盐穴储气库注采管柱内腐蚀速率预测模型研究
2022-07-02骆正山欧阳长风王小完张新生
骆正山,欧阳长风,王小完,张新生
盐穴储气库注采管柱内腐蚀速率预测模型研究
骆正山,欧阳长风,王小完,张新生
(西安建筑科技大学 管理学院,西安 710055)

盐穴储气库;注采管柱;腐蚀速率预测;主成分分析法(KPCA);改进灰狼优化(IGWO);极限学习机(ELM)
近年来,我国天然气供需量稳步增长,高质量发展战略能源储备设施地下储气库具有重大意义[1]。盐穴储气库具有孔隙率低、渗透率小、塑性形变能力强等优势[2-3]。注采管柱是盐穴储气库的重要组成,长期处于地下复杂环境使其易受多种腐蚀因素的影响并造成运维灾害[4-5]。因此,探究盐穴储气库注采管柱的腐蚀机理与规律,建立高精度的腐蚀预测模型意义重大。
目前,国内外学者已对管线腐蚀现象展开了大量研究。张新生等[6]研究了海洋立管的腐蚀发展规律,建立了初始条件滑动的非等间距管道腐蚀预测灰色模型SUGM(1,1,)。Chen等[7]利用主成分分析法提取海底管道内腐蚀的关键腐蚀因素,消除冗余信息并确定管道失效原因。王晓敏等[8]基于时变可靠性方法提出了一种多失效模式腐蚀影响下的地下管道失效概率预测方法。谢飞等[9]从化学反应、电化学反应和传质过程3个方面探究了天然气管道CO2腐蚀机理,提出了基于腐蚀机理的腐蚀速率预测模型。但以上传统研究方法针对管线腐蚀预测问题仍存在不足:SUGM(1,1,)初始条件的确定方式复杂,大幅更新腐蚀数据对预测结果的准确性存在较大影响;主成分分析法仅适用于处理线性映射问题,对非线性数据的特征提取效果较差;基于时变可靠性的失效概率方法难以准确定义失效事件的关联性,预测前提存在主观因素;机理模型研究仅考虑在理想溶液环境内的单一电化学腐蚀作用,未能考虑到非理想环境中管道的复杂流动等问题。