Efficacy and safety of awn needle in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis
2022-03-16CUIHailingLIYanjvCHENXingshengWANGMinjunLILiaoyuanHULingWUZijian
CUI Hai-ling, LI Yan-jv,CHEN Xing-sheng, WANG Min-jun, LI Liao-yuan, HU Ling,3,WU Zi-jian,3✉
1.Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230012, China
2.The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230061, China
3.Institute of Acupuncture and Meridians, Anhui Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the intervention effect of awn needle in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation through meta-analysis.Methods: In CNKI, Wanfang Data, PubMed, VIP and other databases, we searched the clinical observation studies on the treatment of patients with lumbar disc herniation with awn needle.The methodological quality of the included studies was evaluated using Cochrane 5.1.0 bias risk assessment criteria and Jadad scale.Revman 5.3 software was used for meta-analysis.Results: A total of 14 randomized controlled trials involving 1 186 patients were included, with 595 in the awn needle treatment group and 591 in the control group.Meta-analysis showed that the awn needle treatment group was better than that of the control group in the total effective rate[RR=1.17; 95%CI(1.12,1.22);Z=6.66; P<0.000 01]; the awn needle treatment group was better than the control group in ameliorating VAS score [WMD=-1.07, 95%CI(-1.19,-0.95), Z=17.87, P<0.000 01]; the awn needle treatment group was better than the control group in ameliorating JOA score [WMD=3.18,95%CI(2.64,3.71), Z=11.57, P<0.000 01]; the awn needle treatment group was better than the control group in the amelioration of ADL score [SMD =2.44, 95%CI(0.54, 4.35), Z=2.52,P=0.01]; the awn needle treatment group was better than the control group in the improvement of SLRT angle [WMD=12.71, 95%CI(3.21, 22.21), Z=2.62, P=0.009].Conclusion: Awn needle treatment can improve the total effective rate of patients with lumbar disc herniation,relieve the pain of patients, improve the straight leg elevation angle of patients, alleviate the disease development, relieve the symptoms, and improve the quality of life of patients.It is worthy of clinical application.
1.Introduction
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) is a degenerative spinal disease due to the lumbar disc nucleus pulposus and cartilage endplate falling out of the fibrous ring and entering the spinal canal under the action of spatial compression, resulting in pain caused by compression of nerve root and spinal cord [1], the main clinical symptoms include lumbago and leg pain, waist movement limitation, paresthesia, etc[2].Studies have shown that LDH is one of the main causes of low back pain, which usually occurs in 30-50 years old people [3].The occurrence of LDH was related to body mass index, sedentary time, labor intensity, waist injury history, bending degree and occupation [4].In recent years, the prevalence of LDH in young people has increased gradually [5].Currently, there are surgical and non-surgical treatments for LDH.Although surgical treatment has a certain effect in relieving pain in the short term [6], this treatment method has relatively large side effects, and non-surgical treatment or conservative treatment has been considered as the primary choice for most patients [7].Awn needle therapy belongs to one of the traditional Chinese medicine therapies, which combines the advantages of long needle and filiform needle [8], and has little trauma and side effects on the body.Studies have shown that awn needle therapy can effectively relieve the symptoms of lumbar and leg pain in LDH patients, but there is no evidence-based evidence.Therefore, this study evaluated the clinical efficacy of the treatment of lumbar disc herniation through meta-analysis.
2.Data and methods
2.1 Literature sources
The related literatures of clinical randomized controlled trials of awn needle therapy in patients with LDH published in Chinese and English databases were searched by computer.Chinese databases include CNKI, Wanfang Data, VIP and CBM; English databases include PubMed, Cochrane Library and Medline.
