Effect of Drynaria total flavonoids on the expression of NMDAR1,GluR2 and CaMK Ⅱ in the brain of hydrocortisone model mice
2022-03-16WANGYitongXUYanmingZHANGZhiboSUNHuifengZHANGNingYANGBo
WANGYi-tong, XU Yan-ming, ZHANG Zhi-bo, SUN Hui-feng,, ZHANG Ning,,YANGBo✉
1.School of Pharmacy, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, China
2.College of Jiamusi, Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jiamusi 154007, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To study the effect of total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae on the expression of NMDAR1, GluR2 and CAMKⅡ protein in model mice of kidney deficiency induced by exogenous glucocorticoid hydrocortisone and its mechanism.Methods: Kunming (KM) mice were randomly divided into the blank group, the hydrocortisone model group, the anti-brain failure capsule group, the Drynaria total flavonoids group, the Drynaria total flavonoids+ER blocker group, with 15 animals in each group.Except for the blank group, all groups were injected intramuscularly with hydrocortisone (25 mg·kg-1·d-1) to create models.The water maze experiment, new object recognition experiment and platform jump experiment were used to conduct behavioral investigations.HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of mouse hippocampus, and Western blotting detected the expressions of NMDR1,GluR2 and CAMKⅡ proteins in the hippocampus of mice in each group.Results: The experimental results showed that compared with the model group, the learning and memory ability of the mice in the Drynaria fortunei total flavonoids group was significantly improved,and the difference was statistically significant (P <0.01), the expression of NMDR1 and GluR2 proteins in the hippocampus of the mice was significantly increased (P<0.01), and the level of CAMKⅡ protein significantly decreased (P<0.01).Conclusion: The total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae may enhance the expression of NMDAR1 and GluR2 protein in the brain of hydrocortisone model mice through ER, reduce the expression of CAMKⅡ protein, and alleviate the damage to the brain tissue of the model mice and play a neuroprotective effect.
1.Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex and heterogeneous disease caused by a combination of factors, characterized by the entanglement of aggregated amyloid beta (Aβ) and hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated protein (tau).knot [1].In recent years, it has been found that estrogen is closely related to learning and memory ability.If postmenopausal women do not supplement estrogen, memory and cognitive function will be significantly reduced, and the probability of AD will be greatly increased [2].However, experiments have shown that the use of hormone replacement therapy for AD has a time window, and the time window is narrow.If the time window is exceeded, there is no therapeutic effect or even serious side effects [3], so the advantages of traditional Chinese medicine phytoestrogens are highlighted.
Rhizoma Drynariae is a kind of fern from the family Hydrangea,which has the effect of invigorating the kidney, strengthening the bone and activating blood circulation.The main chemical components in its rhizomes are flavonoids, triterpenes and lignins.Drynaria can isolate and purify more than 40 kinds of flavonoids [4],with dihydroflavonoids, catechins and their derivatives as Mainly,naringin and new erioside are both phytoestrogens, which are similar to synthetic estrogens [5], and have less toxic and side effects.Ge[6] verified the protective effect of naringin and kaempferol in total flavonoids on Aβ25-35-induced adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC12)cells in rats, suggesting that drynaria total flavonoids can improve brain function.Learning and memory effect, but its anti-AD effect is unclear and related literatures are few.In addition, studies have shown that the regulatory effect of estrogen on learning and memory is mediated through estrogen receptor (ER) [7], so it is speculated that the total flavonoids of Drynariae may be mediated through the ER pathway to treat AD, and N-methyl flavonoids-D-aspartate(NMDAR1), glutamate receptor (GluR2) and calcium/calmodulindependent protein kinase (CAMKⅡ ) protein expression levels in the brain to verify the speculation.In this study, mice with kidney deficiency induced by hydrocortisone were used as AD model mice,and the model mice were given total flavonoids of Drynariae as the treatment group.The central protective effect of total flavonoids on AD rats provides experimental support for its clinical medication.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental animals
SPF grade KM mice, 75 males, 3 months old, were purchased from Changsheng Biological Company, certificate number: SCXK (Liao)2015-0001.The temperature of the rearing environment was 20~22℃, the relative humidity was 50%~70%, and water was freely fed.The experimental procedures were in compliance with the relevant regulations of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine on the management of experimental animals.
