Antihepatofibrotic effect of Guizhifuling pill (桂枝茯苓丸) on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice
2022-10-14XUBaoguiZHENGJiawenTIANXiaoxiaoYUANFaleiLIUZhongliangYANGZuisuDINGXianjun
XU Baogui,ZHENG Jiawen,TIAN Xiaoxiao,YUAN Falei,LIU Zhongliang,YANG Zuisu,DING Xianjun
XU Baogui,ZHENG Jiawen,TIAN Xiaoxiao,YUAN Falei,YANG Zuisu,School of Food and Pharmacy,Zhejiang Ocean University;Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center of Marine Biomedical Products,Zhoushan 316022,China
LIU Zhongliang,Department of Oncology,Zhoushan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhoushan 316000,China
DING Xianjun,Department of Infectious Diseases,Zhoushan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhoushan 316000,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the protective effects and the underlying mechanism of Guizhifuling pill (桂枝茯苓丸,GZFL) on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice.METHODS: Male ICR mice by intraperitoneally administered with 20% CCl4 (mixed 1∶4 in soybean oil)to induce liver fibrosis.Mice that underwent CCl4 were orally with GZFL.Using hematoxylin and eosin and Masson staining to examine the pathological changes in liver tissue.Serum biochemical parameters,antioxidant enzyme activity and proinflammatory cytokines was assessed.Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) pathway and nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) family members were evaluated by Western blotting.RESULTS: Our findings indicated that GZFL could effectively suppress the progression of liver fibrosis in mice,which was determined based on the improvement in liver function and reduction of collagen deposition.GZFL treatment also decreased the level of cytokines and increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes in livertissue.Moreover,GZFL exerted anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects through regulating the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant system and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway.CONCLUSIONS: GZFL may prevent the progression of liver fibrosis by regulating the Nrf2/ heme oxygenase-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways,thereby highlighting its role in the management of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: liver fibrosis;NF-E2-related factor 2;heme oxygenase-1;NF-kappa B;Guizhifuling pill
1.INTRODUCTION
Liver fibrosis is a chronic pathological process in which several pathogenic factors act on the liver for a prolonged period of time,causing the abnormal deposition of fibrous connective tissue.1Irrespective of the etiology,the progression of chronic liver diseases is driven by an interrelated vicious cycle of continuous chronic inflammation,chronic liver injury,and progressive fibrosis.2Chronic inflammation can activate hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) to promote the deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM).3Oxidative stress and apoptosis also cause chronic inflammation,which seriously affects the prognosis of patients.4Liver fibrosis,as the common pathological stage of most liver diseases,is the central hub in the development and changes in chronic liver diseases and is reversible.5Thus,finding an effective anti-fibrotic drug to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis has become a research hotspot.
To date,there is no standard treatment for hepatic fibrosis.The efficacy of synthetic drugs in the treatment of liver fibrosis is not satisfactory and the price of is relatively high.Besides,synthetic drugs are associated with side effects that can pose further problems during therapy.With the continuous development for medical research,Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) have gradually become one of the most sought-after research fields,especially in the development of therapeutic strategies for the management of chronic diseases including liver fibrosis.The basis of TCMs is their specific formulae,which usually consist of several herbs with different or similar medicinal effects combined together in a single formulation to enhance treatment outcomes.The combination of herbs in a formula can exert synergistic effects;therefore,they could be used to obtain better treatment outcomes in patients with liver fibrosis by virtue of their multiple therapeutic functions including modulating the antioxidant,anti-inflammatory,and anti-HSC-proliferation pathways.6,7
Guizhifuling pill (桂枝茯苓丸,GZFL) is a traditional medicine described in Jin Gui Yao Lue,an ancient Chinese medicine book.GZFL pill comprises Guizhi(Ramulus Cinnamomi),Taoren (Semen Persicae),Chishao(Radix Paeoniae Rubra),Fuling (Poria),Mudanpi(Cortex Moutan Radicis),8which have the function of activating blood and resolving stasis,as well as anti-inflammatory,and analgesic effects.9GZFL has been used to treat gynecological disorders in China for thousands of years.10However,the hepatoprotective mechanism underlying the effect of GZFL is still unclear.In this study,we aimed to elucidate the hepatoprotective effects of GZFL in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis and evaluate the underlying mechanisms.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Drug preparation and chemicals