2.2 Literature retrieval strategy
The topics related to awn needle Treatment of LDH were seared by professional retrieval, and the foreign literature retrieval was combined with subject word and free words.The Chinese search words are “awn needle” “lumbar disc herniation” “low back pain”“lumbar spine pain” “lumbar arthralgia” “lumbar detachment”and “lumbar leg pain”.The search formula is SU = (“lumbar disc herniation” + “lumbar pain” + “lumbar spine pain” + “lumbar detachment” + “lumbar arthralgia” + “lumbar leg pain”) * “awn needle”.English search words are “awn needle” “elongated needle”“lumbar disc herniation” “LDH” “intervertebral disc displacement”“slipped disk” “Herniated disks”, etc.The search format is (“ lumbar disc herniation “or” LDH “or” intervertebral disc displacement “or”slipped disk “or” herniated disks “or” intervertebral disc herniation“or” protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc “or” lumbar arthralgia“or” waist and leg pain “) and (“ elongated needle “or” awn needle“).The retrieval period is from database construction to February 2021.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.3.1 Literature inclusion criteria
(1) Literature scope: Chinese or English literature published by each database before February 2021; (2) Study type: randomized controlled trial (RCT); (3) Subjects: Meet the Criteria for “Diagnosis and Efficacy of TCM Diseases” [9], “Lumbar Disc Herniation” [10],“Bone Injury Science of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine” [11] and other diagnostic criteria for LDH; There is no restriction on gender, age and course of disease of included cases;(4) Intervention measures: The treatment group only received the awn needle(no limit on the location of acupoints) or awn needle combined with other methods (including awn needle combined with filiform needle acupuncture, awn needle combined with traction, awn needle combined with warm moxibustion, awn needle combined with traditional Chinese medicine iontophoresis, awn needle combined with TCM formulae, awn needle combined with massage), and the control group was not treated with awn needle(including conventional filiform needle acupuncture, conventional traction, conventional acupuncture iontophoresis of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine); (5) Outcome measures:total effective rate, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), Japanese Orthopedic Association Scores (JOA), Activity of Daily Living Scale(ADL), Straight Leg Raising Test (SLRT).
2.3.2 Literature exclusion criteria
(1) Non-RCT design; (2) Vague intervention measures; (3) There are no outcome indicators concerned by this study; (4) Conference papers, summary of personal experience, individual cases, rules and regulations, reviews, animal experimental studies, etc.
2.4 Literature screening
Literature retrieval and screening were performed independently by two researchers.Firstly, we briefly read the literature title, abstract and key words for preliminary judgment; then read the full text and decide whether to reject according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria.Finally, cross-check was made to determine the final inclusion of literature.If two researchers disagree on the selection of a paper, a third qualified researcher is invited to make a judgment.
2.5 Literature data extraction
Excel 2019 software was used to collect and summarize basic information of the final included literatures, including the first author and publication year, diagnostic criteria, sample size, average age,sex ratio, intervention measures and treatment courses, and outcome indicators.
2.6 Literature quality evaluation
The risk of publication bias in included studies was evaluated using the Cochrane evaluation manual “Risk Assessment of Bias in RCT” (version 5.1.0) [12].The evaluation included randomization,assignment hiding, blinding, loss of follow-up and withdrawal,selective reporting, and other biases.The methodological quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Jadad scale [13].The evaluation content includes: random sequence generation method,random hiding, blind method, withdrawal and exit.Evaluation scale:1~3 were classified as “low quality” literature, 4~7 were classified as “high quality” literature.
2.7 Statistical methods
RevMan5.3 software was used for data analysis.Q test were used to test heterogeneity among included studies, I2reaction heterogeneity:if P> 0.1 and I250%, it indicates that there is statistical homogeneity, and fixed-effect model was used for meta-analysis.If P 0.1 or I2>50%, it indicates there is statistical heterogeneity,and random effect model is used [14].Odds ratio (OR) was used to represent the counting data, and weighted mean difference (WMD)was used to represent the measurement data.We calculated 95%confidence interval (CI).Combined effect size test: if P 0.05, the difference was statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Literature screening results
By searching various databases, 265 related literatures were obtained.After eliminating duplicate literatures, 111 literatures were obtained.After reading the titles of the articles, 65 articles were obtained by excluding the relevant treatment methods and rules, summary of personal experience, review, non-RCT, etc.After excluding incomplete data, unreasonable experimental design and intervention measures that did not meet the inclusion criteria, 51 literatures were obtained.Carefully read 47 studies with qualitative outcome indicators included.After final selection, 14 literatures were included for quantitative analysis [15-28].The document inclusion process is shown in Figure 1.

Fig 1 Flowchart of literature screening
3.2 Basic features of the included literature
A total of 14 RCT literatures were included in this study, including 1 186 patients.The sample sizes of observation group and control group were 595 and 591 respectively.The baseline data of sex ratio, mean age, mean course of disease and other general data of the experimental group and the control group were consistent and comparable.Basic characteristics of the included literature are shown in Table 1.
