基于自适应布谷鸟搜索和扰动观察法的光伏最大功率点跟踪
2022-04-19商立群
商立群,李 帆
基于自适应布谷鸟搜索和扰动观察法的光伏最大功率点跟踪
商立群,李 帆
(西安科技大学电气与控制工程学院,陕西 西安 710054)
当光伏阵列板暴露在不均匀的光线下时,功率电压(-)特性曲线会变为多峰,在这种情况下,传统的最大功率点跟踪(MPPT)算法将无法跟踪到正确的全局最大功率点(GMPP),而具有全局搜索能力的人工智能算法通常是高度参数化和复杂的。为了解决上述问题,提出了一种结合自适应布谷鸟搜索算法和扰动观察方法(ACS-P&O)的复合跟踪算法。该方法将布谷鸟搜索(CS)算法中的切换概率和Lévy飞行步长系数通过自适应调整,在跟踪早期,扩大算法的搜索范围。引入边界个体的处理策略,可进一步减少算法的迭代次数。该算法使系统更容易跳出局部最大功率点(LMPP),而在跟踪后期,算法精确运行在小范围内,提高了局部开发能力。扰动观察法(P&O)的加入缓解了系统位于GMPP附近时的功率振荡,稳定了输出。仿真结果表明,ACS-P&O复合算法能够适应环境变化的影响,并快速准确地跟踪GMPP。
光伏;MPPT;自适应布谷鸟搜索算法;扰动观察法;Lévy飞行;边界个体
0 引言
为防止环境恶化,响应国家“碳中和”可持续性战略目标,寻找替代性新能源成为当今社会的热点话题[1-3]。光伏能源在众多新能源中分布较广,清洁、高效、易获取,所以受到了广泛的关注。然而,光伏系统的能量转换率较低,输出通常具有非线性的特点。为了最大限度地利用光伏阵列输出的能量,使用最大功率跟踪技术(Maximum Power Tracking technology, MPPT)来减少有效功率的损失[4-6]。在目前的研究中,MPPT方法研究主要分为两类:传统算法和具有全局性的元启发算法。传统算法通常用于寻找光照条件均匀时光伏阵列输出特性曲线的单一峰值,如恒定电压法、扰动观察法(P&O)和增量电导法(Incremental Conductance, INC)[7-10]。恒定电压法的输出只是一个近似值,取决于原始电路的性能,所以通常与其他算法结合使用,以找到最佳解决方案。P&O法和INC法的控制逻辑简单,易于在工程实践中应用,但固定的步长不能适应环境的巨大变化。当光伏系统因云层、飞鸟等物体发生部分遮挡后,在部分遮挡条件(Partial Shading Conditions, PSC)下运行时,输出功率-电压曲线由单峰变为多峰,传统算法因无法跳出局部最大功率点(LMPP)而损失大量能量。
寻找多峰曲线对应的全局最大功率点(Global Maximum Power Point, GMPP)是目前国内外的研究热点[11-13]。常用的元启发算法有粒子群算法[14]、鲸鱼优化算法[15]、差分进化算法[16]、人工蜂群算法[17]等。文献[18]提出了一种结合粒子群和P&O的混合算法,根据电流、电压和功率的变化规律来确定PSC,只在PSC发生时使用PSO算法,在遮阴结束后使用P&O来跟踪系统,提高系统运行效率。文献[19]提出了一种跟踪GMPP的并行组合进化算法,首先使用遗传算法和差分进化算法分别在平行空间进行搜索,然后使用PSO在两个子种群中选择优势种群再继续更新。文献[20]将灰狼优化算法与P&O结合,可减少灰狼优化算法在-曲线上的搜索范围,使系统更快地收敛。文献[21]提出一种改进羊群算法,通过在原始算法的基础上加入反向种群及自适应策略来扩大算法的全局搜索性能,避免陷入局部最优。文献[22]提出了一种免疫萤火虫算法,通过免疫补充环节将较弱个体去除,可有效地提高算法收敛时间。
CS算法[23-24]是Yang和Deb在观察了布谷鸟群寻找其巢穴和繁殖的独特方式后于2009年提出的一种生物启发式算法。与其他优化算法相比,CS算法的初始化参数少,简单高效,运行速度快,所以非常适用于寻找光伏阵列的最大功率点。文献[25]提出了一种确定性CS算法,为克服CS算法的随机性问题,将原有计算方程中的随机数删去,使整个算法流程的结构参数更易调整。文献[26]将CS算法与黄金分割搜索(Golden Section Search, GSS)算法相结合,依靠CS算法的全局性首先定位在GMPP区域,然后切换到GSS算法继续跟踪。CS算法做为元启发算法会因其固有属性导致后期收敛精度较差,在运行前期也有陷入最优的可能性,因此本文首先对传统的CS算法进行改进,使其切换概率和步长系数具有自适应性,还增添了飞跃边界个体的处理条件,使算法在跟踪初期能够加速收敛,顺利跳出LMPP,当自适应布谷鸟搜索算法(Adaptive Cuckoo Search Algorithm, ACS)跟踪到GMPP附近时,算法切换到小步长的P&O继续跟踪,这样可以保证在跟踪后期功率振荡处于最小振幅状态。
1 光伏阵列建模分析
光伏电池的单二极管等效模型如图1所示[27]。