GZFL (SFDA approval number: Z20027562,batch number: 190202) was provided by Chengdu Jiuzhitang Jinding Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,and colchicine (SFDA approval number: H53021534,batch number: 1904A)was purchased from KPC Pharmaceuticals,Inc.Biochemical and antioxidant assay kits,including alanine transaminase (ALT,batch number: C009-2),aspartate transaminase (AST,batch number: C010-2),albumin (ALB,batch number: A028-2),and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT,batch number: C017-2) superoxide dismutase (SOD,batch number: A001-3),glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px,batch number: A005),catalase(CAT,batch number: A007-1),total antioxidant capacity(T-AOC,batch number: A015-2),malondialdehyde(MDA,batch number: A003-1),and hydroxyproline(Hyp,batch number: A030-3) to determine liver function were obtained from Jiancheng Co.Ltd.(Nanjing,China).Enzyme-linked immune-osorbent assay (ELISA) kits,including interleukin-1β (IL-1β,batch number: E-EL-M0037c),interleukin-6 (IL-6,batch number: E-EL-M0044c),and tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α,batch number: E-EL-M0049c) were purchased from Elabscience Biotechnology Co.Ltd.(Wuhan,China) and the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit (batch number: PC0020) was purchased from Solarbio (Beijing,China).Antibodies for Nrf-2,nicotinamide quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1),HO-1,glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM),toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4),IKK alpha (IKKα),IκBα,NF-κB p50,NF-κB p65,and phospho-NF-κB p65 (p-NF-κB p65) were purchased from Proteintech Inc.(Princeton,NJ,USA).
2.2.Animal experiments and treatment
Male ICR mice weighing (20 ± 2) g were purchased from the Experiment Animal Center of Zhejiang Province(Hangzhou,China).All animal studies were approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Ocean University (Zhoushan,China) (Permission No.2020-0026).The mice were housed in a room maintained at a constant temperature of (22 ± 2) ℃ and subjected to a 12-h light/dark cycle.
After a week of acclimatization,50 mice were randomized into two groups: (i) control group (Control,n=10);(ii) model group (CCl4,n=40).The mice in the model group were intraperitoneally injected with 20%soybean oil solution of CCl4(3 mL/kg body weight)twice a week for four weeks.11The control group was injected with an equal dose of saline.In Week 5 of the experiment,the 40 mice treated with CCl4were divided into four groups as follows: model group;positive group(Colchicine,0.1 mg/kg);low-dose GZFL (L-GZFL);high-dose GZFL (H-GZFL).Using the daily dose for clinical patients as a reference,the final dose of GZFL for mice was determined by the dose conversion formula.Two different doses of GZFL were chosen: low dose(150 mg/kg) and high dose (300 mg/kg).These doses were equivalent to 1× and 2× the clinical dose.From the 5th to the 9th weeks,the mice in the GZFL and positive groups were administered the respective drugs once daily.At an endpoint,after fasting for 12 h,all animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation to collect tissue and blood.The serum was collected by centrifuging the blood at 2200 ×gfor 15 min using a high-speed micro centrifuge (HITACHI CF16RN,Tokyo,Japan) at 4 ℃.The liver was obtained from mice and weighed,calculated the liverindex (liver weight/body weight).One portion of the liver was fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde and the other portion was stored at-80 ℃ until further analysis.
2.3.Histological examination
Liver tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h andembeddedinparaffin after dehydration.A microtome (Leica RM2135,Wetzlar,Germany) was used to cut the liver tissues into 4-μm-thick slices.The sections were deparaffinized and dehydrated using a graded-alcohol series for hematoxylin and eosin (HE)and Masson’s trichrome staining to visualize morphological features and determine the extent of fibrosis.
2.4.Serum biochemical analysis
Serum ALT,AST,ALB,and γ-GT activities were determined as indices of liver injury as described in manufacturers’ instructions of the respective assay kits.
2.5.Determination of MDA and antioxidant enzymes in liver tissue
The 10% liver homogenate was prepared and the proteins in the supernatant of homogenates was quantified by BCA total protein assay kit.The activities of SOD,GSHPx,CAT,T-AOC,and MDA in the liver homogenates were determined to evaluate the antioxidant capacity.
