The Taxonomy,Evolution and Host Spectrum of Mpox Virus: a Systematic Review and Analysis of Poxvirus
2023-02-04,
,
(College of Biology,Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Virology,Hunan University,Changsha 410012,China)
Abstract: The sporadic outbreaks of human mpox diseases in the nearly twenty years have seriously influenced the public health and economic.Though the reservoirs of mpox virus (MPXV) are mainly rodents,it could spill over to humans by direct contact and cause self-limiting infection with the symptom of lymphadenopathy and rash on the skin.Since the first case reported outside Africa in the USA at the beginning of this century in America,MPXV has been gradually prevalent globally and become an increasing public threat.With the advancing technology of viral detection and gene sequencing,many novel poxviruses were detected which enriched the variety of Poxviridae family.In this review,we provide a comprehensive overview on the latest classification,host spectrum,genome feature,pathogenicity and the evolution of MPXV and other poxviruses.This information will promote our understanding of the phylogenetic relationship and infectious transmission of pathogenic poxviruses and contribute to future viral researches and disease control.
Key words: poxvirus;pathogenicity;taxonomy;host;evolution
The ongoing human mpox disease since 2022 caused by mpox virus (MPXV) has been prevalent in almost all regions of the world,leading to 90 465 confirmed cases and 157 deaths in 115 countries by September 10,2023 according to WHO (https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/mpx_global/).MPXV,one of the etiologies ofPoxviridae,infects mainly primates and rodents causing smallpox-like symptoms.Since the eradication of smallpox in 1980s,MPXV became the most important and severest pathogen ofPoxviridaein human which caused sporadic epidemics[1].
ThePoxviridaefamily contains 2 subfamilies(ChordopoxvirinaeandEntomopoxvirinae),22 genera and a total of 83 species according to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses Executive on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) (https://ictv.global/taxonomy).Current classification of poxviruses is mainly depended on the symptom,morphology,the isolation of host and pathological findings[2].In 1957,a report described the poxviruses infecting vertebrates which remained the basis and reference of subsequent classification and nomenclature of poxviruses[3].To avoid divergence,the information about viruses listed in this review was primarily in accordance with the latest updated version in the taxonomy system ICTV.Besides,only the classified virus strains listed on the ICTV website were involved,while some strains unclassified or reported elsewhere might not be mentioned.This review presents some basic information such as the taxonomy,host range,structure and pathongenicity of poxviruses.
1 The genome structure of poxvirus
Poxviruses contain a large and complex linear double-strand DNA genome.The genome size of different poxviruses is quite variable,ranging from 127 kb to 456 kb and encoding hundreds of proteins[4].Observed by electron microscope,virions are generally brickshaped (220~450 nm long × 140~260 nm wide×140~260 nm wide) with tubular or globular units being attached to the lipoprotein surface membrane.Also,the virions can be ovoid (250~300 nm long × 160~190 nm diameter) with the surface membrane possessing a regular spiral filament.The negatively-stained electron microscopy images showed a biconcave or cylindrical core containing the genome DNA and proteins organized in a nucleoprotein complex was enclosed by the surface membrane.Several lateral bodies appeared to be present in the concave region between the core wall and a membrane[5-6].
Though the genome sizes of poxviruses vary quite differently,the genomic structures of poxviruses share some significant characteristics.In order to perform an intuitive sight,the genome structure of West African Clade MPXV(NC_063383.1) was used as an example (Fig.1).
