基于混合整数线性规划的含ZIP负荷有源配电网重构方法
2022-04-19张琳娜李昊炅
张琳娜,乐 健,李昊炅
基于混合整数线性规划的含ZIP负荷有源配电网重构方法
张琳娜1,乐 健2,李昊炅1
(1.国网山西省电力公司,山西 太原 030001;2.武汉大学电气与自动化学院,湖北 武汉 430072)
随着分布式电源并网和负荷类型的日益复杂,传统配电网重构模型尚未考虑复杂的综合负荷模型。提出了考虑ZIP综合负荷模型的有源配电网混合整数线性规划方法。在辐射状配电网二阶锥潮流模型的基础上,通过线性回归法将ZIP负荷模型等效为ZP负荷模型,建立基于混合整数二阶锥规划的有源配电网重构模型。通过多面体近似将二阶锥约束进行线性化,建立基于混合整数线性规划的有源配电网重构模型。在三个不同规模配电系统的仿真结果表明,基于混合整数线性规划的有源配电网重构模型精度与基于混合整数二阶锥规划的几乎相同,但优化效率提高了15%~30%,具有较高的优化精度和效率。
ZIP负荷模型;配电网重构;混合整数二阶锥规划;线性回归法;混合整数线性规划
0 引言
配电网重构主要是通过切换联络开关和分段开关的开合状态来改变网络的拓扑结构,从而实现降低网损、提高供电可靠性等运行目标[1-5]。近年来,随着分布式电源(Distributed Generation, DG)大规模并网,负荷类型越来复杂,使得传统配电网重构的优化模型难以适应有源配电网的发展[6-8],另一方面,有源配电网重构的优化模型维数越来越高,亟需高效的求解方法。
从数学优化的角度讲,有源配电网重构是一个典型的组合优化问题,需要从组合问题的可行解集中找到最优解。有源配电网重构的求解方法主要分为启发式方法[9-11]、智能优化方法(也称为亚启发式方法)[12-15]、运筹学方法[16-18]三大类。启发式方法是依据特定的规则或经验构造出的一类寻优方法,所谓特定的经验通常是依据具体的问题所总结出来的一种直观的规律,应用最多是支路交换法(switch exchange method),虽然支路交换法可以减少寻优的范围,但一般很难或不能获得全局最优解,只能得到一个可行的较优解。智能优化方法是基于局部搜索或随机寻优思想的智能化算法,具有较好的可移植性,广泛地适用于配电网重构的各类优化模型。智能优化算法在配电网重构中的研究成果十分丰富,主要包括粒子优化算法、模拟退火算法[12]、教与学优化算法[13]、禁忌搜索方法[14]、遗传算法[19]等,并且在不断的发展。智能优化算法虽然能适应各种非线性约束和目标函数,但也面临着由于收敛性差而难以获得全局最优解的问题。运筹学方法是采用数学规划算法求解有源配电网重构模型,具有严格的数学理论基础,优化结果可靠性高。由于有源配电网重构模型中潮流的非线性,已有的凸优化算法难以求解有源配电网重构的非凸优化模型。为此,文献[19]将辐射状配电网非线性潮流模型转化为二阶锥规划模型,建立了配电网重构的混合整数二阶锥规划模型,可以直接调用商业求解器进行求解,求解效率高。在文献[20]的基础上,文献[16]进一步考虑DG并网情况,综合考虑网损、购电成本、DG发电量建立了有源配电网重构的混合整数二阶锥规划模型。文献[17]在上层以配电网安全域距离最大化为目标,下层以配电网网损最小化为目标,建立了同时考虑安全性和经济性的配电网重构的双层二阶锥规划模型。文献[18]将电动汽车延时充电策略模型和错峰充电策略模型嵌入到配电网重构的混合整数二阶锥规划模型,分析了电动汽车充电策略对配电网重构结果的影响。基于混合整数二阶规划的配电网重构模型虽然在一定程度上获得了较高的求解效率,但非线性二阶锥约束随着配电网重构维数的增加,求解效率将会下降。此外,已有配电网重构中均采用恒功率负荷模型,缺乏考虑ZIP负荷模型的配电网重构模型,这是因为ZIP负荷模型会破坏原有的配电网重构的混合整数二阶锥模型结构,导致不能采用二阶锥规划方法进行求解。
为了解决非线性二阶锥约束的求解效率问题以及嵌入ZIP负荷模型会改变原有的二阶锥模型结构,本文提出了基于多面体近似[21-22]的有源配电网重构混合整数线性规划方法。在配电网重构的混合整数二阶规划模型基础上,本文采用线性回归法[23-24]将ZIP负荷模型近似转化为等效ZP模型以嵌入到配电网重构模型,解决ZIP负荷模型的适应性问题,通过多面体近似将配电网重构的混合整数二阶规划模型线性化为混合整数线性规划模型求解,提高了求解效率。仿真算例结果表明了本文所提出的有源配电网重构混合整数线性规划方法的准确性和高效性。
1 有源配电网重构模型
假设有源配电网线路均为辐射状,且所有支路均配备分段开关或联络开关。有源配电网网损等于网络实际总发电量与负荷实际总需求量之差,也即所有节点净实际注入有功功率之和[25]。因此,以降低有源配电网网损为重构目的时的目标函数可表达为

