Study on Weed Control and Safety of Tembotrione-Atrazine Tank Mixture in Spring Maize Fields
2022-06-18SHAOJialiSUNJinjunDUANGuifang
SHAO Jia-li, SUN Jin-jun, DUAN Gui-fang
1. CAC Shanghai International Trading Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200335, PRC;
2. GreenTech Laboratory, Shanghai 200335, PRC
Abstract This study aimed to explore the effect of 5% tembotrione oil dispersion(OD)-38% atrazine suspension concentrate (SC) tank mixture on the weeds in spring maize fields and the safety of the mixture. To be specific, randomized block design was adopted for the field experiments. The results showed that the application of tankmixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2 and 38% atrazine SC at 570 g a.i./hm2 and the mixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2 and 38% atrazine SC at 1 140 g a.i./hm2 respectively controlled 94.7%~96.3% and 94.0%~96.3% of the grass weeds, 94.7%~96.0% and 93.7%~95.7% fresh weight of grass weeds, 95.3%~96.3%and 93.3%~97.3% of broadleaf weeds, and 94.7%~96.0% and 93.3%~96.3% fresh weight of broadleaf weeds. The efficacy was better than that of the 5% tembotrione alone and the control herbicide and no phytotoxicity of the mixtures was identified.The tank mixture of tembotrione and atrazine should be promoted in the spring maize field for weed control and the recommended dosages were 90 g a.i./hm2 for 5%tembotrione and 570 g a.i./hm2 for 38% atrazine.
Key words 5% Tembotrione OD; 38% Atrazine SC; Maize; Weed control; Crop safety
1. Introduction
Tembotrione, a triketone herbicide developed by Bayer in 2007, is exceptionally tolerated by maize. As a 4-HPPD inhibitor[1], it can block the biosynthesis of isoprenoquinone in plants, thus resulting in plant chlorosis, discoloration, tissue necrosis, and eventually death within two weeks[2]. Moreover, the resistance to tembotrione evolves slowly in weeds, as only the US has confirmed two weeds in the international herbicide resistance database since the advent of the herbicide[3].Tembotrione can control a broad spectrum of weeds, such as the grass and broadleaf weeds. It is highly resistant to rain, and with short residual period in soil, it allows for the free choice of subsequent crops. At the moment, this product has been registered and marketed in some countries, and its global sales in 2018 totaled 231 million US dollars[4],making it the second largest product among all HPPD-inhabiting herbicides. Atrazine, a selective systemic herbicide that acts as both a pre-emergent and post-emergent control, prevents annual weeds and broadleaf weeds in maize field. Moreover, it can inhibit some perennial weeds. However, it remains in field for quite a long period of time, and long-term and large-scale use will cause soil and water pollution[5]. Therefore, it is suggested that atrazine mix with other herbicides to reduce the dosage and thus the residue in soil.
Tembotrione has not been registered and promoted in China. According to previous laboratory tests, the tank mixture of tembotrione and atrazine (at active ingredient ratios of 1 ∶1~1 ∶15) has obvious synergy against some grass weeds and broadleaf weeds. In this study, field experiment was carried out to explore and determine the weed control and crop safety of the tank mixture of tembotrione and atrazine, which was expected to lay a theoretical basis for the development and application of tembotrione products.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Agents
Agents were 5% tembotrione OD (Jiangxi Tianyu Chemical Co., Ltd.), 38% atrazine SC (Jinan Tianbang Chemical Co., Ltd.), and 38% nicosulfuron·atrazine OD (Suzhou Jiahui Chemical Co., Ltd.).
2.2. Maize varieties
Nendan 19 in Heilongjiang test site, Jidan 52 in Jilin test site, and Hengyu 299 in Liaoning test site were used as test varieties.
2.3. Fields
Field plots with flat terrain and uniform soil properties and fertility were selected. Weeds were rampant in these plots and the soils were not treated in blocks. In Heilongjiang test site, the experiment was conducted in Fularji District of Qiqihar City where maize was sown on May 13thand herbicide was applied on June 5th. The annual grass weeds there mainly includedSetaria viridis(L.) Beauv. andPanicum miliaceumvar.ruderaleKit, and the annual broadleaf weeds were dominated byChenopodium albumL.,Amaranthus retroflexusL., andIpomoea trilobaL. As for the experiment in Gongzhuling City, Jilin Province, maize was sown on May 1stand herbicide was applied on May 27th. In this test site,the annual grass weeds were mainlyEchinochloa crusgalli,Eriochloa villosa(Thunb.) Kunth,etc.,and the annual broadleaf weeds mainly includedChenopodium albumL. andAbutilon theophrastiMedicus. The third test site was in Shenbei New District, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, in which maize was sown on April 30thand herbicide was applied on May 21st. The dominant annual grass weeds were wild millet and barnyard grass, and the annual broadleaf weeds were mainly piemarker and other weeds.Herbicides were applied at 3~5-leaf stage (maize),2~5-leaf stage (grass weeds), and 2~6-leaf stage(broadleaf weeds) respectively at the three test sites.
