Bilateral hip heterotopic ossification with sciatic nerve compression on a paediatric patient-An individualized surgical approach: A case report
2022-08-19JoPedroGouveiabregaPedroJordJoanaArcngelo
lNTRODUCTlON
Neurogenic heterotopic ossification (NHO) is a process of ectopic bone deposition in non-skeletal tissue in the setting of an event involving the central nervous system, such as a stroke, cerebral anoxia, or cranial or medullary injury. Its severity and clinical presentation vary depending on the extension of the ossified lesion and the compromise of adjacent neurovascular structures. The etiopathogenesis of NHO is unclear, but existing evidence supports the involvement of neuronal control mechanisms[1] and conversion of mesenchymal progenitor cells to osteoblast lineages[2] with the participation of prostaglandin E2 and osteoblast stimulating factors[3]. In this report, we introduce a case of a paediatric patient who, following a haemorrhagic stroke, developed bilateral hip NHO with entrapment of the sciatic nerve and with the unusual involvement of both the paretic and nonparetic limbs. We describe our surgical approach and resection strategy.
CASE PRESENTATlON
Chief complaints
A 13-yr-old boy with sickle cell trait presented with hip pain and limited range of motion.
History of present illness
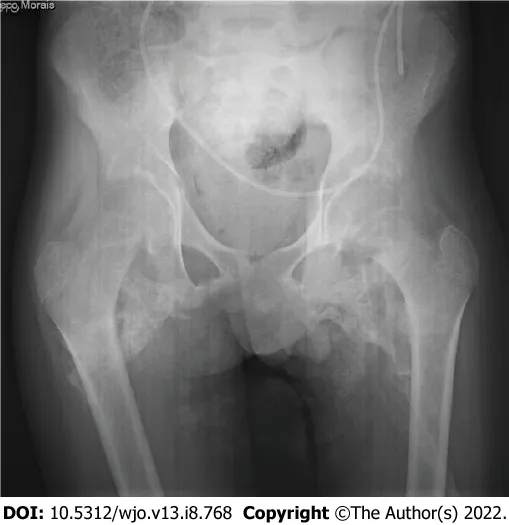
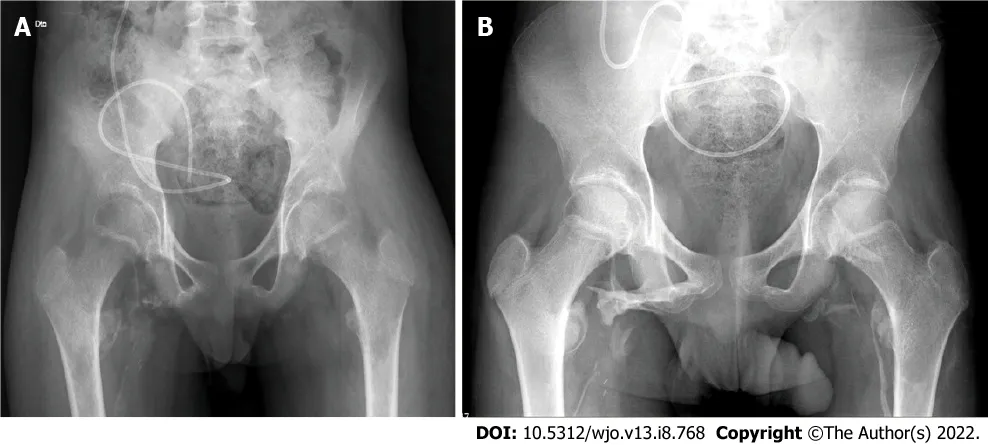
The patient had a 5-mo history of painful bilateral hip stiffness that progressively impaired his gait. Extensive bilateral heterotopic ossification was seen on pelvic radiographs (Figure 1).
History of past illness
The patient had an history of right fronto-temporal haemorrhagic stroke because of an arteriovenous malformation, complicated with a right chronic subdural haemorrhage resulting in right facial nerve palsy with dyspraxia and left hemiplegia that has persisted since then.
Personal and family history
There is no personal and family history.