重构模型约束条件包括以下几个方面。
1) 节点注入有功功率


2) 节点注入无功功率
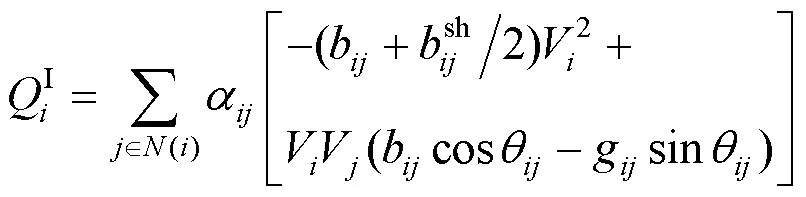

3) 节点电压

4) 支路电流

其中
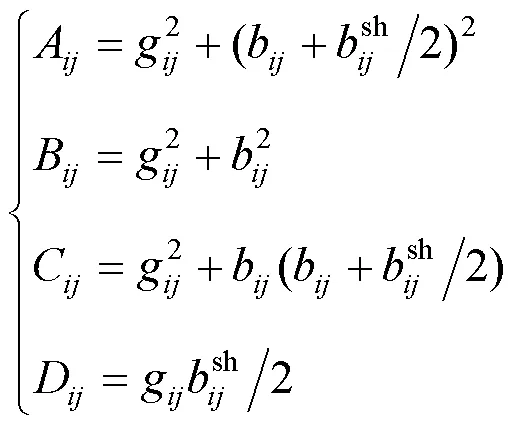
5) 辐射状拓扑结构

6) 联络开关动作次数


2 有源配电网的混合整数线性规划模型
2.1 重构模型的混合整数二阶锥转化
上述建立的有源配电网重构模型是一个典型非凸的混合整数非线性规划模型,本文在辐射状配电网二阶锥规划潮流模型[26-27]的基础上,将该重构模型转化为混合整数二阶锥规划模型,进而可采用凸规划方法求解全局最优解。
引入如下新变量:



式中:

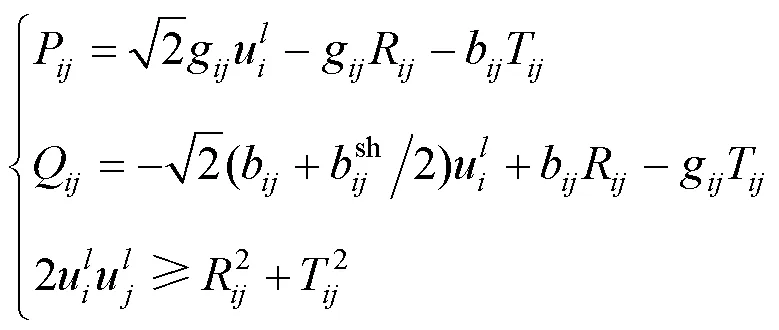

应用式(12)和式(16)可将节点电压约束和支路电流约束分别转化为


2.2 基于线性回归的负荷模型等效
2.1节建立的配电网重构混合整数二阶锥规划模型以式(1)为目标函数、从式(3)、式(5)、式(9)、式(11)以及(13)—式(19)为约束条件。由于式(3)和式(5)中的ZIP负荷模型使得潮流模型无法二阶锥化,因此本文将ZIP负荷模型转化为等效的ZP模型后再进行二阶锥化,即



结合式(20)给出的ZIP负荷模型与式(21),可得


2.3 基于多面体近似的混合整数线性规划模型
2.1节和2.2节所建立的配电网重构混合整数二阶锥规划模型中,除了式(15)和式(16)中的旋转二阶锥约束条件外,其他约束均为线性约束条件。首先将式(15)中的旋转二阶锥约束转换为

