Study on TCM intervention of NF-κB signal pathway in the treatment of bronchial asthma
2022-02-04LAIHaiyanYIWeiDENGKunLONGJuanRENMengyaoQIAOYunZHOUBeiLIWeiwei
LAI Hai-yan, YI Wei, DENG Kun, LONG Juan, REN Meng-yao, QIAO Yun, ZHOU Bei, LI Wei-wei
1. The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, China
2. Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, China
3. College of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, China
4. College of Pharmacy, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530299, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Bronchial asthma is a heterogeneous disease characterized by chronic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness, and its incidence has increased worldwide in recent years. In developed countries such as Europe and the United States, more than 50% of children with asthma have not been effectively controlled under standardized treatment[1]; the third national epidemiological survey of childhood asthma in 2010 found that the incidence of childhood asthma in my country reached 3.02%[2]. At the same time, the adult asthma survey in recent years has found that the incidence of adult asthma has reached 4.2%. It is speculated that the rate of childhood asthma is rising year by year, far exceeding the estimated level [3]. The pathological changes of asthma are mainly chronic airway inflammation and airway remodeling, but the pathogenesis is not yet fully understood. At present, hormones, β2 receptor agonists, leukotriene modulators and other intervention programs are the first choice for traditional asthma treatment. There are controversies about the various side effects of western medicine treatment and the tolerance caused by long-term use [1]. Studies have shown that NF-κB as a classic signal transduction pathway plays a role in inflammation, smooth muscle hyperplasia and hypertrophy, and neovascularization, and its overexpression induces asthma [4-5]. Traditional Chinese medicine regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway, inhibits airway inflammation and resists airway remodeling, so as to achieve the purpose of treating asthma. The research on the mechanism of NF-κB signaling pathway and asthma and the intervention of traditional Chinese medicine are summarized as follows.
2. Overview of NF-κB signaling pathway
Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) is an important nuclear transcription factor that exists in the cytoplasm. The NF-κB family has five members, including p65 (RelA), p105/p50, RelB, c-Rel and p100/p52, Among them, the heterodimer composed of p50 and p65 is the main active form of NF-κB; at the same time, NF-κB has two different pathways. The classical pathway activates p50 and p65,while the non-classical pathway activates RelB and RelB. The activation mechanism of p52 polymer is different. When cells are stimulated by extracellular signals, the phosphorylation-dependent activation of the NF-κB-specific inhibitor IKKs (IκB kinase)complex releases κB transcription factors for transport to the nucleus and activates target genes to induce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as The expression of TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-6. Classical NFκB is activated in response to the diversity of immune response,cell proliferation, differentiation and survival involved in external stimulation of inflammation, to regulate the expression of various pro-inflammatory genes, and act as a key mediator of inflammation.Studies have found that in the pathogenesis of asthma, the NFκB signaling pathway plays a vital role, and plays a key role in the generation, differentiation, immune response, and apoptosis of airway inflammation [6]; not classic The activation of NF-κB is closely related to protein, which is mainly involved in antiviral immune response, autoimmune diseases and other processes, and is closely related to the development of tumor immune lymphoid organs[7-8].
3. The relationship between NF-κB signaling pathway and bronchial asthma
Asthma is a chronic airway inflammatory disease involving a variety of inflammatory cells (such as eosinophils, smooth muscle cells, T lymphocytes, mast cells, etc.) and cellular components [9].Repeated stimulation of airway inflammation promotes the formation of airway remodeling. This process involves airway wall damage,repair, and inflammatory factors involved. The main manifestations are airway wall repair, extracellular matrix deposition, airway mucus accumulation, Subepithelial fibrosis, smooth muscle hyperplasia and hypertrophy, etc. [10, 11]. Among them, it is closely related to the production of Th2 cytokines, including IL-5/IL-13, eosinophils and IgE, and NF-κB is essential for regulating the production of Th2 cytokines, the differentiation of Th2 cells and the excessive production of mucus. Important [12]. Studies have pointed out that NF-κB can reverse the proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells and reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing the airway remodeling, airway hyperresponsiveness and chronic inflammation to a certain extent, thereby alleviating asthma symptoms[13]. Studies have shown that overexpression of the NFκB signaling pathway can induce the proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells. The NF-κB signaling pathway amplifies the waterfall effect by interfering with the cascade between immunity and inflammatory factors and mediators, thereby playing a pivotal role in inflammation and immune response; When the NF-κB pathway in the airway epithelial tissue is activated, the released inflammatory mediators (such as IL-1β, TNF-α, etc.) stimulate airway smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts to proliferate and activate, leading to airway epithelial cells Hyperplasia, airway tissue fibrosis, airway remodeling, etc. [14-15]. It can be seen that NF-κB, as a well-known inflammatory effect factor, has the role of inflammatory cytokines closely related to asthma, and plays a key role in airway remodeling and airway inflammation. The breakthrough in the treatment of asthma is a key scientific issue that is currently urgently concerned and analyzed.
