Establishment,simulation and verification of firepower safety control model
2022-10-17LingjunHoYujieXioBingFuXiodongGuYiChenChongxingYngHiwenSunRongLuoYiHe
Ling-jun Ho ,Yu-jie Xio ,Bing Fu ,Xio-dong Gu ,Yi Chen ,Chong-xing Yng ,Hi-wen Sun ,Rong Luo ,Yi He
a Naval University of Engineering,Wuhan,Hubei,430033,China
b Naval Research Academy,Beijing,100161,China
c Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing,Jiangsu,210094,China
Keywords:Firepower conflict Directed-energy weapons Firepower safety control Polar coordinates Laplace transform
ABSTRACT On a narrow warship platform,the coordinated use of shipborne weapon systems may cause firepower conflicts,which seriously endangers the ship safety.Meanwhile,with directed-energy weapons mounted on ships,firepower conflicts between weapons become a“high probability event”.Aiming at the problem of firepower safety control,based on the research about the collision probability model of air crafts and space targets and according to the cone of fire model of conventional weapons and directed-energy weapons,this paper solved the firepower conflict probabilities between conventional weapons as well as between conventional weapons and directed-energy weapons respectively using the methods of probability theory,and established the firepower safety control model.Then the calculation of firepower conflict probability was carried out using the dimensionality reduction method based on the equivalent conversion of polar coordinates and the power series method based on Laplace transform.The simulation results revealed that the proposed model and calculation methods are effective and reliable,which can provide theoretical basis and technical support for resolution of firepower conflicts between weapons.
1.Introduction
On the small and narrow platforms like naval ships,the firepower safety control of weapons is very important.If certain technical measures are not taken,the coordinated use of multiple weapons may cause them to interfere with each other or even strike each other on a single ship platform.In the paper,the definition of firepower conflict is: shipborne weapons interfere with and attack each other on a single ship platform.If the firepower conflict occurs,the expected combat effectiveness may not be achieved,and the combat mission may not be completed.In severe cases,the ship may be destroyed,which seriously endangers the ship and crew safety.
Besides,with directed-energy weapons mounted on ships,firepower conflicts have become a “high probability event” [1].Compared with conventional weapons,the firepower conflict problem of directed-energy weapons is more prominent.The airspace occupation rate of directed-energy weapons is high,the combat coverage rate is wide and the duration is long,so the probability of firepower conflict between directed-energy weapons is intuitively higher than that between conventional weapons[2-4].
The construction and solution of firepower safety control model is an important problem to be solved,which will provide theoretical basis and technical support for the safe application of weapon firepower.At present,the firepower safety control model mainly falls into two types.One is to calculate the distance between weapons by establishing the ideal exterior ballistic equation based on the principles of geometry,and then set the minimum safety distance and compare it with the calculated distance between weapons[5-14].The other is to construct the cone of fire using the method of probability theory according to the principle of ballistic dispersion,and then judge whether the cones of fire between various weapons intersects [15-20].
According to the above two types of firepower safety control model construction methods,combined with the relevant theories of air control,airspace management and space objects collision,this paper puts forward a new idea for firepower safety control of weapons: to directly calculate and solve the probability of firepower conflict between weapons by integration of probability density functions,and then set the safety threshold of conflict probability;once the firepower conflict probability of weapons exceeds the set safety threshold,it is determined that firepower conflict will occur between weapons.
2.Related work
Refs.[5-7] adopted the Monte Carlo method to solve the collision probability.The Monte Carlo method is able to analyze and solve the collision probability problem directly,with no need to establish a complex mathematical model,which has certain reference significance for the solution for firepower conflicts.
Refs.[8-14] proposed the Paielli algorithm and the Prandini algorithm,conducted an in-depth analysis of the conflict probability problem of aircraft in the air,and solved the conflict probability by integration of probability density function.At present,the Prandini algorithm has been practically applied to the current air control system with a good conflict resolution effect;the Paielli algorithm and the Prandini algorithm serves as a guidance for the establishment and calculation of the firepower conflict probability model.
Refs.[15-20]established mathematical models for the collision probability of orbiting satellites,space debris,space targets,etc.,and adopted methods such as probability density function integration,infinite series,and equivalent conversion to analyze and calculate the models,which has important reference significance for the establishment and solution of firepower conflict probability model.
This paper summarizes and analyzes in-depth the model and algorithm of collision probability of aircrafts and space targets based on the above research.According to the ballistic characteristics,motion equations and control methods of conventional weapons and directed-energy weapons,this paper establishes the firepower conflict probability models between conventional weapons as well as between conventional weapons and directedenergy weapons respectively.Calculation is carried out using two methods,dimensionality reduction method based on the equivalent conversion of polar coordinates and power series method based on Laplace transform,to effectively solve the firepower conflict probability problem.
3.Establishment of firepower safety control model of weapons
For the establishment of firepower safety control model of weapons,two critical concepts and their definitions are as follows:
(1) Ballistic dispersion:For the same weapon system,under the same firing conditions,when the same firing data are adopted,and several rounds are continuously fired in a short time,the impact points will be dispersed.This phenomenon is called ballistic dispersion
(2) Cone of fire:Due to ballistic dispersion,the trajectory of each round fired is different,and these non-overlapping trajectories formed by a single burst is called the cone of fire.
3.1.Problem transformation
One of the criteria for firepower conflicts between two types of weapon is whether the minimum distance between the weapons is less than the safety distance.However,the distance between the weapons that have fired changes over time.Real-time judgement of this distance is not only difficult to realize,but also involves a huge amount of calculation.It is only needed to judge whether the minimum distance between the weapons is greater than the safety distance.Therefore,the firepower conflict probability can be transformed into the probability of whether the minimum distance between the weapons that have fired is less than the safety distance.For the calculation of firepower conflicts probability,once the cone of fire of one weapon enters that of another weapon,it will be judged that firepower conflict occurs.
The sphere model is adopted in the cone of fire model of conventional weapons.Assuming its radius is,as shown in Fig.1(a),and then the spherical area of conventional weapons’cone of zone can be expressed as:
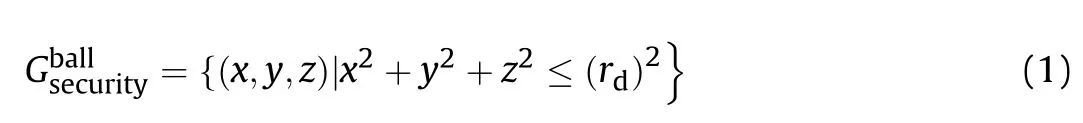

Due to ballistic dispersion,the actual position of the weapon deviates from the ideal trajectory and follows the threedimensional normal distribution,and the graph of its probability density function is an ellipsoid.Here,position error is defined as the variance of the three-dimensional normal distribution.After equaling the fired weapon with cone of fire,it is also necessary to consider the influence of ballistic errors to calculate the firepower conflict probability.
3.2.The establishment of the encounter coordinate system
It can be seen from the problem transformation that the firepower conflict probability between the weapons that have fired is the probability that the minimum separation distance between weapons is less than the safety distance,which can be expressed as:

whereis the safety distance,|ρ|is the distance between the center of mass of two weapons,which is:

Fig.1.Schematic diagram of cone of zone model.