随着智能信息处理技术的高速发展,大量智能优化算法得以应用于管道的腐蚀预测研究。凌晓等[10]通过优化反向传播神经网络(BPNN)参数,对输油管道的内腐蚀速率进行了预测分析。骆正山等[11]建立基于动态贝叶斯网络(DBN)的疲劳寿命模型,预测了海底腐蚀管道的失效概率。Peng等[12]通过优化支持向量回归(SVR)模型参数,对多相流管道的腐蚀速率进行了预测分析。曲志豪等[13]利用网格搜索算法优化了随机森林回归模型,建立了GA–RFC模型并对油气管道腐蚀速率进行了预测。但上述智能算法仍存在不足:BPNN存在结构复杂、训练速度慢、易陷入局部极小值等缺点;DBN的先验概率假设具有较强的主观性,对于属性非完全独立的大规模样本适用性不佳;SVR中参数的确定存在强随机性,使得模型预测结果的波动性较大;RFC模型中含有噪声样本时容易发生过拟合现象。
综上,本文在核主成分分析中引入小波核函数,对盐穴储气库注采管柱内的腐蚀因素进行特征提取,利用改进灰狼优化算法优化极限学习机的输入权值矩阵和隐含层阈值,建立小波KPCA–IGWO–ELM的盐穴储气库注采管柱内腐蚀速率预测模型。在MATLAB中对比分析多种预测模型的仿真结果,验证所建模型的适用性与准确性,为盐穴储气库注采系统安全运行提供可靠支撑。
1 KPCA
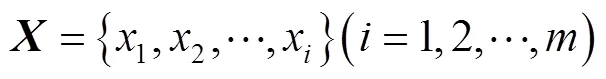
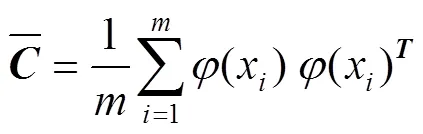


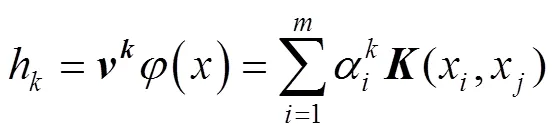
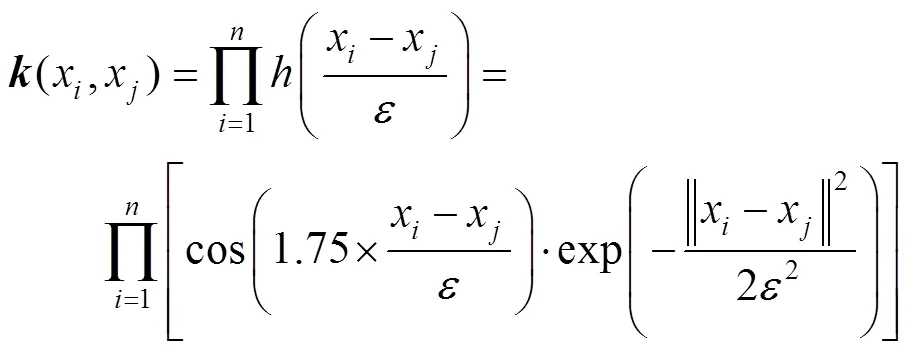
2 IGWO–ELM模型
2.1 ELM