Physical examination
Motor examination revealed left spastic hemiparesis (0/5) with hyperreflexia and right side upper limb motor function of 4+/5 and 3/5 on the ipsilateral lower limb. The patient presented with painful, generalized and progressive limited passive range of motion of both hips, and soon was completely bedridden.
Laboratory examinations
There is no laboratory examinations.
Imaging examinations
A computed tomography (CT) scan documented extensive calcification occupying the ischial-femoral space, with bilateral involvement of the posterior muscles of the thigh, mainly the external obturator, gemellus inferior and the proximal aspect of the biceps femoris. A 2.5 cm extension and oedema resulted in osseous incarceration of the proximal aspect of the sciatic nerve that was more evident on the right side (Figures 2 and 3).
When Muriel and I reached our little garden and sat down, his words came back to me. God had spoken through an inebriated18 old derelict. It is you who is whispering to my spirit, I likes it, tha s good, I said aloud. I may be on the bench, but if you like it and say it s good, that s all that counts.
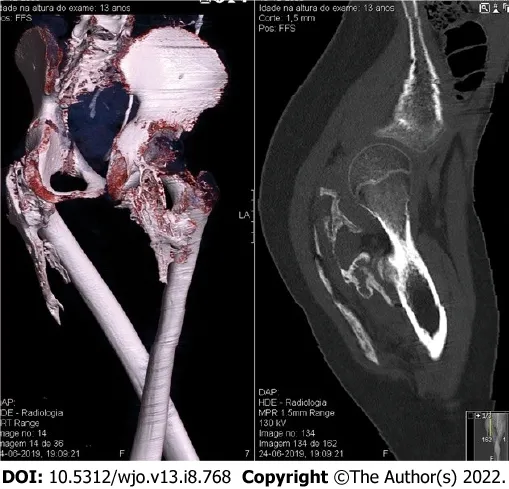
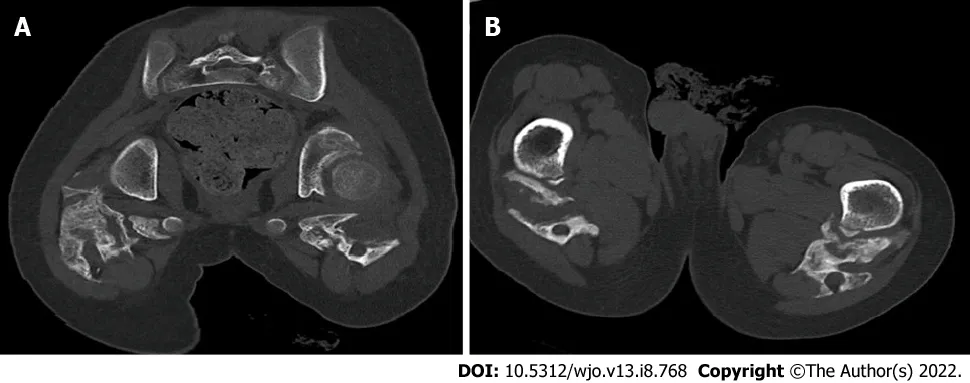
FlNAL DlAGNOSlS
The patient was diagnosed with posteromedial bilateral heterotopic ossification with entrapment of both proximal aspects of the sciatic nerve.
TREATMENT
Surgical resection of the ossified lesion and release of the sciatic nerve were performed, starting with the right hip. A modified posterior thigh approach that was developed by the senior author was used for both hips. The procedure was performed with the patient in a ventral position and began with a “lazy S” incision made in the centre of the gluteal region (Figure 4A). The gluteus maximus was detached from its distal insertion point on the proximal femur and retracted proximally, a manoeuvre intended to preserve gluteus vascularization from the superior gluteal artery. The sciatic nerve was then identified at both extremities of the ossification and subsequently released (Figure 4B and C). Note that a fibrous capsule that had formed between the nerve and the bone facilitated the dissection, which was performed with Kerrison forceps and meticulous haemostasis.