Then at the current moment,the relative position vector between the two weapons is:

In Eq.(6),is the relative velocity vector of weapon 1 and weapon 2.The square of the distance between the two weapons is:|ρ()|=ρ()·ρ().Let the square of the distance be derived from time:

It can be seen from Eq.(8) that the time when the distance between weapon 1 and weapon 2 is minimum,namely,when the closest point is reached,is:

At this moment,the relative position vectors between two weapons is:

Multiplying the relative velocity vectorson both sides of Eq.(10),we can get:
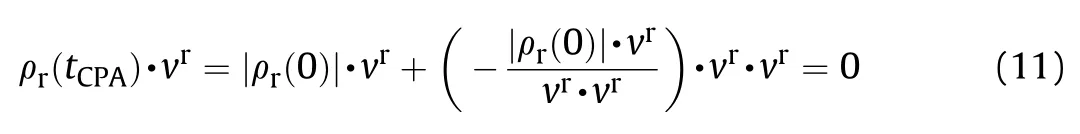
According to Eq.(11),when minimum distance between two weapons is satisfied,its relative position vector ρ()is perpendicular to its relative velocity.This is to say,when distance between two weapons is minimum,and both weapons are in the vertical plane to the relative velocity vectors,then the vertical plane is called Encounter Plane.
It is necessary to establish the encounter plane because the uncertain positions of two weapons can be projected into the encounter plane to transform the encounter problem in three dimension into an integration problem in two dimension,thus saving calculation and reducing the complexity of the algorithm.
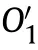
3.3.Projection of ballistic dispersion error in the encounter coordinate system

Fig.2.Schematic diagram of the establishment of the encounter coordinate system.
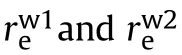
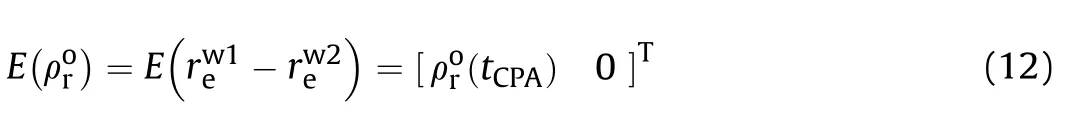
In the encounter plane,the variance of the relative position vector of weapon 1 and weapon 2 is:
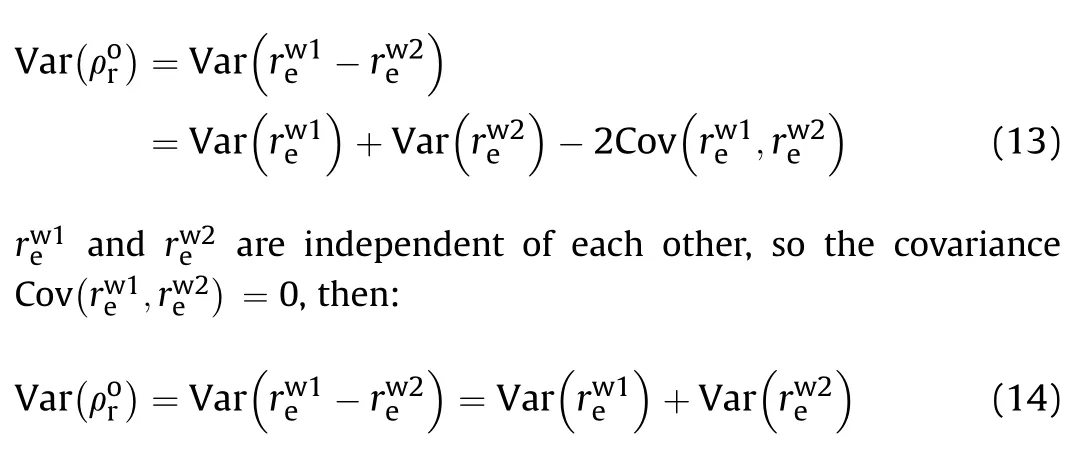
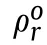
3.4.Simplified expression of firepower conflict probability
fifl
For conventional weapons,the encounter coordinate system is established,the cone of fire model of the weapon is developed,and the ballistic dispersion error is projected into the encounter coordinate system.The expression of conflict probability is simplified to the integration of probability density function in two-dimensional normal distribution within circle domain,and the probability density function of the two-dimensional normal distribution is:

In Eq.(15),μand μare the mean values of the dispersion errors of combined ellipse respectively,σare σthe variance of dispersion error of the combined ellipse respectively,then the simplified expression of the firepower conflict probability is:
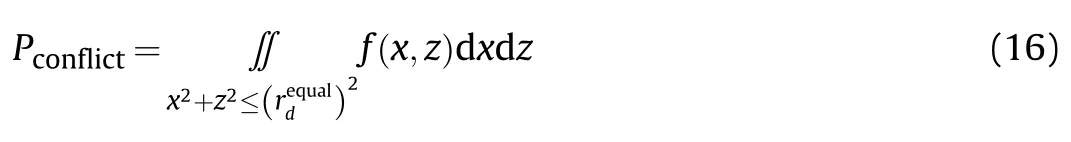
fifl
There is no ballistic dispersion for directed-energy weapons,so the firepower conflict probability between directed-energy weapons and conventional weapons can be solved directly.Regarding the beam of directed-energy weapon as an infinite number of particles,the firepower conflict probability between directed-energy weapons and conventional weapons is transformed into the conflict probability between the particle and the cone of fire.
First,it is necessary to calculate the conflict probability between each particle and conventional weapons’ cone of fire.Since space model does not apply to the particle,and there is no ballistic dispersion,then the radius,mean and variance of the particle are all 0 in the encounter coordinate system,and the expression is:

Then,the firepower conflict probability between directedenergy weapons and conventional weapons is the conflict probability between all particles contained in the cone of fire of directedenergy weapon and the cone of fire of conventional weapons,namely:



To sum up,both the calculation of the firepower conflict probability of conventional weapons and the firepower conflict probability of directed-energy weapons are the double integration of Eq.(16).Therefore,after the integration of the probability density function in the two-dimensional normal distribution is calculated within the circle domain,then the firepower conflict probability of both the directed-energy weapons and the conventional weapons can be easily solved.
3.5.Firepower conflict judgment probability and firepower safety control principle

For the firepower safety control principle and to solve the firepower conflict judgment probability,the following three cases are to be considered.
(1) Weapon 1 and Weapon 2 fire simultaneously.
The firepower conflict probability of weapons can be obtained from Section 3.4.When Weapons 1 and 2 need to fire at the same time,the firepower conflict judgment probability of Weapons 1 and 2 is the firepower conflict probability of the two weapons firing at the current time,and the expression is:


(2) Weapon 1 fires first,and Weapon 1 is a conventional weapon.
Since Weapon 1 fires first and it is a conventional weapon,it cannot be effectively controlled once firing,so only Weapon 2 is subject to firepower safety control.According to the conditional probability,the firepower conflict judgment probability of Weapon 2 is:

where()represents the firing probability of Weapon 1,and this is also the utilization rate of the fixed safety field of fire of the weapon,defined as the ratio of the fixed safety field of fire to the inherent field of fire of the weapon.The inherent field of fire is the area that can be covered by the fire from a weapon,and the fixed safety field of fire refers to the area that can be covered by the fire from a weapon after avoiding the shelter of deck facilities.Polar coordinate representation is used to solve the utilization rate of the fixed safety field of fire.As this method is not the focus of this work,and has been introduced in detail in many research papers,further explanation will not be presented here.

(3) Weapon 1 fires first,and Weapon 1 is a directed-energy weapon
When Weapon 1 fires first,and it keeps firing,the solution of firepower conflict judgment probability of Weapon 2 is consistent with case (2).However,because Weapon 1 is a directed-energy weapon and has the control convenience of immediate firing and stopping,the principle of firepower safety control is thus different.

4.Calculation of firepower safety control model of weapons
From the firepower conflict probability Eqs.(16) and (19),the value of the firepower conflict probability can be calculated,but integral calculation is complicated,resulting in computational complexity.Therefore,this paper proposes two conversion calculation methods,namely,the dimensionality reduction of firepower conflict probability based on the equivalent conversion of polar coordinates and the power series of firepower conflict probability based on Laplace transform.The above integral calculations are deduced and explained in detail.

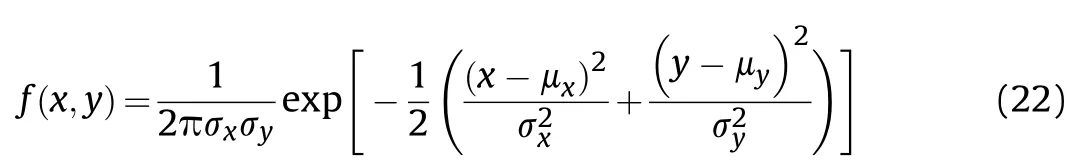
Eq.(16) can be transformed into:

4.1.Dimensionality reduction of firepower conflict probability based on equivalent conversion of polar coordinates
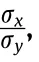

Incorporating Eq.(24)into Eq.(22),the new probability density function can be obtained as follows:

Then Eq.(25)is incorporated into the integrating circle domain of equivalent radius,and a new integral ellipse domain can be obtained:

According to Eqs.(25) and (26),the firepower conflict probability is:
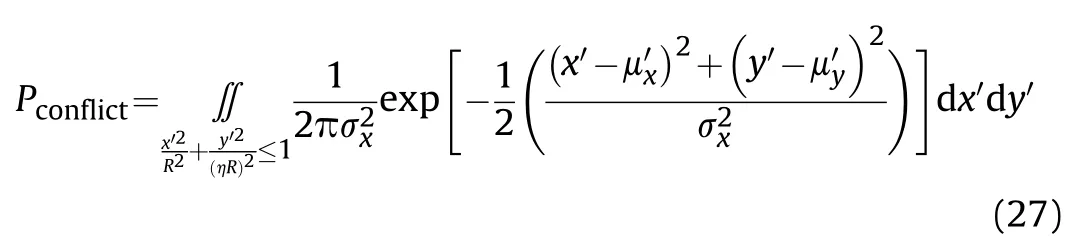
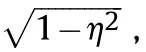

Likewise,in order to simplify the description,we replace the probability density function in Eq.(28)with the following function:

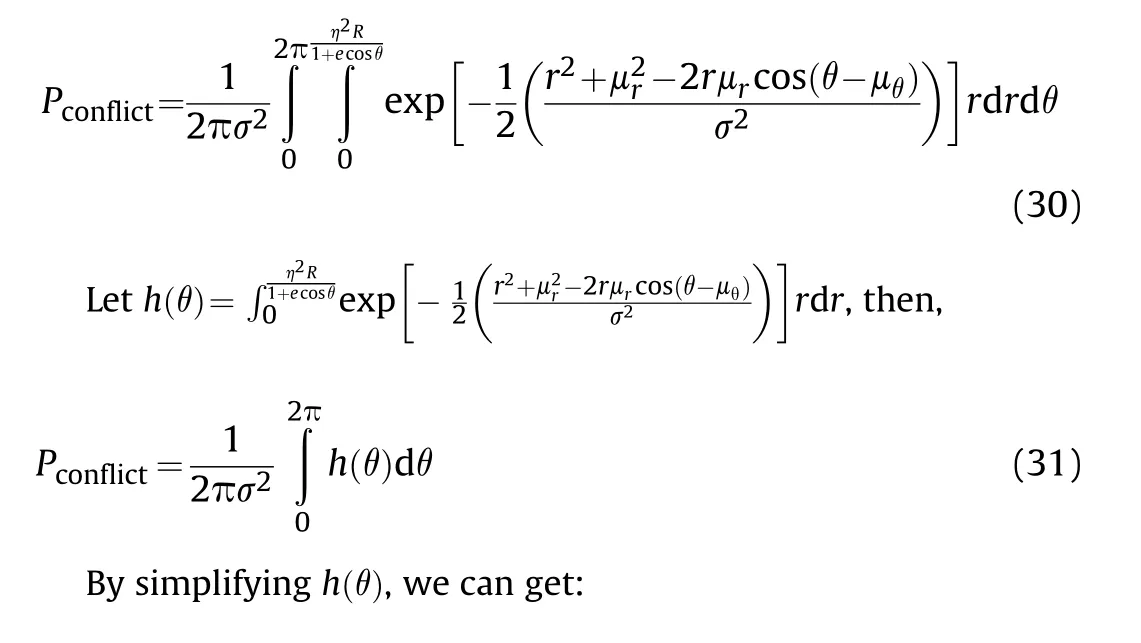
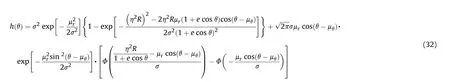