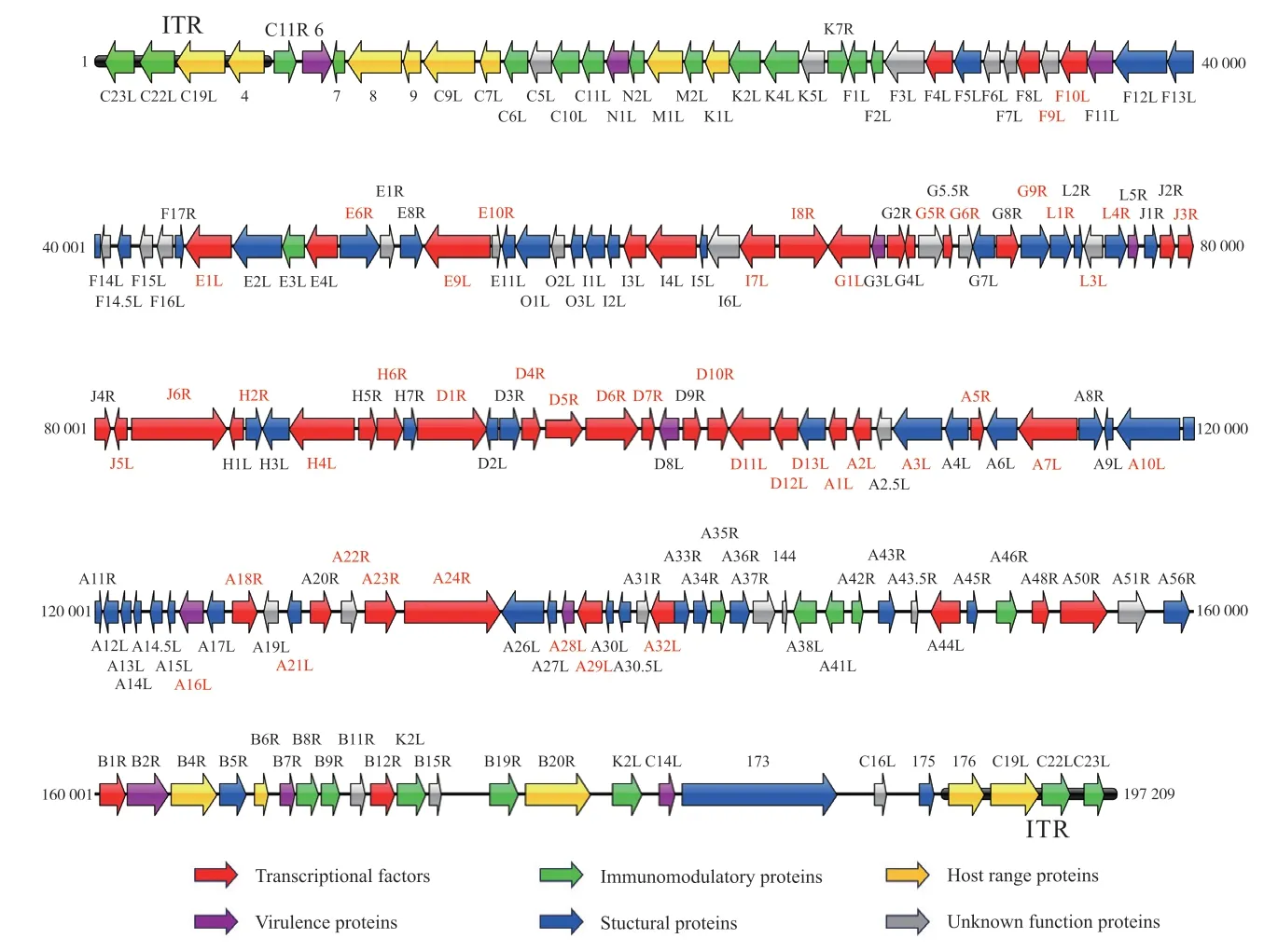
Fig.1 The genome structure of West African Clade MPXV
On the poxvirus genome,the liner double-stranded DNA genomic ends are linked by covalent hairpin.The hairpin terminuses exist in inverted and complementary form and are rich in A-T bases.Connected with the hairpin terminuses are two regions of inverted terminal repeats (ITR).The sizes of ITR vary differently from 0.7 kb to 23.4 kb among all poxviruses encoding several genes except for VARV.The major parts of poxviruses genome are the central conservative region flanked by two variable regions[7].The core conserved genes located in the approximate 100 kb region in the central genome are essential and functional in DNA replication,transcription,RNA processing and virion assembly[8].There are approximate 88 conserved genes present in the subfamilyChordopoxvirinaeand 49 conserved genes found in all sequenced poxviruses.However,with the appearance of new genus of poxvirus,some of these conserved genes are absent[9-10].The genes involved in the interactions with hosts are located in the two terminal sides of the genome and play significant roles in influencing host range and mediating responses to the host immune system which are called host range genes and virulence genes,respectively[11].