图1 光伏电池单二极管模型
在图1中,应用KVL可以得到光伏电池输出电流的表达式。

式中:是光伏电池的输出电流;ph是光生电流;d是二极管的反向饱和电流;是光伏电池的输出电压;s是串联等效电阻;p是并联等效电阻;是二极管的理想系数;T是热电压;s和p分别是串联和并联在光伏阵列中的单个电池数量。其中二极管的光生电流值和反向饱和电流值可以从式(2)和式(3)中得到。


式中:SC_STC和OC_STC分别是光伏阵列在标准环境下(= 25℃,= 1 000 W/m2)对应的短路电流和开路电压;和分别是电流和电压的温度系数;是光伏板接收的辐照度;STC是标准条件下的辐照度。
光伏电池的热电压可以用式(4)表示。

式中:是玻尔兹曼常数,其值通常为1.38×10-23J/K;是绝对温度;值为1.6×1019C。
光伏系统的输出特性通常是非线性的。在光伏系统的运行中,为了避免功率不匹配造成的“热斑效应”,通常会将一个旁路二极管与光伏电池并联起来。当系统处于PSC状态时,处于阴影部分的光伏电池元件并联的旁路二极管会导通,输出特性因此从单峰变为多峰,模块中的电流大小与接收的辐照度成正比。图2显示了当光照条件均匀和发生部分遮挡时,系统的功率-电压曲线的变化。可以注意到,当遮阳发生时,曲线发生了变化,三个峰值中的两个是LMPP,GMPP是唯一存在的。
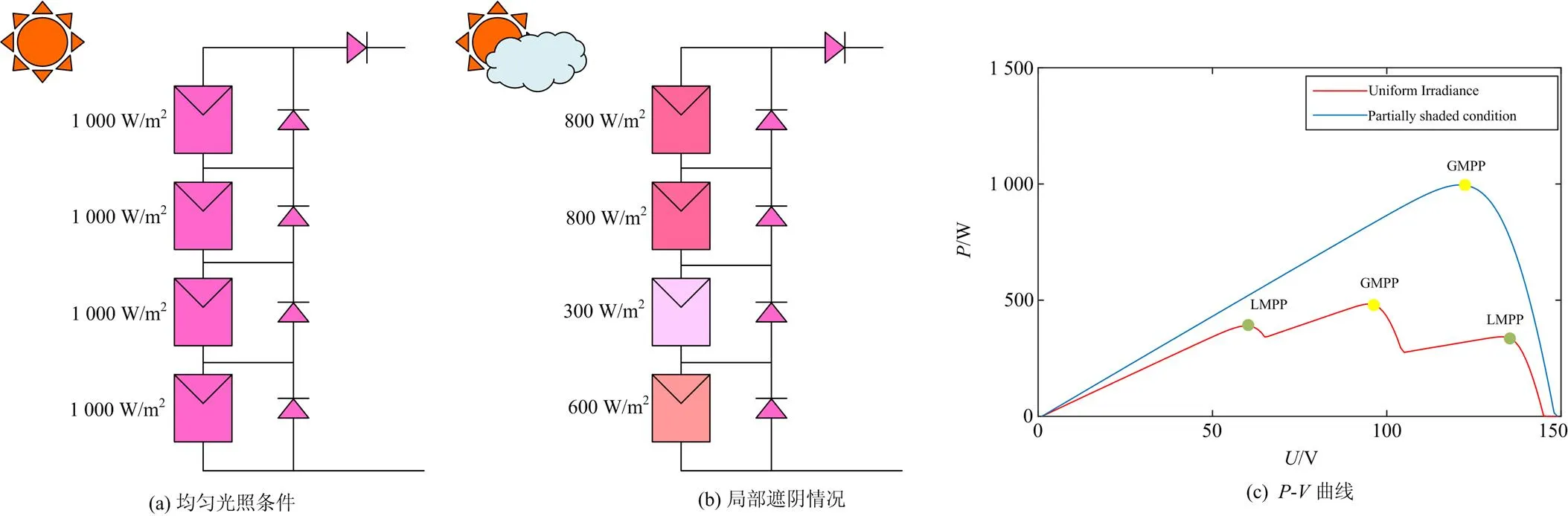
图2 均匀光照和部分阴影下的光伏串和P-V特性曲线
2 ACS-P&O算法在GMPPT中的应用
2.1 布谷鸟搜索算法
布谷鸟种群在繁殖时不建造自己的巢穴,而是将卵产在其他宿主鸟建造的巢里,由宿主鸟代替孵化。然而,如果宿主鸟发现卵是外来的,它将放弃这些卵或重新建造一个新的巢。为了便于建模,提出了以下三个理想规则。
(1) 布谷鸟在繁殖时随机找到一个寄生巢穴后只产一个卵。