2.3 Evaluation of the methodological quality of the included literature
The 14 RCTs included all described intergroup consistency at baseline.13 literatures [15-27] were randomly divided into groups,and five of them were grouped [16,18-19,22,25] by random number method.Another one [28] refered to the order of visit number,which were considered inappropriate according to the evaluation principles of the Jadad scale.Among the included literatures, 1 used distributive concealment [19] and 2 used blind method [19,23].None of the included studies were reported selectively or had any other bias.Quality score of the included studies showed in Figure 2.The methodological quality assessment of the included studies is shown in Table 2.
3.4 Meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Total effective rate
The total effective rates of awn needle in the treatment of LDH were compared in 14 included studies, including 1 186 patients (595 in the experimental group and 591 in the control group).There was homogeneity among the included studies (P=0.34, I2=10%), and the fixed effect model was used to calculate the combined statistics.The results showed that the total effective rate of awn needle in the treatment of LDH was better than that of filiform needle,conventional traction, conventional acupuncture, traditional Chinese medicine ion import alone and western medicine [RR=1.17, 95%CI(1.12,1.22), Z =6.66, P<0.000 01], as shown in Figure 3.The funnel plot of total effective rate publication bias presented a basically symmetrical distribution on both sides, indicating that publication bias was less likely to be included, as shown in Figure 4.
3.4.2 VAS scores

Fig 2 Quality score of the included studies

Fig 3 Forest plot of total effective rate between the awn needle treatment group and the control group
9 studies [15-21,24,28] compared VAS scores, and a total of 740 patients were included (372 in the experimental group and 368 in the control group).Heterogeneity test (P=0.003, I2=54%) indicates that the random effects model should be used to calculate the combined statistics.The results showed that VAS scores of HDL patients in the awn needle group was significantly improved compared with the control group [WMD=-1.09, 95%CI (-1.27, -0.91), Z=12.00, P< 0.000 01].Sensitivity analysis was used to reduce heterogeneity.After excluding the research of Ji Yuejun [17] and Zheng Wenxian[27], the heterogeneity among different studies decreased (P=0.23,I2=26%), the fixed effect model can be used.The results showed that the improvement effect of awn needle therapy on VAS scores of HDL patients was superior to conventional acupuncture and traction[WMD=-1.07, 95%CI (-1.19, -0.95), Z=17.87, P < 0.000 01], as shown in Figure 5.
3.4.3 JOA scores
6 studies [15-16,18-19,20,28] compared JOA scores and included 586 patients (293 in the experimental group and 293 in the control group).Heterogeneity tests showed significant differences among included studies (P<0.000 01, I2=91%), the combined statistics were calculated using the random effects model, and the results showed that the treatment group was statistically significant compared with the control group [WMD=3.82, 95%CI (2.38,5.26), Z=3.82, P< 0.000 01].After sensitivity analysis, excluding the study of Xu Shouchen [15], the heterogeneity among studies was significantly reduced (P=0.36, I2= 7%), and the fixed effect model was adopted.The results showed that the improvement effect of awn needletherapy on JOA scores of HDL patients was superior to conventional acupuncture, conventional traction and Western medicine[WMD=3.18, 95%CI(2.64, 3.71), Z=11.57, P<0.000 01], as shown in Figure 6.

Tab 1 Basic characteristics of the included studies

Tab 2 Methodological quality assessment of the included studies
3.4.4 ADL scores
ADL scores were compared in 3 studies [15,22,25] involving a total of 308 subjects (154 in experimental group and 154 in control group).Heterogeneity test showed significant difference between the results(P<0.000 01, I2=97%), using random effects model.Since the ADL scores criteria used in the included studies were inconsistent, the effect indicators were combined with SDM.The results showed that the improvement effect of awn needle therapy on ADL scores of HDL patients was better than that of conventional acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine iontophoresis alone[SMD=2.44, 95%CI(0.54,4.35), Z=2.52, P=0.01], as shown in Figure 7.