2.4. Test design
Seven treatments were designed: 5% tembotrione alone at 75, 90, and 105 g a.i./hm2, 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2+38% atrazine SC at 570 g a.i./hm2,5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2+38% atrazine OD at 1 140 g a.i./hm2, control treatment of 30%nicosulfuron·atrazine OD 63+477 g a.i./hm2, and blank control, with 4 replicates for each treatment, plot area of 20 m2, and no tillage during the test. Power sprayer(pressure: 0.3 MPa, water consumption: 225 L/hm2)with fan-shaped nozzle was used for the herbicide application.
2.5. Field investigation
Weed control was observed 15 d after the herbicide application, and varieties and number of weeds were investigated 30 d after herbicide application with the numerical survey method. To be specifics, 3 areas (0.25 m2each) were selected at each plot. All the weeds in each area were removed and the fresh weight of the aboveground parts was measured.
Weed control=(weed number or fresh weight in the blank control-weed number or fresh weight in each treatment)/weed number or fresh weight in the blank control×100%.
Maize plants were respectively observed 7, 15,and 30 d after herbicide application to identify any symptom caused by the herbicides. In case of any damage, the outcome or the recovery was recorded.
2.6. Data analysis
DPS v16.05 was employed for statistical analysis, and Duncan’s new multiple range method for the test of the significance of differences.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Maize safety
The leaf color and plant height of maize 7, 15,and 30 d after herbicide application were the same with blank control. No deformity, chlorosis, dead seedlings, or other diseases were found.
3.2. Weed control of the tank mixture of tembotrione and atrazine in maize fields 15 d after application
Weed control was different among the treatments 15 d after application (Table 1). The 5% tembotrione OD at 75~105 g a.i./hm2controlled 73.3%~88.3% of the grass weeds and 76.0%~86.7% of the broadleaf weeds, respectively, and the control rates achieved by the tank mixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine SC at 570~1 140 g a.i./hm2were 91.7%~95.0% and 93.3%~95.0%, respectively. The 30% nicosulfuron·atrazine OD 63+477 g a.i./hm2inhibited 81.7%~83.3% of the grass weeds and 71.7%~73.3% of the broadleaf weeds, respectively. The weed control of the tank mixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine SC at 570~1 140 g a.i./hm2was obviously better than that of 5% tembotrione OD at 75~105 g a.i./hm2or that of 30% nicosulfuron·atrazine OD 63+477 g a.i./hm2. The control effect of 30% nicosulfuron·atrazine OD 63+477 g a.i./hm2was similar to that of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2but better than that of 5% tembotrione OD at 75 g a.i./hm2.
3.3. Weed and weed fresh weight control of the tank mixture of tembotrione and atrazine in maize fields 30 d after application
The control of weeds and weed fresh weight in the treatments 30 d after application was basically the same as that 15 d after application. The weed control effect of the tank mixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine SC at 570~1 140 g a.i./hm2was significantly higher than that of 5%tembotrione OD 75~105 g a.i./hm2and that of 30%nicosulfuron·atrazine OD 63+477 g a.i./hm2. Their control effect on major grass weeds and broadleaf weeds in spring maize fields was excellent and longlasting. Thus, tembotrione and atrazine had obvious synergistic effect and the mixtures were safe for maize. The mixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine at 570 g a.i./hm2showed no significant difference from the mixture of 5%tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine at 1 140 g a.i./hm2. For the sake of low cost and environmental protection, the tank mixture of 5%tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine at 570 g a.i./hm2was recommended.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Tembotrione, a selective herbicide, controlslimited spectrum of weeds. It is particularly effective against crab grass, barnyard grass, goose grass,S. viridis,A. theophrasti, and redroot pigweed in maize field, but has poor control effect on purslane and copperleaf herb[6]. Atrazine, a commonly used herbicide in maize field in China, can also improve the activity of plant stem and soil. However, the longterm and large-scale use of atrazine will reduce its control effect on some weeds. Some atrazine-resistant weeds appear in maize fields, but atrazine has strong mixability and obvious synergistic effect[7]. There have been reports on the mixtures of tembotrione and atrazine, tembotrione and nicosulfuron, and tembotrione and atrazine+nicosulfuron[7-8]. Tembotrione can be applied at any time before the 8-leaf stage of maize, which is thus should be further promoted in maize field in China. Maize field is home to over 30 common weed varieties , making it difficult to control all these weeds with only one herbicide. Tembotrione and atrazine were different in the mechanism of action, which showed synergy against grass weeds.Moreover, the mixture of the two not only expanded the spectrum of the target weeds but also reduced the dosage of atrazine and extended the life cycle of the herbicide[9]. This study concluded the synergy of the two. Mixed with atrazine, tembotrione showed faster onset, longer effect, and broader target weed spectrum.In addition, the dosage of atrazine can be reduced,thus relieving the pollution to the soil and water. To sum up, the tank mixture of 5% tembotrione OD at 90 g a.i./hm2and 38% atrazine SC at 570~1 140 g a.i./hm2was safe for maize when applied at the 3~5-leaf stage of spring maize and at the 2~6-leaf stage of weeds, which presented ideal control effect on the annual grass weeds and broadleaf weeds in spring maize field.