采用两个三维二阶锥对式(25)进行等效,得

式(26)可统一描述为

采用文献[21]提出的多面体近似方法将式(27)进行线性化,从而将混合整数二阶锥规划模型近似转换成混合整数线性规划模型求解。三维的二阶锥约束式(27)的多面体近似表达式为
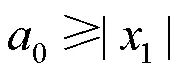


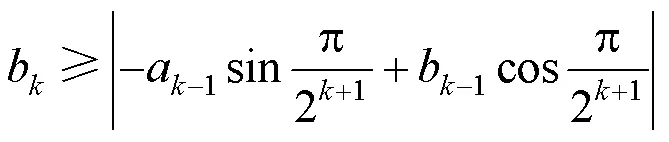


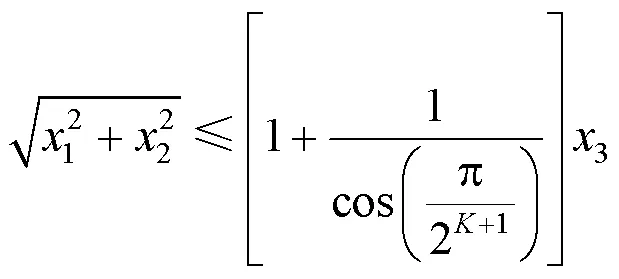
根据式(34),当时,其误差约为。因此,有源配电网重构的混合整数二阶锥规划模型近似等价于混合整数线性规划模型,可以直接基于Matlab的工具箱Yalmip[29]进行建模,并调用商业求解器Cplex12.7[30]求解。图1对本文所建立的两类有源配电网重构优化模型进行了比较,两者主要区别在于约束条件的近似松弛方法不同。
3 仿真验证
本文采用3个配电系统作为测试对象:1) 配电系统#1。83节点配电系统,运行电压11.4 kV,负荷和线路参数详见文献[31];2) 配电系统#2。由5个83节点配电系统#1拼接而成,5个配电系统依次进行编号;3) 配电系统#3。由2个配电系统#2拼接而成,2个415节点配电系统依次进行编号。

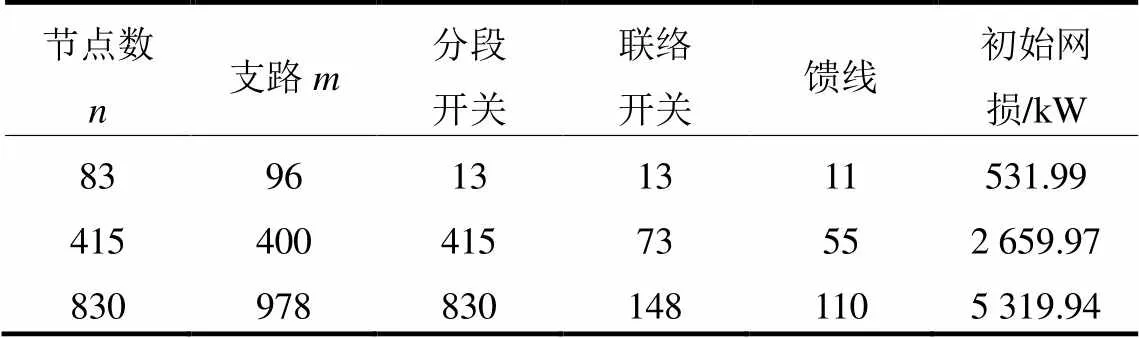
表1 测试系统数据

表2 配电系统#1中DG数据
为验证本文所提出的配电网重构优化模型的精度,采用Bonmin求解原始的配电网重构模型,以所得到的全局最优解为基准。表3给出了分别采用混合整数二阶锥规划模型(Mixed Integer Second-Order Cone Programming, MISOCP)和混合整数线性规划模型(Mixed Integer Linear Programming, MILP)的结果。