Fig 4 Funnel plot of publication bias
3.4.5 SLRT angle

Fig 5 Forest plot of VAS score between the awn needle treatment group and the control group
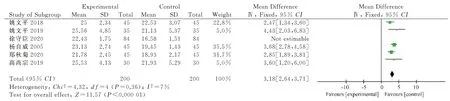
Fig 6 Forest plot of JOA score between the awn needle treatment group and the control group
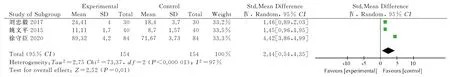
Fig 7 Forest plot of ADL score between the awn needle treatment group and the control group
2 studies [15,19] compared the angle of SLRT, involving a total of 228 patients (114 in experimental group and 114 in control group).Heterogeneity test showed significant difference between the results(P<0.000 01, I2=95%).Therefore, the random effect model was used to calculate the combined statistics.The results showed that the improvement effect of Awn on STRT scores of HDL patients was better than that of conventional filiform needle [WMD=12.71, 95%CI(3.21,22.21), Z=2.62, P=0.009], as shown in Figure 8.
3.5 Safety evaluation
None of the 14 RCTs reported adverse reactions to LDH treated by awned needle, among which 3 studies [19,23,24] have assessed the safety of the awn needle in the treatment of LDH to varying degrees.Wang Haitian[24] showed that there were no adverse events in the group treated with awn needle and the group treated with conventional filiform needle.Gao Shangzong [19] believed that the adult spinal cord only reaches the lower margin of the first lumbar vertebrae, and the spinal cord will not be damaged even if the awn needle is deeply stabbed.Moreover, the awn needle skews to the vertebral body, and the angle is safe.Wang Zichen [23] stimulated the lumbar Jiaji points of 50 LDH patients with 0.35 mm 100 mm awn needle, and selected 3 patients to observe the Deqi layer images under CT scan, which showed that no important organs or large blood vessels were damaged in the deep stimulation of awns needle.There were no complications such as needle-sickness, needlestagnation and local infection in the awn needle group, indicating that the treatment of LDH with awn needle is relatively safe.
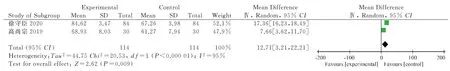
Fig 8 Forest plot of STRT score between the awn needle treatment group and the control group
4.Discussion
LDH is a degenerative disease caused by lumbar disc nucleus pulposus and cartilage endplate breaking through the broken annulus fibrosus and pressing the adjacent lumbosacral nerve root, causing lumbosacral pain, lower limb numbness and pain as the main symptoms [29].It usually occurs at L4/5 and L5/S1 levels, which is one of the most common causes of lumbago [30].Currently, LDH is mainly treated by non-surgical treatment, among which acupuncture treatment is widely used because of its good efficacy and small side effects [31].The mechanism of acupuncture in treating LDH is mainly manifested in improving microcirculation, relieving fatigue of lumbar and back muscles, inhibiting the emotional part of pain matrix in brain area, and inhibiting inflammatory factors[32].Modern research shows that acupuncture can regulate the nervous system by regulating neurohumoral and neural mediators to play an analgesic role [33].The therapeutic effect of awn on LDH was realized based on the theory of acupuncture and moxibustion, but it can also play an irreplaceable role of ordinary filiform needle.The disease location of LDH is deep, while the ordinary filiform needle is very short, which unable reach the disease location and has poor curative effect.Awn needle was developed from the “long needle” in the ancient “Nine Needles”.It is named because its body is slender and shaped like wheat awn.Nine Needles and Twelve Yuan Points of Miraculous Pivot: “the eighth is called a long needle, which is 7 inches long.It is sharp, and can treat deep diseases.” The operation technique of awn needle is characterized by “penetrating acupuncture” or“penetrating point”.Awn needle is long and thin, which can pass through muscles, fascia and ligaments to stimulate the deep part of the body [34].It is believed that the key to the good efficacy of awn needle in the treatment of LDH lies in its ability to strongly stimulate Jiaji points, dredge the meridians and collaterals.Through acupoint stimulation and meridians transmission, it improves blood circulation, blocks the pathological mechanism of “Not General Pain”, and finally blocks the pain reflex arc and relieves pain [35,36].On the other hand, awn needle directed deep puncture and reach the site of the disease, which can directly stimulate nerve roots,reduce nerve tension, promote neurohumoral metabolism, reduce neuroinflammation edema, relieve the pain caused by nerve root compression in LDH patients.