(2) 具有最佳质量卵(最佳适应度值)的寄生巢穴被保留到下一代。
(3) 可选择的寄生巢穴的数量是固定的,宿主鸟将有a(0≤a≤1)的概率发现该卵为外来卵。
为了获得最佳的寄生巢穴,CS算法需要不断地更新位置,然后进行比较,在多次迭代过程中找到对应于最佳适配度的解决方案。CS算法有两种更新位置的方式:偏好局部随机游动与全局Lévy飞行。在布谷鸟把卵放在寄生巢穴中后,宿主鸟有一个发现卵的概率a,每个巢对应一个随机数r,如果r>a,则寄生巢穴被宿主发现并丢弃,此时需要用偏好局部随机游动更新巢穴的位置,更新公式为

全局Lévy飞行的更新公式为



2.2 自适应布谷鸟搜索算法
1) 自适应切换概率
在CS算法中,只有当r>a时,偏好随机游动位置更新方法才会被激活,而原算法通常对a取固定值0.25,这使得算法在整个迭代期中,偏好随机游动出现的概率相同。为了更准确地找到全局峰值,算法在迭代初期需要有良好的全局探索能力,以便跳出LMPP,而在算法运行的后期需要提高局部开发能力,使系统运行更加稳定。根据这一要求,本文提出了自适应切换概率a。在算法运行初期,较小的a值可以增加偏好随机游动的发生概率,使搜索范围增大;在算法运行后期,较小的a可以通过缩小搜索范围来提高精度,加速收敛。自适应切换概率的建议公式为

式中:为当前迭代次数;为最大迭代次数。a的变化区间为0.2~0.54,可以适应算法在搜索过程中的探索和开发需要。
2) Lévy飞行的自适应步长系数
从式(6)中可以看出,当布谷鸟通过Lévy飞行寻找寄生巢时,步长系数可以影响算法的搜索范围。当步长值较大时,寻找鸟巢的范围可以增加,使算法更容易跳出局部最优。当值较小时,可产生的寄生巢的范围会减少,算法可以在小范围内更快地找到最优解。在原来的CS算法中,通常以固定值的形式存在,这就不能平衡算法在早期阶段的探索和后期开发的需要。本文提出了Lévy飞行的自适应步长系数,以提高全局优化求解的能力。改动公式为