2.2 Drugs and Reagents
Drynaria total flavonoids (self-extracted) and Kangnaoshui capsules (batch number KN15112502) were purchased from Siyao Co., Ltd.; rabbit anti-β-actin polyclonal antibody (batch number BM3873) and HRP-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (batch number BA1054) were purchased from Boster Company; NMDAR1 (batch number bs-23343R), GluR2 (batch number bs-9921R), CAMKⅡ(batch number bs11347R) were purchased from Bioss Company,ER blocker (model: ICI182780) was purchased from TOCRIS Company; Hydrocortisone (Lot number: B21001) was purchased from Yuanye Bio.
2.3 Instruments
MiniPROTEANTetra Cell electrophoresis apparatus (BIORAD company); Trans-Blot SD Cell semi-dry membrane transfer apparatus (BIO-RAD company); WD9405B horizontal shaker (Liuyi Instrument Factory); water maze equipment (Zhenghua company); New Object Recognition Equipment (Easu Company); Platform Jumping Equipment (Easu Company).
2.4 Animal grouping and model preparation
Seventy-five 3-month-old KM mice were randomly divided into 5 groups according to their body weight: Blank group, Model group,Kangnaoshui capsule control group (KNSC group), Drynariae total flavonoids group ( TFRD group), total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae+ER blocker group (TFRD+ER group).The blank group and model group were given distilled water by gavage, Kangnaoshui capsule control group and Rhizoma Drynariae total flavonoids group were given Kangnaoshui Capsule 585 mg·kg-1·d-1and Rhizoma Drynariae total flavonoids 97.5 mg·kg-1·d-1; Rhizoma Drynariae total flavonoids + ER blocker group were given intraperitoneal injection of ER blocker IC1182780 0.072 mg·kg-1·d-1, followed by 97.5 mg·kg-1·d-1total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae; continuous irrigation After 3 weeks in the stomach, the blank group was given double distilled water; the other groups were injected with hydrocortisone 25 mg·kg-1·d-1for modeling, and the drug was administered while modeling; one week later, behavioral experiments were performed.
2.5 Behavioral experiments
2.5.1 Novel Object Recognition Experiment (ORT)
The new object experiment was carried out with reference to the literature method method [8].The contact time of mice to new objects and the contact time to old objects within 5 min were recorded, and the recognition index was calculated.
2.5.2 Morris water maze test (MWM)
The water maze experiment was carried out according to the method of literature [9].The first 4 days were the positioning cruise experiment, and the space exploration experiment was started on the 5th day.The number of times the mice crossed the platform within 90 s and the stay time in the target quadrant were recorded.In the platform jumping experiment, mice were trained for 24 h and the latency and the number of jumps were recorded under the condition of electrification.
2.5.3 Materials
After the behavioral study, 6 mice in each group were randomly selected for cardiac perfusion and immersed in paraformaldehyde for 48 h for HE staining experiment; the rest of the mice were quickly stripped of hippocampal tissue on ice and stored in liquid nitrogen tanks for later use.
2.5.4 Histopathological observation
HE staining: The left hemibrain fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 h was embedded in paraffin and sliced.After dewaxing with alcohol, they were placed in double-distilled water for dehydration;stained with hematoxylin for 5 min, washed with water, and placed in hydrochloric acid ethanol for a few seconds; immersed in eosin aqueous solution for 5 min, washed with water; dehydrated,mounted, and observed.
2.5.5 Western blot
The hippocampus of mice was collected on ice and treated with lysate, and the supernatant was obtained by centrifugation, and the protein concentration was determined according to the instructions.After transferring to the membrane by semi-dry transfer method and shaking and blocking for 2 h, the primary antibodies β-actin (1:5 000), NMDAR1 (1:500), GluR2 (1:500) and CAMKⅡ (1:500) were added.The mixture was placed at 4 ℃ overnight, the membrane was washed, the secondary antibody (1:5 000) was added to incubate for 2 h, the membrane was washed 4 times, and the luminescent solution was added and placed in a chemiluminescence imager for analysis.
2.6 Statistical processing
The data were analyzed by SPSS18.0 statistical software, and the comparison between groups was performed by one-way ANOVA.The experimental data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation(±s), and P<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3.results
3.1 The effect of total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae on the behavioral ability of mice in each group
3.1.1 Experimental test results of new object recognition
The results of the new object recognition experiment are shown in Table 1.Compared with the Blank group, the recognition index of the Model group decreased significantly (P<0.01); compared with the Model group, the recognition index of the KNSC group and TFRD group increased significantly (P<0.01); there was no significant difference between the KNSC group and the TFRD group(P>0.05); compared with the TFRD group, the recognition index of the TFRD+ER group was significantly reduced (P<0.01).