2 The taxonomy and pathongenicity of poxvirus
Currently,subfamiles ofChordopoxvirinaeandEntomopoxvirinaeform thePoxviridaefamily.The subfamilies ofChordopoxvirinaeandEntomopoxvirinaehave 18 and 4 viral genera,respectively.Here,the discussion was focused on these zoonotic poxviruses in subfamilyChordopoxvirinae,the subfamilyEntomopoxvirinaewas briefly mentioned.
2.1 Zoonotic poxviruses of Chordopoxvirinae
Members of the subfamilyChordopoxvirinaeare classified into the 18 genera includingAvipoxvirus,Capripoxvirus,Centapoxvirus,Cervidpoxvirus,Crocodylidpoxvirus,Leporipoxvirus,Macropopoxvirus,Molluscipoxvirus,Mustelpoxvirus,Orthopoxvirus,Oryzopoxvirus,Parapoxvirus,Pteropopoxvirus,Salmonpoxvirus,Sciuripoxvirus,Suipoxvirus,VespertilionpoxvirusandYatapoxvirus.Among above genera,partial members ofOrthopoxvirus,Parapoxvirus,Molluscipoxvirus,andYatapoxviruswere reported to infect humans (Tab.1).
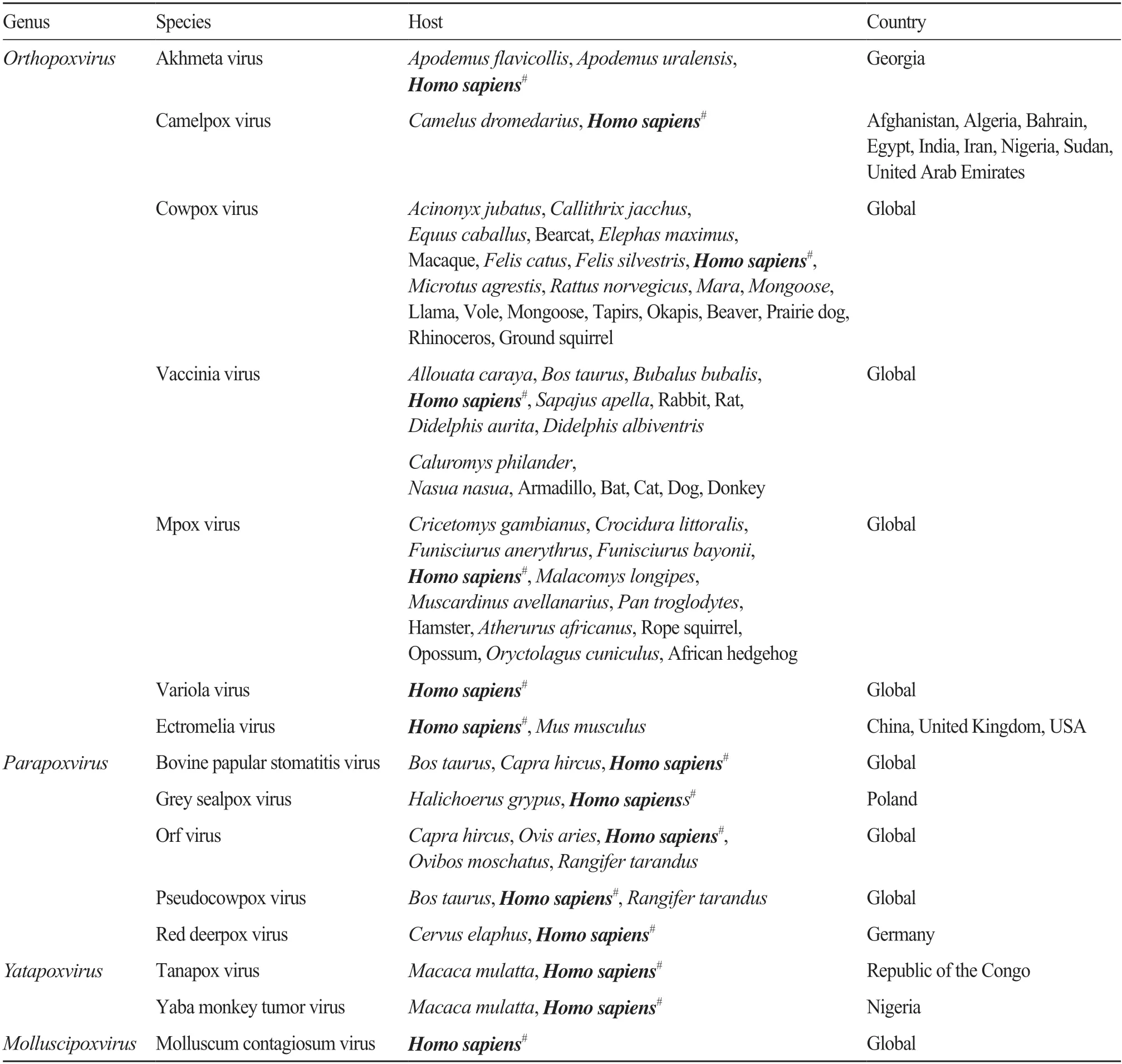
Tab.1 A list of poxviruses with human-infecting reports in Chordopoxvirinae subfamily of Poxviridae family
2.1.1Orthopoxvirus
TheOrthopoxvirusgenus belonging toChordopoxvirinaecontains 12 species,including several pathogenic poxviruses infecting humans,such as MPXV and variola virus (VARV) (Fig.2).The MPXV,VARV,vaccinia virus (VACV),cowpox virus (CPXV),camelpox virus(CMLV) are extensively studied due to their significant harm.Here,above 5 orthopoxviruses with complete genomic sequence were briefly described.Other members inOrthopoxvirusgenus with complete genomic sequence include abatino macacapox virus (AMPV),akhmeta virus (AKMV),ectromelia virus (ECTV),raccoonpox virus(RCNV),skunkpox virus (SKPV),taterapox virus(TATV),and volepox virus(VPXV).