表3 两类重构优化模型精度对比
从表3中不难看出:配电网重构的MISOCP模型精度较MILP模型更高,但两者的模型精度误差最大仅为0.09%。这反映了当=11时,配电网重构的MILP模型精度可以达到9×10-4,几乎等同于配电网重构的MISOCP模型。
进一步,本文对比了配电网重构的MILP模型和MISOCP模型的效率,结果如表4所示。
从表4可以看出,配电网重构MILP模型的配电网网损优化结果小于MISOCP模型的结果,网损下降幅度更大。表明尽管MISOCP模型精度略优于MILP模型,但在寻优的过程中,MILP模型可获得更佳的分段开关组合模式。更为重要的是随着配电系统规模的扩大,MILP模型求解时间较MISOCP模型减小,这充分说明了通过多面体进行二阶锥线性化可以提高优化效率,可达到15%~30%。
表4 配电网重构优化结果对比
Table 4 Comparison of optimization results of distribution network reconfiguration

文献[31]采用模拟退火法对83节点系统进行了配电网重构优化,本文所提出的MILP方法与文献[31]所得结果的对比如表5所示。

表5 83节点系统重构结果对比
从表5中不难看出:模拟退火法的断开支路与本文所提出的配电网重构的MILP方法不一致,该方法结果是一个局部最优解,这也是模拟退火等智能优化算法的固有缺陷,即会限于局部最优。而基于凸优化理论的配电网重构MILP方法具有完善的数学理论,能保证获得可行域中的全局最优解。


