The effect of Huayu Lifei formula on the expression of miR-27a and α-SMA in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis model
2023-02-23LINLingsangCHENJieLISiguangZHANGLeiDINGYipeng
LIN Ling-sang, CHEN Jie, LI Si-guang, ZHANG Lei , DING Yi-peng,3✉
1. Hainan Hospital Affiliated to Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570311, China
2. Department of General Practice, Hainan General Hospital, Haikou 570311, China
3. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Hainan General Hospital, Haikou 570311,China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: Investigating the inhibitory effect of Huayu Lifyei Formula on bleomycininduced rat pulmonary fibrosis and its impact on the expression of miR-27a and α-SMA.Methods: Wistar rats were arbitrarily classified into a normal group, a model group, and a group treated with Huayu Lifyei Formula, each consisting of ten rats.Pulmonary fibrosis rat model was established by injecting bleomycin.Subsequent to the modeling, the Huayu Lifyei Formula treatment group was administered Huayu Lifyei Formula via gavage for a period of 7 days.Rats were sacrificed on the 14th day after modeling.The right lung was taken for HE staining, Masson staining, and immunohistochemical observation of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression.The expression of miR-27a was measured by qRT-PCR, with the miR-27a binding site on ACTA2 (the gene encoding α-SMA protein) confirmed using dualluciferase reporter gene technology.Results: When compared to the model group, the Huayu Lifyei Formula treatment group showed considerable alleviation of pathological morphological changes in lung tissue, with significant reductions in alveolitis, fibrosis, collagen deposition in lung tissue, and the expression of α-SMA protein.Meanwhile, the expression of miR-27a in the Huayu Lifyei Formula treatment group significantly increased, and the dual-luciferase reporter gene confirmed the binding site of miR-27a with the ACTA2 gene.Conclusion:Huayu Lifyei Formula can inhibit bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats, and its mechanism may be related to the promotion of miR-27a expression.
1.Introduction
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a severe chronic interstitial lung disease characterized by abnormal proliferation and fibrosis of the alveolar walls and interstitium[1] These pathological alterations lead to the deposition of fibrous protein in lung tissue, preventing the normal expansion of the alveoli and thereby compromising gas exchange[2].The etiology of the disease is multifaceted and may be associated with long-term inhalation of harmful particulates,certain medications or genetic factors.While there are currently no targeted therapies, extracellular matrix inhibitors, corticosteroids,antioxidants, and immunosuppressive drugs can slow the progression of the disease and help improve symptoms[3,4].
In recent years, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) compound formulas based on syndrome differentiation have shown significant improvement in interstitial pulmonary fibrosis with minimal toxicity[5,6].Of particular interest is a TCM compound formula known as“Huayu Liefang,” which operates on the principle of “activating blood circulation to remove stasis, resolving phlegm and regulating lung function”[7].Existing research has found that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is closely related to the development of pulmonary fibrosis[8], and this pathway is regulated by microRNA-27a-3p (miR-27a-3p)[9].However, it remains unknown whether “Huayu Liefang” would affect the expression of miR-27a and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) during the treatment of bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis.
In this study, we established a model of pulmonary fibrosis in rats using bleomycin[10], and intervened with Huayu Liefang.By observing the expression of -SMA and detecting the expression of miR-27a and verifying their binding sites, we studied the potential mechanisms of action, providing a new perspective for understanding the mechanism of Huayu Liefang.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Animals and Reagents
Healthy male Wistar rats, aged 4-6 weeks, weighing between 180-220 g, were obtained from the Experimental Animal Services Center of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.The animals possessed a certification number of 44005800002779.
Bleomycin was purchased from Sigma.HE staining kit, Masson staining kit, and immunohistochemistry kit were acquired from Beijing Solarbio.α-SMA primary antibody was obtained from abcam.293T cell line was procured from the Cell Resource Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.Fetal bovine serum,DMEM culture medium, and trypsin reagent were purchased from Invitrogen.Reverse transcription kit (P312) and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR kit (Q331) were obtained from Nanjing NuoWeiZan Biotechnology.Dual-luciferase reporter gene was sourced from GenePharma.