The simplified expression for(θ)is
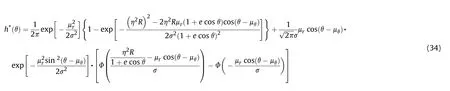
For the calculation of the probability density function of the normal distribution function with equal variances,the polar coordinate method is adopted.Let=cos θ=sin θ,the firepower conflict probability is transformed into:
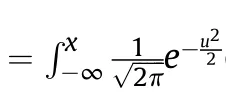
4.2.Power series of firepower conflict probability based on Laplace transform
Convert the conflict probability in Eq.(23)into=():
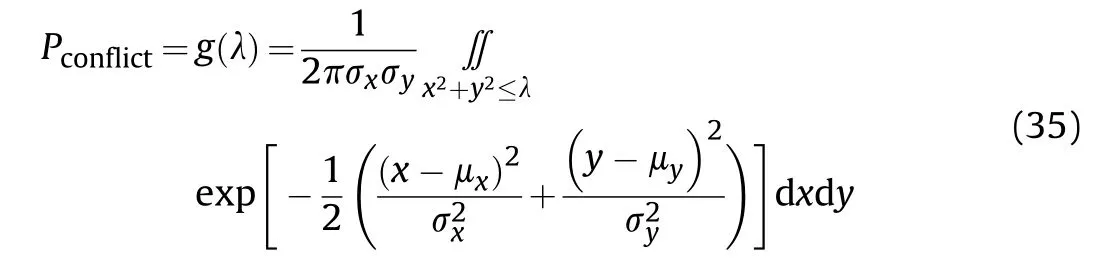
Calculating directly with(λ)can be difficult.If the power series method is used,then the sign of each item is opposite,with the size almost equal,which makes the sum of all items equal to zero under a certain calculation accuracy.To solve this problem,a function ψ can be constructed,withreplaced by ψ·,to avoid the invalid solutions after the expansion of the power series.
This paper adopts the function ψ =,whereis defined as the undetermined factor.
First,according to the Laplace transform,Laplace transform can be applied to(λ),then:

In Eq.(36),represents complex variable.It can be known from Fubini's theorem:
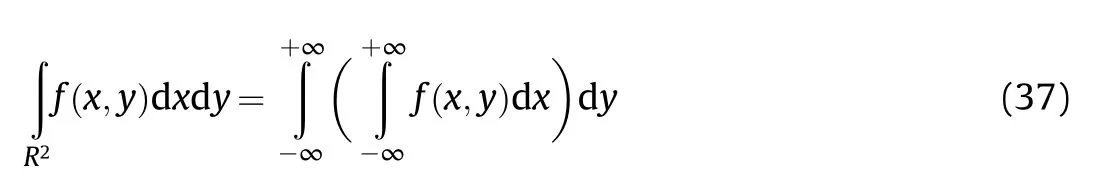
In particular,when(,)=()·(),Eq.(36)can be simplified to:

Simplify Eq.(36) with Eqs.(37) and (38):
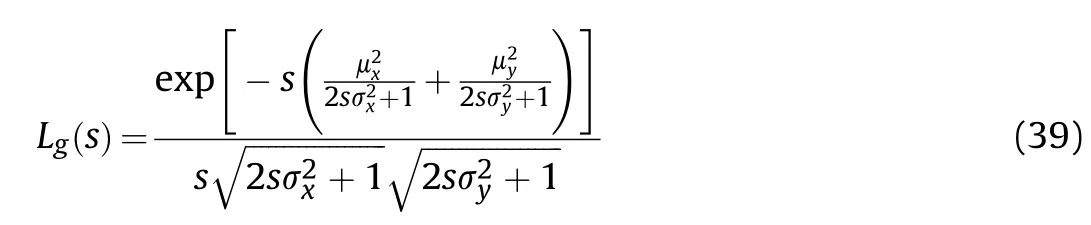
Then,let(λ)=e(λ).After applying Laplace Transform,we can get:

In Eq.(40),because ||>,the parameters in Eq.(40) are replaced with other simple parameters as follows:

where the replaced parameters of ε‘Q‘Q‘are:
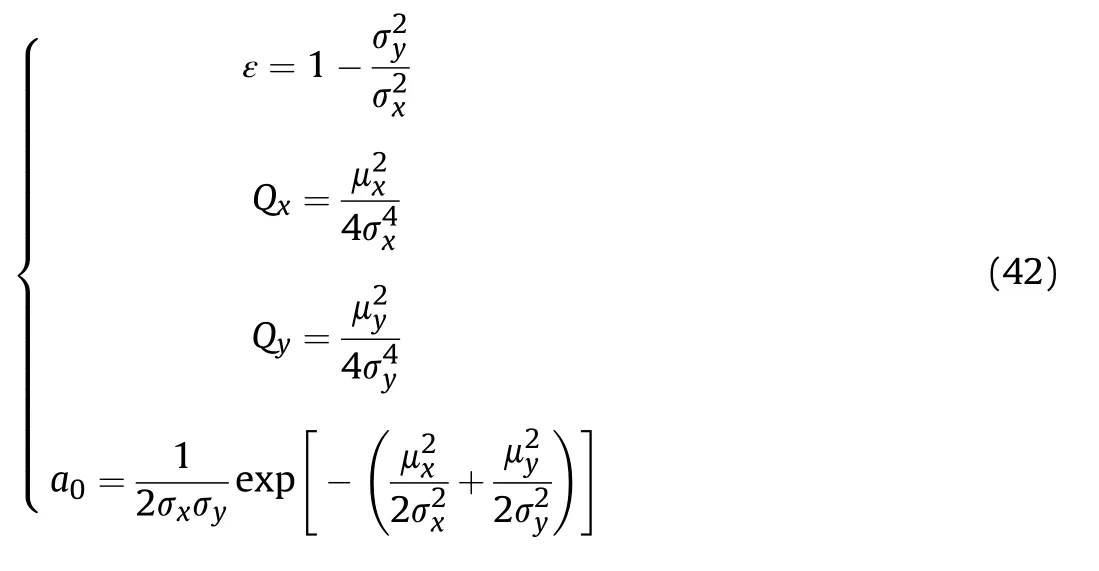
Construct the function L(),and we can see from Eq.(41):