图2 不同开关动作次数对网损的影响
4 结论
本文在辐射状配电网二阶锥模型的基础上,考虑更加复杂的ZIP负荷模型,通过线性回归法将ZIP负荷模型近似等效为ZP模型,建立了有源配电网重构的MISOCP模型,并基于多面体近似建立了有源配电网重构的MILP模型,所得主要结论包括:
1) 提出了基于线性回归法的等效ZP负荷模型参数近似估算方法,实现了ZIP负荷模型的有效处理,拓展了配电网二阶锥潮流模型的适应性;
2) 所提出的有源配电网重构的MILP模型具有与MISOCP模型几乎相同的优化精度,误差数量级为10-4,但优化效率较后者可提高15%~30%;
3) 配电网重构结果的网损下降幅度随开关动作次数限制的增大而增加,最后趋于平稳。
在未来关于配电网重构的研究中可以考虑将储能等新型装置拓展到重构模型中,建立更加完善的约束条件和目标函数;也可以考虑负荷和分布式电源的不确定性,将本文的确定性重构方法延伸到不确定性应用场景。
[1] 易海川, 张彼德, 王海颖, 等.提高DG 接纳能力的配电网动态重构方法[J].电网技术, 2016, 40(5): 1431-1436.
YI Haichuan, ZHANG Bide, WANG Haiying, et al.Distribution network dynamic reconfiguration method for improving distribution network’s ability of accepting DG[J].Power System Technology, 2016, 40(5): 1431-1436.
[2] LIU Y, LI J, WU L.Coordinated optimal network reconfiguration and voltage regulator/DER control for unbalanced distribution systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(3): 2912-2922.
[3] 姜萌萌, 佟永吉, 陈明丰, 等.基于灾害条件的主动配电网快速重构策略研究[J].智慧电力, 2021, 49(5): 85-92.
JIANG Mengmeng, TONG Yongji, CHEN Mingfeng, et al.Rapid reconfiguration strategy of active distribution network under disaster conditions[J].Smart Power, 2021, 49(5): 85-92.
[4] 马倩, 苟亮, 张海峰, 等.考虑开关动作次数的多时段配电网动态重构[J].电测与仪表, 2021, 58(3): 9-14.
MA Qian, GOU Liang, ZHANG Haifeng, et al.Multi-period dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network considering the number of switching actions[J].Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2021, 58(3): 9-14.
[5] 章博, 刘晟源, 林振智, 等.高比例新能源下考虑需求侧响应和智能软开关的配电网重构[J].电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(8): 86-94.
ZHANG Bo, LIU Shengyuan, LIN Zhenzhi, et al.Distribution network reconfiguration with high penetration of renewable energy considering demand response and soft open point[J].Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(8): 86-94.
[6] 郑能, 胡瑞馨, 丁晓群, 等.考虑多种类型的分布式电源和网络重构的配电网无功优化[J].智慧电力, 2019, 47(3): 90-96.
ZHENG Neng, HU Ruixin, DING Xiaoqun, et al.Reactive power optimization of distribution network considering multiple types of distributed generations and network reconfiguration[J].Smart Power, 2019, 47(3): 90-96.
[7] WANG Y, HUANG Z, SHAHIDEHPOUR M, et al.Reconfigurable distribution network for managing transactive energy in a multi-microgrid system[J].IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(2): 1286-1295.
[8] 谢琳宇, 唐忠, 黄星宇, 等.考虑分布式电源和电动汽车不确定性的双层动态配网重构[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(10): 1-11.
XIE Linyu, TANG Zhong, HUANG Xingyu, et al.Bi-layer dynamic reconfiguration of a distribution network considering the uncertainty of distributed generation and electric vehicles[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(10): 1-11.
[9] 李辰雷, 卫志农, 韩连山, 等.序优化理论在配电网重构中的应用[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(8): 41-48.
LI Chenlei, WEI Zhinong, HAN Lianshan, et al.Application of ordinal optimization in distribution network reconstruction[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(8): 41-48.
[10] ZHAN J, LIU W, CHUNG C Y, et al.Switch opening and exchange method for stochastic distribution network reconfiguration[J].IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(4): 2995-3007.
[11] 陈永进.基于混合整数凸规划的有源配电网重构与无功电压协调优化[J].电力电容器与无功补偿, 2020, 41(6): 21-29.
CHEN Yongjin.A coordinated optimization for active distribution network reconfiguration and volt/var optimization based on mixed integer convex programming[J].Power Capacitor & Reactive Power Compensation, 2020, 41(6): 21-29.
[12] 徐小琴, 王博, 赵红生, 等.基于布谷鸟搜索和模拟退火算法的两电压等级配网重构方法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(11): 84-91.
XU Xiaoqin, WANG Bo, ZHAO Hongsheng, et al.Reconfiguration of two-voltage distribution network based on cuckoo search and simulated annealing algorithm[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(11): 84-91.
[13] 潘本仁, 王和春, 张妍, 等.含分布式电源的主动配电网重构策略研究[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(15): 102-107.
PAN Benren, WANG Hechun, ZHANG Yan, et al.Study on an active distribution network reconstruction strategy with distributed power supply[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(15): 102-107.
[14] 吴泓俭, 雷霞, 刘斌, 等.基于遗传膜算法的含风电机组和电动汽车的配电网分时段动态重构[J].电工技术学报, 2016, 31(2): 196-205, 220.
WU Hongjian, LEI Xia, LIU Bin, et al.Membrane computing based genetic algorithm for dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network with dividing time and considering electric vehicles and wind turbines[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(2): 196-205, 220.
[15] 李扬, 韦钢, 马钰, 等.含电动汽车和分布式电源的主动配电网动态重构[J].电力系统自动化, 2018, 42(5): 102-110.
LI Yang, WEI Gang, MA Yu, et al.Dynamic reconfiguration of active distribution network considering electric vehicles and distributed generations[J].Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(5): 102-110.
[16] 汪芳宗, 王兆丰.基于混合整数二次锥规划方法的含分布式电源配电网优化重构方法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2016, 44(24): 24-30.
WANG Fangzong, WANG Zhaofeng.An optimumreconfiguration method for distribution networks with DG based on mixed integer second-order cone programming[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2016, 44(24): 24-30.
[17] 江钧, 成乐祥, 孙国强, 等.考虑安全域的配电网重构二阶锥双层规划模型[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(4): 9-16.
JIANG Jun, CHENG Lexiang, SUN Guoqiang, et al.Distribution network reconfiguration based on second order cone bi-level programming considering security distance[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(4): 9-16.
[18] 李洪美, 崔翰韬, 万秋兰.考虑电动汽车充电策略的配网重构二阶锥规划模型[J].中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(18): 4674-4681.
