吴杰,等. 夹持自锁式棉花精量穴播器的设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2006(5):54-56,82.
WANG Jikui, KAN Za, WU Jie, et al. Design and experiment on clamping and self-locking cotton precision dibbler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006(5): 54-56, 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[64] 王吉奎. 夹持自锁式棉花精量点播轮的研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2006.
WANG Jikui. Study on Clamping and Self-Locking Cotton Precision Dibbler[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[65] 王吉奎,郭康权,吕新民,等. 夹持式棉花精密穴播轮改进设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(4):43-47.
WANG Jikui, GUO Kangquan, LYU Xinmin, et al. Experiment and improvement on clamping cotton precision seeding dibbler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(4): 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[66] 陈学庚,赵岩. 棉花双膜覆盖精量播种机的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(4):106-112.
CHEN Xuegeng, ZHAO Yan. Development of double-film mulch precision planter for cotton seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(4): 106-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[67] 肖旭,全腊珍,全伟,等. 棉花精量排种器排种性能试验研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2018,23(9):148-155.
XIAO Xu, QUAN Lazhen, QUAN Wei, et al. Design and experiment of a cotton precision bunch sowing device[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018, 23(9): 148-155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[68] 王龙,贺小伟,胡灿,等. 基于离散元法的棉花窝眼式穴播器排种性能模拟与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2021,43(1):151-156.
WANG Long, HE Xiaowei, HU Can, et al. Simulation and experiment for seeding performance of socket cotton dibbler based on discrete element method[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2021, 43(1): 151-156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[69] 李娟娟,张和平,毕新胜,等. 转轴型孔式精量排种器充种性能仿真分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(5):38-49.
LI Juanjuan, ZHANG Heping, BI Xinsheng, et al. Simulation analysis and test on the filling performance of rotary type-hole precision seed-metering device for cotton[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(5): 38-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[70] 天诚2MBJ-3/12机械式铺膜播种机[EB/OL]. [2022-06-05]. https://www.nongjitong.com/product/1749.html
[71] 钵施然2MBJF-2/12机械式铺膜播种机[EB/OL]. [2022-06-08]. https://www.nongjitong.com/product/bishiran_2mbj-2-12_ seeder.html
[72] 鑫昌盛2MBJ-2/12机械式铺膜播种机[EB/OL]. [2022-06-07]. https://www.nongjitong.com/product/shzxcs_2mbj-2-12_ seeder.html
[73] 天诚2MBQ4/8气力式铺膜播种机[EB/OL]. [2022-06-06]. https://www.nongjitong.com/product/181_2mnq4-8_planter_with_plastic_sheeting.html
[74] 祥和2MBQ-3/6气吸式铺膜播种机[EB/OL]. [2022-06-07]. https://www.nongjitong.com/product/mnsxhnj_2mbq-3-6_ seeder.html
[75] 祥和2MBJ-1/2机械式铺膜播种机[EB/OL]. [2022-06-07]. https://www.nongjitong.com/product/mnsxhnj_2mbj-1-2_ seeder.html
[76] 苑严伟,白慧娟,方宪法,等. 玉米播种与测控技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(9):1-18.
YUAN Yanwei, BAI Huijuan, FANG Xianfa, et al. Research progress on maize seeding and its measurement and control technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(9): 1-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[77] 廖庆喜,雷小龙,廖宜涛,等. 油菜精量播种技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(9):1-16.
LIAO Qingxi, LEI Xiaolong, LIAO Yitao, et al. Research progress of precision seeding for rapeseed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(9): 1-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[78] 陈焕轩,韩迎春,冯璐,等. 智慧农业在棉花生产管理中的应用[J]. 棉花学报,2020,32(3):269-278.
CHEN Huanxuan, HAN Yingchun, FENG Lu, et al. Application of smart agriculture in cotton production management[J]. Cotton Science, 2020, 32(3): 269-278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[79] 张峰. 棉花生产管理中智慧农业的应用分析[J]. 农业工程技术,2021,41(24):33,36.
[80] 李笑,李宏鹏,牛东岭,等. 基于全球导航卫星系统的智能化精细平地系统优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(3):48-55.