Let=0,then M(0)=.According to Eq.(44),we can get that M()is complex differentiable in the complex plane,and power series expansion can be carried out through Taylor formula,which is:
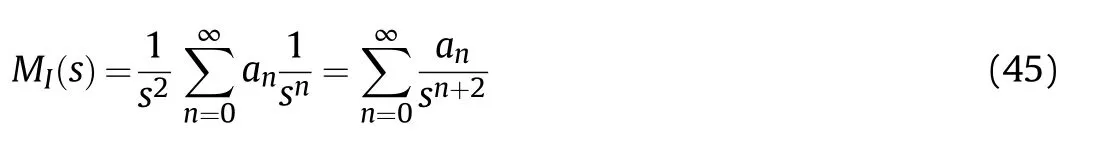
In Eq.(45),ais the coefficient of the power series,and we can apply the Inverse Laplace transform for each term of the power series expansion to obtain the power series expression of the integral formula of the firepower conflict probability.Based on one of the formulas of the rational function Laplace transform and the Inverse Laplace transform:

The power series expression of the integral formula of the firepower conflict probability can be obtained:
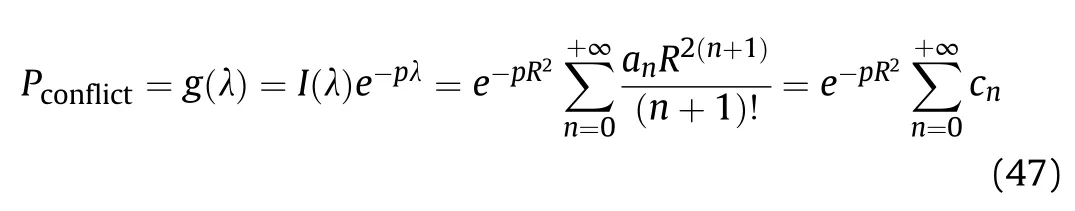
In Eq.(47),calculations of all the expansion items are as follows:



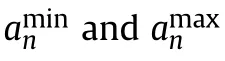

According to Eqs.(50)and(51),the range of the truncation error
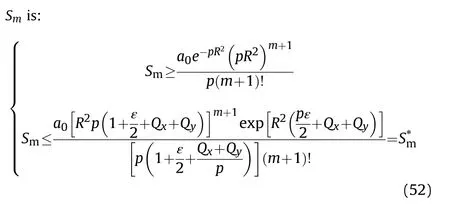
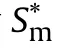