2.6.Cytokine assays
10% liver homogenate was prepared by replacing saline with phosphate-buffered saline.ELISA kits were used to measure the levels of IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-α in the liver homogenate.
2.7.Determination of hydroxyproline
The fresh liver tissue was subjected to high-temperature hydrolysis,and hydroxyproline levels were measured according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.8.Western blotting
The liver tissue was quickly ground with liquid nitrogen to obtain a powder,following which,the liver-protein extracts were harvested with RIPA buffer.The expression and phosphorylation of tissue proteins were determined using Western blotting as previously described by Konget al.12The membranes were incubated overnight at 4℃ with the appropriate primary antibody.The protein bands were developed using ECL chemiluminescence detection reagent (ECL,TransGen Biotech,Beijing,China) and FluorChem FC3 imaging system (ProteinSimple,Waltham,MA,USA).GAPDH was used as an internal control.
2.9.Statistical analysis
The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n=10) and IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows,Version 26.0 (IBM Corp.,Armonk,NY,USA) was used for analysis of variance.P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Effects of GZFL pill on body weight and liver index
The whole experiment lasted for 9 weeks.Mice were weighed every week during the experimental period.?Compared with the control group,the bodyweight of mice in the CCl4-induced groups was significantly decreased during the modeling period (weeks 1-5,Table 1) and the liver index was significantly higher (Table 2),which indicated liver damage and swollen.However,the liver index of colchicine group and GZFL group were significantly decreased compared to the corresponding values in the model group.
3.2.GZFL attenuates CCl4-induced liver injury and fibrosis in mice