LI Xiao, LI Hongpeng, NIU Dongling, et al. Optimization of GNSS-controlled land leveling system and related experiments[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(3): 48-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[81] 赵岩,陈学庚,温浩军. 北斗卫星导航系统助力新疆兵团精准农业发展[J]. 农业工程技术,2018(18):28-33.
[82] 任樱,薛文华. GPS导航无人驾驶技术在棉花春播生产中的应用[J]. 农村科技,2018(2):11-12.
[83] KAIVOSOJA J, LINKOLEHTO R. GNSS error simulator for farm machinery navigation development[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2015, 119: 166-177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[84] ERKAN K, ERDAL K, HERMAN R, et al. Distributed nonlinear model predictive control of an autonomous tractor-trailer system[J]. Mechatronics, 2014, 24: 926-933.
[85] 方震. GPS棉花铺膜播种机演示成功棉花铺膜播种机演成功[J]. 农业机械,2013(13):28.
[86] 张超. 基于卫星导航自动驾驶技术在播种作业中的试验研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2015.
ZHANG Chao. Design and Experimental Study of Excitation Device of Self-propelled Dwarf and Close Planting Jujube Harvester[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[87] 王晨. 适于棉花铺膜播种的视觉导航控制系统的设计与研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2016.
WANG Chen. The Design and Research of the Visual Navigation Control System for Cotton Spreading and Seeding[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[88] 张学军,张海涛,史增录,等. 棉花精量穴播器取种状态监测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(5):9-19.
ZHANG Xuejun, ZHANG Haitao, SHI Zenglu, et al. Design and experiments of seed pickup status monitoring system for cotton precision dibblers[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(5): 9-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[89] 曹叶,郭文松,赵鹏飞,等. 基于LabVIEW的穴播器排种自动监测系统[J]. 农机化研究,2022,44(11):135-141.
CAO Ye, GUO Wensong, ZHAO Pengfei, et al. Design of automatic detection system for cotton drill seed metering performance based on LabVIEW[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2022, 44(11): 135-141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[90] 曹叶. 基于机器视觉的穴播器排种性能检测系统的设计[D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2021.
CAO Ye. Design of Performance Testing System for Seed Metering of Dibbler Based on Machine Vision[D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[91] 周利明. 基于电容法的棉花产量和播种量检测技术研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学,2014.
ZHOU Liming. Research on Detection of Yield and Seeding Rate of Cotton Based on Capacitive Method[J]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[92] 周利明,李树君,张小超,等. 基于电容法的棉管籽棉质量流量检测[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(6):47-52.
ZHOU Liming, LI Shujun, ZHANG Xiaochao, et al. Detection of seedcotton mass flow based on capacitance approach[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(6): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[93] 廖宜涛,李成良,廖庆喜,等. 播种机导种技术与装置研究进展分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2020,51(12):1-14.
LIAO Yitao, LI Chengliang, LIAO Qingxi, et al. Research progress of seed guiding technology and device of planter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(12): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[94] 康建明,陈学庚,王士国,等. 超窄行棉花精量排种器设计与性能试验[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2016,51(2):134-139.
KANG Jianming, CHEN Xuegeng, WANG Shiguo, et al. Design and experiment of precise metering device for cotton ultra narrow row[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2016, 51(2): 134-139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[95] 王顺利. 机械钳夹式棉花精量排种器排种机理研究及计算机仿真分析[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2009.
WANG Shunli. The Mechanism of Seeding about Mechanical Precision Clamp-Type Cotton Seed Metering Device & Computer Simulation Analysis[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[96] 佟超. 零速投种技术及其理论设计[J]. 机械研究与应用,1995(1):16-25.
[97] 陈学庚,钟陆明. 气吸式排种器带式导种装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(22):8-15.
CHEN Xuegeng, ZHONG Luming. Design and test on belt-type seed delivery of air-suction metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(22): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[98] RAJEEV K, HIFJUR R. Detection of flow of seeds in the seed delivery tube and choking of boot of a seed drill[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 153: 266-277.