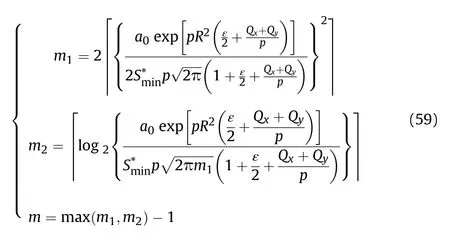
5.Simulation,verification and analysis of firepower conflict probability model
In order to verify the validity of the firepower safety control model and the feasibility of the dimensionality reduction method based on the equivalent conversion of polar coordinates and the power series method based on the Laplace transform,simulation and analysis of the example is carried out.
5.1.Example verification
As the relevant test data of weapons are confidential,and the radius size and motion law of space debris are almost the same as those of ordinary projectiles,this paper takes the China-US debris collision on January 17,2005 as Example 1,and the US-Russia satellite collision on February 10,2009 as Example 2 to verify the correctness of the model.
Set the initial parameters and we make the following assumptions:
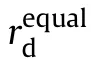
②The shape and size of the position error ellipsoid of the two collision bodies are the same,i.e.,the position error variance matrix is equal and σ:σ:σ=1:1:1.
③The utilization rate of the fixed field of fire of weapons can reach 100 %.
(1) Example 1
Fig.3 shows the comparison results between the 2005 China-US space debris collision probability curve and the firepower conflict judgment probability curve established in this paper.The black dotted line represents the curve of the 2005 China-US space debris collision probability varying with position variance,and the green curve represents the curve of firepower conflict judgment probability obtained by direct integration of probability density function according to the firepower safety control model proposed in this paper varying with position variance.
As is seen from Fig.3,the changing trends of the two curves are almost the same,and the maximum collision probability of the collision event in 2005 is almost equal to the maximum firepower conflict judgment probability obtained by direct integration,which is 3.172 × 10.As the internationally stipulated safety threshold for conflicts between aircraft and space targets is 10,the two space debris did collide in fact.Therefore,this reveals that the weapon firepower safety control model proposed in this paper is correct for firepower safety control.
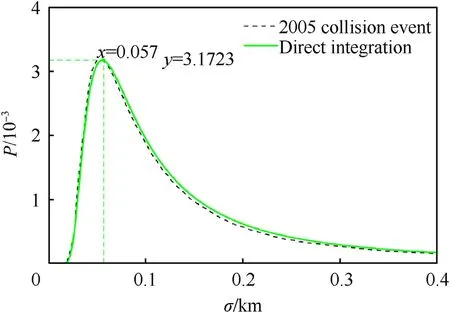
Fig.3.Comparison between the 2005 China-US space debris collision probability curve and firepower conflict judgment probability curve.
In addition,the variance of the collision probability curve for the 2005 event at the extreme point is 0.058 km,and the variance of the firepower conflict judgment probability at the extreme point is 0.057 km.The difference between the ordinates of the extreme points of the two curves is 3.57×10,and the abscissa difference is 1 m.When the variance of the two curves is equal,the maximum difference of the ordinate probabilities is 0.213 × 10,demonstrating that the firepower safety control model proposed in the paper can realize the acceptable error range and is thus effective.
(2) Example 2
Fig.4 presents the comparison results between the 2009 USRussia satellite collision probability curve and the firepower conflict judgment probability curve established in this paper.
As illustrated in Fig.4,the two curves are highly coincident,and the maximum collision probability of the 2009 collision event is almost equal to the maximum firepower conflict judgment probability obtained by direct integration.The extreme value of the USRussia satellite collision probability curve is 7.568 × 10,the maximum conflict probability obtained using the firepower safety control model is 7.364 × 10.As the internationally stipulated safety threshold for conflicts between aircraft and space targets is 10,the two space debris did collide in reality,showing that the firepower safety control model proposed in the paper is reliable for firepower safety control.
In addition,the variance of 2009 event collision probability curve at the extreme point is 0.359 km,and the variance of firepower conflict judgment probability at the extreme point is 0.338 km.The difference between the ordinates of the extreme points of the two curves is 2.04×10,and the abscissa difference is 21 m.When the variance of the two curves is equal,the maximum difference of the ordinate probabilities is 0.304 × 10,demonstrating that the firepower safety control model proposed in the paper can give results within the acceptable error range and is thus effective.
(3) Determination of the number of termsbased on the Laplace transformed power series technique
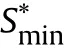
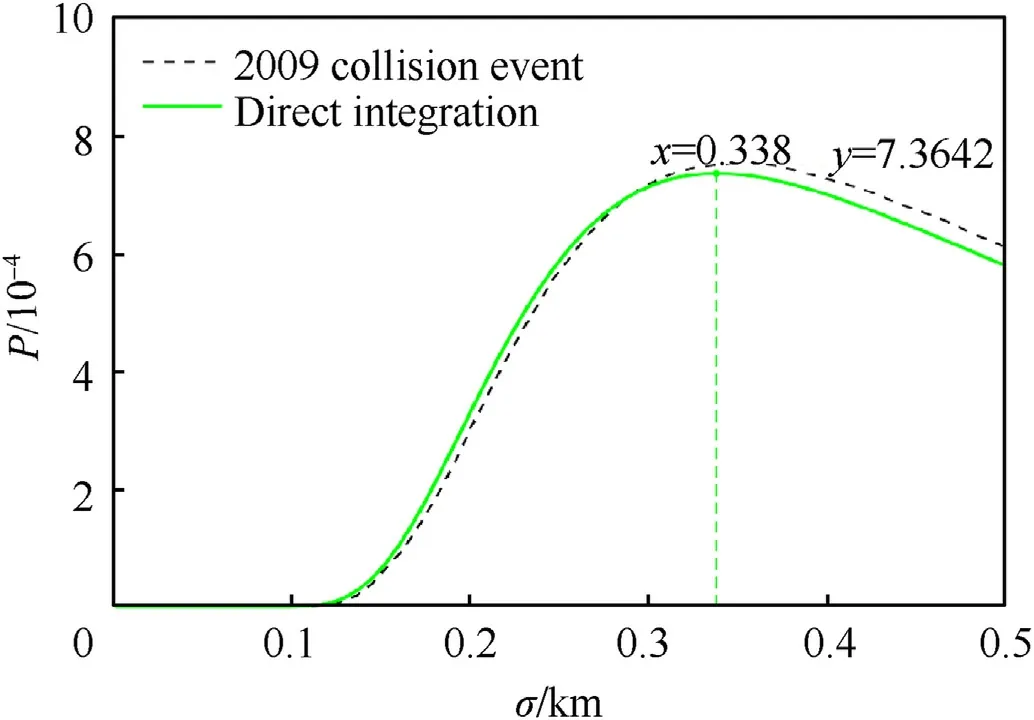
Fig.4.Comparison between the 2009 US-Russia satellite collision probability curve and the probability curve of firepower conflict judgment.
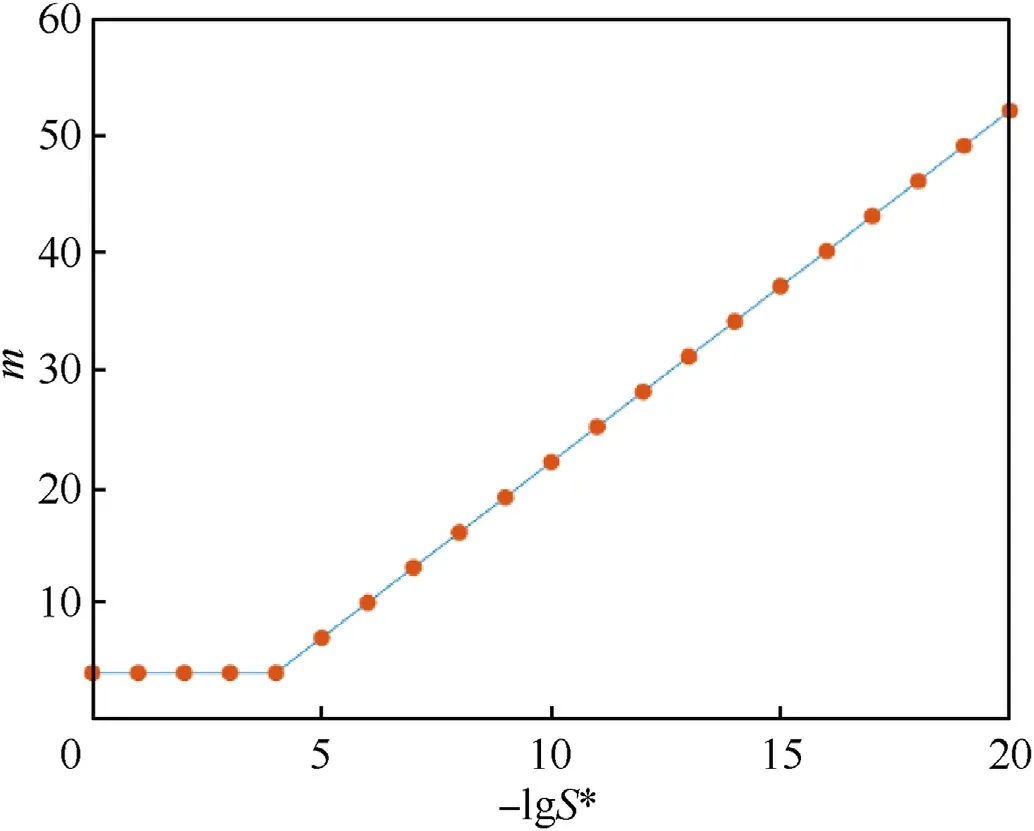
Fig.5.Curve of the number of terms m varying with -log

(4) Verification of dimensionality reduction method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion and power series method based on Laplace transform
When the position error of the two space targets meets σ:σ:σ=1:1:1,for Example 1 and Example 2,three calculation methods are employed respectively: direct integration of probability density function,method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion and method based on Laplace transform.The simulation results are shown in Fig.6 and Table 1.

Table 1 Extreme point coordinates and relative errors of Example 1 and Example 2.