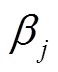

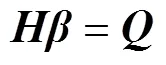
求解线性方程组式(7)得到最小二乘解:
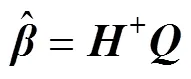
2.2 IGWO
改进灰狼优化[23](IGWO)是Mirjalili等人于2020年提出的一种新型群体智能优化算法,算法在灰狼优化[24](GWO)的基础上引入了基于维度学习狩猎(DLH)的改进搜索策略,有效解决了GWO种群多样性差、后期收敛速度慢、易陷入局部最优等缺点。
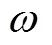
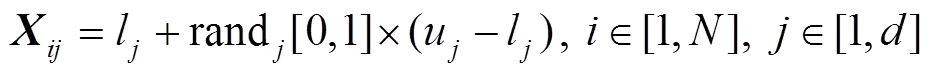
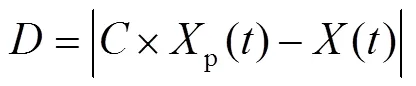
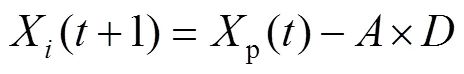
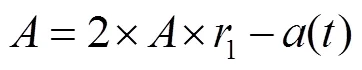
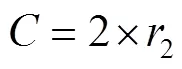

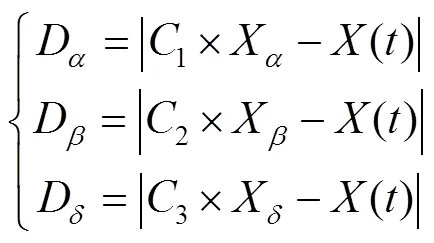
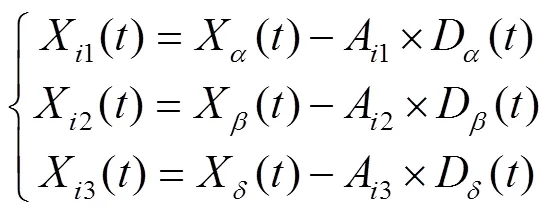
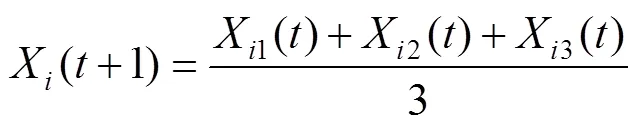
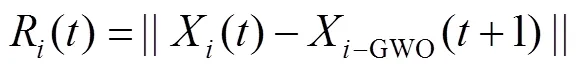

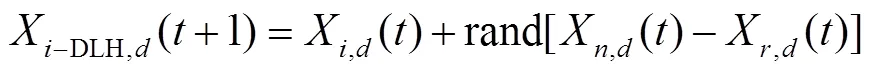
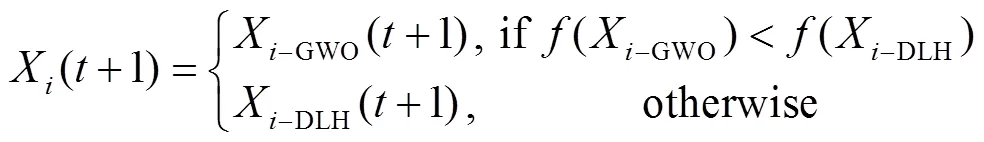