Another conservative treatment applied is physical therapy, but whether it plays a significant role in the mitigation of NHO lesions remains unclear. It has been suggested that forced manipulation of the extremity can induce HO formation by increasing inflammation[11], whereas lack of movement can cause HO formation and progression to ankylosis. Cautious use of a gentle range of motion is considered the best approach. In this case, we believe that recurrence of the HO on the right hip was promoted by the immobilization incurred while the patient waited for surgery of his left hip. It was only after both hips were operated and freed of ossification, and mobilization was resumed that the HO on the right side stopped progressing. Besides that, postoperative low-dose radiation therapy could have also contributed to minimization of the high risk for recurrence of HO lesions after resection on the right hip.
First of all, surgical intervention should not aim for a complete resection, as this could incur an increased risk of haemorrhage and infection. A “functional” resection that increases mobility and alleviates pain is preferable. Furthermore, the location of the heterotopic ossification on the hip, which will guide the choice of surgical approach, is largely determined by certain aetiologies; for example, posterior lesions, like in our case, are typically associated with cerebral anoxia.
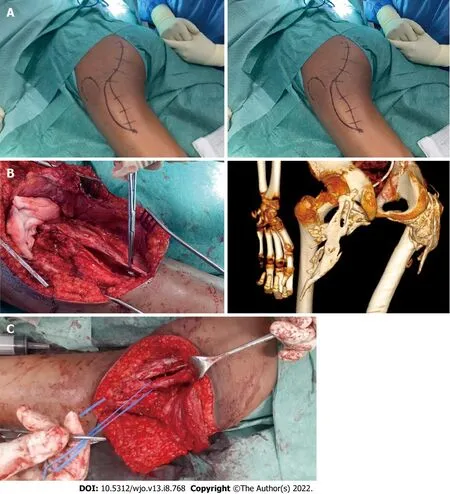
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Resection was performed on the left hip 6 wk later, and radiographic evaluation revealed a limited NHO relapse on the right hip (Figure 5A). Postoperatively, the patient began partial weight-bearing walking and participation in a rehabilitation program. After 1-yr of follow-up, there was no further development of the NHO lesions on radiographic evaluations and the patient had experienced a significant clinical improvement, being able to resume walking (Figure 5B).
DlSCUSSlON
NHO is not often encountered in the paediatric population, and that has resulted in the use of diagnostic and treatment methods based on experience and evidence obtained in adults. To our knowledge, this is the first published case of a post-stroke bilateral NHO of the hip with sciatic nerve entrapment in a paediatric patient. Management of these patients is complex and requires multidisciplinary intervention. Even though there is a lack of evidence to support their effectiveness, and there are some conflicting viewpoints, conservative measures remain the first approach in the early stages of NHO. Pharmacological therapy with bisphosphonates and indomethacin has demonstrated efficacy in the early inflammatory phase of NHO, reducing disease progression. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, particularly indomethacin, reduce the incidence of NHO in patients with spinal cord injury[4] but increase the risk of haemorrhagic complications that could be serious in patients with sickle cell trait, such as ours.
Furthermore, peri-articular radiation is considered another valid early-stage therapeutic modality that has been found to be more effective than non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[5]. It is considered useful for inactivating the high mitotic rate of the pluripotent osteoprogenitor cells recruited by the inflammatory cascade and their differentiation into osteoblasts and chondrocytes[6]. Low-dose radiation therapy administered preoperatively or less than 72 h postoperatively represents an effective treatment[7], not only in reducing the size of NHO lesions[8] but also the risk of recurrence[9], with minimal side effects[10].
If you choose 1 year for your marriage, you shall pay as much as 2, 000 sterling4 pounds plus receiving a dictionary-thick reference of rights and responsibilities
For this particular case, the patient presented with severe pain, gait impairment and the presence of signs of neurological compromise. It is generally agreed in the orthopaedic community[12] that fully matured hip HO limits the use and efficacy of conservative treatment modalities as curative options. Therefore, surgical intervention remains the mainstay for treatment of mature HO lesions.
13.Angel:In the second and third centuries, angels were recognized by the Church (Lindahl, McNamara, Lindow 10). According to the Apocalypse of Saint Paul , guardian66 angels protect the virtuous67 who have renounced68 the world (Lindahl, McNamara, Lindow). In some ways, the maiden has renounced the world when she left her father s house.
In terms of the revision, the first author Nóbrega JPG has complemented the text with the reviewers’ requests and the other authors corrected and complemented the text.
In our case, the heterotopic calcification had an extension below the plane of the greater gluteus muscle, from the trochanteric region to the ischiatic region. Traditional approaches (such as the posterolateral Gibson approach) do not allow for a clear exposition of this space. The transgluteal approach has the disadvantage of muscle denervation, and proximal disinsertion of the greater gluteus muscle may jeopardize its vascularization (gluteal artery, branch of the internal iliac artery). Thus, through an Sshaped incision that allows a wide area of exposure, the distal tendinous release of the greater gluteus muscle and the progressive disinsertion of this muscle exposes the entire plane of the rotators and hamstrings (where the major HO lesion lies) without compromising innervation and vascularization.
Controversy persists in the timing of surgery. It is accepted that HO lesions should not be surgically treated until bone maturation is complete with presence of defined cortical margins, which often appear around 6 mo after the beginning of ossification. Some authors suggest waiting 18 mo[8,13]. A recent study suggests that the risk of recurrence is independent of the time to surgery. Early surgery was found to prevent the development of joint ankylosis, and subsequent induction of epiphyseal osteoporosis, progressive cartilage loss, loss of function, joint stiffness, and bone demineralization with increased risk of fracture.
All authors report no relevant conflict of interest for this article.
CONCLUSlON
A posterior approach of the gluteal region with gluteus maximus distal disinsertion from proximal femur and proximal retraction with a meticulous sciatic nerve release are favorable therapeutic options for severe posterior heterotopic ossifications. This case illustrates the practical difficulties of managing such patients and reinforces the need for specific guidelines not only for treatment and timing but also for the use of adjuvant therapy in the paediatric population, for which the literature is sparse.
FOOTNOTES
For a few days they lived in this way as well as might be, and came to the end of all their provisions. Then the man said, Wife, we cannot go on any longer eating and drinking here and earning nothing. You weave23 baskets. He went out, cut some willows18, and brought them home. Then she began to weave, but the tough willows24 wounded her delicate hands.
Then little Gerda was very much frightened, and began to cry, but no one heard her except the sparrows, and they could not carry her to land, but they flew along by the shore, and sang, as if to comfort her, “Here we are! Here we are!” The boat floated with the stream; little Gerda sat quite still with only her stockings on her feet; the red shoes floated after her, but she could not reach them because the boat kept so much in advance
Lauren Hodge: If you were going to a restaurant and wanted a healthier option, which would you choose, grilled or fried chicken? Now most people would answer grilled, and it's true that grilled chicken does contain less fat and fewer calories. However, grilled chicken poses a hidden danger. The hidden danger is heterocyclic amines -- specifically phenomethylimidazopyridine, or PhIP -- (laughter) which is the immunogenic or carcinogenic compound.
The informed consent was signed and explained to the mother of this patient in portuguese language.
The authors have read the CARE Checklist (2016), and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CARE Checklist (2016).
After pausing a moment to give her time to admire him, the Enchanter made her the most complimentary21 speech he could invent, which, however, did not please her at all, though he was extremely delighted with it himself
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Portugal
João Pedro Gouveia Nóbrega 0000-0002-1866-5575; Pedro Jordão 0000-0002-1659-9586; Joana Arcângelo 0000-0001-9722-2547.
Wu YXJ
The boy made one of those hand signs at me as I was about to leave. I asked his sister if your brother is so smart then why is he doing things like that with his hands? She told me that he was saying that he loved me with his hands. I didn t say anything back to her at all because I didn t believe her. People can t talk with their hands and everybody knows that. People can only talk with their mouth.
A
Wu YXJ
杂志排行
World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Rates of readmission and reoperation after operative management of midshaft clavicle fractures in adolescents
- Quantitative alpha-defensin testing: ls synovial fluid dilution important?
- Effect of pelvic fixation on ambulation in children with neuromuscular scoliosis
- Epidemiology of pelvic and acetabular fractures across 12-mo at a level-1 trauma centre
- Risk modeling of femoral neck fracture based on geometric parameters of the proximal epiphysis
- Higher cost of arthroplasty for hip fractures in patients transferred from outside hospitals vs primary emergency department presentation