Fig.2 Phylogenetic relationships of poxviruses in Orthopoxvirus genus
MPXV infections have been reported in human,various non-human primates (cynomolgus monkeys,sooty mangabeys,chimpanzees and common marmosets),and rodents (hamsters,rope squirrels,African dormice and giant pouched rats)[12].There is an incubation period of 5~21 days after infection with MPXV,the signs and symptoms of infection may change for a period of 2~5 weeks.The disease begins with non-specific symptoms,including chills,headache,lethargy,weakness,and fever.Then the rash of varying sizes appears on the face,body,hands,legs,and feet.The specific feature of mpox is lymphadenopathy[13-14].Mpox causes fatality rate much lower than smallpox.The fatality rate of West Africa Clade mpox is approximately 1%~3.6% while the Central Africa clade is deadlier with a mortality rate of up to 11%.The fatality rate of ongoing human mpox is less than 1%[15].During 2022 outbreak of mpox,sexual contact played a leading role in the transmission[16].Recent evidence showed that MPXV could be detected in wastewater indicating wastewater could be a new infec-tion source and surveillance approach in mpox transmission[17].According to the genome sequences and clinicepidemiologic comparisons,MPXV is divided into three clades: Central African Clade (Clade 1),West African Clade (Clade 2) known as IIa,and the ongoing MPXV(Clade 3) known as IIb (Fig.3).