Tab 1 Effects of total flavonoids of Drynaria fortunei on new object recognition experiment in mice (n=15, ±s)

Tab 1 Effects of total flavonoids of Drynaria fortunei on new object recognition experiment in mice (n=15, ±s)
Note: Compared with Blank group, **P<0.01; compared with Model group,##P<0.01; compared with TFRD group, &&P<0.01.
Group Identification Index Blank group 0.441±0.017 Model group 0.252±0.012**KNSC group 0.385±0.015##TFRD group 0.364±0.010##TFRD+ER group 0.290±0.014&&
3.1.2 Test results of water maze test
In the positioning route experiment, the results are shown in Table 2.Compared with the Blank group, the latency of the Model group was significantly increased (P<0.01); compared with the Model group, the latency of the KNSC group and TFRD group was significantly decreased (P<0.01); There was no significant difference between the KNSC group and the TFRD group (P>0.05); compared with the TFRD group, the latency of the TFRD+ER group was significantly increased (P<0.01).
Tab 2 Effects of total flavonoids of Drynaria fortunei on navigation latency of mice in each group (n=15, ±s)

Tab 2 Effects of total flavonoids of Drynaria fortunei on navigation latency of mice in each group (n=15, ±s)
Note: Compared with Blank group, **P<0.01; compared with Model group, ##P<0.01; compared with TFRD group, &&P<0.01.
Group Day 1(s) Day 2(s) Day 3(s) Day 4(s)Blank group 45.953±1.702 37.899±2.596 31.674±1.380 25.152±3.509 Model group 69.262±3.301** 61.180±2.621** 55.895±3.255** 45.523±2.206**KNSC group 48.930±1.305## 41.372±1.864## 40.065±1.957## 32.352±1.383##TFRD group 49.946±2.141## 41.873±2.626## 42.582±2.658## 34.638±2.201##TFRD+ER group 58.951±1.905&& 52.858±3.346&& 49.007±2.389&& 39.656±2.157&&
In the spatial exploration experiment, the results are shown in Table 3.Compared with the Blank group, the spatial exploration ability of the Model group decreased significantly (P<0.01); compared with the Model group, the spatial exploration ability of the KNSC group and TFRD group increased significantly (P<0.01); there was no significant difference between the KNSC group and the TFRD group(P>0.05); compared with the TFRD group, the spatial exploration ability of the TFRD+ER group was significantly reduced (P<0.01).
In the platform jumping experiment, the results are shown in Table 4.Compared with the Blank group, the Model group's escape latency was significantly reduced, and the number of errors was significantly increased (P<0.01).Compared with the Model group,the KNSC group and TFRD group mice escaped.The latency was significantly increased, and the number of errors was significantly decreased (P<0.01); there was no significant difference between the TFRD group and the anti-KNSC group (P>0.05); compared with the TFRD group, the escape latency of the TFRD+ER group mice was significantly decreased, and the number of errors was significantly increased (P<0.01).The experimental results show that the total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae can significantly improve the learning and memory ability of hydrocortisone model mice.
Tab 3 Effects of Drynaria total flavonoids on space exploration of mice in each group(n=15, ±s)
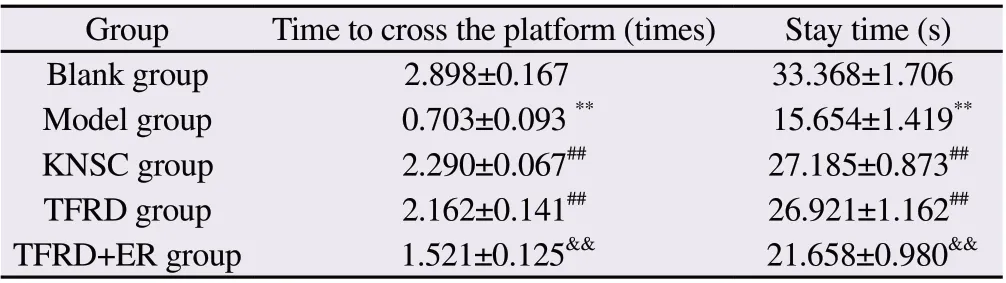
Tab 3 Effects of Drynaria total flavonoids on space exploration of mice in each group(n=15, ±s)
Note: Compared with Blank group, **P<0.01; compared with Model group,##P<0.01; compared with TFRD group, &&P<0.01.