重复以上过程,当迭代次数等于最大迭代次数时循环结束,输出最优适应度值作为猎物最终位置,IGWO获全局最优解。
2.3 IGWO–ELM预测模型构建

2.4 预测模型评价指标
本文选用均方根误差(RMSE)、平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)和决定系数(2)3个指标[25]对IGWO–ELM模型预测结果进行评价,计算公式见式(22)—(24)。


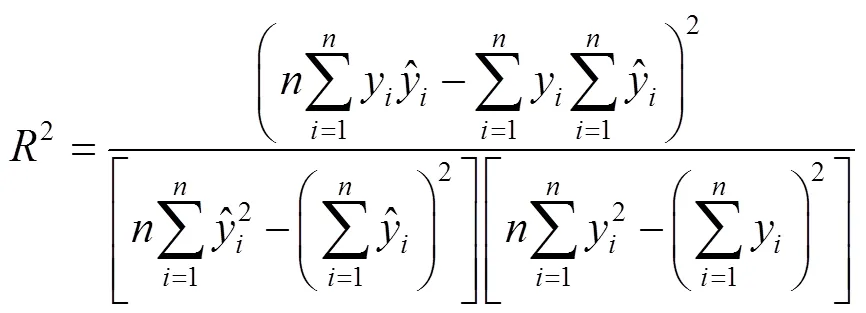

图1 IGWO–ELM模型腐蚀预测流程
3 实例应用
3.1 指标构建与数据采集
以某盐穴储气库注采管柱的实测试验为例,选取10种常见腐蚀因素构建盐穴储气库注采管柱的内腐蚀指标体系,如图2所示。结合项目运行资料,设定预测模型工况条件适用范围如表1所示,取250组实测数据用作预测模型样本,部分数据见表2。
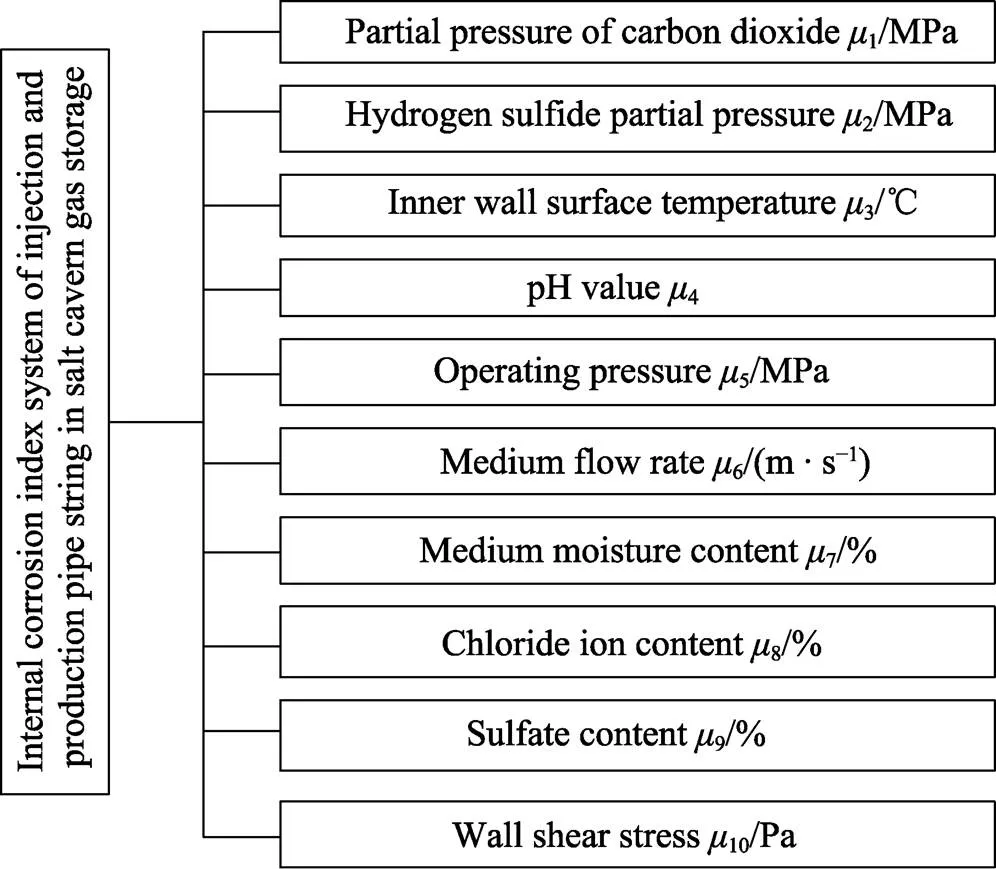
图2 盐穴储气库注采管柱的内腐蚀指标体系
3.2 特征提取
将采集的250组数据做归一化处理,后用小波KPCA对腐蚀指标进行特征提取,得出综合腐蚀因素特征值与贡献率,如表3所示。
KPCA规定,被选主成分的累计贡献率应不低于95%。分析表3易知,前3项主成分的累计贡献率高达98.61%,故将前3项作为影响盐穴储气库注采管柱内腐蚀的特征指标。
表1 预测模型工况适用范围
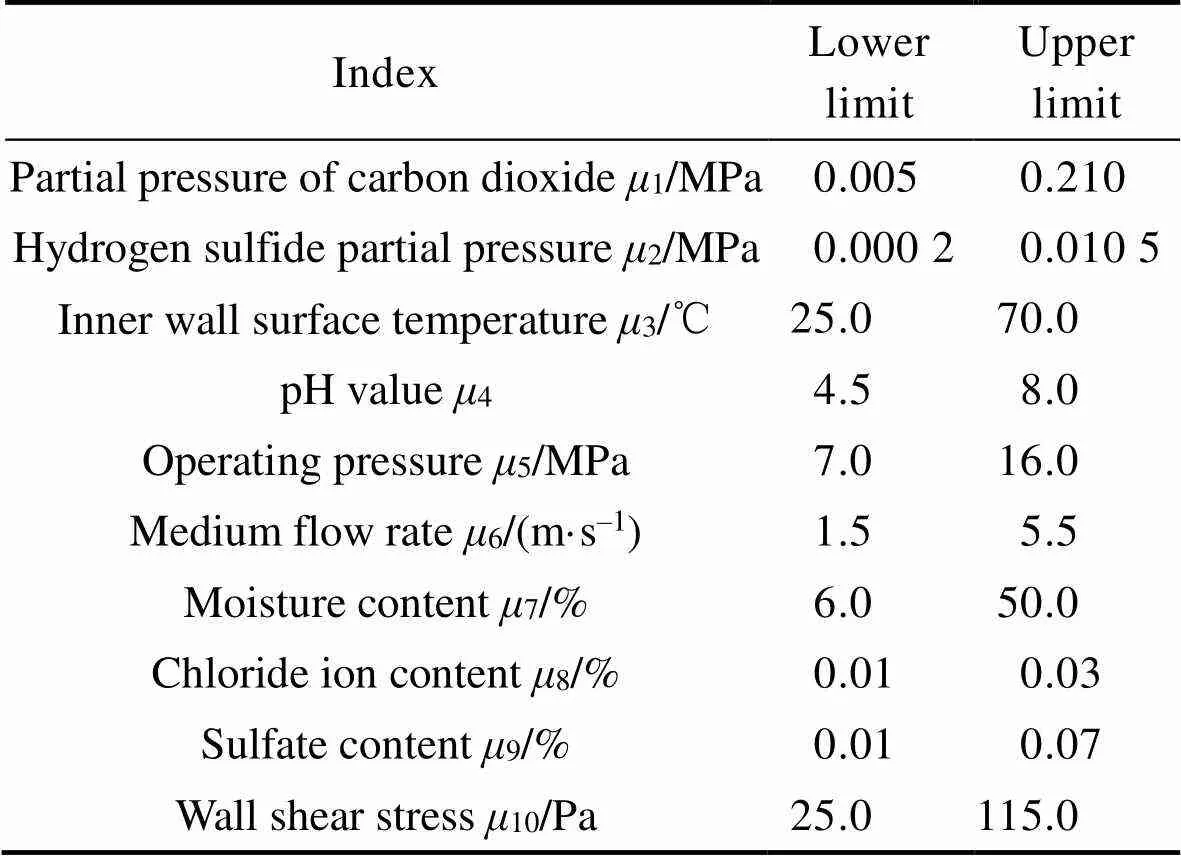
Tab.1 Application range of prediction model
3.3 腐蚀速率预测结果分析