2.2 Preparation and Source of Huayu Lifu Formula
The components of Huayu Lifu formula included Pinellia ternata, Salvia miltiorrhiza, Angelica sinensis, Hirudo, Astragalus membranaceus, Coix seed, among others.Concentrated granules of each herbal ingredient were used, manufactured by Jiangyin Tianjiang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.The production batch number was 0509025.After dissolution, the solvent containing 1 341 mg/mL of crude herbs was prepared, subjected to high-pressure sterilization,and stored at 4 ℃ for subsequent use[11].
2.3 Preparation and Grouping of Pulmonary Fibrosis Rat Model
After acclimatization for one week in the rearing environment,Wistar rats were weighed and numbered.Ten rats per group were categorized as follows: Control group, Model group (treated with bleomycin), and Huayu Lifu group (treated with bleomycin and Huayu Lifu formula).Bleomycin-induced pathological changes closely resemble human pulmonary fibrosis, thus it is widely used for establishing animal models[10].In this study, rats were anesthetized with 1% pentobarbital sodium (35 mg/kg) administered intraperitoneally.After anesthesia, the limbs and head of the rats were immobilized.A catheter connected to a 1 ml syringe was inserted into the trachea, and 0.25 mL of 0.4% concentration bleomycin (5 mg/kg) was injected into the lungs.For the Control group, an equivalent volume of physiological saline was injected.Immediately after injection, the animals were rotated upright to ensure uniform drug distribution in the lungs, thereby constructing the pulmonary fibrosis model.The Huayu Lifu group received an oral administration of 2 mL Huayu Lifu formula suspension(13.4 g∙kg-1∙day-1) for one week after model induction, followed by continuous administration of the same dose for the subsequent week[11].The control group and model group were gavaged daily with 2 ml of physiological saline.After 14 d of modeling, the rats were euthanized, and the right middle lobe of the lung was extracted for further analysis.
2.4 HE and Masson’s Staining of Lung Tissues
The right middle lobe of the experimental rats’ lungs was excised and fixed in 10% formaldehyde.Subsequently, routine paraffin embedding processes were carried out to prepare continuous 4 μm thick paraffin sections.These sections were stained using the Hematoxylin and Eosin method (also known as HE) and Masson’s trichrome method.The morphological changes in the lung tissues were examined under the light microscope.The HE staining was primarily used to observe the pathological changes in the inflammatory lung tissues of the experimental rats, including phenomena such as fatty degeneration and inflammatory cell infiltration.The Masson’s staining was used to assess the degree of pulmonary fibrosis in experimental rat lung tissues, including the number of fibrotic cell infiltrations, morphological changes in lung tissues, and changes in alveolar wall structure.
2.5 Immunohistochemical Detection
The paraffin sections of each group of rat lung tissues were defatted with 75% ethanol, soaked in 95% and 100% ethanol for 5 min each, and then submersed in xylene twice, each time for 10 min.The sections were deoxygenated with a 0.3% H2O2formaldehyde solution for 30 min to effectively eliminate the interference caused by endogenous peroxidase on lung tissue sections.The sections were washed with PBS buffer for 5 min, three times.The sections were then incubated with α-SMA primary antibody at room temperature for 1 h, and then washed again with PBS buffer for 5 min, three times.The sections were incubated with a fluorescein secondary antibody at room temperature for 1 h, washed with PBS buffer, and then incubated with sufficient fluorescein at room temperature for 30 min.Finally, the sections were washed with PBS buffer three times,each time for 5 min, rinsed with distilled water, and mounted.The sections were observed under a microscope, and image recording and analysis were carried out.