Fig.3 A phylogenetic tree differentiating the three clades of MPXV
VARV is the highly pathogenic pathogen responsible for smallpox,killing 300 million to 500 million people in the last century and causing widespread suffering at least several centuries ago[18].According to the mortality rate and symptoms of infection,VARV can be divided into two epidemiological types,variola minor virus and variola major virus.VARV is generally transmitted through close contact or the respiratory tract.The incubation period of the VARV is about 10~14 days in most cases.In the early stages of the disease,patients develop fever with headaches,back pain and vomiting until they become bedridden.The eruption phase is characterized by a rash on the face that spreads throughout the body over a period of 24 to 48 hours,gradually developing into papules,vesicles,and pustules.In addition,complications of smallpox include bacterial infection,generalised sepsis and corneal ulcers.Sequelae included facial pockmarks,blindness,and limb deformities[19].After a worldwide vaccination campaign in 1980,the World Health Organization declared the completely eradication of VARV[19].
VACV and other related viruses (buffalopox virus and rabbitpox virus) have been reported and isolated in humans,multiple domestic animals (dogs,cats and cows),non-human primates (capuchin monkeys and black-howler monkeys),rabbits,bats,procynoides and many wild rodents (capybara andrat).Current knowledge is insufficient about natural reservoirs of VACV,but rodents have long been suspected as maintenance reservoirs for VACV and VACV-related viruses[12].VACV can be transmitted from vaccinated people and cause severe and fatal disease,especially in immunocompromised condition[20].VACV is one of the most studied poxviruses as it is a model on the basic biology,virulence,host range and the host immune response of poxvirus[21].In the beginning,VACV and CPXV were considered to be the same pathogen because of CPXV can induce immunity against smallpox.However,it was finally found that the smallpox vaccines were actually not CPXV but VACV in 1939.As time passed by,VACV gradually got rid of CPXV in the eradication of smallpox as it only caused mild infections in human and could induce protective immunity to other orthopoxviruses[18].
CPXVs have been reported to infect more than 60 animal species including human,non-human primates (macaques and common marmosets),domestic animals (dogs,cats and cows),lions,cheetahs,beavers,ground squirrels,rhinoceros and voles.Vole species and wild rodents are considered natural reservoirs of CPXV[18].Human can be infected by contacting with infected animals through skin lesions.The symptoms of immunocompetent individuals are usually localized.However,immune-compromised patients are at higher risk for systematic and even fatal infections.For example,fatal and disseminated cowpox infection has been reported in an adolescent renal transplant recipient immunosuppressed by antirejection therapy[22].
CMLV,pathogen of a highly contagious disease of camels,was first identified in India in 1909 which can cause high mortality in camels leading to great economic loss.Recently,cases that human infected with CMLV were reported.It can cause drop in milk production,weight loss and debilitating condition in infected animals.Clinical features are fever,rash and pustule on the skin[23].
2.1.2Parapoxvirus
Parapoxviruses are significant causative agents causing proliferative skin lesions around oral cavity and epidermis.Human infections often occur via direct contact with infected animals or objects[24].Members of this genus include bovine papular stomatitis virus (BPSV),grey sealpox virus (GSPV),orf virus (ORFV),pseudocowpox virus (PCPV) and red deerpox virus (RDPV) threatening those who handle or hunt cattle,sheep,goats,seals and deer.For example,two deer hunters were infected with PCPV while hunting white-tailed deer[25].A shepherd got infected with ORFV when raising sheep with ulcerative cutaneous lesions around the lip and mouth[26].
2.1.3Molluscipoxvirus
molluscum contagiosum virus (MOCV) is the only known member in genusMolluscipoxvirus.It is a significant skin pathogen which can infect human and replicate in basal keratinocytes[27].Typical clinical feature is lesions and dome-shaped papules on the skin.Sexual contact plays an important role in spreading virus.Besides,contact to infected objects or patients can also spread virus[28].