Group Time to cross the platform (times) Stay time (s)Blank group 2.898±0.167 33.368±1.706 Model group 0.703±0.093 ** 15.654±1.419**KNSC group 2.290±0.067## 27.185±0.873##TFRD group 2.162±0.141## 26.921±1.162##TFRD+ER group 1.521±0.125&& 21.658±0.980&&
Tab 4 Effects of Drynaria total flavonoids on error times and dark avoidance latency of mice in each group (n=15, ±s)
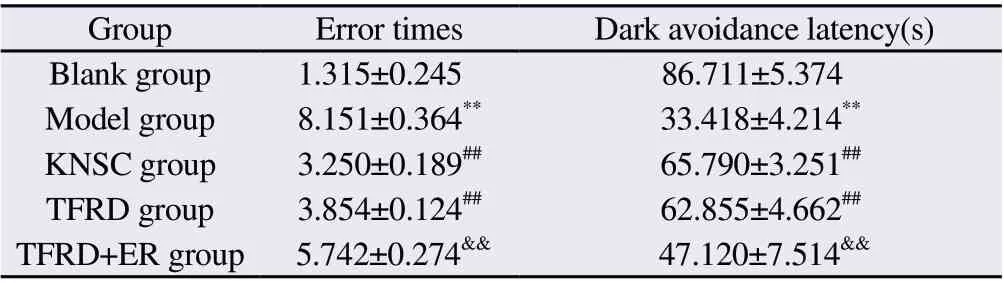
Tab 4 Effects of Drynaria total flavonoids on error times and dark avoidance latency of mice in each group (n=15, ±s)
Note: Compared with Blank group, **P<0.01; compared with Model group,##P<0.01; compared with TFRD group, &&P<0.01.
Group Error times Dark avoidance latency(s)Blank group 1.315±0.245 86.711±5.374 Model group 8.151±0.364** 33.418±4.214**KNSC group 3.250±0.189## 65.790±3.251##TFRD group 3.854±0.124## 62.855±4.662##TFRD+ER group 5.742±0.274&& 47.120±7.514&&
3.2 HE staining results of total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae on the hippocampus of mice in each group
The results are shown in Figure 5.The cells in the hippocampus of the mice in the Blank group are complete, tightly arranged,with a large number of neurons and clear nucleoli.The cells in the hippocampus of the Model group mice are disorderly arranged,and the number of some neurons is reduced.The phenomenon of pyknosis was obvious; the TFRD group was similar to the KNSC group, the cells in the hippocampus were more closely arranged, the number of neurons was more, and the nucleoli were clear; Normal,but clear nucleoli without obvious pyknosis.
3.3 Effects of total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae on the expressions of NMDAR1, GluR2 and CAMKⅡ proteins in the hippocampus of mice in each group
The results are shown in Figure 6: Compared with the Blank group,the CAMKII content of the Model group increased (P<0.01), while the NMDAR1 and GluR2 contents decreased (P<0.01); compared with the Model group, the CAMKII content of the KNSC group and TFRD group decreased (P<0.01).P<0.01), the contents of NMDAR1 and GluR2 in KNSC group and TFRD group increased (P<0.01);there was no significant difference between TFRD group and KNSC group (P>0.05).Compared with TFRD group, CAMKⅡ contents in TFRD+ER group increased.(P<0.01), the content of NMDAR1 and GluR2 decreased (P<0.01).The experimental results showed that the total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae could significantly increase the expression of NMDAR1 and GluR2 proteins in the hippocampus of hydrocortisone model mice, and at the same time significantly reduce the level of CAMKⅡ protein.
Tab 5 Effects of Drynaria total flavonoids on the expression of NMDAR1, GluR2 and CAMK Ⅱ in the hippocampus of mice in each group(n=15,±s)
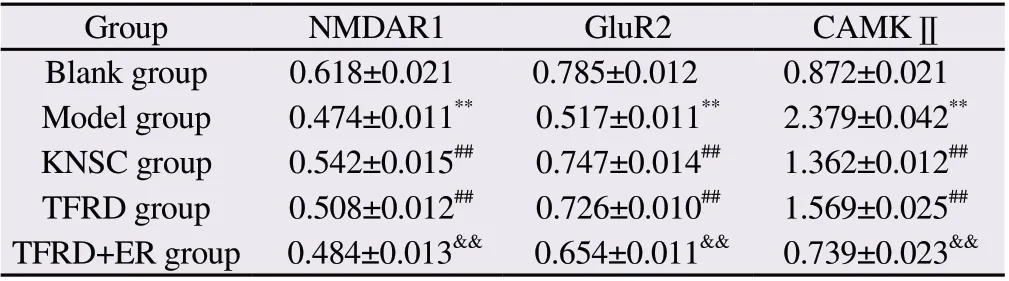
Tab 5 Effects of Drynaria total flavonoids on the expression of NMDAR1, GluR2 and CAMK Ⅱ in the hippocampus of mice in each group(n=15,±s)
Note: Compared with Blank group, **P<0.01; compared with Model group,##P<0.01; compared with TFRD group, &&P<0.01.
Group NMDAR1 GluR2 CAMKⅡBlank group 0.618±0.021 0.785±0.012 0.872±0.021 Model group 0.474±0.011** 0.517±0.011** 2.379±0.042**KNSC group 0.542±0.015## 0.747±0.014## 1.362±0.012##TFRD group 0.508±0.012## 0.726±0.010## 1.569±0.025##TFRD+ER group 0.484±0.013&& 0.654±0.011&& 0.739±0.023&&
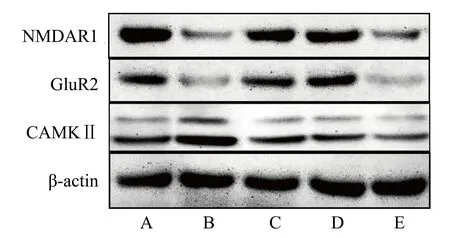
Fig 2 Expression of NMDAR1, GluR2 and CAMKⅡ protein in mouse hippocampus(n=3)
4.Discussion
As the population ages, Alzheimer's disease is becoming a major health crisis worldwide.Although the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease has been greatly understood in the past few decades, there is still a lack of effective treatments in the clinic [10].Chinese medicine believes that "the kidney controls the bones, generates the marrow,and communicates with the brain", which mainly means that the kidney stores the essence, and then the essence is the marrow [11].The mouse model of Alzheimer's syndrome is a common animal model for the study of Alzheimer's disease based on the theory of traditional Chinese medicine [12].After injecting a large amount of glucocorticoid hydrocortisone into the animal, it will cause negative feedback in the body, disturb the hormone level in the body, and appear mentally depressed, Symptoms such as unresponsiveness,dry hair, and frequent nocturia can create a pathological model of kidney-yang deficiency in animals, and glucocorticoids can promote oxidative stress and cause the death of hippocampal neurons, which can acutely damage various components of working memory.[13].Therefore, this paper adopts the kidney deficiency model made by hydrocortisone to study the mechanism of the total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae in improving AD-related diseases.
Western medicine studies believe that estrogen may be related to AD treatment in some pathways through its receptors.After estrogen binds to estrogen receptors, it acts on the estrogen response element(ERE) located in the DNA of the upstream promoter region of the target gene., under the regulation of a variety of factors, enhance or inhibit the transcription of target genes [14].Although estrogen has obvious anti-AD potential, long-term use of synthetic estrogen can easily cause endometrial lesions, causing side effects such as venous thrombosis and breast cancer.Therefore, the use of natural Chinese herbal medicines and their preparations has become a hot spot in the treatment and prevention of AD.Yuanchao [15] and other studies have shown that phytoestrogens can improve the learning and memory function of ovariectomized rats.The main components of Rhizoma Drynariae, naringenin (flavonoids), quercetin (flavonols) and other compounds are all bisphenols, which are similar to synthetic estrogens and can stimulate ER and ERβ, regulate hypothalamuspituitary- Gonadal axis, and then stimulate various systems in the body to prevent AD.Estrogen exhibits multiple physiological effects in the brain, including neuronal differentiation, neurogenesis,and neuroplasticity, which are critical for inhibiting homeostasis,cognition, and retention [16].Estrogen can improve the expression of targeted proteins in AD-related hypotheses, and its role is mainly through binding to ER to induce the expression of target genes [17],mediated by second messengers, and activating multiple related pathways to exert neuroprotection.effect.ER belongs to the steroid hormone family of the supranuclear receptor family, and it was previously believed that ER is a transcription factor mainly localized in the nucleus [18].However, the ER is also present at the plasma membrane and is involved in rapid estrogen signaling.Song et al.[19]verified through experiments that phytoestrogens also play an antiosteoporosis effect through this process, and the authors speculated that phytoestrogens Drynariae also regulate the preventive effect on AD through ER mediation.