本文提出的自适应步长系数从1到0.6非线性递减,使算法在运行初期有较大的搜索空间,防止在局部最优处收敛,并在算法后期减少可搜索空间,有效提高运行精度。
3) 边界个体的处理
在原始CS算法中,当检测到布谷鸟飞离系统设定边界值时,会令飞离的个体停留在边界值处。尽管此方法可在一定程度上限制搜索范围的无限扩大,但停留在边界的个体到达最优解处仍需要进行多次的迭代,本文为提高收敛速度,增强算法的全局性能重新设定了边界处理条件:当有个体值大于系统的搜索空间上界,或小于系统的搜索空间下界,则令其返回目前迭代最优值与边界值中间的随机位置,新的搜索路径使个体更易接近最优值处,也有助于算法的全局寻优能力,其公式可表示为

式中,与均表示为[0,1]中可能出现的随机数。
2.3 算法性能验证
生物启发式算法因自身特点问题会存在很强的随机性,为了验证改进算法针对多种情况均有良好的适用性,选取4个国际通用的基准测试函数来对CS算法与ACS算法进行对比测试,基准函数的基本信息如表1所示。将函数的维度设置为30,种群数为100,最大迭代次数设置了400次,图3中列出了在算法运行20次后目标值的箱线图。

表1 基准测试函数
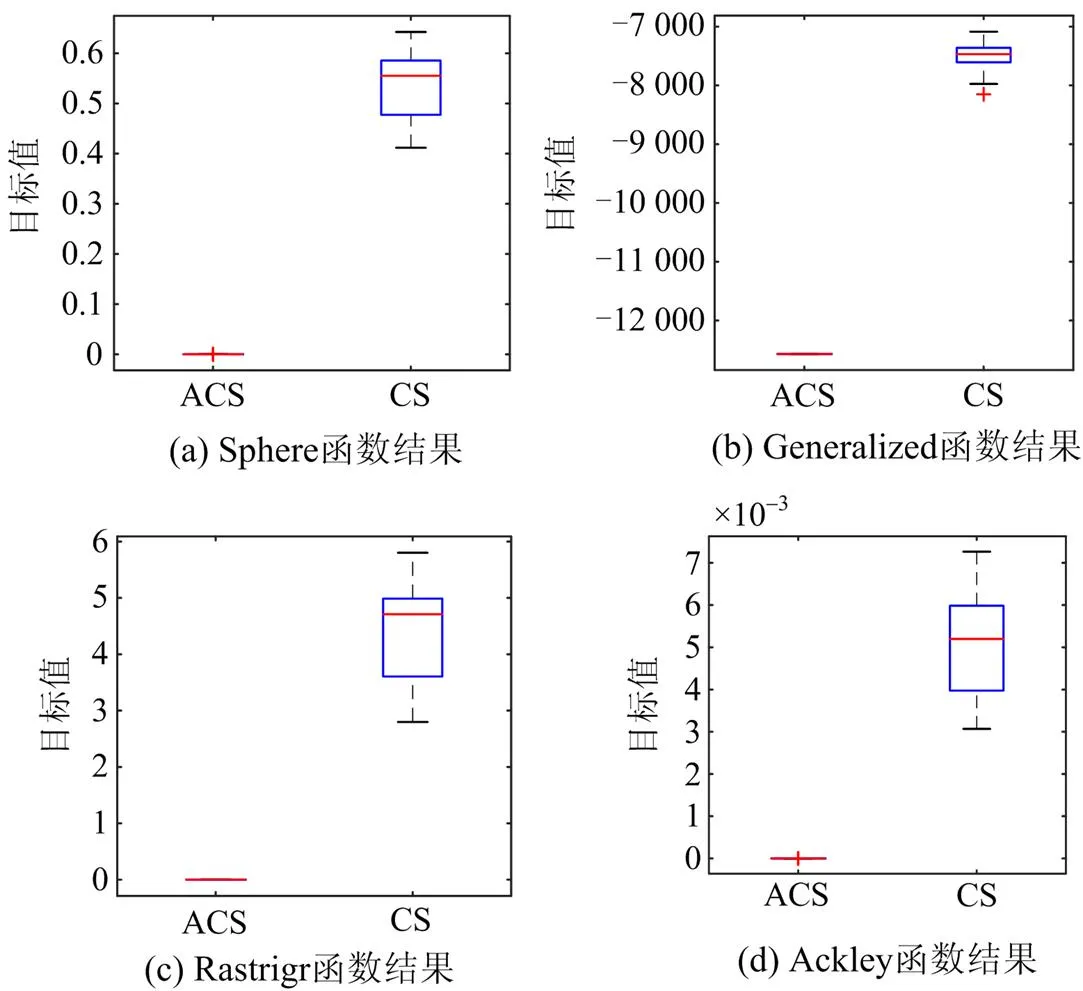
图3 算法测试箱线图
由图3可以看出,CS算法在对基准函数进行跟踪时目标值的波动范围较大,表现出较强的随机性。在跟踪Generalized函数时,明显停留在局部最优值处,全局搜索性能较差。ACS算法在应对不同的基准函数所求目标值均可达到其理论最优值,无陷入局部最优的现象,且所得目标值的范围相对集中,稳态性较好。综上可以看出,ACS算法在准确性与稳定性上均优于CS算法。
2.4 结合P&O算法
在光伏MPPT应用中,与人工智能算法相比,小步长P&O算法在稳态跟踪过程中的输出更为稳定,因此本文采用ACS算法和P&O算法结合寻优方式,P&O算法可以通过式(11)来更新占空比。首先利用ACS算法的全局搜索性能进行迭代到GMPP附近,当满足以下两个条件之一时,将目前找到的最佳值作为P&O算法的起始占空比,在-曲线上继续进行精确搜索。1) 满足设定的最大跳转迭代次数;2) 迭代更新的寄生窝点位置和目前发现的最佳窝点位置满足式(12)的比较关系。