As shown in Figure 1A,mice in the model group exhibited enlarged livers with a rough surface and plaque degeneration.The livers of mice treated with colchicine,and 150 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg GZFL showed alleviation of CCl4-induced liver injury.
HE staining results showed that the hepatic lobule was structurally intact,and the hepatocytes were normal and almost without vacuoles in the control group.The polygonal hepatocytes were connected in a cord and lined up with the hepatic sinusoids around the central vein with the hepatic structure clearly visible.In the model group,we found disrupted liver lobules andcords,inflamed and necrotic hepatocytes,and con-nective tissuehyperplasia.After the administration of GZFL and colchicine,the hepatic cords were clear,the sinusoidal space resumed normal morphology,and the vacuoles were reduced (Figure 1B).
The results of Masson’s trichrome staining are shown in Figure 1C.It can be seen that a large amount of collagen exists in the liver tissue of the model group.A significant increase in liver hydroxyproline (Hyp) levels was observed in mice with fibrosis (Table 2).However,treatment with GZFL reduced the increased collagen distribution in the livers of CCl4-treated mice.
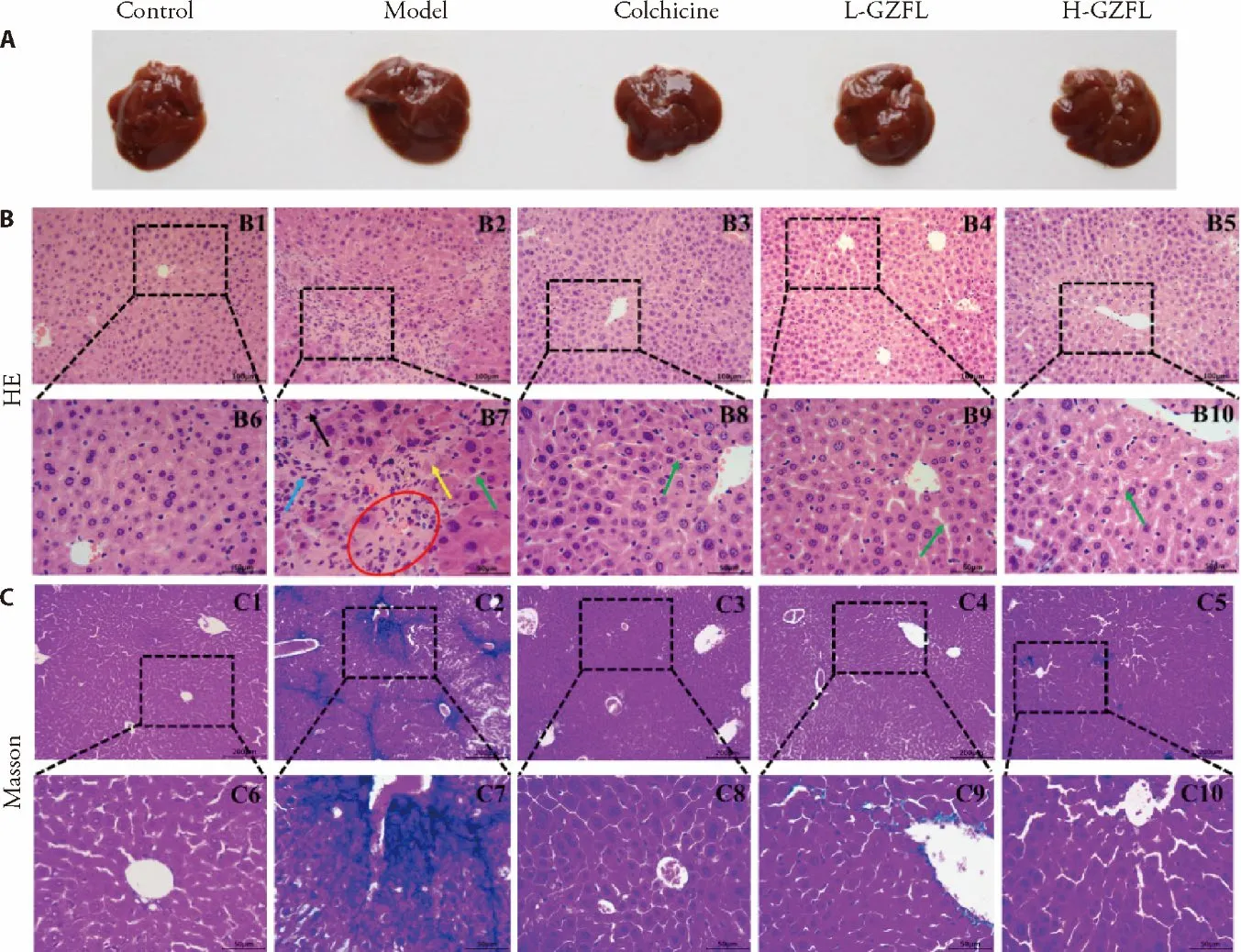
Figure 1 GZFL attenuates CCl4-induced liver injury and fibrosis in mice
3.3.Effect of GZFL on the serum liver indices in mice
We measured serum ALT,AST,ALB,and γ-GT levels to evaluate liver function in mice (Table 3).The activities of ALT,AST,and γ-GT in the model group were significantly higher than in the control group,whereas ALB levels were significantly lower in the model groupthan in the control group.GZFL treatment significantly inhibited the increase in serum ALT,AST,and γ-GT activities.Administration of GZFL increased serum ALB levels,but there was no significant difference compared to the corresponding levels in the model group.