4. Research progress on the effect of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of bronchial asthma through NF-κB signaling pathway
The name "asthma" was seen earlier in the "Danxi Heart Method".Traditional Chinese medicine believes that phlegm and blood stasis accumulates in the lungs as the perennial root and the key pathology of childhood asthma. When the phlegm and blood stasis accumulates in the lungs caused by external pathogens, it becomes asthma[16,17,18], Zhao Wenhan[19]and others believe that hypersecretion of airway mucus is an important cause of asthma, and phlegm is the core of asthma, and hypersecretion of mucus is closely related to the pathogenesis of phlegm in traditional Chinese medicine. Laboratory examinations have shown that [20]children with recurrent asthma have typical abnormal changes in hemorheology, and their blood is in a state of obvious hypercoagulability. The NF-κB pathway is a classic pathway that regulates asthma airway inflammation.The mechanism of NF-κB anti-asthmatic airway inflammation and airway remodeling through Chinese medicine has great potential value.
4.1 Research on the regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway in asthma by compound prescription of traditional Chinese medicine
The related experimental research of traditional Chinese medicine intervention on asthma has found that Chaipu Decoction[21]can up-regulate the expression of MAL in asthmatic rats and downregulate TGF-β1 by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway,thereby reducing chronic inflammation and airway inflammation in asthmatic rats. Remodeling, so as to achieve the purpose of prevention and treatment of asthma. Maimendong Decoction[22]can inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway by reducing the levels of IL-1β,IL-4, IL-6, and IL-13 in asthmatic rat models.
Yang Yan[23] et al. used the experience of Professor Yu Jianer, a famous TCM doctor, to use Pingchuan Fang to study its mechanism of treating airway inflammation on asthma models, and found that Pingchuan Fang regulates NF-κB/ TLR4 signaling pathway inhibits inflammatory cell infiltration, reduces IL-6 and TNF-α levels, and inhibits the expression of NF-κBp65, IκB, TLR4, and MyD88 proteins, thereby improving airway inflammation and treating asthma.
Hong Tianyi[24] According to Professor Feng Xiaochun’s experience, Xiehuang Jiejingzhixiao Granules can be used to intervene in the mouse model of asthma and found that Xiehuang Jiejingzhixiao Granules can effectively inhibit NF-κB/HIF-1α and downstream VEGF , TGF-β1, MMP-9 and other protein expression,thereby reducing airway hyperresponsiveness and slowing down airway remodeling, preventing repeated asthma attacks.
Sun Liping[25] conducted bronchial asthma mouse model experiments, and the results showed that Yiqi Guben Capsules can reduce NF-κBp65 in BALF of mice and increase IkBa (P<0.05),confirming that Yiqigu This capsule can inhibit NF-κB activity and improve asthma symptoms.
Zhang Wenbin[26] established an asthma rat model, and the results showed that the bronchial tube wall thickness and smooth muscle thickness of rats after intervention by Jianpi Yifei Decoction, NFκB and pNF-κB in lung tissue Compared with the asthma model group, STAT3 and p-STAT3 were all decreased, and IFN-γ in the alveolar lavage fluid increased (p<0.05). It was confirmed that Jianpi Yifei Decoction may alleviate asthma model rats by inhibiting the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway Inflammation of the airway,thereby inhibiting airway remodeling.
Sun Tianyi[27] conducted animal experiments and found that the bronchial walls of asthmatic mice were thickened, lumen stenosis,mucus hyperplasia, alveolar wall thickening, Airway mucosal edema and other clinical symptoms have been significantly improved compared with the previous; NF-κBp65 protein expression in lung tissue was significantly reduced by the immunological combination method, which confirmed that Ephedra to fix asthma decoction regulates NF-κBp65, p-ERK, p-p38MAPK, etc. Factors inhibit airway remodeling. Shi Suofang[28] et al. used Qufeng Xuanbi Decoction to treat asthmatic rat models and found that Qufeng Xuanbi Decoction can inhibit the activation of inflammatory cells by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and achieve the effect of inhibiting airway inflammation.
Therefore, it has been proven that Chinese medicine prescriptions regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway, inhibit airway inflammation,relieve airway smooth muscle spasm, reduce airway resistance, and control acute asthma attacks. At the same time, the clinical use of Chinese medicine in the treatment of bronchial asthma has great potential value.