2.1.4Yatapoxvirus
Yatapoxviruscontains two kinds of viruses that mainly infect primate species which are tanapox virus(TPV) and yaba monkey tumor virus (YMTV).A yabalike disease virus (YLDV) which is considered a member of the same species with TPV.TPV was first isolated near the Tana River in Kenya in 1957 endemic in Africa,though two infected cases were reported outside Africa who had the history of trip in Africa.YMTV was isolated from laboratory rhesus monkeys in Nigeria.Tumors were developed on the face and limbs with the progress of disease[29].Clinical features include fever and skin lesions.Mosquitoes play significant role in spreading virus.No evidence shows that it can be transmitted directly from human to human.Due to that yatapoxviruses can infect a variety of primates including human,they are potential threats to human society.The adequate understanding about the biology of yatapoxviruses is still insufficient.
2.2 Subfamily Entomopoxvirinae
Entomopoxvirinaeis one of two subfamilies of poxviruses,members are mainly infecting insects and their host range is found to be limited to one or a few related species[30].According to the insect host and morphology of virions,theEntomopoxvirinaeis now divided into four major genus (Alphaentomopoxvirus,Betaentomopoxvirus,DeltaentomopoxvirusandGammaentomopoxvirus)and some unclassified species.Alphaentomopoxviruses mainly infect beetles;betaentomopoxviruses mainly infect butterflies and moths;deltaentomopoxviruses mainly infect locusts and gammaentomopoxviruses mainly infect flies and mosquitos[31].
2.3 The phylogeny of poxviruses
Not only do the conserved genes vary differently among different poxviruses,but also the ITR possesses great discrepancies even in the same genus,for example,the length of ITR is about 0.7 kb in VARV but about 12 kb in VACV.The terminal region where ITRs locate is extremely inclined to cause recombination which is important for the assimilation of new genes[9].Due to the restriction of technique,ITR of some poxviruses were not sequenced.Here,two phylogenetic trees based on 34 conserved proteins and ITR region of typical poxviruses were constructed and their topological structures were compared (Fig.4)[32].Besides,in order to explore the evolutionary relationship among MPXV and other orthopoxviruses,a phylogenetic tree of Orthopoxvirus was constructed (Fig.2).

Fig.4 The topological differences between ITR tree and conserved protein tree of poxvirus
The phylogenetic tree ofPoxviridaeshowed thatPoxviridaewas clustered into two subfamilies which wereChordopoxvirinaeandEntomopoxvirinaedistinctly.According to previous research,Yatapoxvirus,Leporipoxvirus,Capripoxvirus,CervidpoxvirusandSuipoxvirusformed the sister clade toOrthopoxviruswhich were called Clade II poxviruses[11].With the discovery of new poxviruses,some of them were clustered into Clade II poxviruses.InChordopoxvirinae,orthopoxviruses share the closest relationship with centapoxviruses.SGPV was clustered into a sole branch compared to other chordopoxviruses.Both two trees showed thatOrthopoxviruswas clustered into two subclades which were New World Orthopoxvirus and Old World Orthopoxvirus.InEntomopoxvirinae,the unclassified entomopoxvirusDiachasmimorpha entomopoxviruswas clustered into separate branch with other entomopoxviruses.
As was shown in the phylogenetic tree based on the right ITR,the topological structure was significantly different from the phylogenetic tree of conserved genes.In ITR phylogenetic tree,thePoxviridaewas no longer divided intoChordopoxvirinaeandEntomopoxvirinaesubfamilies.However,orthopoxviruses still share the closest phylogenetic relationship with centapoxviruses,whereas different from the conserved proteins tree,ECTV rather than VACV shares the closest relation with MPXV in the ITR tree.Besides,EPTV was clustered with entomopoxviruses.
To verify the precise sequence identities between conservative gene,the nucleotide sequence identities of 45 concatenated conserved genes of classified poxviruses and selected orthopoxviruses with complete genome were compared (Tab.2 and Tab.3).