当使用P&O算法继续跟踪GMPP时,由于外部环境的动态变化,-曲线可能会发生偏移,GMPP的位置可能会发生变化,如果继续使用P&O算法,可能无法找到新的GMPP,需要重新启动ACS算法进行跟踪。本文设置了两个算法重启条件,当满足其中一个条件时重新启动。1)设定重启时间为1min;2) 功率变化情况满足式(13),采用ACS-P&O复合算法跟踪光伏系统GMPP的流程图如图4所示。

具体步骤为
步骤1 初始化ACS算法中的参数。主要有:种群大小、跳跃迭代次数jump以及每个系数参数值的大小。
步骤2 根据采集的电流、电压值计算适应度值,保留计算所得的最佳适应度值。
步骤3 判断迭代次数是否满足跳转迭代数jump,若满足则转至步骤8。
步骤4 结合式(6)与式(9)来更新寄生巢穴的位置,若优于上一代则保留其值。
步骤5 通过式(8)计算本次迭代的切换概率a的值,并产生一个随机数r(0≤r≤1)与a进行比较,若r 步骤6 根据式(5)更新寄生巢穴的位置,若优于上一代则保留其值。 步骤7 计算本次迭代更新的寄生巢穴位置与目前找到的最佳鸟巢位置是否满足式(12),若不满足转回步骤2。 步骤8 将最前得到的最佳占空比做为P&O的起始步长值,根据式(11)来对占空比进行更新。 步骤9 查看是否到达重启时间或满足式(13),若符合重启条件则转至步骤1,否则转至步骤8。 步骤10 输出当前的最优占空比值,结束算法迭代。 图4 光伏系统MPPT控制算法的流程图 为了验证所提光伏MPPT算法的性能改进,ACS-P&O算法与PSO算法和CS算法在Matlab/Simulink上进行了仿真和验证。用于仿真系统的模型结构如图5所示。光伏阵列是由四个单独的电池元件串联而成的,所使用的单个光伏组件型号为TP250MBZ。控制方法为直接控制法,利用占空比的变化配合boost电路来促使外接负载阻值与光伏阵列的内阻相匹配,从而使功率输出最大化。电路中的原始参数设置如下:1= 400mF,2= 0.5 mF,= 0.8 mH,load= 20 Ω,开关频率为20 kHz。 图5 光伏系统MPPT控制系统 该模拟将分别在STC(模式1)和PSC(模式2)和动态变化环境(模式1突变至模式2)中进行,模拟所用的曲线如图6所示。为了比较,种群数量都被设定为4。 图6 仿真实验阵列的P-V曲线变化情况 光伏阵列的设置通常是为了在宽阔、无遮挡的环境中接受较大面积的光线,因此一般来说,接受均匀光线的光伏阵列在曲线上有一个且只有一个极值点。模式1显示了标准条件下的曲线,最大系统功率为996 W。设置仿真时间为1 s,三种算法的仿真结果如图7所示。 从图7中可以看出,三种算法都收敛到了接近GMPP的水平。PSO、CS和ACS-P&O算法跟踪到的平均功率值分别为975.28 W、994.65 W和995.95 W。当迭代进行到接近GMPP时,PSO算法和CS算法仍然存在比较明显的电流和电压纹波及功率振荡现象。相比之下,本文提出的算法在功率收敛到GMPP附近时自动切换到小步长的P&O算法,调整占空比变化的形式,使功率输出更加稳定。表2记录了在光照均匀时的三种算法跟踪时间、功率波动范围与发电效率(发电效率=平均输出功率/最大功率点处功率)。 图7 无遮挡情况下的光伏阵列输出波形 表2 实验结果对比 当光伏阵列被云层、鸟类等遮挡时,-曲线从单峰转变为多峰。模式2是四个串联的光伏板分别接收800 W/m2、800 W/m2、300 W/m2和600 W/m2的辐照度的曲线。同一条曲线上有三个极值点,其中两个LMPP的功率值分别为389.6 W、342.1 W,GMPP的功率值为483.8 W。图8中显示了三种算法在1 s模拟时间内的光伏电池输出波形。 图8 部分遮挡下的光伏阵列输出波形 从图8中可以看出,PSO、CS和ACS-P&O算法跟踪的平均功率分别近似为482.29 W、483.31 W和483.76 W。在图8中还可以发现,PSO算法在跟踪GMPP时,首先在LMPP附近的功率上有波动,然后在0.2 s后跳出局部最优。与其他算法相比,ACS-P&O算法收敛速度更快,精度更高,跟踪时振荡更小。三种算法的实验结果对比值如表3所示。 表3 实验结果对比 为了模拟改进后的算法在动态环境中跟踪光伏系统GMPP的能力,模拟时间被设定为3 s,光伏电池的-输出特性曲线在1.5 s时从模式1切换到模式2。三种算法的仿真输出如图9所示。 如图9所示,尽管PSO算法在环境突然变化后跟踪到了正确的GMPP,但存在明显的功率振荡,系统难以保持稳定。观察CS算法的仿真结果可发现,在光线变化后的0.5 s,系统重新追踪到新的GMPP,但在2 s后趋于平稳之前,系统仍然经历了小幅度的功率振荡。而ACS-P&O算法在1.5 s时检测到功率的突然变化,并将P&O算法切换到ACS算法,以确保系统不会陷入局部最优,只有当算法检测到收敛至GMPP附近时才会再次切换P&O算法,以保持稳定的跟踪,而重新收敛到最大功率点只需要0.18 s。P&O算法的小步长也能满足后续跟踪的要求,且功率振荡始终处于最小振幅,很大程度上提升了跟踪效率。 图9 动态变化下的光伏阵列输出波形 本文提出了一种基于ACS-P&O算法的光伏阵列最大功率点跟踪控制方法。为了解决CS算法问题,将Lévy飞行方程中的步长系数改为自适应递减形式,以满足前后期探测与开发的需要;令CS算法的切换概率随着迭代的进行而线性增长,这使得布谷鸟在早期有更大的机会随机游动,以保证算法在运行初期顺利跳出LMPP,同时也加速了后期的收敛;边界个体处理条件的加入使个体向最优值处靠拢,减少迭代次数;为避免算法收敛在全局最优值后产生不必要的功率振荡,将在GMPP附近时切换小步长P&O算法,以保持功率输出的稳定性。仿真结果表明,所提出的方法在早期收敛速度和后期稳态振荡方面都优于PSO算法和CS算法,并有效提高了光伏系统的能量利用率。 [1] KERMADI M, BERKOUK E M.Artificial intelligence-based maximum power point tracking controllers for Photovoltaic systems: comparative study[J].Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 69: 369-386. [2] MOHAPATRA A, NAYAK B, DAS P, et al.A review on MPPT techniques of PV system under partial shading condition[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 80: 854-867. [3] 王志豪, 李自成, 王后能, 等.