一种基于高阶内模的新型自适应迭代学习算法
2022-03-09张国山李思祺
张国山,李思祺
一种基于高阶内模的新型自适应迭代学习算法
张国山,李思祺
(天津大学电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072)
本文针对一类含多个时间迭代变化参数控制方向未知的非线性离散时间系统的输出跟踪问题,提出了一种基于高阶内模的新型自适应迭代学习算法.假设多个时间迭代变化参数由不同的高阶内模所生成,本文所提出的算法借鉴了模型预测控制的思想,通过构建预测输入,将获得的当次迭代预测跟踪误差作为先验知识,应用到系统输入的控制律的设计中,从而在预测跟踪误差的基础上进一步缩小系统的跟踪误差.相较于基于高阶内模的传统迭代学习算法,大幅度缩减了系统的输出跟踪误差,明显地提高了跟踪精度.此外,由于预测跟踪误差作为先验知识参与了系统输入控制律的设计,该方法对于系统扰动和输出噪声具有较强的鲁棒性.通过Lyapunov稳定性理论,证明了该方法下系统跟踪误差的收敛性和所提算法的优越性.通过两组仿真算例,考虑在控制方向已知和未知两种情况下,和两种基于高阶内模的已有迭代学习算法进行了对比,验证了理论结果.
自适应迭代学习控制;高阶内模;非线性离散时间系统;时间迭代变化参数
迭代学习控制是一种解决重复环境下动态系统跟踪问题的有效方法,当系统输出重复跟踪参考轨迹时,利用上一次迭代的跟踪误差信息更新当前迭代控制输入[1-5].近年来,迭代学习控制在工业过程中有很多应用,如高速公路交通控制[6]、机器人操纵器[7]、高速火车[8]、微型飞行器(MAV)[9]和多智能体系统等[10-11].
传统的迭代学习控制框架要求过程具有严格的可重复性,但实际应用中很难满足这一要求.迭代变化初始状态[12]、迭代变化扰动[13]和迭代变化轨迹[14]在工业过程中会经常遇到,有时还会同时遇到多个迭代变化因子[15].实际上,在工业过程中所遇到的一些变化方向是已知的迭代变化因子可以沿迭代轴用高阶内模来进行描述;即当前迭代中的迭代变化因子是前几次迭代中对应项的线性组合[16].
因此基于高阶内模的迭代学习算法对于含有时间迭代变化因子的系统的输出跟踪问题时效果极好.文献[17-18]研究了含迭代变化因子的线性离散时间系统的输出跟踪问题.文献[19]考虑了含迭代变化因子的非线性离散时间系统的输出跟踪问题.在此基础上,Liu等[20]针对一类具有二阶内模参数不确定性的离散时间非线性系统,提出了一种基于最小二乘法自适应迭代学习控制算法.虽然考虑了状态扰动对系统的影响,但并未将二阶内模推广至高阶内模.Yu等[21]针对一类同时具有参数和非参数不确定性的离散时间非线性系统,提出了一种新的鲁棒自适应迭代学习控制算法,得益于良好的死区函数设计,参数和非参数不确定性可以同时进行学习.文献[22]讨论了与文献[20]相同的系统在控制增益未知的情况下的迭代学习控制,由于控制增益也成为了学习对象,系统的状态扰动无法有效描述,导致该算法与文献[20]所提算法均无法有效削减状态扰动对系统输出造成的影响,鲁棒性也无法得到保证.
本文针对一类含多个迭代变化参数的非线性离散时间系统,提出了一种基于高阶内模的同时适用于控制方向已知和未知两种情况的新型迭代学习控制算法.该方法借鉴了预测控制的思想,通过构造一个预测输入,得到当次迭代的预测跟踪误差,并将其作为先验知识去构建系统输入控制律,进而有效地减小了跟踪误差,提升了跟踪效果.通过理论证明,该方法可以在存在多个迭代变化参数且控制方向未知的情况下实现对非线性离散系统的有效输出跟踪.与现有方法相比较,本文所提方法适用于控制增益已知和未知两种情况,在跟踪精度和收敛速度上有明显提升,且在存在外部扰动的情况下具有一定的鲁棒性.最后通过两个算例验证了理论结果.
1 问题描述
考虑离散时间非线性系统


式中为已知连续函数.
下面是后文中要用到的两个假设.


