应急管理中自组织任务分配的博弈模型与应用
2022-11-03苏军陈怡林张东煜
苏军 陈怡林 张东煜




摘 要:非常規的突发事件发生后,群众的各种自组织救灾活动发挥着至关重要的作用。应用合作博弈刻画自组织活动中群众的策略选择与协作机制,研究群众如何根据特定目标自发建立联盟并实现最优的任务分配。首先在群众的自组织任务分配过程中引入多Agent系统(MAS),以自治Agent的交互行为与合作策略模拟群众联盟形成与任务分配的过程,通过定义分布式社交网络结构,以图限制下的合作博弈为分析工具,构造带技能的联盟形成博弈模型,确定任务与Agent联盟之间的映射。其次引入系统效用函数和偏好顺序,在联盟形成博弈模型的基础上建立优化模型,通过求解该优化模型获得最优的联盟结构及任务分配方案。最后介绍联盟结构形成和优化的相关算法,在自组织救灾案例“互联网人YO!群”中验证模型和算法的合理性。结果表明:应急管理中群众的自组织任务分配过程可在MAS中建模为带技能的联盟形成博弈,该博弈模型可实现任务与Agent联盟之间的一一对应,通过进一步优化可找到使得系统效用最大的联盟结构及最优的任务分配方案。
关键词:合作博弈;应急管理;多Agent系统;自组织;任务分配
中图分类号:N 94;F 224
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-9315(2022)05-1046-08
DOI:10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2022.0525开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Game model and application of self-organized task allocation in emergency management
SU Jun,CHEN Yilin,ZHANG Dongyu
(College of Sciences,Xi’an University of Science and Technology,Xi’an 710054,China)
Abstract:After unconventional emergencies,various self-organized disaster relief activities of the masses play a vital role.The cooperative game was applied to describe the strategy selection and cooperation mechanism of the masses in self-organized activities,and to study how the masses spontaneously establish coalitions according to specific goals with the optimal task allocation achieved.Firstly,multi-agent system(MAS)was introduced into the process of mass self-organized task allocation.The process of mass coalition formation and task allocation was simulated by the interaction behavior and cooperation strategy of autonomous agents.By determining the structure of distributed social network and using the cooperative game under graph constraints as an analysis tool,a skilled coalition formation game model was constructed,and the mapping between tasks and agent coalitions was confirmed.Secondly,the system utility function and preference order were introduced,an optimization model was established based on the coalition formation game model,and the optimal coalition structure and task allocation scheme were obtained by solving this optimization model.Finally,an introduction was made to the relevant algorithms for the formation and optimization of the coalition structure,and the rationality was verified of the model and algorithm in the self-organized disaster relief case“Internet people yo! Group”.The results show that the self-organized task allocation process of the masses in emergency management can be modeled in MAS as a skilled coalition formation game model.The game model can realize one-to-one correspondence between tasks and agent coalitions.Through further optimization,the coalition structure and the optimal task allocation scheme that maximize the system utility can be found out.