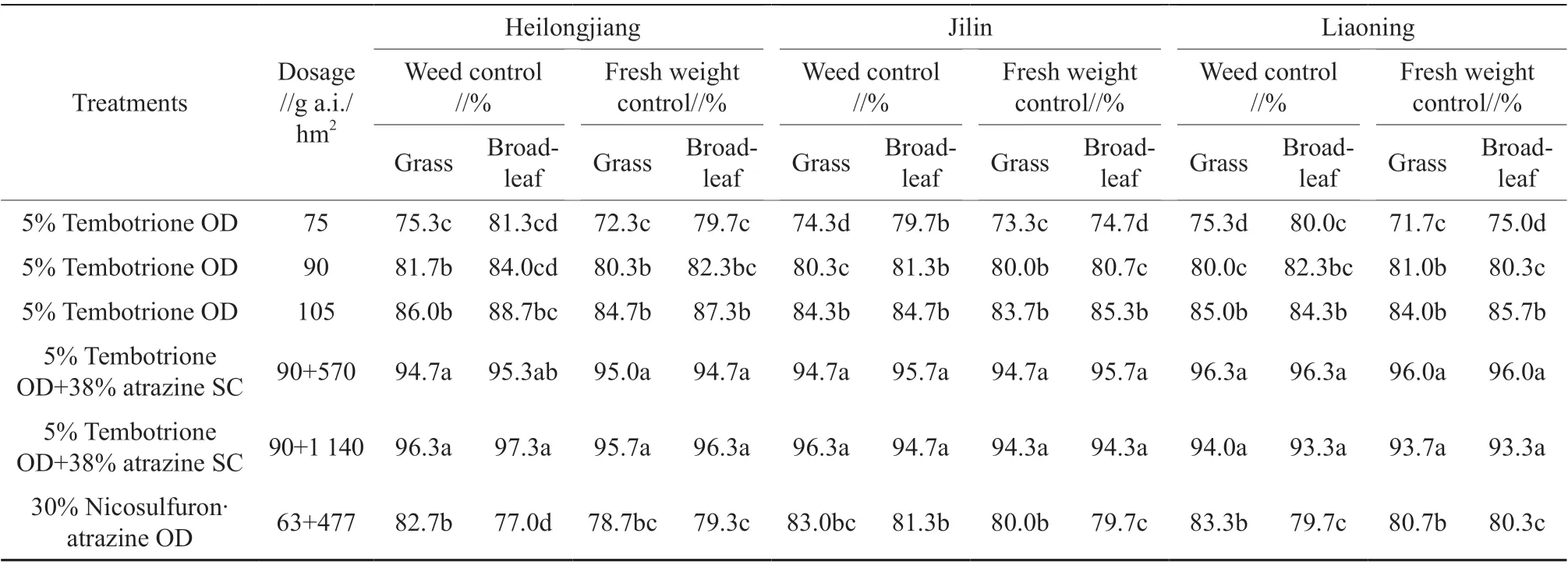
Table 2 Control of the tank mixture of tembotrione and atrazine on weed and weed fresh weight in maize field 30 d after application
The combined use of tembotrione and atrazine had a good market prospect. In the future, multi-point verification should be performed on the proportions of tembotrione and atrazine in the control of more target weeds, so as to provide technical support for the development and application of tembotrione products.
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Different Cultivation Media and Periods on the Content of Main Active Components of Cordyceps militaris Strain QC04
- TIB for Micropropagation and the Relationship between Anthocyanins and Chlorophyll of Strawberry Seedlings
- Control Effects of Mixture of Metamifop and Cyhalofopbutyl on Annual Weeds Barnyard Grass in Directseeding Paddy Field
- Mechanism of Solid State Fermentation in Reducing Free Gossypol in Cottonseed Meal and the Effects on the Growth of Broiler Chickens
- Analysis on Interaction Effects Between Variety and Site of Silage Maize Regional Test in Guizhou Province
- Effects of Different Intercropping Patterns on Population Yield and Benefit of Fresh Maize and Mung Bean