本文所提出的两个假设均为该类问题所需的一般假设.
引理1[23]如果

式(4)的高阶内模可以描述为多项式

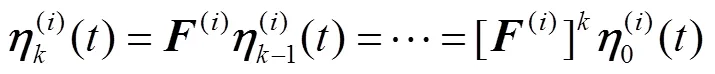

式(8)也可以写作
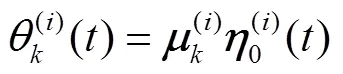
将式(9)代入系统(1)得
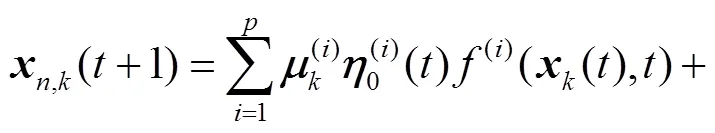

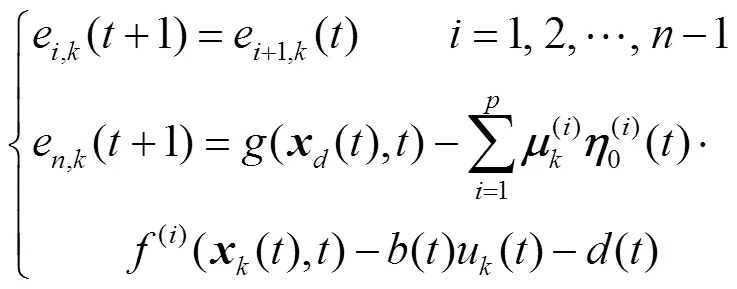
根据式(8)可得

进而有


式(12)可以表示为
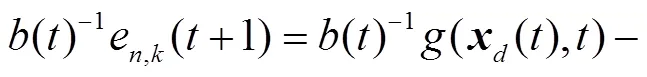

2 算法设计
本文所提出的迭代学习算法借鉴了模型预测控制思想,以第次迭代为例,进行控制律算法设计.
首先,构建一个预测输入



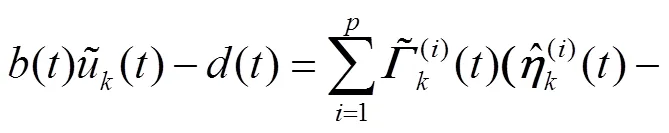
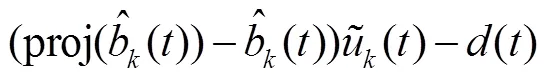


式中为一正常数.
然后,将得到的预测跟踪误差加入到系统输入的控制律的设计当中


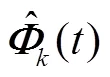
3 收敛性分析
定理 1 对于非线性离散系统(1),在假设1和2的前提下,控制律(15)、(20)和参数更新律(18)、(19)满足:



将式(18)代入式(22)右边第1部分可得



同理可以得到式(22)右边的第2部分为


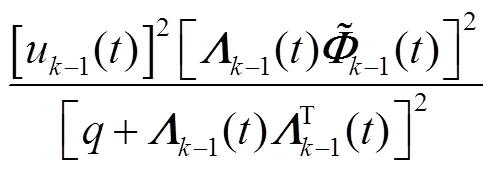
则式(22)可以表示为



由式(25)可得
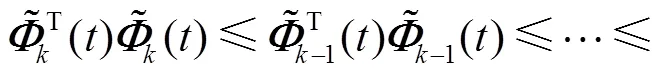
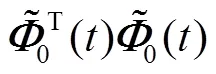
即
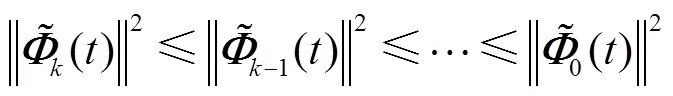
由式(25)可得