Key words:cooperative game;emergency management;Multi-Agent System;self-organization;task allocation
0 引 言
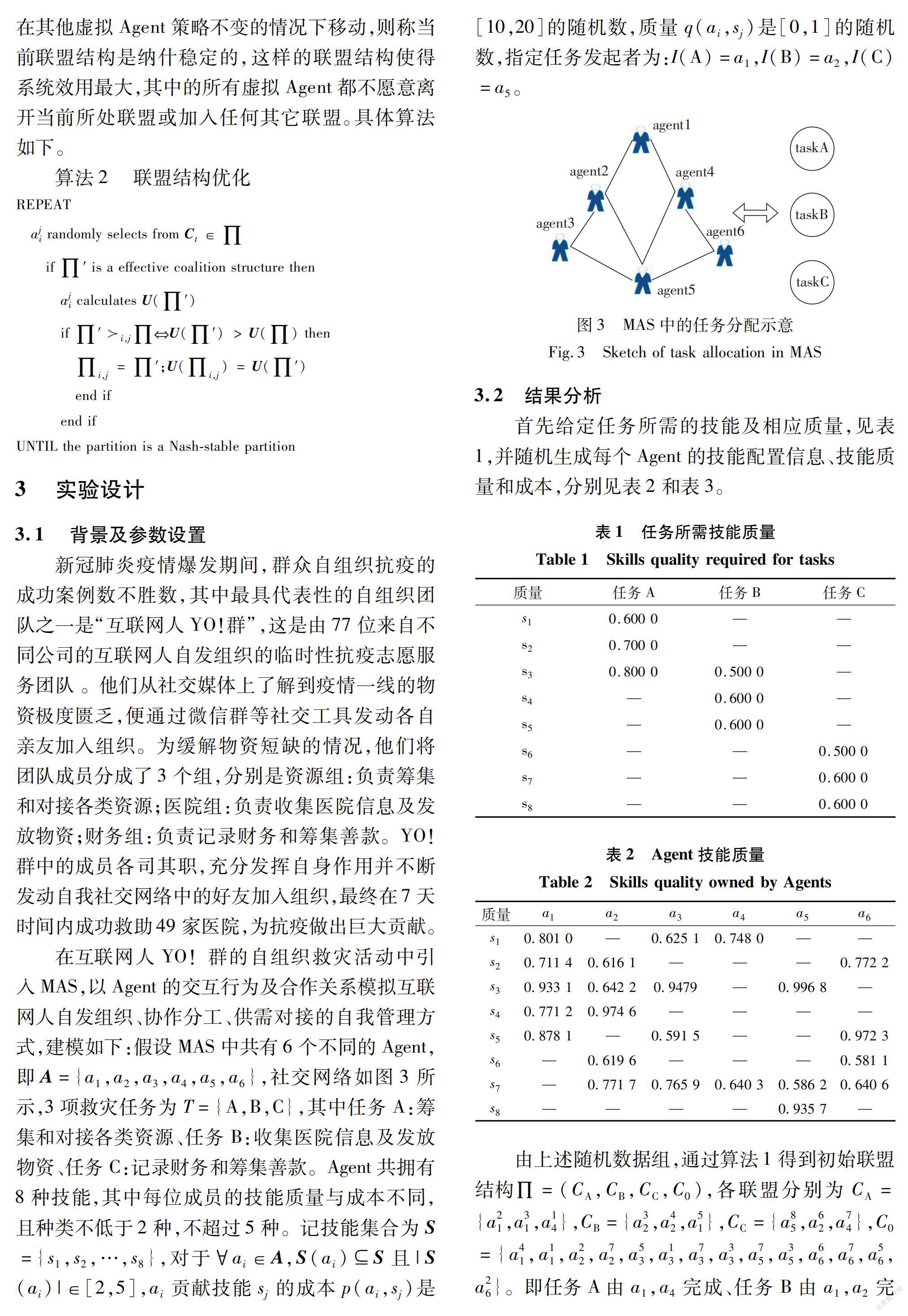
新冠疫情爆发以来,中国部分城市在必要时紧急采取封城管理,会导致决策迟缓、行动低效、物资调配困难等问题。群眾自发组织快递人员及志愿者,根据防控态势自行确定“任务”,能有效地保障部分市民的交通、餐饮等各项服务。上述案例说明:在非常规突发事件发生后的短时间内,群众可通过自发、自愿组织形成团队并完成应急任务,这一基于自组织的应急管理方式发挥着至关重要的作用,进一步提高应急管理的时效性和科学性。
多Agent系统(multi-agent system,MAS)是一种以社会形式出现的分布式结构自组织系统,系统中没有中央权威或领导者,各Agent之间地位和作用平等、可以相互交流与合作,能有效地实现目标、共享资源和解决冲突。应急管理中的群众参与过程具有MAS的自组织特性,各方往往会通过相互合作形成联盟,为社会产生最大利益。联盟形成博弈正是模拟这种行为的自然方式,但在联盟形成博弈或MAS的相关文献中,很少有研究将应急管理自组织的问题与二者联系起来,文中的研究就是为了更好地建立这种联系。
Agent的联盟形成通常涉及3个过程:首先,每个Agent使用一些谈判程序自主加入联盟;其次,解决每个联盟的优化问题,使其效用最大化;最后,将每个联盟的价值公平分配给联盟中的成员。自组织的联盟形成问题最突出的一类是任务分配问题,即Agent之间如何自发形成最大化系统效用或最小化偏离联盟动机的联盟结构,使得联盟结构中每个联盟各自对应一项或多项任务。任务分配问题在众多背景中得到应用:ZHU等将复杂任务划分为多个子任务并提出一个实用的任务调度方案,包括任务调度机制、赢家联盟形成机制和报酬共享机制,实现有限云资源的合理调度;YIN等在联盟形成的任务分配中考虑任务利润随时间流逝的情况,通过设计一种“退出-选择”机制以形成更多的联盟,从而提高系统的整体效用;SUN等通过将多卫星系统中的自组织任务分配问题公式化为一个势博弈,提出一种基于博弈的分布式任务分配算法并证明博弈的每个纳什均衡是最大化执行任务数量的一个任务覆盖。
在应急管理自组织系统中,Agent存在于一个特定的社交网络中,在无法独立完成某项任务时通常会充分调动自身资源,发动那些自己认识且有能力完成任务的Agent形成联盟,因此任意2个Agent之间并非彼此分散,而存在着一定的潜在关系,例如通信距离、信用度或组织层级等,可能会对博弈的效用和其他特征产生重大影响。为刻画Agent之间的潜在关系及限制联盟形成过程的信息交互,文中在联盟形成过程中引入社交网络结构。此外,许多现有的研究中假设每个Agent有且只能加入一个联盟并完成一项任务,但实际上系统中的部分Agent并没有贡献任何技能或资源,部分还有冗余,一对一的任务分配方式会导致大量资源浪费,因此在联盟形成过程中还考虑联盟的重叠属性,用于解决传统的联盟形成过程中存在的问题并改进任务分配的结果。