将训练好的IGWO–ELM对其余50组腐蚀数据进行测试。为体现IGWO–ELM预测模型的准确性,选用ELM、PSO–ELM、SSA–ELM对相同数据进行预测分析,模型的预测结果对比见图4,预测相对误差对比见图5。表4为分别用高斯核函数和小波核函数进行特征提取后,4个预测模型的相对误差分析结果。
表2 盐穴储气库注采管柱的内腐蚀数据
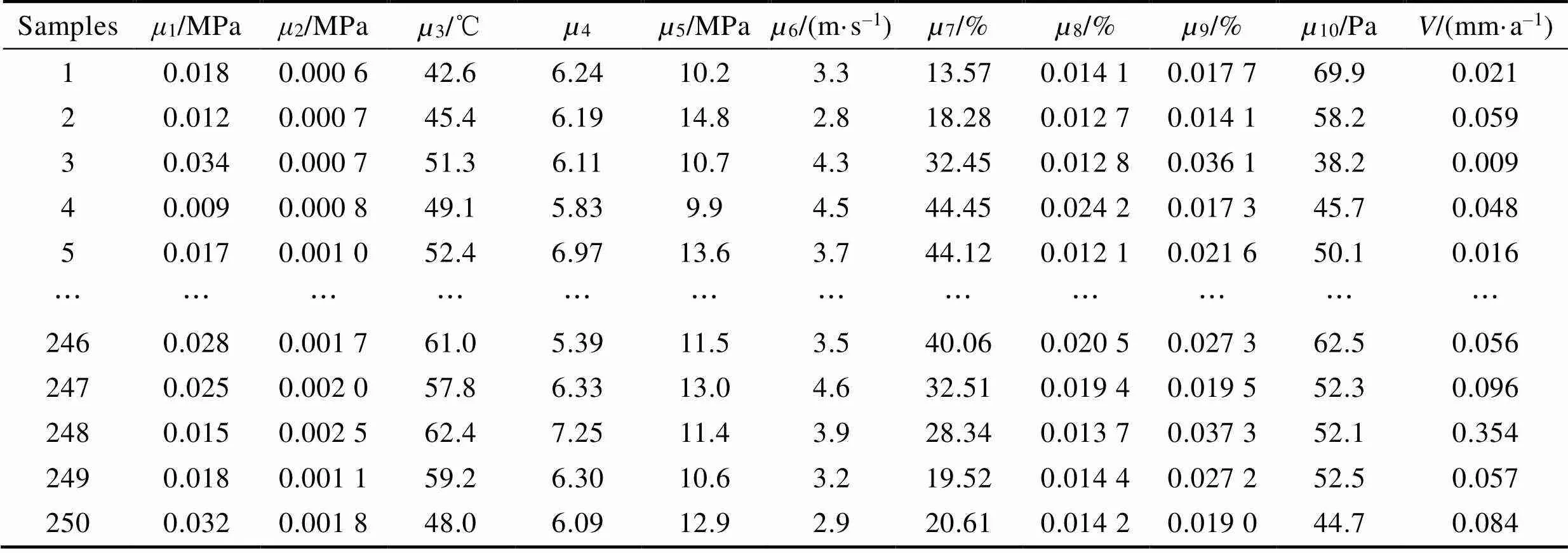
Tab.2 Internal corrosion data of injection and production string in salt cavern gas storage
表3 特征变量提取
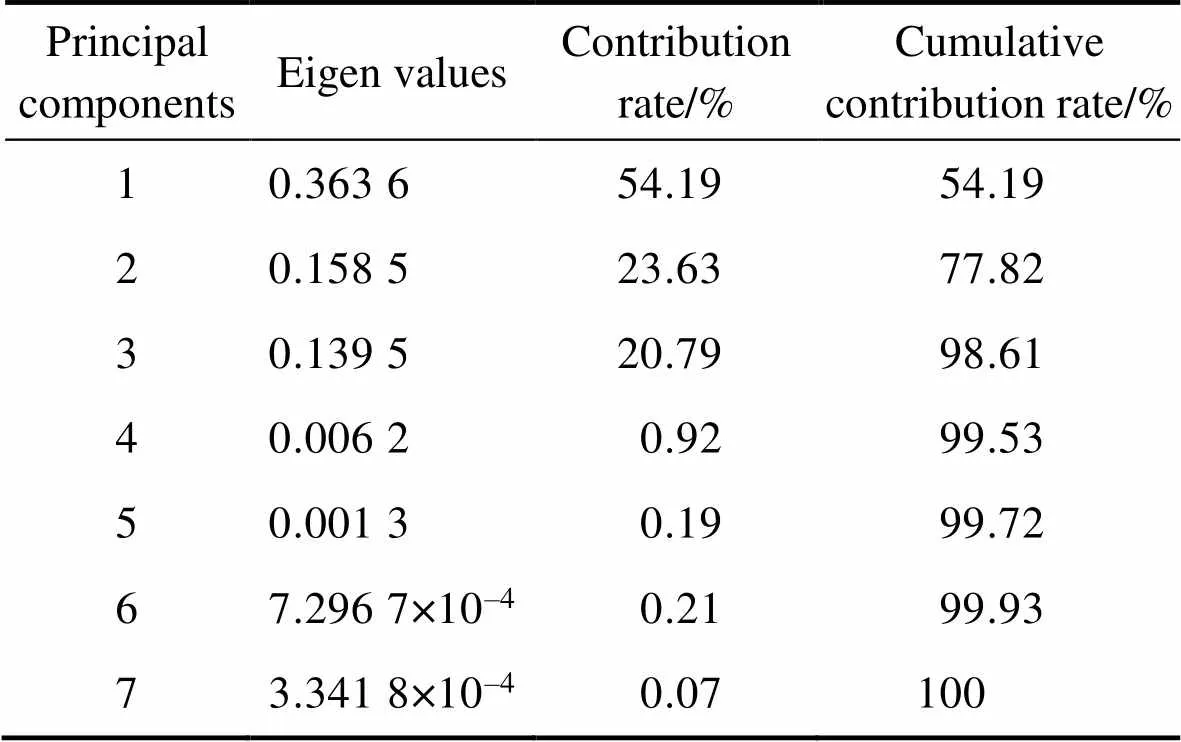
Tab.3 Extraction of characteristic variables

图3 IGWO–ELM适应度收敛曲线
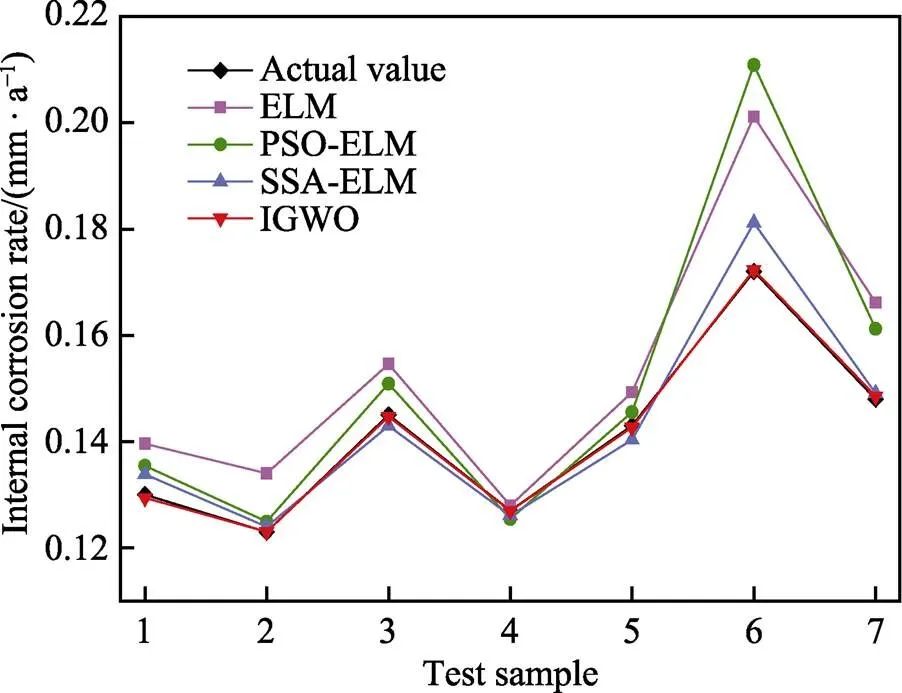
图4 预测结果对比图
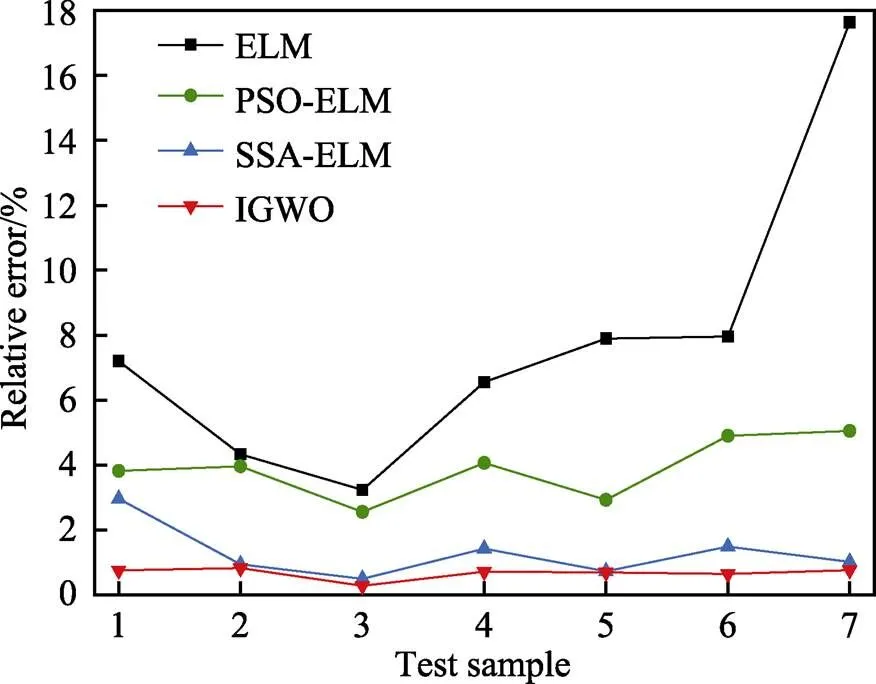
图5 预测相对误差对比图
表4 不同核函数的预测结果相对误差分析
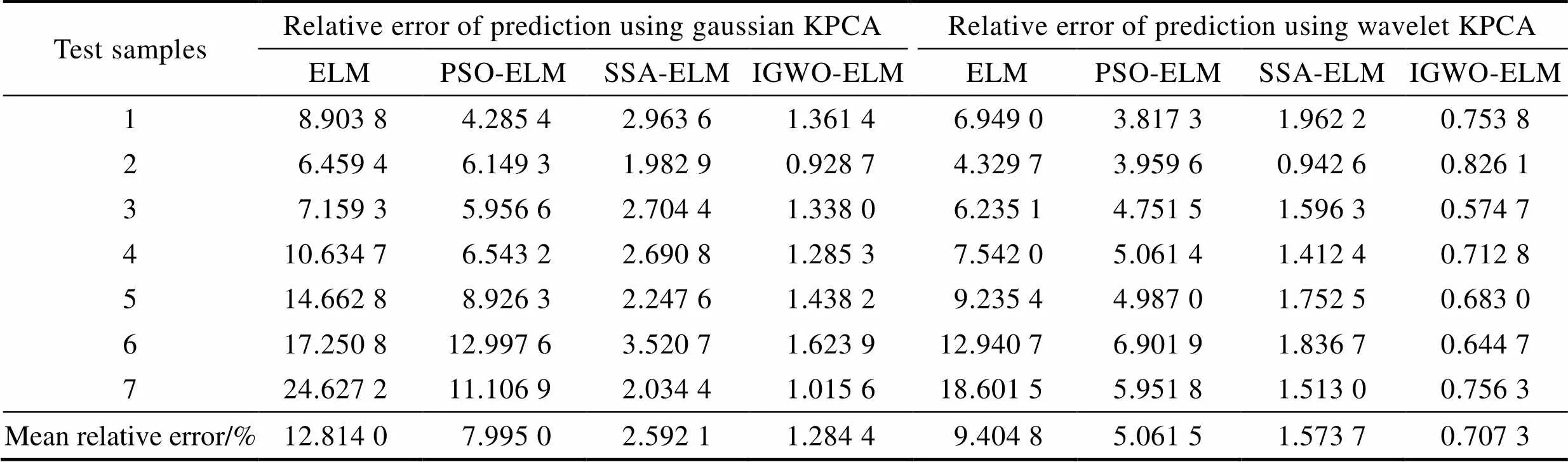
Tab.4 Relative error analysis of prediction results of different kernel functions
由图4可知,相较于ELM、PSO–ELM和SSA– ELM,IGWO–ELM的预测结果更接近于实际值,拟合程度更高。