4.2 Research on the intervention of traditional Chinese medicine monomers and their extracts in the regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway in asthma
Coptis has the functions of clearing away heat and dampness,purging fire and detoxification. Lee[29] et al. used Coptidis to treat asthma model rats and found that Coptidis extract can downregulate the expression of MCP-1, NF-κB, IκB, and MAPKs,thereby inhibiting IL-6, IL-8, IL-4,and IL-5, IL-13, IgE and other inflammatory cytokines play an anti-inflammatory effect. Xu Youdong[30] et al. found that through reverse screening of the proteins in the three pathways of TLR4/NF-κB, p38, JAK2/STAT3,berberine can inhibit PI3Kδ, PI3Kγ, IKKβ, PI3Ktarget proteins, and affect inflammation. Pass, play an anti-inflammatory effect.
Turmeric has the power of breaking blood and promoting qi. Using curcumin to interfere with asthma model mice, the results show that curcumin can significantly inhibit the expression of NF-κB, MCP-1,PPARγ, MUC5AC[31]. Yin Zhenghai[32] proposed that curcumin inhibits the activation of p38MAPK and NF-κBp65 in asthma model rats, thereby reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells to achieve anti-inflammatory effects.
Scutellaria baicalensis has the functions of clearing away heat and dampness, reducing fire and detoxification. Zhai[33] et al. reported that baicalin can inhibit airway inflammation in asthmatic rat models to a certain extent, and its mechanism is related to the up-regulation of MiR-103, while reducing IL-6 and TNF-α levels, and inhibiting TLR4/NF- κB signaling pathway is related.
Houttuynia has the effects of clearing away heat, detoxifying,and eliminating carbuncle and pus. In the treatment of asthma,houttuyfonate sodium has good antibacterial, anti-inflammatory,and immune-enhancing effects[34]. Experimental studies have found that[35] that different doses of houttuyfonate sodium affect the expression of IL-4 and MCP-1 by inhibiting the TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway in lung tissue, thereby improving alveolar collapse and inflammation in asthma model mice Symptoms such as cell infiltration and a large amount of secretions can achieve the effect of treating asthma.
Astragalus has the functions of replenishing qi and raising yang,solidifying the surface and antiperspirant. Wang Jinlei[36]et al.used Astragalus extract to treat asthma model rats and found that Astragalus extract can significantly inhibit the activity of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway; Hsieh[37] also proved that Astragalus extract can inhibit MAPK/NF-κB signal pathway expression, and increase the expression of HO-1/Nrf2, thereby improving airway inflammation.
Burdock has the functions of evacuation of wind-heat, spreading lung and rash, detoxification and throat relief. Chen Haitao[38]used burdock seed extract intraperitoneal injection to treat asthma model mice. The results showed that compared with the model group, the contents of E-selectin, NF-κB p65, IL-1, TNF, and LPS in the treatment group were significantly reduced . Therefore,the mechanism of burdock seed reducing airway inflammation in asthmatic mice may be achieved by intervening in the NF-κB signaling pathway.