笔者在应急管理自组织的大背景下,以合作博弈理论与MAS为基础,提出基于联盟形成的任务分配机制,通过找到使得系统效用最大的联盟结构,实现最优的任务分配,并设计联盟形成和优化的相关算法,最后在实际应用中检验模型和算法的可行性。
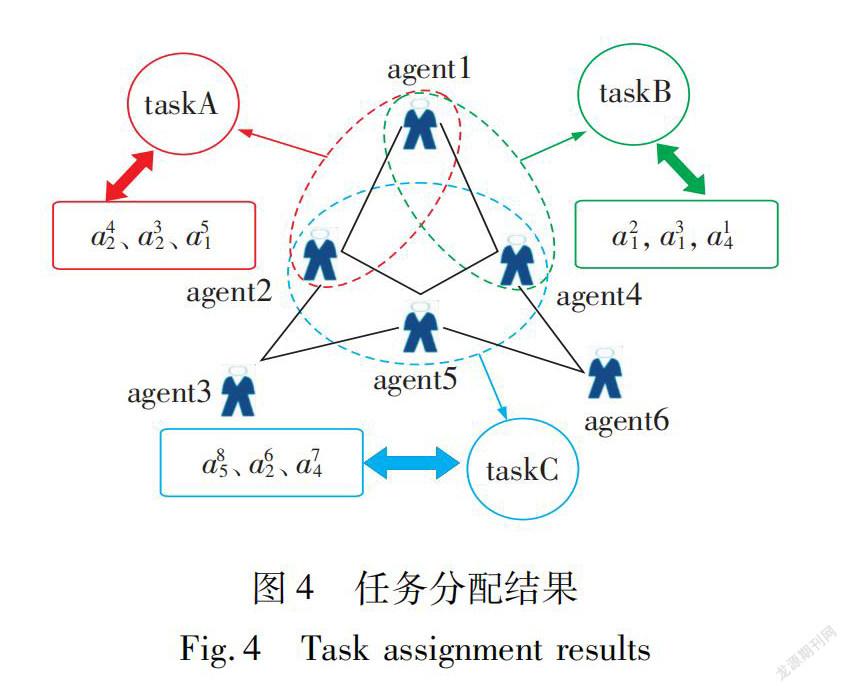
由上述随机数据组,通过算法1得到初始联盟结构∏=(CA,CB,CC,C0),各联盟分别为CA={a21,a31,a14},CB={a32,a42,a51},CC={a85,a62,a74},C0={a41,a11,a22,a72,a53,a13,a73,a33,a75,a35,a66,a76,a56,a26}。即任务A由a1,a4完成、任务B由a1,a2完成、任务C由a2,a4,a5完成,而a3,a6目前对任务没有任何贡献,将其暂时放入空闲联盟C0,分配结果如图4所示。
实验结果表明,互联网人YO!群的任务分配机制可在MAS中建模为一个带技能的联盟形成博弈,其中的社交网络结构充分反映社会分布式网络环境的真实情况、降低联盟结构形成的复杂度、加快优化过程的收敛速度;同时,通过算法1可找到合理的初始联盟结构,实现任务与联盟的一一对应,从而验证算法的有效性和模型的适用性。
应急管理中群众的自组织救灾机制不同于传统的自上而下管理机制,尽管自组织系统本身是杂乱无章的,但带技能的联盟形成博弈模型要求群众根据任务的技能需求形成对应联盟,其实质是自组织系统中遵循的一种特定规则,可使得系统从无序走向有序、从低效走向高效,符合应急管理的宏观秩序,能为组织化救援创造一定的缓冲时间。同时,该模型也实现了应急管理、博弈论和人工智能3个领域的结合。
4 结 论
1)突发事件应急管理中的自组织任务分配问题可引入MAS中考虑,图博弈与带技能的联盟形成博弈的结合,刻画社交网络中的自组织群体合作完成任务的过程。基于Agent的群体理性,通过构建系统效用函数,在联盟形成博弈模型的基础上建立优化问题,可找出使得系统效用最大的联盟结构和任务分配方案。
2)从互联网人YO!群的实例分析中可以看出,算法1对任务导向的初始联盟形成具有较好的求解效果。通过定义Agent的偏好顺序,利用算法2可实现联盟的动态更新与优化,进一步验证了模型的可行性,也为突发事件应急管理中的群众自组织救灾工作提供了理论指导。
3)文中的任務分配机制是基于最大化系统效用的并行分配,而在现实情况中各项任务的紧急程度与难易程度不同,后期的研究可以在分配过程中考虑任务的完成顺序和完成效率,以期提高任务分配的有效性和科学性。
