The effect of miR-129-5p in pancreatic cancer cells on apoptosis through targeted of HMGB1
2023-02-23WANGYuyangSUShixiangQINZongshuaiCENLanyingHUANGXiuquanHUANGGuixiangXUJianQINYueqiu
WANG Yu-yang, SU Shi-xiang, QIN Zong-shuai, CEN Lan-ying, HUANG Xiu-quan,HUANG Gui-xiang, XU Jian, QIN Yue-qiu✉
1. Department of Gastroenterology, Youjiang Medical College for Nationalities Affiliated Hospital, Baise 533000, China
2. Youjiang Medical College for Nationalities Graduate School, Baise 533000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the role of miR-129-5p in regulating HMGB1 expression in pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis.Methods: The untreated pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells were used as the control group.Mimics-NC (empty vector), miR-129-5p mimics, inhibitor-NC (empty vector)and miR-129-5p inhibitor were transfected into SW1990 cells by liposome transfection method as the mimics-NC group, miR-129-5p overexpression group (miR-129-5p mimics group), inhibitor-NC group and miR-129-5p low expression group (miR-129-5p inhibitor group).The binding site of miR-129-5p and HMGB1 was predicted by online target gene prediction website Target genes, and the targeting relationship between miR-129-5p and HMGB1 was verified by dual luciferase gene report experiment.The expression of miR-129-5p in each group was detected by qRT-PCR, and the expression of HMGB1 protein and apoptosis-related proteins Caspase 3 and Bcl-2 by Western blot.Hoechst staining was used to observe the changes of apoptosis.Results: Compared with the mimics-NC group and control group, miR-129-5p mimics transfection significantly up-regulated miR-129-5p level(P<0.01), inhibited HMGB1(P<0.01)and Bcl-2(P<0.05)protein expression, pro-moted Caspase 3 protein expression (P<0.05), and promoted apoptosis; compared with the inhibitor-NC group and control group, miR-129-5p inhibitor transfection significantly down-regulated miR-129-5p level (P<0.05), promoted HMGB1 and Bcl-2 protein expression (all P<0.05), inhibited Caspase 3protein expression (P<0.01), and inhibited apoptosis.The results of dual luciferase reporter gene assay showed that miR-129-5p could inhibit the fluorescence activity of wildtype HMGB1 cells and target the expression of HMGB1.Conclusion: miR-129-5p promotes the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells by targeting inhibition of HMGB1 expression.
1.Introduction
Pancreatic cancer(PC) is a common malignant tumor of the digestive system.Its early diagnosis is difficult and the mortality rate is high[1].Studies have shown that apoptosis is closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of pancreatic cancer, but the related mechanism is still unclear[1].High mobility group protein B1(HMGB1) is a highly conserved nuclear protein, which belongs to non-histone chromatin-associated protein.It was first extracted from mouse thymus chromatin in 1973 and named for its high fluidity in gel electrophoresis.Studies have found that the expression level of HMGB1 in pancreatic cancer tissues is increased, and it has been proved to be involved in the occurrence and development of pancreatic cancer by increasing autophagy, inhibiting apoptosis and regulating mitochondrial function[2-4].By inhibiting the expression of HMGB1 protein, it can promote the expression of Bax protein and inhibit the expression of Bcl-2 protein, thus promoting the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells[5,6].miR-129-5p belongs to a conserved microRNA family and is a small molecule RNA related to various biological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis,invasion, migration and drug resistance[7-10].Studies have found that mir-129-5p expression is down-regulated in pancreatic cancer tissues and is related to cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and prognosis[11,12].Bioinformatics analysis and literature reports have shown that miR-129-5p has a targeted regulatory relationship with HMGB1[13], but its effect on the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells is not clear.Therefore, this paper intends to explore the effect of miR-129-5p on the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating HMGB1 expression, and provide a theoretical basis for finding new therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Cell strain
Human pancreatic cancer cell line SW1990 was purchased from Arrowsay Biotechnology (Shanghai ) Co., Ltd.