Fig.6.Trend of firepower conflict judgment probability varying with position error when σx :σy :σz =1:1:1
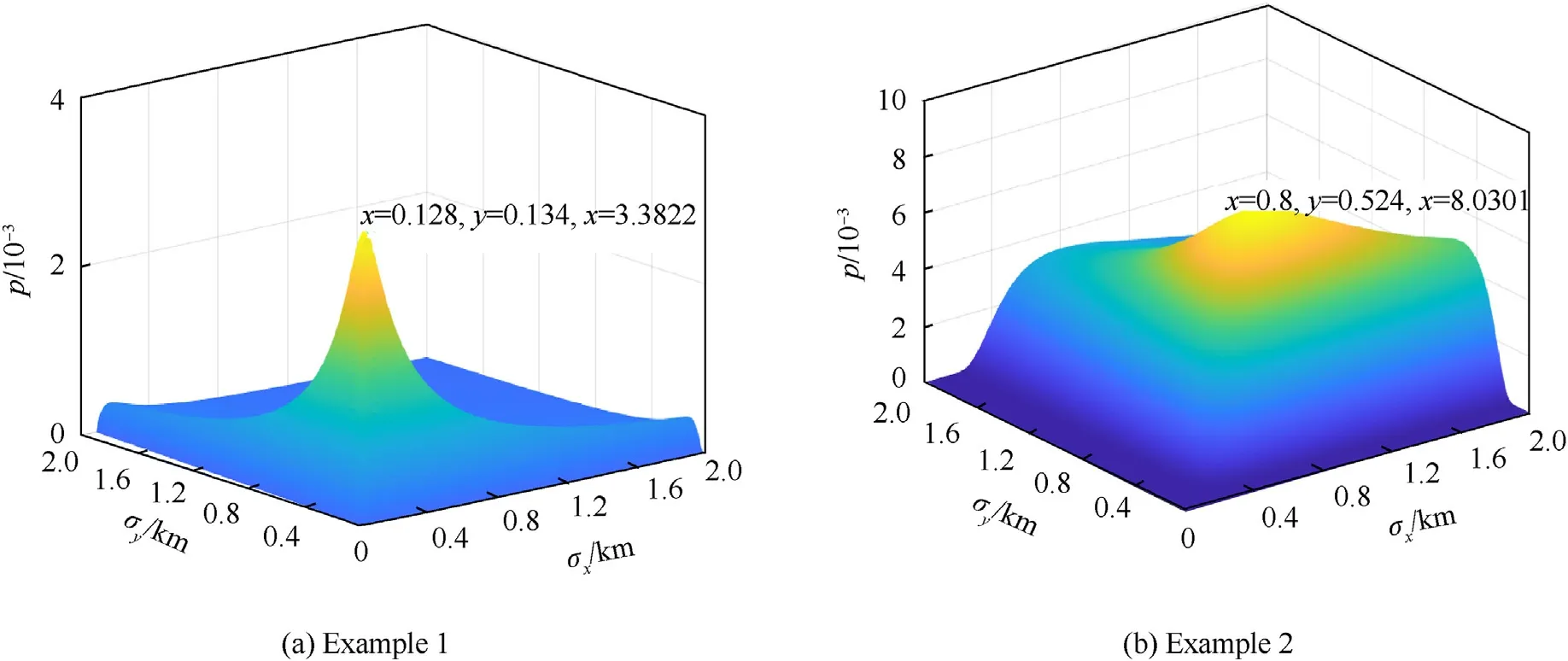
Fig.7.Curve of firepower conflict judgment probability varying with σx and σy.
As can be seen from Fig.6 and Table 1,the curves obtained by using the dimensionality reduction method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion and the power series method based on Laplace transform are almost consistent with the conflict probability curve obtained by direct integration,and the changing trend is also identical.In addition,the relative errors of the direct integration method and the actual collision probability curve are about 1 %,the relative error of the method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion is about 3%,and the relative errors of the power series method based on Laplace transform and the direct integration method are about 5%.The results show that the two simplified calculation methods proposed in this paper,namely,the dimensionality reduction method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion and the power series method based on Laplace transform,produce results within the controllable error range and meet the accuracy requirements.Therefore,the proposed two calculation methods are reliable and effective.
5.2.Position error sensitivity analysis
Considering that in the actual firepower safety control of weapons,the ratio of position error ellipsoid of each type of weapon is different as well,the relationship between the firepower conflict judgment probability and the position variances σand σis obtained by changing the ratio of position error and using the firepower safety control model,as shown in Fig.7.
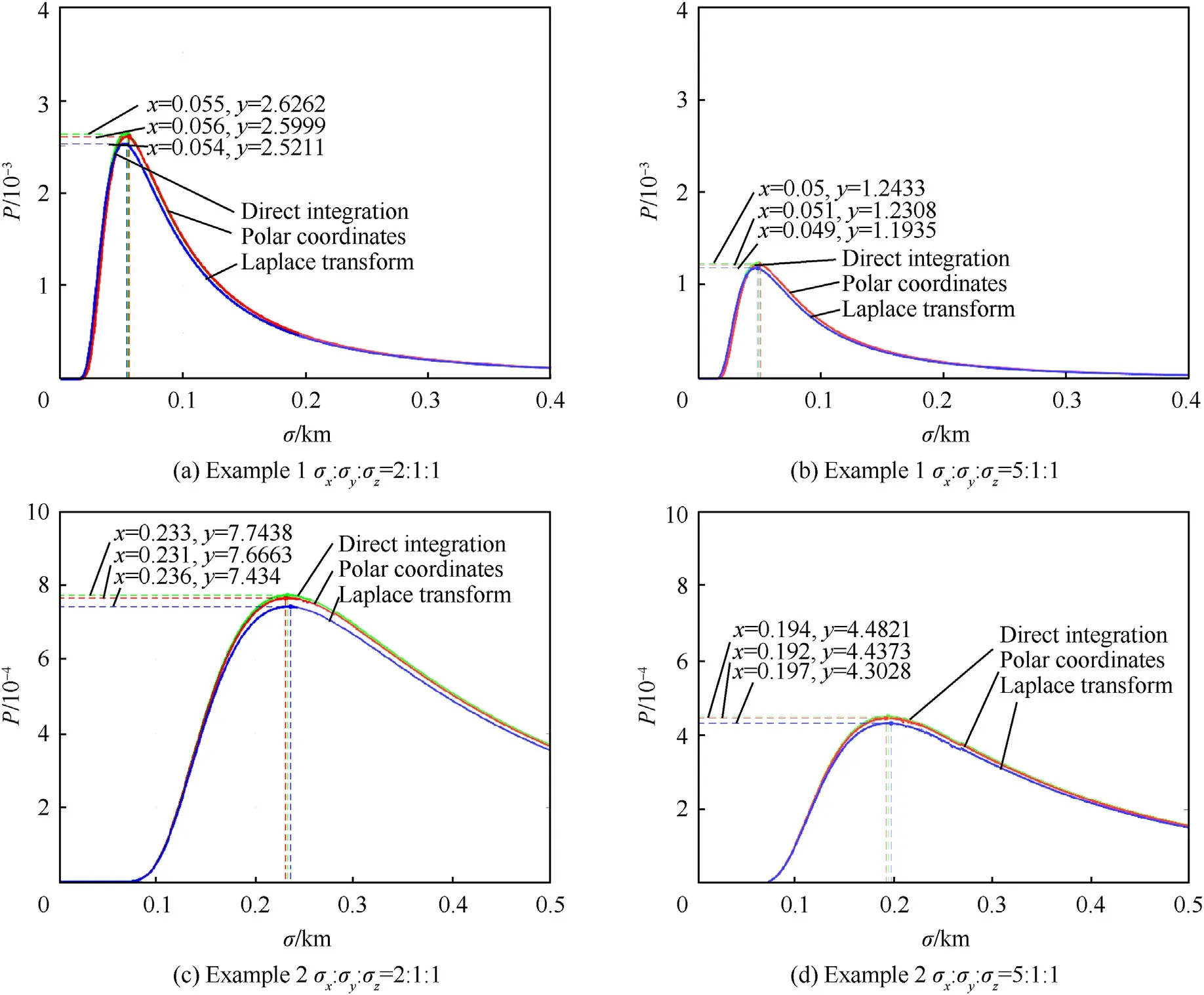
Fig.8.Firepower conflict judgment probability curves when σx :σy :σz =2:1:1 and σx :σy :σz =5:1:1.
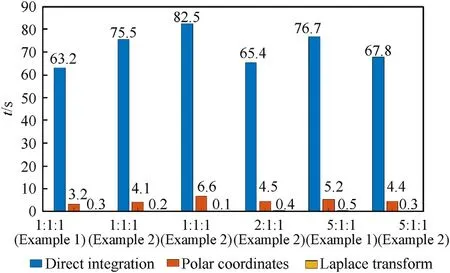
Fig.9.Comparison of time complexity of the three calculation methods.
According to Fig.7,it can be concluded that the trend of firepower conflict judgment probability varying with position error is as follows.When the position error is small,the firepower conflict judgment probability basically remains unchanged.As the position error increases,it first increases rapidly and then decreases slowly.This is consistent with the actual situation because in the case of small position error,which means small position uncertainty,the probability of firepower conflict is very low as long as the trajectories does not intersect;with the increase of position uncertainty,the distribution range of weapons will increase accordingly,and the probability of firepower conflict will rise as well;when the position uncertainty increases to a certain extent,the distribution range of weapons will become so wide that even if the trajectories of the two weapons are close,the probability of firepower conflict will begin to decrease gradually.
Fig.8 not only confirms the above conclusion,but also draws a law: as the ratio of position error increases,the peak value of the firepower conflict judgment probability curve decreases,and the abscissa of the extreme point decreases as well.
5.3.Computation efficiency analysis
To analyze calculation efficiency,in this work,statistics and analysis of the calculation time of the three methods are done on the same computer(Intel(R)Core(TM)i7-6700HQ processor,CPU@2.60GHz) using Matlab software.Fig.9 shows the computation efficiency of the three methods: direct integration,polar coordinates equivalent conversion,and Laplace transform.The blue bar represents the direct integration method,the orange bar represents the polar coordinate equivalent conversion method,and the yellow bar represents the Laplace transform method.Moreover,Fig.9 specifically presents the average time taken for 100 times of calculations for Example 1 and Example 2 respectively when the variance ratio σ:σ:σis 1:1:1,2:1:1,and 5:1:1.
From Fig.9,it is concluded that the direct integration method has the highest time complexity with an average time of over 1 min,much higher than the two calculation methods adopted by the paper.Polar coordinates equivalent conversion has the medium time complexity,and Laplace transform has the lowest time complexity.