2.6 qRT-PCR Detection
RNA was extracted from the lung tissues of different groups of rats using Trizol reagent.Subsequently, the concentration and purity of the RNA were assessed using the NanoDrop 2 000 from Thermo Fisher Scientific.Following this, the RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using a reverse transcription reagent kit,and a qPCR reaction was performed using the ABI 7500QPCR instrument.The PCR reaction parameters were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 ℃ for 5 min, followed by denaturation at 95℃ for 5 sec, annealing at 62 ℃ for 20 sec, and extension at 72℃ for 30 sec, for a total of 40 cycles.U6 was used as an internal reference, and the 2-ΔΔctmethod was used to calculate the expression of miR-27a.The upstream and downstream primers of miR-27a were 5′- TGCGGTTCACAGTGGCTAAG -3′ and 5′-CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGA-3′, respectively.The upstream and downstream primers of U6 were 5′- CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′and 5′- AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′, respectively.
2.7 Dual-Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
The dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was carried out using 293T cells.Firstly, the wild-type 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of ACTA2 and its mutant were inserted into the pMIR-RB-REPORT™luciferase mRNA expression reporter vector.Next, 5×104cells/well of 293T cells were seeded into a 6-well plate, and four groups of samples were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000: ACTA2-WT and miR-NC group, ACTA2-WT and miR-27a group, ACTA2-MUT and miR-NC group, and ACTA2-MUT and miR-27a group.Fortyeight hours post-transfection, the activity of Firefly and Renilla luciferases were evaluated using a luminometer and normalized to Renilla luciferase activity.
2.8 Statistical Analysis
Data were statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.0, with measurements that fit a normal distribution presented as±s.A t-test was used for comparisons between two groups, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for comparisons among multiple groups.Statistical significance was defined as P<0.05.
3.Results
3.1 Pathological Observations of Rat Lung Tissues in Each Group
Pathological features of rat lung tissues in each group were observed using hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining.The results showed that one week after the model was established, the lung tissues of the control group rats displayed a normal alveolar morphology:the lung tissues were intact and clearly visible, the alveolar wall was thin and relatively continuous, and there were no obvious signs of inflammatory cell infiltration.This indicates no abnormal pathological changes or apparent inflammatory reactions in the lungs of the rats in the control group.In contrast, the lung tissues of the model group rats showed diffuse consolidation.Observations showed a significant thickening of the alveolar walls, destruction of the alveolar septa, and a large amount of inflammatory cell infiltration within the alveoli.The septa were also widened, and there were many fibroblasts in the lung interstitium.However, the effect of the Huayu Liefang on rat lung tissue was similar to that in the normal group, with only occasional observations of a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration, and most remained normal,as shown in Figure 1.These results indicate that Huayu Liefang can effectively improve pulmonary fibrosis caused by bleomycin in rats.

Fig 1 The impact of Huayu Lifei formula on the pathological alterations in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis model(HE, 400×)
3.2 Huayu Liefang Improves Collagen Deposition in Lung Tissue Induced by Bleomycin
Through Masson staining observation, the lung tissues of the control group rats showed a clear structure, and no obvious inflammatory cell infiltration and collagen deposition (blue deposition) were observed.The lung interstitial lesions in the model group rats were severe, accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration and obvious blue collagen deposition.The collagen structure of the lung tissue of the rats in the Huayu Liefang group was basically consistent with that of the control group, as shown in Figure 2.Thus, it can be inferred that Huayu Liefang helps to reduce the collagen deposition in lung tissues caused by bleomycin.