分析图5和表4可知,经小波KPCA的模型预测性能均优于经高斯KPCA的模型,且经小波KPCA的ELM、PSO–ELM、SSA–ELM、IGWO– ELM的平均相对误差分别为9.404 8%、5.061 5%、1.573 7%、0.707 3%,相较于经高斯KPCA的平均相对误差分别降低了3.409 2%、2.933 5%、1.018 4%、0.577 1%,说明小波KPCA–IGWO–ELM模型的性能提升较大。为验证模型的预测效果,采用2.4节中的3项指标分别对4种预测模型进行评价分析,结果见表5。
由表5可知,IGWO–ELM的2高达0.992 5,其RMSE和MAPE分别比ELM降低了0.116 6、16.175 1%,比PSO–ELM降低了0.073 2、8.410 6%,比SSA–ELM降低了0.072 3、4.656 7%。在一定工况条件适用范围内,说明IGWO–ELM模型的性能优良,盐穴储气库注采管柱内腐蚀速率的预测结果更精准。
表5 模型性能评价指标对比
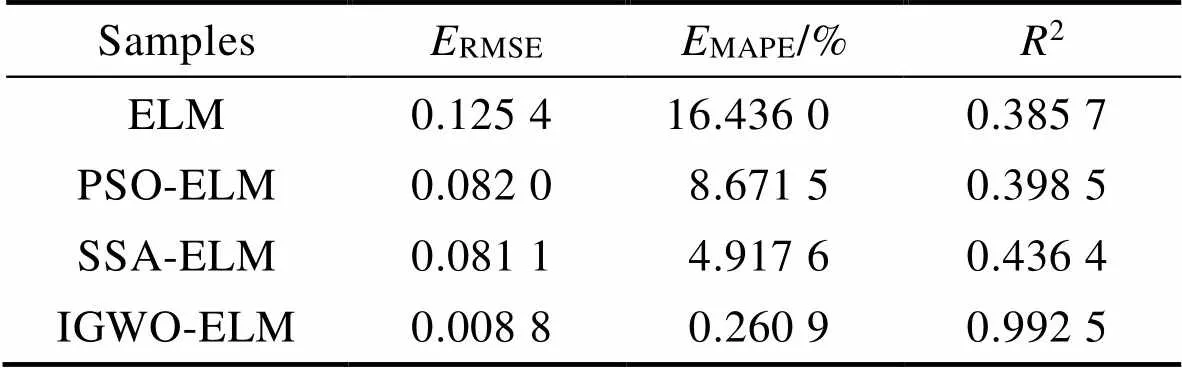
Tab.5 Comparison of model performance evaluation indicators
4 结论
1)利用小波KPCA提取出包含98.61%腐蚀信息的3项主成分,基于此的预测结果相对误差最小。经小波KPCA的ELM、PSO–ELM、SSA–ELM、IGWO– ELM的平均相对误差分别为9.404 8%、5.061 5%、1.573 7%、0.707 3%,相较于经高斯KPCA的平均相对误差分别降低了3.409 2%、2.933 5%、1.018 4%、0.577 1%。
[1] 魏国齐, 郑雅丽, 邱小松, 等. 中国地下储气库地质理论与应用[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(12): 1519-1530.