LI Hongmei, CUI Hantao, WAN Qiulan.Distribution network reconfiguration based on second-order conic programming considering EV charging strategy[J].Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(18): 4674-4681.
[19] 李锰, 王利利, 刘向实, 等.基于门当户对遗传算法的配电网多目标主动重构研究[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(7): 30-38.
LI Meng, WANG Lili, LIU Xiangshi, et al.Multiobjective active reconfiguration of distribution network based the “properly matched marriage” genetic algorithm[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(7): 30-38.
[20] JABR R A.Minimum loss network reconfiguration using mixed-integer convex programming[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2012, 27(2): 1106-1115.
[21] BEN T, AHARO N, NEMIROVS K I, et al.On polyhedral approximations of the second-order cone[J].Mathematics of Operations Research, 2001, 26(2): 193-205.
[22] 郭清元, 吴杰康, 莫超, 等.基于混合整数二阶锥规划的新能源配电网电压无功协同优化模型[J].中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(5): 1385-1396.
GUO Qingyuan, WU Jiekang, MO Chao, et al.A model for multi-objective coordination optimization of voltage and reactive power in distribution networks based on mixed integer second-order cone programming[J].Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(5): 1385-1396.
[23] NAZIR F U, PAL B C, JABR R A.Approximate load models for conic OPF solvers[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36(1): 549-552.
[24] 邵尹池, 袁绍军, 孙荣富, 等.基于空间相关性的分布式光伏实用化功率预测及误差分析[J].中国电力, 2021, 54(7): 185-191, 207.
SHAO Yinchi, YUAN Shaojun, SUN Rongfu, et al.Practical method and error analysis for distributed photovoltaic power prediction based on spatial correlation[J].Electric Power, 2021, 54(7): 185-191, 207.
[25] 刘一兵, 吴文传, 张伯明, 等.基于混合整数二阶锥规划的三相有源配电网无功优化[J].电力系统自动化, 2014, 38(15): 58-64.
LIU Yibing, WU Wenchuan, ZHANG Boming, et al.Reactive power optimization for three-phase distribution networks with distributed generators based on mixed integer second-order cone programming[J].Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38(15): 58-64.
[26] BOSE A, TIAN Z, WU W, et al.Mixed-integer second- order cone programing model for VAR optimisation and network reconfiguration in active distribution networks[J].IET Generation Transmission & Distribution, 2016, 10(8): 1938-1946.
[27] 张福民, 刘国鑫, 李占凯, 等.基于二阶锥规划的交直流混合配电网优化调度[J].智慧电力, 2020, 48(3): 117-123.
ZHANG Fumin, LIU Guoxin, LI Zhankai, et al.Optimal dispatch of AC/DC hybrid distribution network based on second-order cone programming[J].Smart Power, 2020, 48(3): 117-123.
[28] 高红均, 刘俊勇, 沈晓东, 等.主动配电网最优潮流研究及其应用实例[J].中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(6): 1634-1644.
GAO Hongjun, LIU Junyong, SHEN Xiaodong, et al.Optimal power flow research in active distribution network and its application examples[J].Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(6): 1634-1644.
[29] LOFEBRG J.YALMIP: a toolbox for modeling and optimization in Matlab[C] // 2004 IEEE International Symposium on Computer Aided Control Systems Design, September 2-4, 2004, Taibei, China: 284-289.
[20] 李晓明, 刘翔宇, 李安昌, 等.配电网电压控制的分布式光伏无功仿射可调鲁棒优化方法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(12): 124-131.
LI Xiaoming, LIU Xiangyu, LI Anchang, et al.Distributed photovoltaic reactive power affine adjustable robust optimization method for voltage control of a distribution network[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(12): 124-131.
[31] SU C T, LEE C S.Network reconfiguration of distribution systems using improved mixed-integer hybrid differential evolution[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2003, 18(3): 1022-1027.
Reconfiguration method of an active distribution network with a ZIP load model based on mixed integer linear programming
ZHANG Linna1, LE Jian2, LI Haojiong1
(1.State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Company, Taiyuan 030001, China; 2.School of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China)
There is grid connection of distributed generation and an increasing complexity of load types.However, the traditional distribution network reconfiguration model has not considered an integrated load model.Therefore, this paper proposes a mixed integer linear programming model of an active distribution network considering the ZIP load model.Based on the second-order cone power flow model of a radial distribution network, the ZIP load model is equivalent to a ZP load model by linear regression method.The active distribution network reconfiguration model based on mixed integer second-order cone programming is established.The second-order cone constraint is linearized by polyhedron approximation, and the active distribution network reconfiguration model is established.The simulation results of three different scale distribution systems show that the accuracy of this active distribution network reconfiguration model is almost the same as that based on mixed integer second-order cone programming, but the optimization efficiency is improved by 15% ~ 30%.This shows high optimization accuracy and efficiency.
ZIP load model; distribution network reconfiguration; mixed integer second-order cone programming; linear regression method; mixed integer linear programming
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.210903
2021-07-15;
2021-10-15
张琳娜(1974—),女,高级工程师,主要研究方向为电网规划;E-mail: zhanglinna@sx.sgcc.com.cn
乐 健(1975—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事智能电网运行与控制技术研究。E-mail: lej01@tsinghua.org.cn
国家自然科学基金项目资助(51877154)
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51877154).
(编辑 周金梅)