2.1.2 Main reagents
Super fetal bovine serum was purchased from Wuhan Punosai Life Science and Technology Co., Ltd.DMEM, PBS, Bcl-2, 10 × SDSPAGE electrophoresis buffer, 10 × Tris-Glycine transfer buffer,PAGE gel rapid preparation kit were purchased from Wuhan Sevier Biotechnology Co., Ltd.Hoechst staining kit, QuickBlock Western rapid blocking solution and Rainbow Marker were purchased from Shanghai Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd.RIPA lysis buffer was purchased from English Biotechnology ( Beijing ) Co., Ltd.Trypsin-EDTA digestive juice, penicillin-streptomycin mixture 20× TBST, PMSF, protein phosphorylase inhibitor were purchased from Beijing Solarbio Science and Technology Co., Ltd.HMGB1,Caspase 3, β-actin, goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin ( H + L )HRP, goat anti-mouse IgG ( H + L ) HRP were purchased from Jiangsu Qianke Biological Research Center Co., Ltd.Plasmids were purchased from Shanghai Jima Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.Lipofectamine3000 transfection reagent and Trizol were purchased from Shanghai Thermo Fisher Technology ( China ) Co.,Ltd., PVDF membrane was purchased from Millpore, USA, and opti-MEM medium was purchased from Gibco.The hypersensitive ECL chemiluminescence kit was purchased from Mona ( Suzhou )Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and the miRNA reverse transcription kit and SYBR Master Mix were purchased from Nanjing Novozymes Biotechnology Co., Ltd.The qRT-PCR primers were purchased from Guangzhou Yijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Cell culture and transfection
The pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells were cultured in DMEM complete medium ( containing 10 % fetal bovine serum and double antibody ) and placed in a 5 % CO2cell incubator at 37 ℃.When the cell confluence reached 80% ~ 90%, subsequent experiments were performed.
SW1990 cells in logarithmic growth phase were seeded in 6-well plates at 2×105cells/well.Cell transfection was performed according to the instructions of liposome Lipofectamine3000 reagent, and untreated pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells were used as the control group (Control group).Mimics-NC (empty vector), miR-129-5p mimics, inhibitor-NC (empty vector) and miR-129-5p inhibitor were transfected into SW1990 cells by liposome transfection method as mimics-NC group, miR-129-5p overexpression group (miR-129-5p mimics group), inhibitor-NC group and miR-129-5p low expression group (miR-129-5p inhibitor group).The transfected liposomes and Lipofectamine3000 in each group were diluted with OPTI-MEM serum-free medium and allowed to stand for 10 min, and then the two were mixed and allowed to stand for 10 min.The cells were added to each well, and 1.7ml OPTI-MEM bloodless medium was added to each well for further culture for 8 h, and then replaced with complete medium for subsequent experiments.
2.2.2 Target gene prediction of miR-129-5p
The binding site of miR-129-5p to HMGB1 was predicted by online target gene prediction website Target genes (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_71/).
2.2.3 Dual luciferase reporter gene detection experiment
LT-h-HMGB1-3UTR-wt and LT-h-HMGB1-3UTR-mut plasmids( Hanheng Shanghai ) were constructed.LT-h-HMGB1-3UTR-wt and LT-h-HMGB1-3UTR-mut were co-transfected with miR-129-5p mimics and miR-129-5p-NC into 293 T cells by Lipofectamine3000 transfection reagent, respectively.The luciferase activity of each group was detected 48 hours after transfection.The experiment was repeated three times.
2.2.4 qRT-PCR detection
After 24 h of transfection of each group of cells according to different target genes, the total RNA of each group of cells was extracted by Trizol, and the cDNA was synthesized by Novozymes miRNA reverse transcription kit.The internal reference of miR-129-5p was U6.The reaction conditions of RT-qPCR were as follows :pre-denaturation 95 ℃ 300 s, denaturation 95 ℃ 15 s, annealing /extension 60 ℃ 30 s, 40 cycles.The results were analyzed by 2-∆∆ctmethod, and the experiments in each group were repeated three times.Primers are shown in Table 1.