参考文献(References):
[1]聂磊.透析危机管理中的自组织现象[J].社会科学,2011(6):84-89.NIE Lei.Study on phenomena of self-organization in crisis management[J].Journal of Social Sciences,2011(6):84-89.
[2]李琦.自组织视阈下应急管理的社会参与[J].理论月刊,2016(8):130-134.LI Qi.Social participation in emergency management from the perspective of self-organization[J].Theory Monthly,2016(8):130-134.
[3]龚志文,刘太刚.公共危机中民众的自组织机制及其约束——以抗击新冠肺炎疫情为例[J].天津行政学院学报,2021,23(2):11-23.GONG Zhiwen,LIU Taigang.Social self-organization mechanism and constraits in public crisis management:Taking the prevention of the COVID-19 as an example[J].Journal of Tianjin Administration Institute,2021,23(2):11-23.
[4]伏明兰.联盟技能博弈中自利agent的协作与任务分配研究[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2018.FU Minglan.Research on collaboration and task allocation of self-interested agents in coalitional skill games[J].Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2018.
[5]SU X,WANG Y C,JIA X B,et al.Two innovative coalition formation models for dynamic task allocation in disaster rescues[J].Journal of Systems Science and Systems Engineering,2018,27(2):215-230.
[6]STALLINGS R A,QUARANTELL E L.Emergent citizen groups and emergency management[J].Public Administration Review,1985,45:93-100.