Tab.3 The nucleotide identities of complete genome of Orthopoxviruses
InChordopoxvirinae,orthopoxviruses shared the closest relationship with centapoxviruses.The identities of these 45 concatenated conserved genes of orthopoxviruses shared the high similarity to that of centapoxviruses with 75.43%~76.93% identities.SGPV showed low similarity with all the other poxviruses which might be the result of remote relationship between their hosts.In the phylogenetic tree ofOrthopoxvirus,some species were clustered into several clades,one representative genomic sequence in each clade was selected and compared.The identities between New World Orthopoxvirus and Old World Orthopoxvirus varied distinctively.As for conserved genes,Old World Orthopoxvirus shared the identities all above 94% within each other,but only around 87% with New World Orthopoxvirus.While for the complete genome sequence,Old World Orthopoxvirus shared the identities around 80% within each other and around 70% with New World Orthopoxvirus.Both two phylogenetic trees showed that MPXV shared the closest relationship with VACV.The identity of 45 conserved genes between MPXV and VACV was the highest reaching 97.9%,though identity of complete genome sequence between MPXV and VACV was close to other Old World Orthopoxviruses.Both identities of complete genome and 45 conserved genes showed the highest similarity between West Africa Clade and MPXV in epidemic.The identity of complete genome revealed that the West Africa Clade MPXV was of 96.53% similarity with the Central Africa Clade of MPXV,which might be due to some small discrepancies.For example,as reported in previous research,the West Africa Clade contains a 17 amino acids (aa) insertion in VACV-Cop C7L ortholog.Also,in VACV-Cop B16R ortholog,the West Africa Clade contains several deletions.Besides,in West Africa Clade,a 2.3 kb insertion containing three ORFs existed in the left inverted terminal repeat while the Central Africa Clade had a 684 bp insertion containing three small ORFs that were fragments of CPXV-GRI C3L and C4L.The Central Africa Clade exhibited a 1.9 kb insertion containing three ORFs that were fragments of a 512 aa kelch-like protein of VACV-Cop C2L ortholog.And in West Africa Clade,there was a 2.2 kb insertion containing a 112 aa ORF compared with Central Africa Clade[33].
3 Conclusions and perspectives
The sudden outbreak of mpox disease drew the public attention to poxviruses again after the eradication of VARV.Due to divergences in conceptualisation and approaches to virus classification and nomenclature,suggestions and principles were approved to establish a universal taxonomy of viruses to provide a comprehensive knowledge of vi-ruses and complicated evolutionary relationships among viruses[34].With the newly detected poxviruses,knowledge about the host spectrum,diversity and genetic evolution has expanded and been updated which resulted in novel standards of poxviruses classification.Therefore,a new taxonomy was approved and released by ICTV[35].The variety species of viruses,broad host range,consistency and variation of genome of poxviruses may provide information about the evolutionary path of these viruses.Though some poxviruses possess a clear taxonomic status,they lack the genomic sequences on GenBank.Here,only viruses with clear taxonomic status and genome sequences were used in order to avoid divergency.
Poxviridaecontains many pathogens that infect humans and are harmful to the public health.Cross-species transmission events of poxviruses have been frequently reported.Previous researches revealed that human shortor long-term contacts with animals can result in spill-over of viruses among different species.The first mpox outbreak outside Africa was due to the contact with infected rodents.The sporadic outbreaks of mpox in the nearly twenty years remind the threat of epidemic MPXV to public health.Recent researches have shown that MPXV could be transmitted together with other pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2 and HIV[36].Thus,monitoring natural poxviruses and keeping safety distance with potential reservoirs are critical to prevent the cross-species transmission of poxviruses to humans.Furthermore,in-depth investigations of virus diversity,viral genes functions,viral infection characteristics,viral cross-species transmission patterns and vaccines can contribute to better understanding of poxvirus evolution and pathogenicity characteristics,and facilitate disease prevention and control.