基于RBF神经网络的光伏系统MPPT研究[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(6): 85-91. WANG Zhihao, LI Zicheng, WANG Houneng, et al.MPPT study of solar PV power system based on RBF neural network algorithml[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(6): 85-91. [4] YANG B, ZHU T, WANG J, et al.Comprehensive overview of maximum power point tracking algorithms of PV systems under partial shading condition[J].Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 268. [5] 李立雄, 阳同光, 袁越阳, 等.基于改进有限集模型预测控制策略的光伏发电系统最大功率点追踪算法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(17): 28-37. LI Lixiong, YANG Tongguang, YUAN Yueyang, et al.Maximum power point tracking algorithm of a photovoltaic power generation system based on an improved finite set model predictive control strategy[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(17): 28-37. [6] 韩鹏, 李银红, 何璇, 等.结合量子粒子群算法的光伏多峰最大功率点跟踪改进方法[J].电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(23): 101-108. HAN Peng, LI Yinhong, HE Xuan, et al.Improved maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic multi-peak based on quantum-behaved particle swarm potimization algorithm[J].Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(23): 101-108. [7] BDEL-SALAM M, EL-MOHANDES M T, EL-GHAZALY M.An efficient tracking of MPP in PV systems using a newly-formulated P&O-MPPT method under varying irradiation levels[J].Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2020, 15(1): 501-513. [8] 盛四清, 陈玉良.基于功率预测的新型变步长电导增量法最大功率点跟踪策略[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2017, 45(23): 42-48. SHENG Siqing, CHEN Yuliang.Maximum power point tracking strategy based on power predication for a novel variable step-size incremental conductance algorithm[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45(23): 42-48. [9] 陈景文, 张文倩, 李晓飞.基于改进电导增量法的光伏MPPT控制[J].智慧电力, 2021, 49 (9): 47-55. CHEN Jingwen, ZHANG Wenqian, LI Xiaofei.Photovoltaic MPPT control based on improved conductance[J].Smart Power, 2021, 49(9): 47-55. [10] SHANG L, GUO H, ZHU W.An improved MPPT control strategy based on incremental conductance algorithm[J].Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2020, 5(2): 176-163. [11] 吴志程, 江智军, 杨晓辉.一种基于功率闭环控制的改进全局MPPT方法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(1): 57-62. WU Zhicheng, JIANG Zhijun, YANG Xiaohui.An improved global MPPT method based on power closed-loop control[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(1): 57-62. [12] 商立群, 朱伟伟.基于全局学习自适应细菌觅食算法的光伏系统全局最大功率点跟踪方法[J].电工技术学报, 2019, 34(12): 2606-2614. SHANG Liqun, ZHU Weiwei.Photovoltaic system global maximum power point tracking method based on the global learning adaptive bacteria foraging algorithm[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(12): 2606-2614. [13] SHANG L, ZHU W, LI P, et al.Maximum power point tracking of PV system under partial shading conditions through flower pollination algorithm[J].Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2018, 3(4): 400-406. [14] SEN T, PRAGALLAPATI N, AGARWAL V, et al.Global maximum power point tracking of PV arrays under partial shading conditions using a modified particle velocity-based PSO technique[J].IET Renewable Power Generation, 2018, 12(5): 555-564. [15] PREMKUMAR M, SOWMYA R.An effective maximum power point tracker for partially shaded solar photovoltaic systems[J].Energy Reports, 2019, 5: 1445-1462. [16] TEY K S, MEKHILEF S, SEYEDMAHMOUDIAN M, et al.Improved differential evolution-based MPPT algorithm using SEPIC for PV systems under partial shading conditions and load variation[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(10): 4322-4333. [17] 盛四清, 陈玉良, 张晶晶.基于差分进化人工蜂群算法的光伏最大功率跟踪策略研究[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(11): 23-29. SHENG Siqing, CHEN Yuliang, ZHANG Jingjing.Research on maximum power point tracking strategy based on differential evolution artificial bee colony algorithm of photovoltaic system[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(11): 23-29. [18] MANICKAM C, RAMAN G R, RAMAN G P, et al.A hybrid algorithm for tracking of GMPP based on P&O and PSO with reduced power oscillation in string inverters[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(10): 6097-6106. [19] 朱梓嘉, 肖辉, 赵帅旗, 等.基于并行组合进化算法的光伏阵列最大功率点追踪[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(4): 1-10. ZHU Zijia, XIAO Hui, ZHAO Shuaiqi, et al.Maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic array based on parallel combination evolutionary algorithm[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(4): 1-10. [20] MOHANTY S, SUBUDHI B, RAY P K.A grey wolf-assisted perturb & observe MPPT algorithm for a PV system[J].IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2016, 32(1): 340-347. [21] 吴忠强, 谢宗奎, 王国勇, 等.一种基于改进羊群算法的光伏系统最大功率跟踪策略[J].电子学报, 2020, 48(10): 2017-2024. WU Zhongqiang, XIE Zongkui, WANG Guoyong, et al.A maximum power point tracking strategy for photovoltaic system based on improved sheep behaviors optimization[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(10): 2017-2024. [22] 张明锐, 陈喆旸, 韦莉.免疫萤火虫算法在光伏阵列最大功率点跟踪中的应用[J].电工技术学报, 2020, 35(7): 1553-1562. ZHANG Mingrui, CHEN Zheyang, WEI Li.Application of immune firefly algorithms in photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(7): 1553-1562. [23] AHMED J, SALAM Z.A maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for PV system using cuckoo search with partial shading capability[J].Applied Energy, 2014, 119:118-130. [24] 赵帅旗, 肖辉, 刘忠兵, 等.