Due to truncation error,the accuracy of power series calculation method based on Laplace transform is a bit lower,but the error is within a reasonable range.Although the direct integration method has good accuracy,it requires a lot of calculation time,which is often not conducive to practical application.Therefore,in urgent situations,the method of Laplace transform is undoubtedly the best choice;when accurate calculation and reduced calculation time are needed,the polar coordinates equivalent conversion method is advantageous.
6.Conclusions and prospect
This work aims to solve the problem that shipborne weapon effectiveness cannot be fully exerted due to of high firepower density.According to the cone of fire of traditional weapons and directed-energy weapons,and by using the methods of probability theory and transforming the problem of weapon firepower conflict,we established the firepower safety control model for shipborne weapons,obtained the firepower conflict probability expression,introduced the firepower conflict judgment probability into the model,and proposed the principle of weapon firepower safety control;then we used the dimensionality reduction calculation method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion and power series calculation based on Laplace transform to solve and calculate the firepower conflict probability.According to the simulation results,we obtain the following conclusions:
(1) The model proposed in this paper and the two fast calculation methods -the dimensionality reduction calculation method based on polar coordinates equivalent conversion and the power series calculation method based on Laplace transform can produce results within the controllable error range and meet the accuracy requirement,indicating that the proposed model and calculation method are effective and reliable.
(2) The trend of firepower conflict judgment probability varying with position error is:in the case of small position error,the firepower conflict judgment probability basically remains unchanged;with the increase of position error,the firepower conflict judgment probability first increases rapidly and then decreases slowly;as the position error ratio increases,the peak value of the fire conflict judgment probability curve declines,and the abscissa of the extreme point decreases accordingly.
(3) Although the direct integration method is accurate,it requires a great amount of calculation time,which is not conducive to practical application.In time-critical situations,Laplace transform is undoubtedly the best choice;when accurate calculation and reduced calculation time are needed,the polar coordinates conversion method is advantageous.
The research results of this paper provide theoretical basis and technical support for firepower safety control of weapons,and can guide the subsequent research on weapon firepower conflict resolution,firepower planning,firepower application and effectiveness evaluation.In the follow-up research,in-depth and specific analysis on weapon firepower conflict and firepower safety control can be made according to the research ideas and calculation methods provided in this paper,and by considering the influencing factors such as accurate control in time domain,weapontarget allocation,effectiveness exertion and risk avoidance,a firepower control method with more practical and higher accuracy will finally be designed.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
杂志排行
Defence Technology的其它文章
- Burning characteristics of high density foamed GAP/CL-20 propellants
- Cell-type continuous electromagnetic radiation system generating millimeter waves for active denial system applications
- Sandwich structure for enhancing the interface reaction of hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane and nanoporous carbon scaffolds film to improve the thermal decomposition performance
- Ablation characteristics of insulator under high-temperature gas dualpulse erosion
- Influence of shaped charge structure parameters on the formation of linear explosively formed projectiles
- Novel aluminum-based fuel: Facile preparation to improve thermal reactions