WEI Guo-qi, ZHENG Ya-li, QIU Xiao-song, et al. Geological Theory and Application of Underground Gas Storagein China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 1519-1530.
[2] 完颜祺琪, 丁国生, 赵岩, 等. 盐穴型地下储气库建库评价关键技术及其应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(5): 111-117.
WANYAN Qi-qi, DING Guo-sheng, ZHAO Yan, et al. Key Technologies for Salt-Cavern Underground Gas Storage Construction and Evaluation and Their Application[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(5): 111-117.
[3] WANG Tong-tao, YANG Chun-he, CHEN Jia-song, et al. Geomechanical Investigation of Roof Failure of China's First Gas Storage Salt Cavern[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 243: 59-69.
[4] LIU Wei, CHEN Jie, JIANG De-yi, et al. Tightness and Suitability Evaluation of Abandoned Salt Caverns Served as Hydrocarbon Energies Storage under Adverse GeologicalConditions (AGC)[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 178: 703-720.
[5] CHEN Xiang-sheng, LI Yin-ping, LIU Wei, et al. Study on Sealing Failure of Wellbore in Bedded Salt Cavern Gas Storage[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(1): 215-228.
[6] 张新生, 叶晓艳. 不同初始条件的UGM(1,1)管道腐蚀预测建模研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(3): 63-69.
ZHANG Xin-sheng, YE Xiao-yan. Study on UGM(1,1) Modeling for Prediction of Pipes Corrosion under Different Initial Conditions[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(3): 63-69.
[7] CHEN Xiao-xu, WANG Lin-yuan, HUANG Zhi-yu. Principal Component Analysis Based Dynamic Fuzzy Neural Network for Internal Corrosion Rate Prediction of Gas Pipelines[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 3681032.
[8] 王晓敏, 骆正山, 高懿琼, 等. 基于多种失效模式及其随机相关性的地下管道腐蚀可靠性分析[J]. 表面技术, 2022, 51(4): 202-210.
WANG Xiao-min, LUO Zheng-shan, GAO Yi-qiong, et al. Reliability Analysis of Corrosion Affected Underground Steel Pipes Considering Multiple Failure Modes and Their Stochastic Correlations[J]. Surface Technology, 2022, 51(4): 202-210.
[9] 谢飞, 李佳航, 王新强, 等. 天然气管道CO2腐蚀机理及预测模型研究进展[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(10): 109-118.
XIE Fei, LI Jia-hang, WANG Xin-qiang, et al. Research Progress on CO2Corrosion Mechanism and Prediction Model of Natural Gas Pipelines[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(10): 109-118.
[10] 凌晓, 徐鲁帅, 余建平, 等. 基于改进的BP神经网络的输油管道内腐蚀速率预测[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2021, 40(2): 124-127.
LING Xiao, XU Lu-shuai, YU Jian-ping, et al. Prediction of Corrosion Rate in Oil Pipeline Based on Improved BP Neural Network[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2021, 40(2): 124-127.
[11] 骆正山, 赵乐新, 王小完. 基于动态贝叶斯网络的海底管道点蚀疲劳损伤失效模型研究[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(1): 269-275.
LUO Zheng-shan, ZHAO Le-xin, WANG Xiao-wan. Failure Model for Pitting Fatigue Damaged Pipeline of Subsea Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network[J]. Surface technology, 2020,49(1): 269-275.
[12] PENG Shan-bi, ZHANG Zhe, LIU En-bin, et al. A New Hybrid Algorithm Model for Prediction of Internal Corrosion Rate of Multiphase Pipeline[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 85: 103716.
[13] 曲志豪, 唐德志, 胡丽华, 等. 基于优化随机森林的H2S腐蚀产物类型及腐蚀速率预测[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(3): 42-49.
QU Zhi-hao, TANG De-zhi, HU Li-hua, et al. Prediction of H2S Corrosion Products and Corrosion Rate Based on Optimized Random Forest[J]. Surface Technology, 2020, 49(3): 42-49.
[14] SCHÖLKOPF B, SMOLA A, MÜLLER K R. Nonlinear Component Analysis as a Kernel Eigenvalue Problem[J]. Neural Computation, 1998, 10(5): 1299-1319.
[15] FEZAI R, MANSOURI M, TAOUALI O, et al. Online Reduced Kernel Principal Component Analysis for Process Monitoring[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 61: 1-11.
[16] HU Qin, QIN Ai-song, ZHANG Qing-hua, et al. Fault Diagnosis Based on Weighted Extreme Learning Machine with Wavelet Packet Decomposition and KPCA[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(20): 8472-8483.