基于CSA-IP&O的局部遮阴下光伏最大功率点追踪[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(5): 26-32. ZHAO Shuaiqi, XIAO Hui, LIU Zhongbing, et al.Photovoltaic maximum power point tracking under partial shading based on CSA-IP&O[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(5): 26-32. [25] PENG B R, HO K C, LIU Y H.A novel and fast MPPT method suitable for both fast changing and partially shaded conditions[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 65(4): 3240-3251. [26] NUGRAHA D A, NUGRAHAD A, LIAN K L.A novel MPPT method based on Cuckoo search algorithm and golden section search algorithm for partially shaded PV system[J].Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2019, 42(3): 173-182. [27] 刘宜罡, 邹应全, 张晓强, 等.基于差分进化的光伏MPPT算法改进[J].太阳能学报, 2020, 41(6): 264-271. LIU Yigang, ZOU Yingquan, ZHANG Xiaoqiang, et al.An improved photovoltaic MPPT algorithm based on differential evolution algorithm[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 264-271. PV power point tracking based on adaptive cuckoo search and perturbation observation method SHANG Liqun, LI Fan (School of Electrical and Control Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi'an 710054, China) When a photovoltaic array panel is exposed to uneven light, the power-voltage (-) characteristic curve becomes multi-peaked, and conventional maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms will not be able to track the correct global maximum power point (GMPP), and artificial intelligence algorithms with global search capabilities are usually highly parameterized and complex.To address the above problems this paper proposes a composite tracking algorithm combining the adaptive cuckoo algorithm and perturbation observation method (ACS-P&O).This improved method takes the switching probabilities and Lévy flight step coefficients from the cuckoo search (CS) algorithm and adaptively adjusts them to extend the search range of the algorithm at an early stage.The introduction of a processing strategy for bounding individuals further reduces the number of algorithm iterations.The improved algorithm makes it easier for the system to jump out of the local maximum power point (LMPP), while at a later stage the algorithm operates precisely in a small area, improving the local exploitation capability.The addition of the perturbation and observation (P&O) method mitigates power oscillations when the system is located near the GMPP and stabilizes the output.Simulation results show that the ACS-P&O composite algorithm can adapt to the effects of environmental changes and track the GMPP quickly and accurately. photovoltaic; MPPT; adaptive cuckoo search algorithm; perturbation and observation method; Lévy flight; boundary individuals 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.211309 2021-09-25; 2021-11-12 商立群(1968—),男,博士,教授,研究方向为电力系统分析与控制、新能源发电及微网技术;E-mail: shanglq@ xust.edu.cn 李 帆(1996—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为光伏发电及并网技术。E-mail: 903806082@qq.com 陕西省自然科学基金项目资助(2021JM-393) This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No.2021JM-393). (编辑 张爱琴)
3 算法性能验证与仿真结果分析


3.1 无阴影状况下的仿真


3.2 局部遮阴状况下的仿真


3.3 动态变化状况下的仿真

4 结论