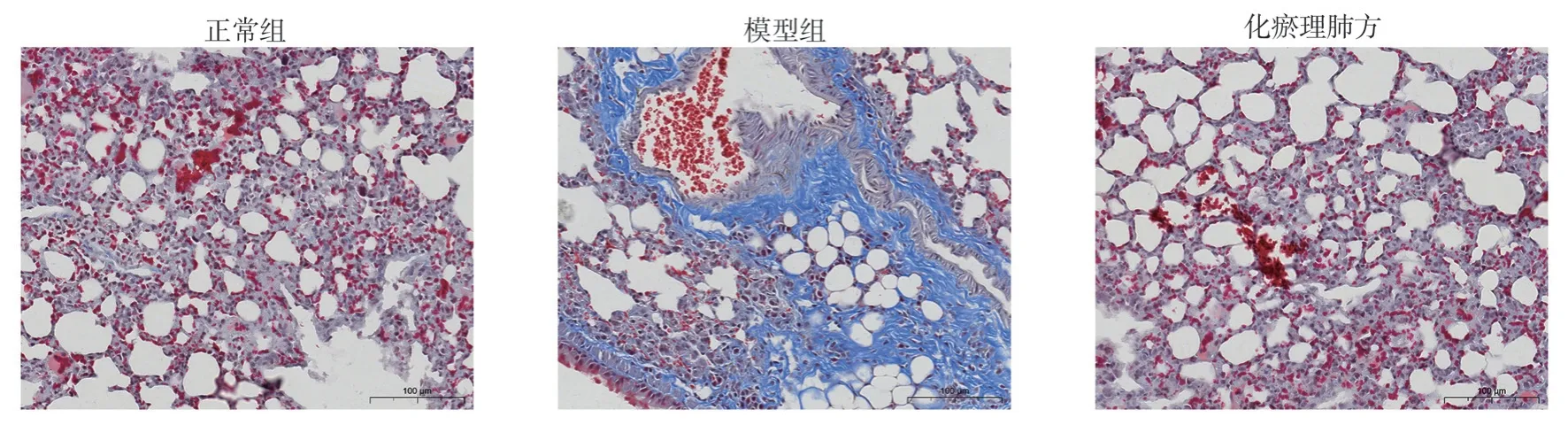
Fig 2 The effect of Huayu Lifei formula on the collagen in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis model(MASSON, 400×)
3.3 Huayu Liefang Inhibits α-SMA Expression Induced by Bleomycin
The expression of pulmonary fibrosis marker α-SMA was detected through immunohistochemistry.The immunohistochemical results suggest a high expression of α-SMA in the model, indicating the successful construction of the pulmonary fibrosis model.However,the expression of -SMA in the normal group and Huayu Liefang group lung tissues was significantly reduced, as shown in Figure 3.The above results suggest that Huayu Liefang can inhibit pulmonary fibrosis in rats induced by bleomycin.

Fig 3 The effect of Huayu Lifei formula on the α-SMA in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis model(400×)
3.4 Huayu Liefang Promotes miR-27a Expression
The effect of Huayu Liefang on miR-27a in lung tissues of rats with pulmonary fibrosis was detected by qRT-PCR.The qRT-PCR detection showed that compared with the control group, the level of miR-27a in the lung tissue of the model group was significantly reduced (0.46 ± 0.06 vs 0.99 ± 0.05, P < 0.001, t = 11.14).Compared with the model group, the expression of miR-27a in the lung tissue of the Huayu Liefang group was significantly increased (2.97 ± 0.38 vs 0.46 ± 0.06, P < 0.001, t = 11.19), as shown in Figure 4.Based on this, it can be speculated that miR-27a plays a role in the inhibitory effect of Huayu Liefang on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
3.5 miR-27a Targets ACTA2 Gene
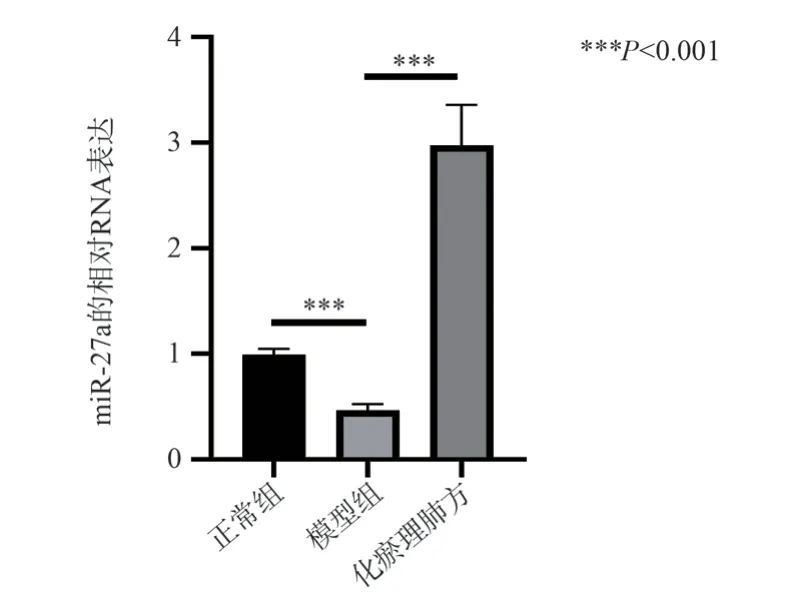
Fig 4 The effects of oleic acid and cordycepin treatment on apoptosis in LO2 cells The effect of Huayu Lifei formula on the miR-27a in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis model, *** means P < 0.001.