[7]周跃进,郝巳玥,张连敏,等.自组织团队特征分析[J].管理学报,2010,7(8):1159-1164,1170.ZHOU Yuejin,HAO Siyue,ZHANG Lianmin,et al.Feature analysis of self-organizing teams[J].Chinese Journal of Management,2010,7(8):1159-1164,1170.
[8]SIMS M,GOLDMAN C V,LESSER V.Self-organization through bottom-up coalition formation[C]//Proceedings of the second international joint conference on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems.2003:867-874.
[9]朱大奇,李欣,颜明重.多自治水下机器人多任务分配的自组织算法[J].控制与决策,2012,27(8):1201-1205,1210.ZHU Daqi,LI Xin,YAN Mingzhong.Task assignment algorithm of multi-AUV based on self-organizing map[J].Control and Decision,2012,27(8):1201-1205,1210.
[10]SAAD W,HAN Z,DEBBAH M,et al.Coalitional game theory for communication networks[J].IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,2009,26(5):77-97.
[11]SAAD W,HAN Z,HJORUNGNES A,et al.Coalition formation games for distributed cooperation among roadside units in vehicular networks[J].IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,2010,29(1):48-60.
[12]SAAD W,HAN Z,DEBBAH M,et al.Coalitional games for distributed collaborative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks[C]//Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Comunications Societics,2009:2114-2122.
[13]RAHWAN T,MICHALAK T P,WOOLDRIDGE M,et al.Coalition structure generation:a survey[J].Artificial Intelligence,2015,229:139-174.
[14]李勇.多Agent系统联盟及任务分配的研究[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2008.LI Yong.Research on coalition and task allocation in multi-agent system[D].Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2008.
[15]周瑜.基于联盟形成博弈的任务分配方法研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2019.ZHOU Yu.Research on task allocation method based on coalition formation game[D].Yangzhou:Yangzhou University,2019.
[16]ZHOU Y,ZHANG Y,LI B.Coalition formation game for task allocation in the social network[C]//2018 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design(CSCWD).IEEE,2018:133-139.
[17]WANG L,WANG Z L.Ant colony optimization for task allocation in multi-agent system[J].China Communications,2013,10(3):125-132.
[18]IIJIMA N,SUGIYAMA A,HAYANO M,et al.Adaptive task allocation based on social utility and individual preference in distributed environments[J].Procedia Computer Science,2017,112:91-98.
[19]SHEHORY O,KRAUS S.Methods for task allocation via agent coalition formation[J].Artificial Intelligence,1998,101(1):165-200.
[20]ZHU J,SONG H,JIANG Y,et al.On complex tasks scheduling scheme in cloud market based on coalition formation[J].Computers & Electrical Engineering,2017,58:465-476.
[21]YIN X,LI B,LI D,et al.Task allocation via coalition formation in agent networks[J].Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems,2016,30(1):197-210.
[22]SUN C,WANG X,QIU H,et al.Game theoretic self-organization in multi-satellite distributed task allocation[J].Aerospace Science and Technology,2021,112:106650.
[23]MARTIN H,DANIEL V,WAGNER L.Dynamics in matching and coalition formation games with structural constraints[J].Artificial Intelligence,2018,262:222-247.
[24]胡军,张振兴,邹立.面向社交网络基于协作度协商的联盟形成機制[J].湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2015,42(2):100-108.HU Jun,ZHANG Zhenxing,ZOU Li.Social network oriented collaboration degree based negotiation coalition formation mechanism[J].Journal of Hunan University(Nature Science),2015,42(2):100-108.
[25]MAHDIRAJI H A,RAZGHANDI E,HATAMI-MARBINI A.Overlapping coalition formation in game theory:a state-of-the-art review[J].Expert Systems with Applications,2021,174:114752.
[26]MYERSON R B.Graphs and cooperation in games[J].Mathematics of Operations Research,1977,2(3):225-229.
[27]王先甲,刘佳.具有外部性的合作博弈问题中的稳定的联盟结构[J].系统工程理论与实践,2018,38(5):1173-1182.WANG Xianjia,LIU Jia.Stable coalition structure in coooperative game with externalities[J].Systems Engineering Theory & Practice,2018,38(5):1173-1182.