14 RCTs were included in this study, with a total of 1 186 patients.Meta-analysis results showed that awn needle therapy was superior to other therapies in total response rate, improved VAS scores, JOA scores, ADL scores, SLRT Angle and other outcome indicators with statistically significant differences.In addition, 14 included RCTs reported no adverse reactions or complications in the treatment process, indicating that the treatment of LDH by awned needle is safe and effective, which is worthy of clinical application and promotion.
There are still some limitations in this study: (1) the included literatures are all domestic studies and lack of foreign studies, which may lead to publication bias; (2) Only 14 literatures were included,which was less quantity, and the included literatures lacked multicenter RCT studies with large sample size; (3) 2 studies did not specify diagnostic criteria[21, 22], there may exist diagnostic suspicion bias; (4) Although all the included studies showed that the basic data of the experimental group and the control group were consistent at baseline, 2 of them lacked an accurate description of the “mean age”[7,24], 3 studies lacked specific reports on “average age” and “sex ratio”[22,23,26]; (5) The heterogeneity among the included studies was large and the methodological quality was poor.According to Jadad scoring criteria, only 1 of the included studies was of “high quality” [19], the rest were of “low quality”.① Only 5 of the 14 RCTs described the specific methods of randomized control[16,18, 19, 22, 25] ,1 of the included studies adopted an unreasonable random method [28].other studies only roughly mentioned the “use of random grouping” and did not explain the specific method of random sequence, so the possibility of selection bias cannot be ruled out.② Only 1 study adopted allocation hiding [19]; ③ Blind method was used in 2 studies[19, 23], other studies did not explain the use of blinding method, which may have “placebo effect” or be influenced by “observer preference”, resulting in implementation bias and measurement bias; (4) Only 2 studies described the case shedding in the experiment [19,24]; (6) Only 2 studies were followed up 6 months later to observe the recurrence rate [15,28], other studies only focused on short-term efficacy without long-term follow-up of cases, lacking follow-up investigation and evaluation of followup effects.In addition, there were differences among RCTs in the course of disease, treatment course, specific acupoint selection site,manipulation technique and combined treatment method of the included patients.Meanwhile, the scores of each outcome index were subjective and unreliable.These factors may influence the results, and may also be the reason for the large heterogeneity among the RCTs.Based on the above discussion, the final conclusion of this meta-analysis cannot be drawn at present.It is necessary to further verify through a large number of high-quality randomized controlled clinical trials.It is suggested that future studies should clarify diagnostic criteria and use universally recognized and unified diagnostic criteria; General information of the experimental group and the control group should be reported in detail to ensure consistent baseline of included cases; To improve the scientific and rigorous nature of clinical trials, pay more attention to strengthening methodological standards, report in detail the specific methods for the generation and distribution of random sequences, conduct clinical trials using double-blind methods, record the termination,withdrawal and shedding of cases in detail, avoid subjective sensation scale as the therapeutic effect of awn needle for LDH, and make objective outcome indicators as therapeutic support.At the same time, attention should be paid to the observation of long-term efficacy, the interval and content of follow-up should be determined,and the follow-up data should be strictly recorded and managed to increase the credibility of the study results.In conclusion, the quality of clinical randomized controlled trials on LDH treated by awn needle therapy should be further improved in the future, and the authenticity and reliability of research results should be improved, so as to better guide clinical practice.
Author's contribution:
The article was designed by Wu Zi-jian, Li Yan-ju, Chen Xingsheng and Hu Ling.Wang Min-jun and Li Liao-yuan collected information.Cui Hai-ling wrote this paper, meanwhile, Wu Zi-jian reviewed it.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Advances in pharmacological action of bergamot lactone
- Progress of improvement of pain and joint function of knee osteoarthritis treated with thunder-fire moxibustion in the last five years
- Abnormal expression of TGFβ1 in acute myeloid leukemia and its regulation effect on leukemia cells
- Analysis of key pathogenic target genes of ovarian cancer and experimental verification of cells in vitro
- Investigation of paeonol-geniposide on acute alcoholic liver injury based on uniform design method
- Effect of Drynaria total flavonoids on the expression of NMDAR1,GluR2 and CaMK Ⅱ in the brain of hydrocortisone model mice