2.2.5 Western blot experiment
SW1990 cells were collected 48 h after transfection and washed three times with pre-cooled PBS.100 μL RIPA Lysis Buffer(including PMSF, protein phosphorylase inhibitor) was added.The cells were lysed on ice and centrifuged at 12 000 rpm for 20 min.The supernatant was placed in a new EP tube and theprotein concentration was detected by BCA method.Proteins were separated by 12.5% SDS-PAGE polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis,concentrated gel 80V, 30min, separation gel 120 V, 90 min, placed on ice 250 mA constant flow membrane 1h transferred to 0.45 μm PVDF membrane, QuickBlock Western blocking solution closed 1h.After washing the membrane three times with TBST, the diluted rabbit anti-human HMGB1 antibody (1:1 000), rabbit anti-human Caspase 3 antibody (1:1 000), mouse anti-human Bcl-2 antibody(1:1 000), rabbit anti-human β-actin antibody (1:5 000) were added and incubated overnight at 4 ℃.The diluted goat anti-rabbit IgGHRP (1:6 000) and goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP (1:6 000) secondary antibodies were incubated at room temperature for 2 h.According to the ECL development kit instructions, the gel scanning analysis system of American Bole company was used to detect and image,and the gray value analysis was carried out by Image J software.Relative expression level of target protein = gray value of target protein/gray value of β-actin.The experiment was repeated 3 times in each group.

Tab 1 RT-qPCR primer sequences
2.2.6 Hoechst staining
The logarithmic phase SW1990 cells were seeded in 6-well plates at 2×105cells/well and cultured overnight in a 5% CO2cell incubator at 37 ℃.Suck out the culture medium, wash three times with PBS,add 0.5 mL fixative, and fix for 10 min.Remove the fixative and place it on a shaker.Wash it twice with PBS to drain the liquid.Add 0.5 mL Hoechst 33258 staining solution to the shaker and incubate in dark for 5 min.Wash the dye solution twice with PBS and drain the liquid.Apoptosis was observed under a fluorescence microscope and photographed.The experiments in each group were repeated three times.
2.2.7 Statistically treated
SPSS23.0 statistical software was used.The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.One-way analysis of variance and LSD-t test were used to compare the measurement data between multiple groups after cell transfection.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 There is a targeted interaction between miR-129-5p and HMGB1
The results of the target gene prediction website Targetgenes showed that miR-129-5p had a binding region with the 3’-UTR domain of HMGB1 (see Fig.1).
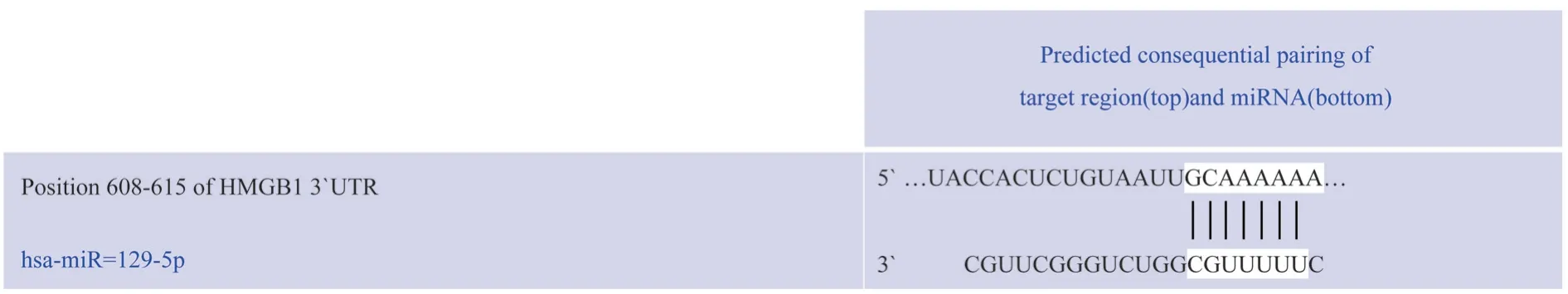
Fig 1 The binding diagram of miR-129-5p and HMGB1-3'UTR target site
3.2 Dual luciferase reporter gene assay was used to verify the targeting relationship between miR-129-5p and HMGB1
After transfection of wild-type HMGB1 gene expression vector WT-HMGB1, the expression of luciferase in miR-129-5p-3’UTRWT was significantly down-regulated compared with the NC mimics control group (t=29.39, P<0.001).After transfection of mutant HMGB1 gene expression vector MUT-HMGB1, the expression of luciferase in miR-129-5p-3’UTR-MUT was not significantly different from that in NC mimics control group(t=0.61, P=0.57>0.05).It can be seen that miR-129-5p can target the expression of HMGB1 (see Fig.2).
3.3 The expression level of miR-129-5p mRNA in each group of cells
The results of qRT-PCR showed that the expression level of miR-129-5p mRNA in miR-129-5p mimics group was significantly higher than that in mimics-NC group and Control group (all P<0.001).The expression level of miR-129-5p mRNA in miR-129-5p inhibitor group was significantly lower than that in inhibitor-NC group and Control group (all P<0.05).There was no significant difference in the expression level of miR-129-5p mRNA between the Mimics-NC group, the Control group and the inhibitor-NC group (all P>0.05)(see Fig.3).
3.4 Effects of overexpression and inhibition of miR-129-5p expression on the expression of HMGB1, Bcl-2 and Caspase 3
Western blot results showed that compared with mimics-NC group and Control group, the relative expression level of HMGB1 protein in miR-129-5p mimics group was significantly decreased(all P<0.01), and the relative expression level of Bcl-2 protein was significantly decreased (all P<0.05).Compared with inhibitor-NC group and Control group, the relative expression level of HMGB1 protein in miR-129-5p inhibitor group was significantly increased(all P<0.05), and the relative expression level of Bcl-2 protein was significantly increased (all P<0.05).The relative expression level of Caspase 3 protein in miR-129-5p mimics group was significantly higher than that in mimics-NC group (P<0.01) and Control group(P<0.05).The relative expression level of Caspase 3 protein in miR-129-5p inhibitor group was significantly lower than that in inhibitor-NC group (P<0.01) and Control group (P<0.001).
Tab 2 The relative expression of miR-129-5p mRNA in each group was detected by qRT-PCR(±s )
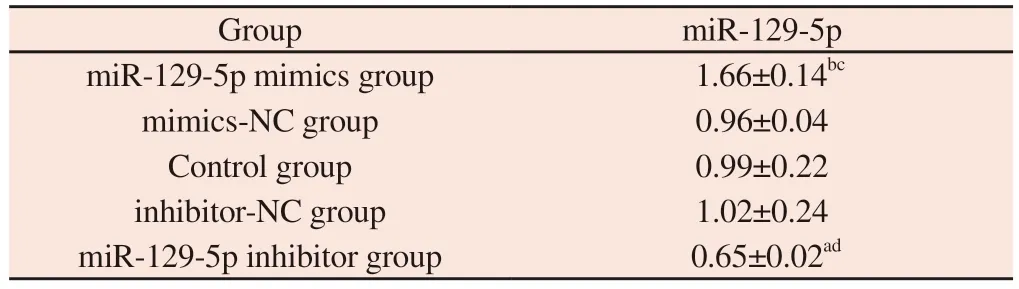
Tab 2 The relative expression of miR-129-5p mRNA in each group was detected by qRT-PCR(±s )
Note : a represents compared with the Control group,P<0.05;b represents compared with the Control group, P<0.01;c represents compared with mimics-NC group, P<0.01;d represents compared with inhibitor-NC group,P<0.05.
Group miR-129-5p miR-129-5p mimics group 1.66±0.14bc mimics-NC group 0.96±0.04 Control group 0.99±0.22 inhibitor-NC group 1.02±0.24 miR-129-5p inhibitor group 0.65±0.02ad
Fig 3 The relative expression of miR-129-5p mRNA in each group detected by qRT-PCR
3.5 The effect of miR-129-5p targeting HMGB1 on apoptosis of SW1990 cells
Hoechst 33258 staining results showed that compared with the mimics-NC group and the Control group, the number of SW1990 cells in the miR-129-5p mimics group was significantly reduced, and the number of apoptotic cells, nuclear fragmentation and chromatin aggregation were increased, showing strong blue fluorescence (see Fig.5A) ; compared with the inhibitor-NC group and the Controlgroup, the number of SW1990 cells in the miR-129-5p inhibitor group was significantly increased, the number of apoptotic cells was decreased, the nucleus was full, the cytoplasm was rich, and the uniform light blue fluorescence was observed (see Fig.5E) ; the mimics-NC group, Control group, and inhibitor-NC group had full nuclei, abundant cytoplasm, and uniform light blue fluorescence.There was no significant difference in fluorescence between the groups (see Fig.5B~D).
Tab 3 The effects of each group on the expression of HMGB1 protein and apoptosis-related protein in pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells(±s)

Tab 3 The effects of each group on the expression of HMGB1 protein and apoptosis-related protein in pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells(±s)
Note : a represents compared with the Control group, P< 0.05;b represents compared with the Control group, P<0.01;c represents compared with the Control group, P<0.001;d represents compared with mimics-NC group, P<0.05;e represents compared with mimics-NC group, P<0.01;f represents compared with inhibitor-NC group, P<0.05;g represents compared with inhibitor-NC group, P<0.01.
Group HMGB1 Bcl2 Caspase 3 miR-129-5p mimics 0.66±0.20be 0.52±0.19ad 1.18±0.05ae mimics-NC 0.94±0.03 0.96±0.05 0.91±0.09 Control 1 1 1 inhibitor-NC 1.02±0.10 1.04±0.14 0.91±0.10 miR-129-5p inhibitor 1.26±0.06af 1.45±0.12af 0.62±0.08cg
Fig 4 The effects of each group on the expression of HMGB1 protein and apoptosis-related protein in pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells

Fig 5 Apoptosis in each group (Hoechst 33258, 20 ×)
4.Discussions
Pancreatic cancer has a high mortality rate and is the seventh leading cause of cancer-related death[14].The high mortality of pancreatic cancer is related to its difficulty in early diagnosis and high metastasis rate.In recent years, the incidence of pancreatic cancer has been increasing, and its 5-year overall survival rate has increased from 3% in the 1970 s to 9% in 2020.Among all cancers,pancreatic cancer patients have the worst prognosis[14].Statistics from China’s National Cancer Center show that the incidence of pancreatic cancer has risen to ninth place, and the mortality rate ranks sixth[15].The study of the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer is of great significance to improve the early diagnosis rate of the disease and reduce the mortality rate.Recent studies have found that HMGB1 plays an important role in the development of pancreatic cancer[6].
Members of the HMGB protein family are less than 30 kda in length, including HMGB1, 2, 3, and 4.They can bind to DNA in a structure-dependent manner without being affected by specific sequences[16].Among them, the HMGB1 pathway is involved in a variety of physiological processes such as proliferation, inflammatory response, apoptosis, and tumor resistance[6,16-19].HMGB1 is a highly conserved nuclear protein, which is a non-histone chromatinassociated protein.Studies have found that HMGB1 is up-regulated in most types of tumors such as colorectal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer or melanoma, and is associated with biological behaviors such as cell proliferation and apoptosis[20,21].Apoptosis is closely related to the occurrence and development of pancreatic cancer.Studies have found that apoptosis is an evolutionarily conserved form of regulated cell death (RCD), usually involving caspases of the cysteine-aspartate protease family[22].The caspases family plays an important role in the process of apoptosis, and Caspase 3, as an apoptotic executive protein, plays a particularly prominent role in the process of apoptosis.In addition, the Bcl-2 gene family also plays an important role in inhibiting apoptosis in pancreatic cancer[23].Studies have shown that HMGB1 is up-regulated in pancreatic cancer tissues and has been shown to be involved in the regulation of proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells[4].Inhibition of HMGB1 expression can promote the expression of Caspase 3, Bax,and inhibit the expression of Bcl2, thereby promoting the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells[24,25].This study found that compared with the Control group and the mimics-NC group, after transfection of miR-129-5p mimics, the expression level of HMGB1 protein in pancreatic cancer cell SW1990 was significantly decreased, the expression level of Caspase 3 protein was significantly increased, the expression level of Bcl-2 protein was significantly decreased, and the level of apoptosis was increased, which was consistent with the results of previous studies.
The relationship between miRNA and the pathological process of pancreatic cancer is a hot topic in recent years at home and abroad.Many studies have shown that miRNA has a regulatory effect on many molecular biological processes such as proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of pancreatic cancer[26, 27], but the mechanism has not been elucidated.miR-129-5p is a member of the microRNA family.Studies have found that miR-129-5p is lowly expressed in various tumor tissues such as colon cancer, breast cancer, and lung cancer.Overexpression of miR-129-5p can inhibit cell proliferation,promote apoptosis, inhibit cell invasion, migration, and reduce tumor cell resistance[7-10].In pancreatic cancer, it has been confirmed that the expression of miR-129-5p is down-regulated and related to various biological processes such as cell proliferation and apoptosis[28-32].This study found that compared with the Control group and the mimics-NC group, after overexpression of miR-129-5p, the expression level of Caspase 3 protein increased significantly,the expression level of Bcl-2 protein decreased significantly, and the apoptosis increased.Compared with the Control group and the inhibitor-NC group, after inhibiting miR-129-5p, the expression level of Caspase 3 protein decreased significantly, the expression level of Bcl-2 protein increased significantly, and the apoptosis decreased,which was consistent with previous studies.
At present, the regulatory mechanism of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells is not completely clear.Studies have found that miR-129-5p and HMGB1 are involved in the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells[4,30], but the relationship between the two is not clear.It has been reported that miR-129-5p can target HMGB1, downregulate the expression of HMGB1, promote the apoptosis of breast cancer and inhibit the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells[24,33].In this paper, we found that miR-129-5p and HMGB1 have complementary binding sites by bioinformatics, and further found that miR-129-5p can target the expression of HMGB1 by double luciferase reporter gene detection.
In order to clarify whether miR-129-5p can regulate apoptosis through HMGB1, this study up-regulated and down-regulated the expression of miR-129-5p by miR-129-5p mimics and miR-129-5p inhibitor, respectively.It was found that after up-regulating the expression of miR-129-5p, the expression of HMGB1 and Bcl-2 protein decreased, the expression of Caspase 3 protein increased,and Hoechst staining showed that the number of apoptotic cells increased, showing strong blue fluorescence ; after down-regulation of miR-129-5 p expression, the expression of HMGB1 and Bcl-2 protein increased, the expression of Caspase 3 protein decreased,and Hoechst staining showed that apoptotic cells decreased, showing uniform light blue fluorescence.The results suggest that miR-129-5p can regulate apoptosis by targeting HMGB1 to regulate the expression of apoptosis-related genes Caspase 3 and Bcl-2.
In summary, miR-129-5p promotes the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting the expression of HMGB1, while downregulating the expression of miR-129-5p promotes the expression of HMGB1, thereby inhibiting the apoptosis of SW1990 cells.Therefore, miR-129-5p may be an important regulator of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells, which provides a new idea for exploring the anti-tumor mechanism of miR-129-5p.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- The effect of Huayu Lifei formula on the expression of miR-27a and α-SMA in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis model
- Prevalence and influencing factors of cognitive frailty in elderly with diabetes mellitus in China: A meta-analysis
- Correlation between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis based on Fibrotouch
- Pharmacodynamic study of cannabidiol on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats
- Clinical efficacy of leprerelin acetate with different dosage forms in central precocious puberty girls
- Exploring the mechanism of moist exposed burn ointment for the treatment of diabetic ulcer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