The Targetscan database(http://www.targetscan.org/) predicts that miR-27a has complementary binding sites with the 3’UTR of the ACTA2 gene encoding α-MA, as shown in Figure 5A.The luciferase reporter vector containing the binding site of the ACTA2 gene 3’UTR was co-transfected with the miR-27a mimic and miR-27a inhibitor into 293T cells.After 24 hours of culture, the luciferase activity was co-tested.The results showed that co-transfection of ACTA2 3’-UTR-WT and miR-27a significantly inhibited luciferase activity (0.35 ± 0.03 vs 1.02 ± 0.04, P < 0.001, t = 22.6), while co-transfection of ACTA2 3’-UTR-MUT and miR-27a had no significant effect on luciferase activity (0.98 ± 0.09 vs 1.02 ± 0.04, P= 0.49, t = 0.75), as shown in Figure 5B, it suggests the existence of a binding site between ACTA2’s 3’UTR and miR-27a.These results hint that miR-27a might suppress the expression of α-SMA protein by specifically targeting and binding to ACTA2, thereby contributing to the inhibitory role of the Huayu Liphu Formula on bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.

Fig 5 miR-27a binds to ACTA2
4.Discussion
Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic lung disease primarily occurring in lung tissues, characterized by structural damage between alveoli and lobules.The pathology is typified by inflammatory cell infiltration between lung alveolar interstitium, abnormal proliferation of fibroblasts, leading to interstitial fibrosis and respiratory dysfunction[12].The progression of pulmonary fibrosis is rapid, with patients having an average survival period of 3-5 years post-diagnosis, and clinical manifestations primarily include dry cough and difficulty in breathing[1].Given the current lack of effective prevention and treatment measures, an in-depth study of its pathogenesis is of significant importance[2].
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) plays a vital role in Chinese clinical medicine, often applied in the prevention and treatment of various diseases.Compared to Western medicine, TCM has advantages such as fewer side effects, long-lasting efficacy, and a wide range of applicability[13].Studies have reported that the compound Bu Fei Li Qi Tang can improve pulmonary fibrosis,reducing the mRNA levels of TGF-β1 and α-SMA[14].In the present study, we developed a Huayu Li Fei formula based on TCM theory.In this formula, Dan Shen invigorates the blood and resolves stasis, while Ban Xia dries dampness and resolves phlegm.Their combined efforts effectively eliminate phlegm and blood stasis in the collaterals.Leech and Angelica sinensis, as minister drugs,aid the sovereign drugs in resolving phlegm and unblocking the collaterals; Astragalus enhances qi and strengthens yang.These three drugs work together to promote the dissipation of blood stasis and smooth flow of the meridians.Houttuynia cordata, Coix seed,and Earthworm, as assistant drugs, coordinate the overall medicinal properties of the formula, jointly exhibiting effects of tonifying the lungs, astringing the exterior, removing stasis, and benefiting qi.In this study, we treated a bleomycin-induced rat model of pulmonary fibrosis with the Huayu Li Fei formula.Experimental results showed that this formula effectively improved the pathological condition of the bleomycin-induced rat model of pulmonary fibrosis and reduced collagen deposition, consistent with the research results of Li Fei et al[15], that Huayu Li Fei formula has a certain preventive therapeutic effect on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.α-SMA, as one of the fibrosis markers, is often highly expressed in pulmonary fibrosis[16,17].Our experimental results show that the expression of α-SMA in the lung tissues of the normal group and Huayu Li Fei formula group significantly decreased, further indicating that the Huayu Li Fei formula can inhibit bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