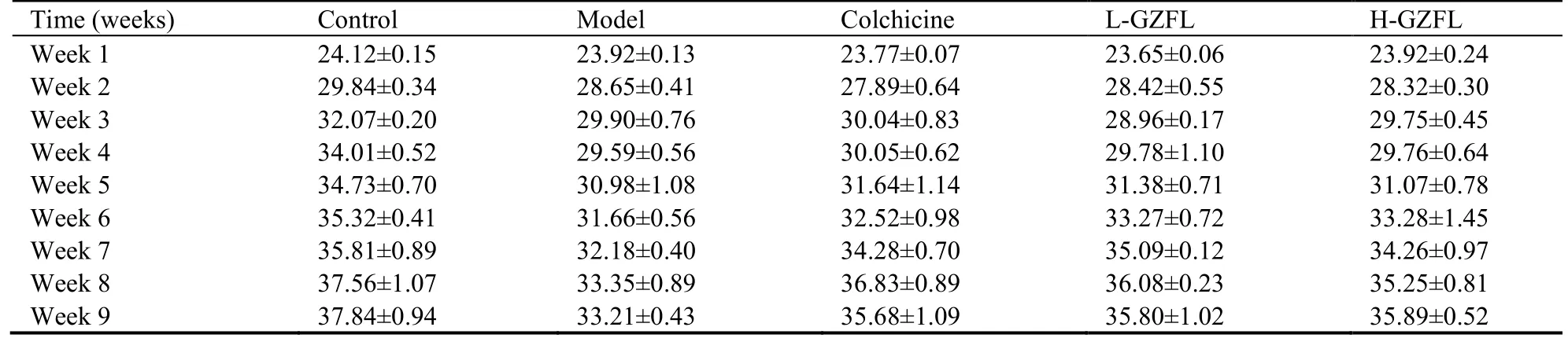
Table 1 Changes of body weight in each group (g)

Table 2 Change in liver index and the expression of hydroxyproline of mice
3.4.Effect of GZFL on antioxidant capacities and MDA in liver tissues
Oxidative stress indicators mainly include MDA,SOD,GSH-Px,CAT and T-AOC,and the determination of these indicators can evaluate whether GZFL reduces the effect of hepatic oxidative stress.As shown in Table 4,GZFL administration significantly enhanced SOD,GSHPx,T-AOC,and CAT,while inhibiting the increase ofMDA.
3.5.Effect of GZFL on the levels of proinflammatory cytokines in liver tissue
In this study,we measured the expression of the related proinflammatory cytokines.The levels of the three cytokines were significantly increased in the model group.The expression of them were significantly decreased after treatment with GZFL or colchicine for four weeks (Table 5).
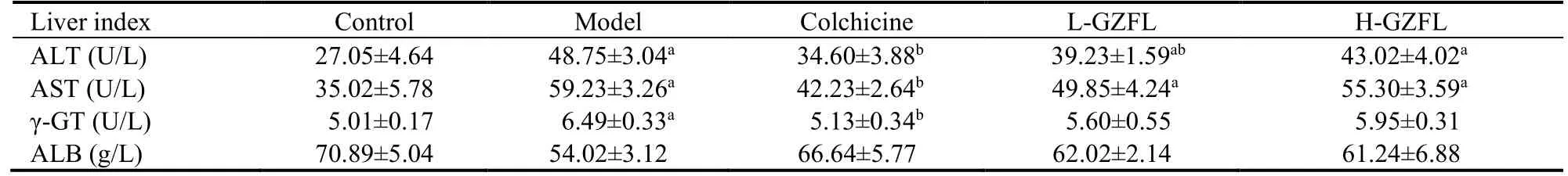
Table 3 Effect of GZFL on liver indices in mice
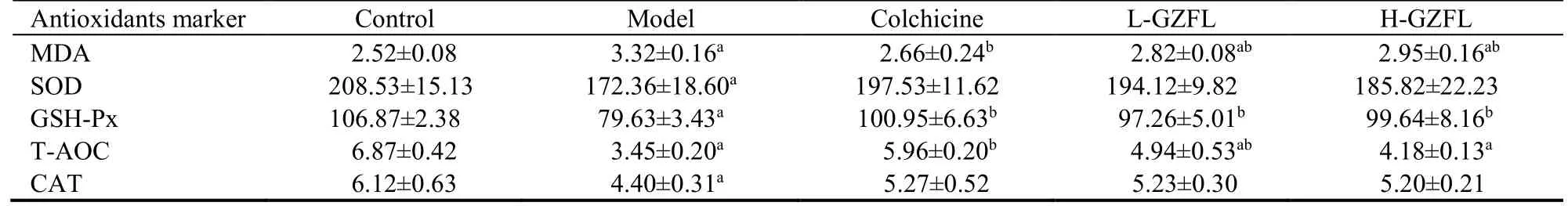
Table 4 Effect of GZFL on antioxidant capacities and MDA levels in liver tissues

Table 5 Effect of GZFL on the levels of proinflammatory cytokines in liver tissue (pg/mL)
3.6.GZFL regulates Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling
As shown in Figure 2,CCl4treatment reduced the expression of Nrf2,there was no significant difference compared with the control group.However,CCl4treatment significantly downregulated the expression of the downstream antioxidants,NQO1,HO-1,and GCLM.GZFL and colchicine exerted hepatoprotective effects by enhancing the antioxidative capability of the liver because these compounds most likely increase Nrf2 expression and upregulate the downstream proteins expression of HO-1,NQO1,and GCLM.
3.7.GZFL regulates NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response
In this study,Western blotting was used to analyze the concentrations of the proteins related to NF-κB signaling.We found that TLR4,IKKα,NF-κB p50,and p-NF-κB p65 were significantly upregulated after exposure to CCl4.However,after treatment with GZFL and colchicine,there was a significant reduction in the levels of the NF-kB signaling pathway-related proteins including IKKα,NF-κB p50,and p-NF-κB p65 (Figure 3A-3F).
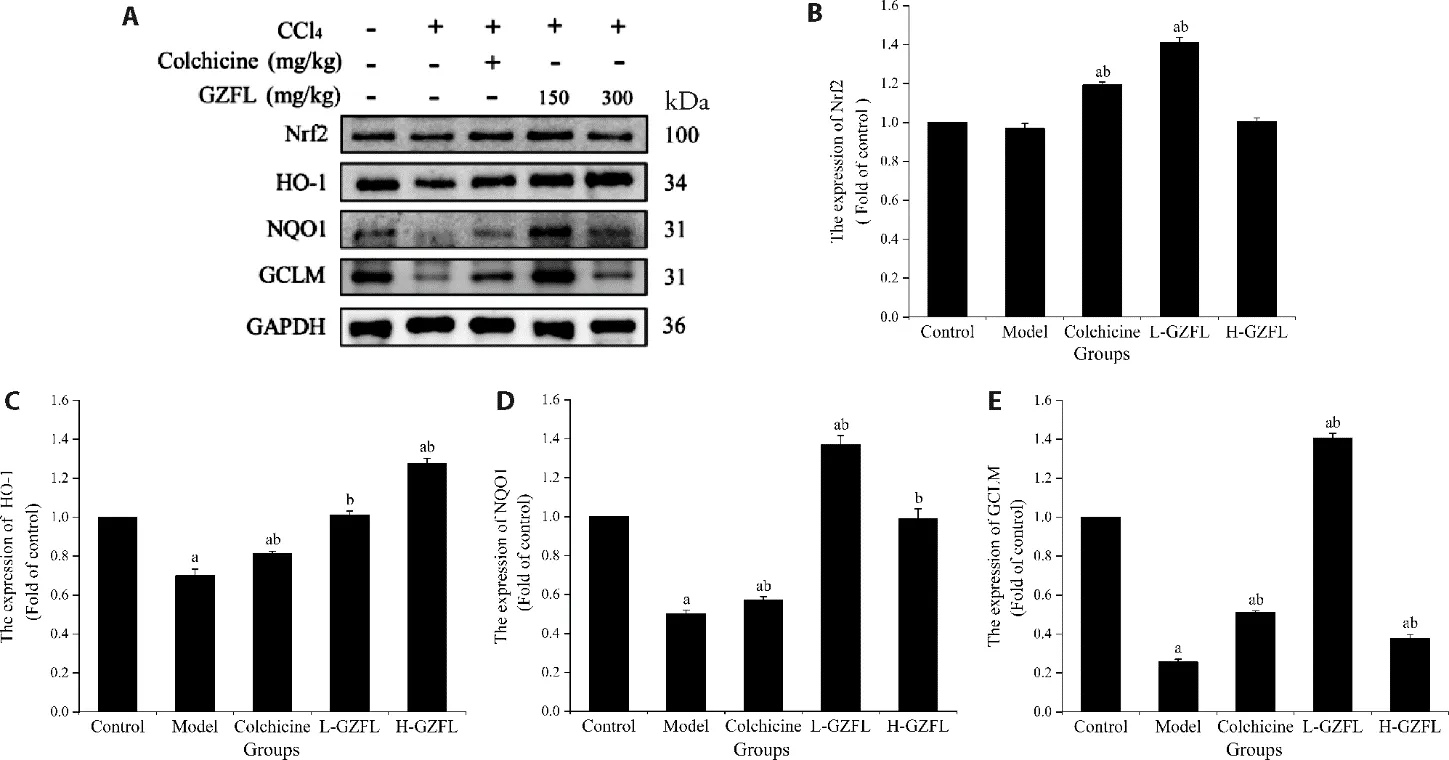
Figure 2 Western blotting to determine the protein expression of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling
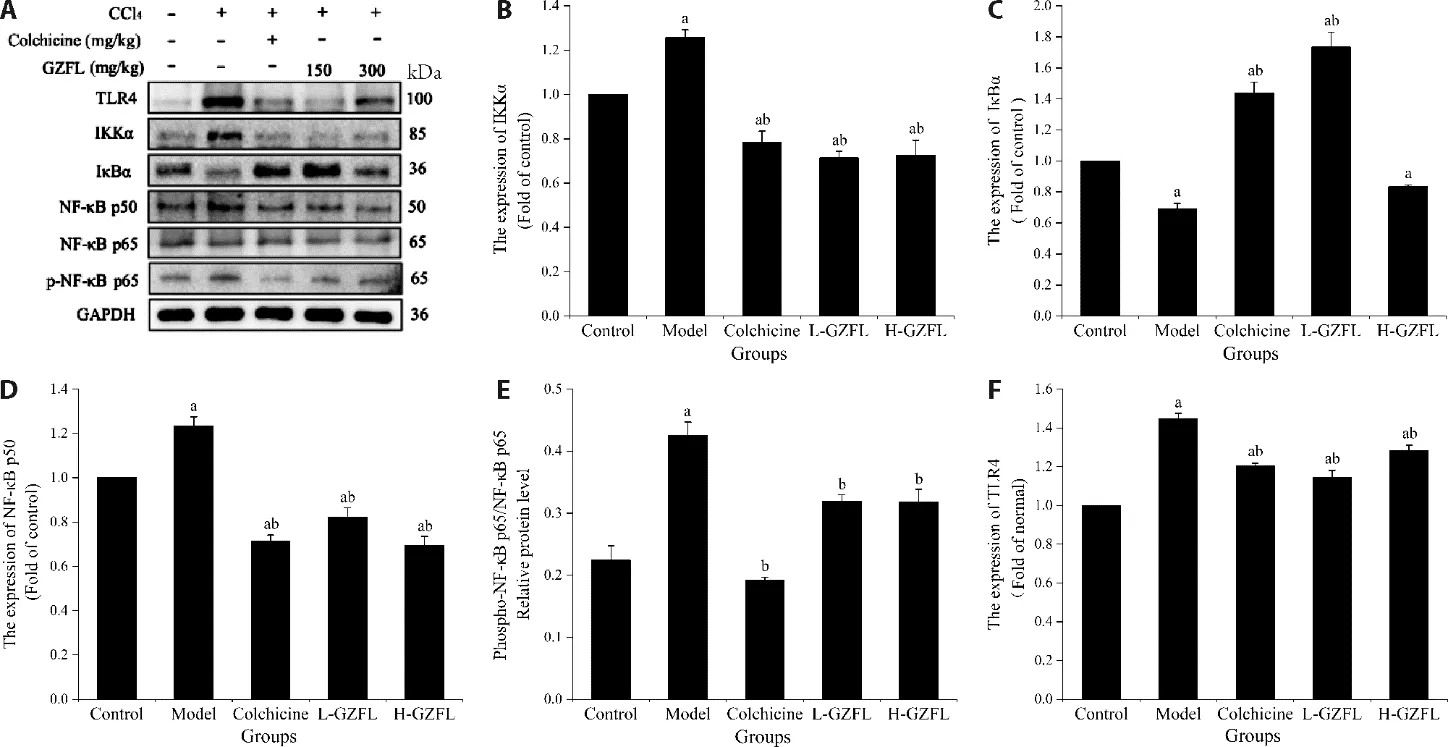
Figure 3 Determination of protein expression in the NF-κB signaling pathway using Western blotting
4.DISCUSSION
Liver fibrosis is a multifactorial disease,blocking a single node will usually not be sufficient or effective.In the present study,GZFL exerts remarkable anti-liver fibrosis effects in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis mice as confirmed by histopathological improvements and quantitative analysis of protein of NF-κB pathway and Nrf2 family members.This suggesting that the targets of GZFL may be the key signaling pathways pertaining to liver fibrosis.Liver fibrosis is characterized by an excessive accumulation of ECM.13Reducing the deposition of the ECM helps improve liver fibrosis.Our findings indicated that GZFL could remodel the liver structure and reduce collagen deposition.
During liver damage,ALT and AST in the cytoplasm enter the blood,resulting in a significant spike in the serum levels of these markers.14ALB is synthesized by the liver and is the most important and abundant protein in human plasma.A decrease in serum albumin reflects the degree of liver function in cirrhosis and is indicative of continuous liver damage,thereby highlighting its clinical significance.15Serum γ-GT is another diagnostic marker for liver and gallbladder diseases and its levels are increased in active or chronic hepatitis.16We found that GZFL can improve the liver function of mice by the biochemical analysis of mouse serum ALT,AST,ALB,γ-GT.
Oxidative stress is the primary pathological condition of liver fibrosis.Upon entering the hepatocytes,CCl4is acted upon by cytochrome P450 to release trichloromethyl radicals,which covalently bind to the macromolecules in the liver cells,attack the unsaturated lipids in the membrane,and trigger the production of reactive oxygen free radicals and lipid peroxidation.17These reactions,in turn,induce apoptosis and necrosis of the liver cells.The indicators of oxidative stress mainly include MDA,SOD,and GSH-Px.SOD protects against cellular damage by scavenging superoxide anions and GSH-Px protects cell membranes by specifically catalyzing the reduction of hydrogen peroxide.MDA is an important indicator reflecting the levels of free radicals and lipid peroxidation in the body.18Nrf2 is essential for a transcription factor that regulates redox equilibrium in the cellular defense against oxidative stress.When activated,Nrf2 undergoes phosphorylation and translocate from the cytosol to the nucleus.Next,it induces the expression of the antioxidant defense enzymes to protect against oxidative damage.19This study found that GZFL treatment increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes,attenuated lipid peroxidation in mouse liver,and up-regulated the expression of Nrf2 and its downstream proteins.It is suggested that GZFL may activate the antioxidant system by inducing the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway,thereby reducing liver fibrosis in mice.Anujaet al 20found that ethyl acetate fraction of Drynaria quercifolia could against CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in ratsvia Nrf2/ARE pathway.Our findings were similar to the results reported in their study.
The imbalance of proinflammatory cytokines may lead to tissuedamage and immune-mediated diseases.21Substantial evidence suggests that inflammation is one of the most important features of liver fibrosis.22During an inflammatory response,high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines lead to damage of the liver tissue,after which,the damaged liver parenchyma releases large amounts of inflammatory cytokines and multiple chemokines.The NF-κB signaling pathway can induce the secretion of proinflammatory and profibrotic cytokines during liver fibrosis,further aggravating liver damage.23Under physiological conditions,NF-κΒ is located in the cytoplasm;its p65 subunit combines with the IkB monomer to form an inactive complex,which cannot enter the nucleus to function.24IkB dissociates from the NF-κB dimer and is phosphorylated when stimulated externally.NF-κB is then activated and transferred to the nucleus,where it initiates gene transcription and protein expression,thereby regulating inflammation.Our findings suggest that GZFL treatment can reduce the levels of IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α and inhibit the activation of NF-κB signaling.This is similar to the findings of Zhenget al.25
In conclusion,based on our findings,it can be inferred that GZFL could potentially be used as a therapeutic agent to attenuate liver fibrosis.The probable underlying mechanism of GZFL in alleviating liver fibrosis is by enhancing microsomal enzyme activity,upregulating the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant system and inhibiting the NFκB signaling pathways.These findings highlight the importance of the small traditional prescription of GZFL in the management of liver fibrosis.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Effectiveness and safety of tripterygium glycosides tablet (雷公藤多苷片) for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Efficacy of green tea extract on PC3 prostate cancer cells through upregulation of miR-195 expression and suppression of epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- Qilan preparation (芪蓝颗粒) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by down-regulating microRNA-21 in human Tca8113 tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells
- Tenglong Buzhong granules (藤龙补中颗粒) inhibits the growth of SW620 human colon cancer in vivo
- Yajieshaba prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis
- Huangqi decoction (黄芪汤) attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis via transforming growth factor-β1/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in 5/6 nephrectomy mice