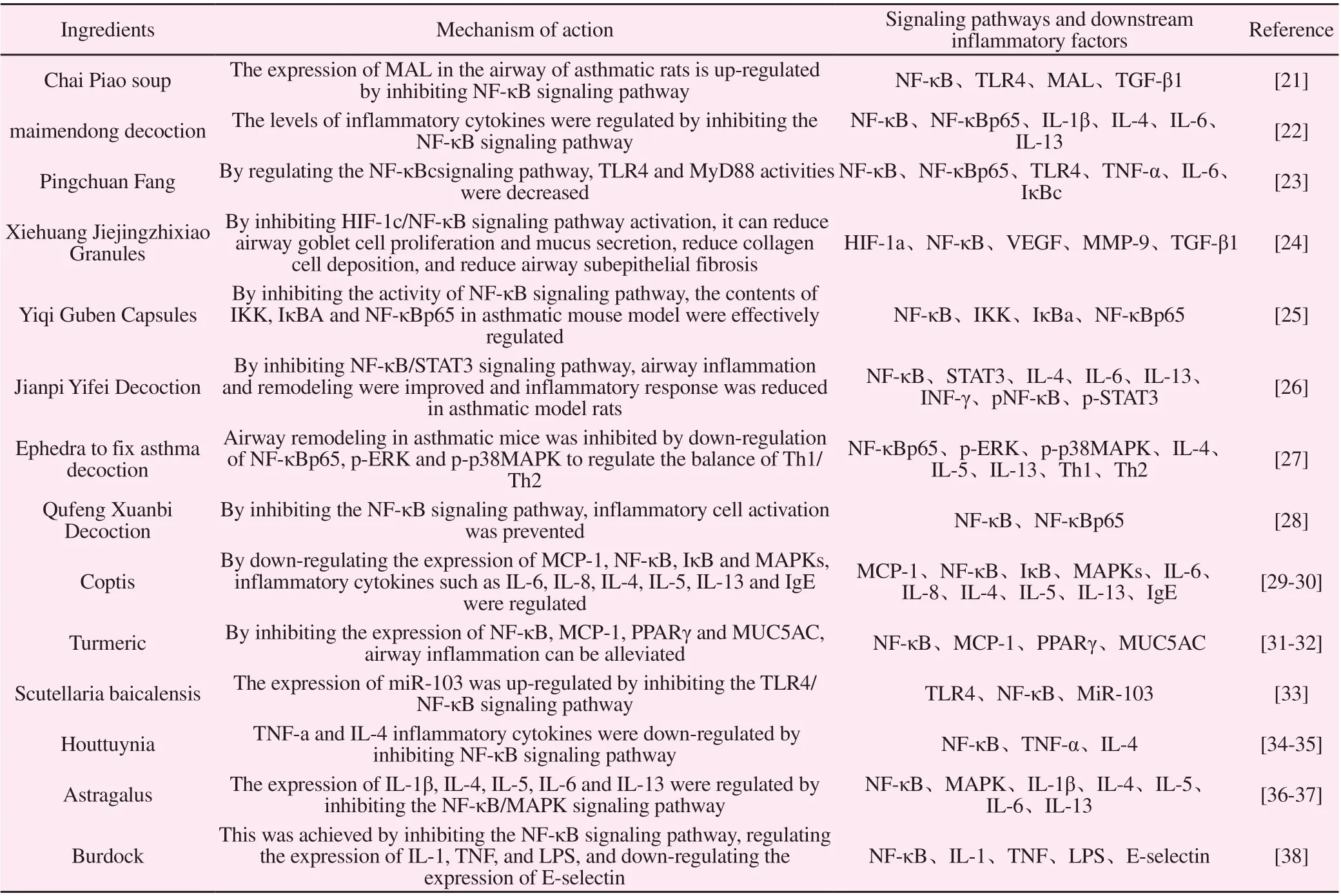
Tab1 The mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine and its compound prescriptions in treating asthma
5. Discussion
Asthma is a common and frequently-occurring disease in clinic. On the one hand, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, tumors,and inflammation caused by injury can all induce the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway; on the other hand, the activated NF-κB signaling pathway can be induced and activated by the expression of inflammatory cytokines Inflammatory factors, leading to asthmatic airway smooth muscle cell proliferation, airway mucus accumulation, subepithelial fibrosis and other damage. Traditional Chinese medicine has a long history of treating asthma and has formed a unique theoretical system in long-term medical practice.It has the advantages of economic safety and fewer side effects.However, there are still limitations: First, the active ingredients of many Chinese medicines are more complicated, and the treatment mechanism of Chinese medicine compounds needs more in-depth and comprehensive research; second, the research on Chinese medicine compounds is mostly based on the experience of famous Chinese medicine prescriptions, and many are accompanied by them. Regional characteristics, while the use of regional restrictions;third, there are few reports of adverse reactions related to Chinese medicine compound or Chinese medicine single animal experiments.Based on the NF-κB signaling pathway has become a classic pathway, it has shown great clinical potential in the treatment of asthma with Chinese herbal compound and Chinese herbal medicine monomers. However, the in-depth mechanism of this signaling pathway needs to be further explored in the use of molecular biology to study traditional Chinese medicine. The treatment of asthma provides scientific basis to better serve the clinic.
Author contribution:
This article was written by Lai Haiyan; Yi Wei participated in providing comments and suggestions on the research direction of the review; Deng Kun, Ren Mengyao, and Long Juan participated in the search of related literature; Qiao Yun participated in the review of the literature and the relevance and polishing of the research direction of the review; Zhou Bei participated in the review of the literature Format and details; Li Weiwei reviews the article.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- In vitro study on the antiviral activity of 9 extracts of traditional Chinese herbal medicine against the human respiratory syncytial virus
- Study on gene regulation mechanism of Qiliqiangxin capsule on myocardial fibrosis in myocardial infarction rats
- Pharmacokinetics of Jiaotai pill self-microemulsion in insomnia rats
- Correlation between IL-33/sST2 signaling pathway and patients with essential hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy
- Design and characterization of a bi-functional bybrid antibacterial peptide LLM against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Screening and comprehensive analysis of key genes in liver hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics