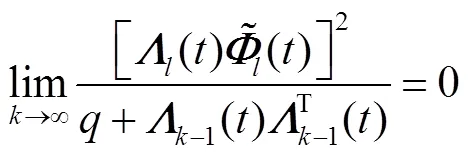
根据学习律式(18)和式(19)可得


同理



由式(29)和式(31)可得


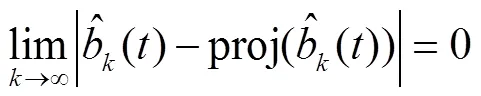
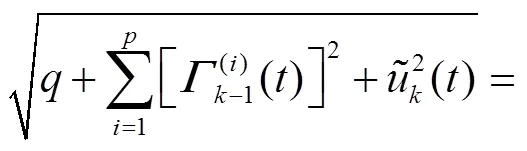

因此


由式(34)可得

由式(17)、式(32)和式(37)可得
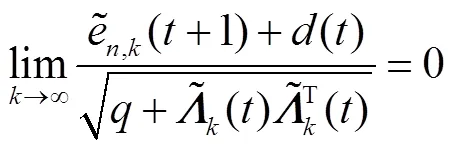




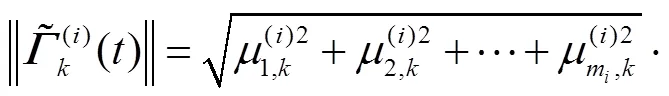

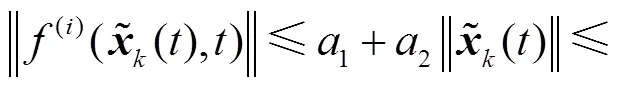

由式(42)和式(43)可得
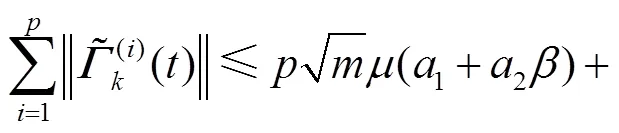

将式(41)和(44)代入式(40),可得

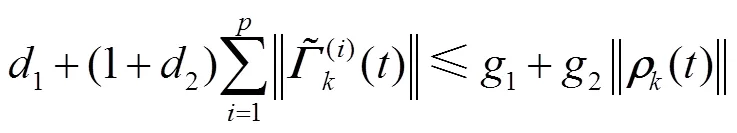
由式(11)可以得到


进而


综上可得
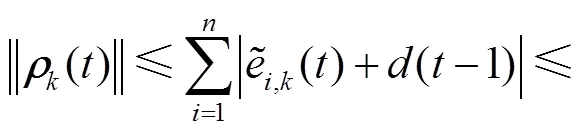
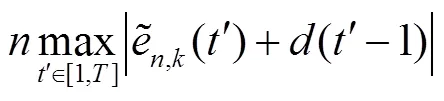
将式(48)代入式(45)
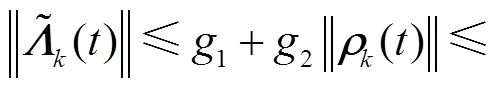


由式(10)和式(15)可知



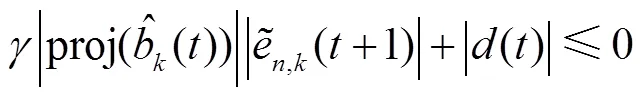



根据控制律(15)可知


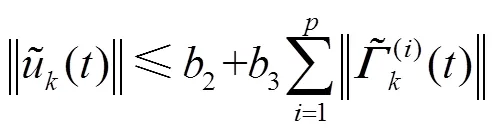
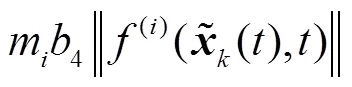

将式(57)代入式(40)可得
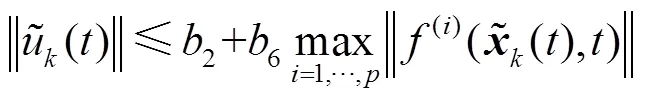

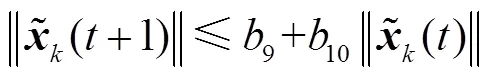

4 仿真算例
例1:考虑文献[20]中的非线性系统



图1 时间迭代变化因子和




例2:考虑文献[22]中的非线性系统


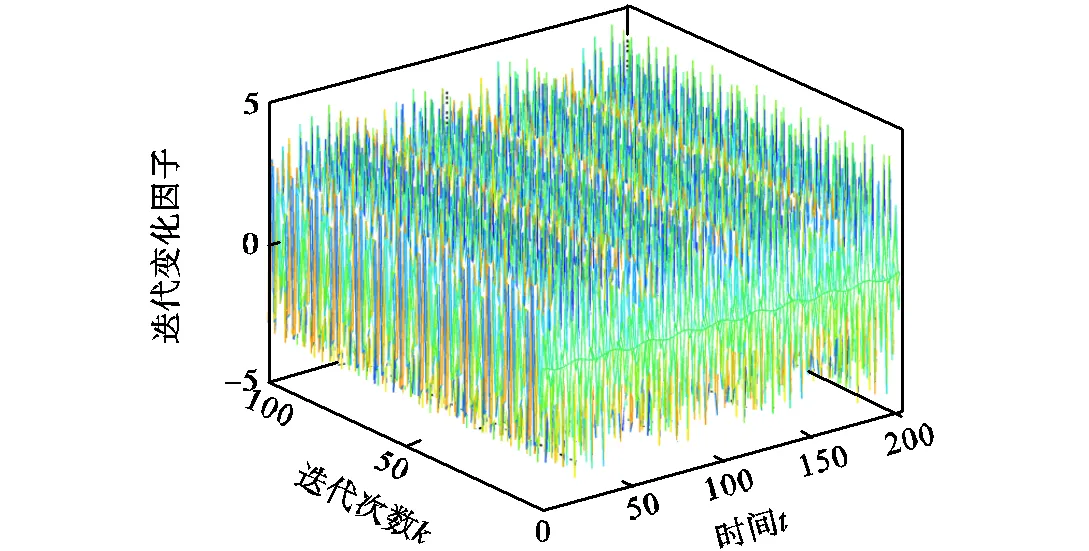
图4 时间迭代变化因子

图5 例2中输入增益估值

图6 例2中跟踪误差绝对值的最大值
本文所研究的两个仿真实例均为离散时间系统,其采样周期为0.05s.作为对比,文献[20]中的方法是在控制方向已知的情况下设计的;文献[22]中的方法是在控制方向未知的情况下设计的.
5 结 语
本文针对一类含多个迭代变化参数的非线性离散系统,提出了一种新的基于高阶内模的迭代学习控制方法.借鉴预测控制的思想,通过构建预测输入并将其代入系统的方式获得预测跟踪误差作为先验知识,然后将其运用到系统输入的控制律设计中.在已有的基于高阶内模的迭代学习控制方法的基础上,成功引入了当次迭代的跟踪信息,从而进一步提高了跟踪精度,缩小了跟踪误差,加快了跟踪误差的收敛速度,并分别通过理论证明和仿真对比验证了其有效性和优越性.
[1] Zhang B,Wang D W,Ye Y Q. On learning transient,auto-tunings of learnable bandwidth and lead step in iterative learning control[J]. International Journal of Systems Science,2010,41(4):353-363.
[2] Yu M,Ye X D,Qi D L. Repetitive learning control for triangular systems with unknown control directions[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications,2011,5(17):2045-2051.
[3] Dabkowski P,Galkowski K,Cai Z,et al. Iterative learning control based on relaxed 2D systems stability criteria[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology,2013,21(3):1016-1023.
[4] Bu X,Hou Z,Yu F,et al. H∞iterative learning controller design for a class of discrete-time systems with data dropouts[J]. International Journal of Systems Science,2014,45(7/8/9):1902-1912.
[5] Meng D,Moore K L,et al. Robust iterative learning control for nonrepetitive uncertain systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2017,62(2):907-913.
[6] Jin X. Adaptive iterative learning control for high-order nonlinear multi-agent-systems consensus tracking[J]. Systems & Control Letters,2016,89:16-23.
[7] Zhang H G,Jiang H,Luo Y H,et al. Data-driven optimal consensus control for discrete-time multi-agent systems with unknown dynamics using reinforcement learning method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics2017,64(5):4091-4100.
[8] Sun S T,Li X D,Zhong R X. An open-closed-loop iterative learning control approach for nonlinear switched systems with application to freeway traffic control[J]. International Journal of Systems Science,2017,48 (13):2752-2763.
[9] Sun S,Endo T,Matsuno F. Iterative learning control based robust distributed algorithm for non-holonomic mobile robots formation[J]. IEEE Access,2018,6:61904-61917.
[10] Yu Q X,Hou Z S,Xu J X. D-type ILC based dynamic modeling and norm optimal ILC for high-speed trains[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology2018,26(2):652-663.
[11] He W,Meng T T,He X Y,et al. Iterative learning control for a flapping wing micro aerial vehicle under distributed disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics2019,49(4):1524-1535.
[12] Xu J X,Yan R. On initial conditions in iterative learning control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2005,50(9):1349-1354.
[13] Ahn H S,Moore K L,Chen Y Q. Stability analysis of discrete-time iterative learning control systems with interval uncertainty[J]. Automatica,2007,43(5):892-902.
[14] Chi R H,Hou Z S,Xu J X. Adaptive ILC for a class of discrete-time systems with iteration-varying trajectory and random initial condition[J]. Automatica,2008,44(8):2207-2213.
[15] Yin C K,Xu J X,Hou Z S. A high-order internal model based iterative learning control scheme for nonlinear systems with time-iteration-varying parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2010,55(11):2665-2670.
[16] Liu C P,Xu J X,Wu J. On iterative learning control with high-order internal models[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control & Signal Processing,2010,24(9):731-742.
[17] Zhu Q,Xu J X,Huang D,et al. Iterative learning control design for linear discrete-time systems with multiple high-order internal models[J]. Automatica,2015,62:65-76.
[18] Zhou W,Yu M,Huang D Q. High-order internal model based iterative learning control scheme for discrete-time nonlinear system[J]. International Journal of Automation and Computing,2015(3):104-110.
[19] Liu B B,Zhou W. Projection algorithm based adaptive iterative learning control for a class of discrete-time systems[C]//Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Qingdao,China,2015:2993-2998.
[20] Liu B B,Zhou W. On adaptive iterative learning control algorithm for discrete-time systems with parametric uncertainties subject to second-order internal model[J]. Control and Intelligent Systems,2015,43(4):183-190.
[21] Yu M,Huang D Q,He W. Robust adaptive iterative learning control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with both parametric and nonparametric uncertainties[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control & Signal Processing,2016,30(7):972-985.
[22] Zhao D,Yang Y. An iterative learning control design method for nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown iteration-varying parameters and control direction[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2016,2016:1-7.
[23] Goodwin G C,Ramadge P J. Discrete-time multivariable adaptive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic control,1980,25(3):335-340.
[24] Yan W,Sun M. Adaptive iterative learning control of discrete-time varying systems with unknown control direction[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing,2013,27(4):340-348.
A New Adaptive Iterative Learning Algorithm Based on a High-Order Internal Model
Zhang Guoshan,Li Siqi
(School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China)
In this paper,a new adaptive iterative learning algorithm based on a high-order internal model is proposed. The algorithm is applied to the output tracking problem of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems with multiple time-iteration-varying parameters and unknown control directions. Assuming that multiple time-iteration-varying parameters are generated by different high-order internal models,the proposed algorithm draws on the idea of model predictive control. Through the construction of predictive input,the predictive tracking error obtained in the current iteration is used as a priori knowledge for system input control law design. This has the effect of further reducing the tracking error of the system on the basis of predictive tracking error. Compared with the traditional iterative learning algorithm based on a high-order internal model,the output tracking error of the system is greatly reduced,and the tracking accuracy is evidently improved. In addition,as predictive tracking error is involved in the design of the input control law as a priori knowledge,the method is robust to system disturbance and output noise. Through the Lyapunov stability theory,the convergence of the system tracking error and the superiority of the proposed method are proved. Through two groups of sample simulations,and considering the two cases of known and unknown control direction,the theoretical results are verified by comparison with two existing iterative learning algorithms based on a high-order internal model.
adaptive iterative learning control;high-order internal model;nonlinear discrete-time system;time-iteration-varying parameters
10.11784/tdxbz202103063
TK13
A
0493-2137(2022)05-0480-09
2021-03-26;
2021-08-18.
张国山(1961— ),男,博士,教授.
张国山,zhanggs@tju.edu.cn
国家自然科学基金资助项目(62073237).
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 62073237).
(责任编辑:孙立华)