[99] 喻树迅,周亚立,何磊. 新疆兵团棉花生产机械化的发展现状及前景[J]. 中国棉花,2015,42(8):1-4,7.
YU Shuxun, ZHOU Yali, HE Lei. Development of mechanization of cotton production in the xinjiang production and construction corps[J]. China Cotton, 2015, 42(8): 1-4, 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[100] 赵存鹏,赵贵元,郭宝生,等. 棉花机械播种方式的现状及存在问题[J]. 河北农机,2017(4):18.
Research progress in the key technologies and equipment for cotton planting mechanization
YUAN Yanwei1,2, BAI Shenghe1,2, NIU Kang2, ZHOU Liming2, ZHAO Bo2, WEI Liguo2, LIU Lijing1,2※
(1.,100083,; 2.,,100083,)
Cotton is one of the most important strategic materials and cash crops. The planting area and output of cotton have been ranked among the top in the world. Among them, cotton planting has been one of the basic links in the whole process during production. The mechanization of cotton planting has been the key bottleneck to restricting the cotton industry at present. The reason can be that the mechanical planting of cotton can be utilized to improve the quality and efficiency of cotton production, and then enhance the competitive advantage of cotton production, which is directly related to the sustainable development of the national cotton industry. The cotton mechanization planting can be divided into the cotton live broadcast and transplanted seedlings. Most previous efforts were focused on the optimization of equipment structure, flow field simulation, and operation performance tests. The cotton planting mechanization technology and equipment system have begun to take shape during this time. Cotton planting mechanization should follow the development direction of precision agriculture for the promising goal of high yield, quality, and efficiency, indicating a major practical demand in the cotton industry. The development mode of the cotton industry can be changed to enhance the quality and efficiency, as well as the competitiveness of the international market. It is also the research focus of the whole process mechanization and scale of the cotton industry. In this review, the current situation and characteristics of cotton planting were summarized on the key technologies and equipment in China. There was a trend of westward expansion of the cotton area in the Yangtze River basin and the Yellow River basin, whereas, the northwest inland cotton area gradually served as the main body of cotton planting in China. Especially, the sowing area of cotton in Xinjiang increased the fastest, while the proportion of cotton gradually increased, and the cotton in Xinjiang was the backbone of national cotton production for the new main producing area. Two technologies of cotton planting mechanization were proposed to emphatically analyze the research status and trends during cotton seedling cultivation, transplanting, and cotton live streaming. Furthermore, the opportunities and challenges were summarized to combine with the background of precision agriculture and the production requirements of the cotton industry. The future research directions and suggestions were addressed to optimize the layout of cotton-producing areas, in order to improve the competitiveness of cotton production efficiency under the planting structure at a reasonable level. Moreover, the independent innovation ability and technology reserve can be expected to strengthen the independent research and development of the cotton industry. A scientific and reasonable system can be formed to promote the deep integration of agricultural machinery, agronomy, and credit under mechanized cotton seeding. Therefore, the allocation of resources can be optimized to comprehensively promote the green, high-quality, and sustainable development of cotton production. The finding can provide a strong reference for cotton planting mechanization and equipment innovation.
crops; agricultural machinery; plant; cotton; mechanization; seedling transplanting; direct seeding
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202212139
S223.2
A
1002-6819(2023)-06-0001-11
苑严伟,白圣贺,牛康,等. 棉花种植机械化关键技术与装备研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报,2023,39(6):1-11.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202212139 http://www.tcsae.org
YUAN Yanwei, BAI Shenghe, NIU Kang, et al. Research progress in the key technologies and equipment for cotton planting mechanization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2023, 39(6): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202212139 http://www.tcsae.org
2022-12-19
2023-03-05
国家重点研发计划项目(2022YFD2002401);自治区区域协同创新专项(科技援疆计划)项目(2021E02055)
苑严伟,研究员,博士生导师,研究方向为农业机械自动控制与智能化仪器。Email: yyw215@163.com
刘立晶,研究员,博士生导师,研究方向为种植机械装备。Email:xyliulj@sina.com
中国农业工程学会会员:苑严伟(E040100027M)