[17] BRO R, SMILDE A K. Principal Component Analysis[J]. Anal Methods, 2014, 6(9): 2812-2831.
[18] JOLLIFFE I T, CADIMA J. Principal Component Analysis: A Review and Recent Developments[J]. Philosophical Transactions Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2016, 374(2065): 20150202.
[19] 迟恩楠, 李春祥. 基于优化组合核和Morlet小波核的LSSVM脉动风速预测方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(18): 52-57.
CHI En-nan, LI Chun-xiang. Forecast of Fluctuating WindVelocity Using LSSVM with Optimized Combination Kernel and Morlet Wavelet Kernel[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(18): 52-57.
[20] HUANG Guang-bin, ZHU Qin-yu, SIEW C K. Extreme Learning Machine: Theory and Applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1-3): 489-501.
[21] HUANG Guang-bin, ZHOU Hong-ming, DING Xiao- jian, et al. Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multiclass Classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Part B, Cybernetics: A Publication of the IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Society, 2012, 42(2): 513-529.
[22] HUANG Gao, HUANG Guang-bin, SONG Shi-ji, et al. Trends in Extreme Learning Machines: A Review[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 32-48.
[23] NADIMI-SHAHRAKI M H, TAGHIAN S, MIRJALILI S. An Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer for Solving Engineering Problems[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2021, 166: 113917.
[24] MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, LEWIS A. Grey Wolf Optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61.
[25] 骆正山, 秦越, 张新生, 等. 基于LASSO-WOA-LSSVM的海洋管线外腐蚀速率预测[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(5): 245-252.
LUO Zheng-shan, QIN Yue, ZHANG Xin-sheng, et al. Prediction of External Corrosion Rate of Marine Pipelines Based on LASSO-WOA-LSSVM[J]. Surface Technology, 2021, 50(5): 245-252.
Research on Prediction Model of Internal Corrosion Rate in Injection and Production String of Salt Cavern Gas Storage
,,,
(School of Management, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an 710055, China)
The injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage has been in a complex underground environment for a long time, making it susceptible to a variety of corrosion factors. This work aims to improve the prediction accuracy of the corrosion rate in the injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage, thereby ensuring the health and operational safety of these facilities. To accomplish the above objectives, the solution proposed is to establish an internal corrosion rate prediction model based on wavelet kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) and an extreme learning machine (ELM) after improved gray wolf optimization (IGWO).First of all, in the actual operation data of the injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage, 10 indicators with larger corrosion factors are selected, such as: partial pressure of carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide partial pressure, inner wall surface temperature, etc. Subsequently, the internal corrosion index system of the injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage was established.Secondly, the wavelet KPCA is used to extract the key features that affect the internal corrosion rate of the injection and production string, and then IGWO is used to iteratively optimize the input weight matrix and hidden layer threshold of the ELM model, and stop the loop until the termination condition is met. Furthermore, a prediction model of corrosion rate in the injection and production string of IGWO-ELM salt cavern gas storage is established. Finally, numerical simulation and simulation calculation are carried out in MATLAB software, and the prediction errors of the IGWO-ELM model are compared with the three models of ELM, PSO-ELM and SSA-ELM respectively. The research results show that the wavelet KPCA effectively extracts the three principal components that contain 98.61% of the original information in the corrosion data of the injection-production pipe string of the salt cavern gas storage.Applying the reconstructed corrosion data to the ELM, PSO-ELM, SSA-ELM, and IGWO-ELM models, their average relative errors are 9.404 8%, 5.061 5%, 1.573 7%, and 0.707 3%. The prediction results of the IGWO-ELM model are in good agreement with the actual values.The root mean square error of the constructed IGWO-ELM model is 0.008 8, the average absolute percentage error is 0.260 9%, and the coefficient of determination (2) is as high as 0.992 5. Its prediction result is better than the other three comparison models. The kernel principal component analysis with the introduction of wavelet kernel function has an excellent ability to extract corrosion characteristics of the injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage. Within the applicable range of certain working conditions, the established IGWO-ELM model can effectively predict the internal corrosion rate of the injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage.It not only provides a reference basis for the integrity evaluation and risk warning of the injection and production system of the salt cavern gas storage, but also provides new ideas and methods for the corrosion study of the injection and production string of the salt cavern gas storage.
salt cavern gas storage; injection and production string; corrosion rate prediction; principal component analysis (KPCA); improved gray wolf optimization (IGWO); extreme learning machine (ELM)
TG174
A
1001-3660(2022)06-0283-08
10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2022.06.026
2021–04–28;
2021–12–07
2021-04-28;
2021-12-07
国家自然科学基金(41877527);陕西省社科基金(2018S34)
National Natural Science Foundation of China (41877527); Shaanxi Provincial Social Science Fund (2018S34)
骆正山(1969—),男,博士,教授,主要研究方向为油气管道风险评估。
LUO Zheng-shan (1969-), Male, Doctor, Professor, Research focus: oil and gas pipeline risk assessment.
骆正山, 欧阳长风, 王小完, 等.盐穴储气库注采管柱内腐蚀速率预测模型研究[J]. 表面技术, 2022, 51(6): 283-290.
LUO Zheng-shan, OUYANG Chang-feng, WANG Xiao-wan, et al. Research on Prediction Model of Internal Corrosion Rate in Injection and Production String of Salt Cavern Gas Storage[J]. Surface Technology, 2022, 51(6): 283-290.
责任编辑:万长清