Hyperactive glutamatergic signaling occurs in the early stages of AD pathology, which is thought to be mediated by reduced glutamate uptake [20].One mechanism that has emerged is the coupling of canonical estrogen receptors to glutamate receptors(Glu) to initiate G protein signaling cascades that ultimately affect neuronal physiology, structure, and behavior.The association of ER with different subtypes of glutamate receptors appears to drive distinct molecular outcomes that can affect processes such as cognition, motivation, movement, and pain.Glutamate receptors(Glu) are one of the most important excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the central nervous system and are usually found in glial cells and neurons.Glutamate receptors are closely related to energy metabolism in the brain and are essential for maintaining glutamatergic neurotransmission [21].Glutamate receptors are divided into two types: ionotropic glutamate receptors and metabolic glutamate receptors.Among them, ionotropic receptor channels include N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), α-aminohydroxymethyl oxazole propionic acid (AMPA) and jujube acid salt (KA) receptor channels, among which α- Aminohydroxymethyl oxazole propionic acid receptors have four subunits: GluR1, GluR2, GluR3, and GluR4, and GluR1 and GluR2 are the main ones.Metabotropic glutamate receptors are closely related to calcium ion channels on cell membranes.Studies have shown that abnormal Ca+signaling pathway may be the potential pathogenic mechanism of Alzheimer's disease due to kidney deficiency.Calmodulin (CaM/CALM) can combine with Ca+in neurons to form calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CAMK) II initiates a variety of downstream signaling pathways, and CAMK II is activated in the hippocampus to participate in the formation of synaptic plasticity, brain learning and memory [22].N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDAR) is the most widely studied ionotropic glutamate receptor, and it is ubiquitously present in the central nervous system and plays an important role.They are involved in excitotoxicity, which is a major factor in AD.Widely accepted causative factor for neuronal and synaptic loss [23].It has been confirmed that the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases may be closely related to the dysregulation of NMDAR activity.NMDA receptors and estrogen receptors are co-expressed in the hippocampus, which are closely related to learning and memory ability, and are the main mediators of glutamatergic neuron damage in the pathogenesis of AD.The total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae may rapidly activate the ERK1/2 signaling pathway through estrogen receptors, phosphorylate the NR2B subunit [24],and then activate NMDA receptors.Estrogen, estrogen receptors,and NMDA receptors all affect synapses plasticity.
This study showed that compared with the control group, the expression of NMDAR and GluR2 proteins in the brain of the model mice was significantly reduced, and the expression of CAMKⅡ protein was significantly enhanced, the regulation of Rhizoma Drynariae on Appellate protein was reversed, and the improvement effect on learning and memory in mice basically disappeared.Combined with the contents of Appellate, it is speculated that the total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae may improve the learning of hydrocortisone model mice through the ER pathway.Memory impairment, unresponsiveness and other symptoms can reduce the damage to the brain tissue of the model mice and play a neuroprotective role, thereby achieving the effect of treating AD, and providing a new direction for the development of safe and effective new drugs for the treatment of AD.
Author's contribution:
Wang Yi-tong: index detection, data analysis, and paper writing;Xu Yan-ming: model establishment, index detection; Zhang Zhibo: model establishment, index detection; Sun Hui-feng: model establishment and material selection; Yang Bo: research director;Zhang Ning: instructor.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Advances in pharmacological action of bergamot lactone
- Progress of improvement of pain and joint function of knee osteoarthritis treated with thunder-fire moxibustion in the last five years
- Abnormal expression of TGFβ1 in acute myeloid leukemia and its regulation effect on leukemia cells
- Analysis of key pathogenic target genes of ovarian cancer and experimental verification of cells in vitro
- Investigation of paeonol-geniposide on acute alcoholic liver injury based on uniform design method
- Screening and functional analysis of the long-range interaction elements of β-globin genes