From the perspective of molecular mechanisms, the occurrence of pulmonary fibrosis is closely related to the abnormal activation and imbalance of pathways such as TGF-β, Wnt/β-catenin, and PI3K/Akt[8,18,19].The abnormal activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway is considered one of the core mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis development[20].Recent studies show that microRNAs(miRNAs) play key roles in the formation and development of pulmonary fibrosis, but their specific regulation and individual pathological roles are largely still unknown.Some miRNAs, such as miR-21 and miR-33, have been found to affect processes such as fibroblast proliferation and differentiation, matrix synthesis,and immune responses[21-24].miRNAs are also seen as potential therapeutic targets for pulmonary fibrosis, and interventions targeting specific miRNAs can inhibit the progression of pulmonary fibrosis[25].miR-27a is a pleiotropic microRNA located on human chromosome 19[26].Studies have found that overexpression of miR-27a can effectively alleviate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting and inhibiting the Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathway,reducing damage to the extracellular matrix of lung tissue cells, thus improving the symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis[9,27].In the present study, we observed a significant decrease in the level of miR-27a in the lung tissues of the model group, while treatment with the Huayu Li Fei formula significantly increased the expression of miR-27a,suggesting that miR-27a plays a role in the treatment of bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis in rats with the Huayu Li Fei formula.Based on this, we hypothesized that miR-27a plays a role in the inhibitory effect of the Huayu Li Fei formula on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
miRNAs play important functions in regulating target gene expression and have a key impact on processes related to gene regulation, cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis[28].α-SMA is encoded by the ACTA2 genein humans[29,30].It is a smooth muscle-specific actin isoform and a marker of myofibroblast differentiation and fibrosis.The overexpression of α-SMA is one of the key features of fibroblast activation and transformation into myofibroblasts, which play a critical role in the development of pulmonary fibrosis[31].Research has revealed that within the tumor microenvironment, the knockdown of miR-27a induces the expression of ACTA2, augmenting the differentiation of lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, and further bolstering fibrosis[27,32].In the present study, we utilized the Targetscan database for prediction, and validated it via dual-luciferase reporter gene technology, confirming the existence of binding sites between miR-27a and the gene ACTA2 encoding α-SMA.These data corroborate previously published research findings[32].Thus, we hypothesize that miR-27a mediates the therapeutic effect of Huayu Liefang on bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by targeting and binding to ACTA2, thereby inhibiting α-SMA protein expression.
Our results demonstrate that bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis can be treated with Huayu Liefang, which promotes miR-27a expression and significantly decreases α-SMA expression.Whether Huayu Liefang exerts its effective therapeutic action on bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by stimulating miR-27a expression and inhibiting α-SMA expression, thus exploring the causal relationship, requires further investigation with simultaneous drug treatment and intervention in miR-27a and α-SMA expression.In summary, our research shows that Huayu Liefang can effectively treat rat pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin, by promoting miR-27a expression and suppressing α-SMA expression.These findings provide a theoretical basis for a deeper understanding of the mechanism of Huayu Liefang treatment.This strategy could potentially be a new viable approach in traditional Chinese medicine for the clinical prevention of pulmonary fibrosis.
Author’s statement
All authors agree to submit this manuscript and have no conflicts of interest.
Authors’ contributions
Lin Lingsang: Animal Experiments and Manuscript Writing.
Chen Jie: Reagent procurement.
Li Siguang: Pathological staining.
Zhang Lei: Analysis and revision of experimental results.
Ding Yipeng: Funding support and manuscript confirmation.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Prevalence and influencing factors of cognitive frailty in elderly with diabetes mellitus in China: A meta-analysis
- Correlation between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis based on Fibrotouch
- The effect of miR-129-5p in pancreatic cancer cells on apoptosis through targeted of HMGB1
- Pharmacodynamic study of cannabidiol on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats
- Clinical efficacy of leprerelin acetate with different dosage forms in central precocious puberty girls
- Exploring the mechanism of moist exposed burn ointment for the treatment of diabetic ulcer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
