Systematic review and meta-analysis on efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of inflammatory factors in patients with poststroke depression
2022-02-04WANGHuiyingGOUJinYANGLixuanGUORongjuan
WANG Hui-ying, GOU Jin, YANG Li-xuan, GUO Rong-juan
1. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2. Dongfang Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Second Department of Neurology, Beijing 100078, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Stroke has a high incidence, disability and mortality worldwide[1].Stroke patients are prone to secondary psychiatric problems, the most common of which is post-stroke depression (PSD), which affects about 30% of stroke patients[2]. Studies have shown that depression prevents people from functioning and increases the risk of death and relapse[3]. Post-stroke depression not only affects patients' physical and cognitive rehabilitation and their quality of life, but also becomes a major social and public health problem in the world[4]. Modern medicine preferred antidepressants for treatment, but there were more adverse reactions.Systematic reviews indicate that compared with the use of western medicine alone, the treatment of PSD with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine has better effect and less adverse reactions[5]. In addition,TCM therapy has the advantages of low addiction and high recovery rate for PSD[6]. Inflammatory factors are involved in the occurrence and development of PSD[7], so it is necessary to explore the influence of traditional Chinese medicine on inflammatory factors in PSD patients.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Inclusion criteria
2.1.1 Types of studies
All published Chinese and English randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with inflammatory factors in the outcome of traditional Chinese medicine for post-stroke depression were included,regardless of whether blind method was used.
2.1.2 Research objects
The patient was clinically diagnosed as having a stroke, regardless of age, sex, and source of cases. At the same time, it met the relevant depression diagnostic criteria of the "Chinese Mental Disorder Classification and Diagnostic Criteria (CCMD-3)"[8].
2.1.3 Intervention measures
The experimental group could use Chinese herbal medicines,Chinese patent medicines and other formulations of traditional Chinese medicine alone, or add western medicine to the basis of traditional Chinese medicine. The specific types of western medicines were not limited; the control group did not intervene or applied the western medicines used in the experimental group. In addition, both groups could perform basic diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases.
2.1.4 Outcome indicators
The main outcome indicators were tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8(IL-8) and homocysteine (Hcy) in serum.The secondary outcome indicators are Hamilton Depression Scale(HAMD), NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS), Barthel Index (BI) and Hamilton Anxiety Scale(HAMA).
2.2 Exclusion criteria
Non-clinical randomized controlled trials; no relevant inflammatory factors were found in outcome indicators; TCM treatment with external therapy; repeated published literature; studies that could not accurately extract data or had missing data.
2.3 Literature retrieval strategy
We searched CNKI, Wanfang database, VIP, SinoMed, PubMed,Cochrane Library and Web of Science.The search started from the time when the database was built until August 11, 2021. Chinese search terms: "脑卒中后抑郁", "卒中后抑郁", "中风后抑郁", "中医药", "草药", "中药", "中成药", "中药制剂","炎性". English search terms: “cerebral infarction” “post-stroke depression”“cerebral hemorrhage” “cerebral ischemia” “Depressive Disorders”“stroke” “inflammatory” “Medicine, Chinese Traditional”“traditional Chinese patent medicines” “Chinese materia medica preparation”.
2.4 Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers selected the studies that met the inclusion criteria and excluded the studies that met the exclusion criteria from all the articles obtained by the retrieval strategy. When different views appeared, the third researcher discussed with the researchers. The researchers extracted the data at the same time. The contents were extracted as follows: name of the first author, year of publication,sample size of included patients, gender, mean age, course of disease, diagnostic criteria, name and usage of intervention drugs,course of treatment, outcome indicators, and adverse reactions.
2.5 Evaluation of methodology quality
The quality of the included studies was evaluated according to the Cochrane Collaboration risk bias assessment tool[9], and there were 3 evaluation results, namely "low risk", "high risk" and"unclear". A total of 7 items needed to be evaluated. These included the generation of randomization, the concealment of allocation,the blinding of researchers, subjects and outcome evaluators, the integrity of outcome data, the selectivity of reporting of study results,and other sources of bias.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The RevMan 5.4 from the Cochrane website was used, and each effect size was expressed as mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD) (all outcome measures in this study were continuous variables) with 95% confidence interval (CI).The heterogeneity was determined by I2. I2≤50% indicated good homogeneity, and fixed effects model was used. If I2 is greater than 50%, it is necessary to explore the causes of high heterogeneity and apply the random effects model. Funnel plot is used for analysis of publication bias, usually when the number of included studies is greater than or equal to 10.
3. Results
3.1 Literature retrieval and screening process
3.2 Basic characteristics of the included literature
A total of 6 randomized controlled trials are included in this study,all of which are published Chinese literature, with a total of 636 subjects, including 318 in the experimental group, 318 in the control group, 356 men (55.97%), and 280 women (44.03%).The average age is (43.26±4.29)-(59.98±10.43) years old, and all studies are divided into 2 groups. In terms of intervention methods, the dosage forms of traditional Chinese medicine include decoctions and proprietary Chinese medicines. Regarding the course of treatment,the studies range from 4 weeks to 2 months. The outcome indicators all include inflammatory factors. In terms of adverse reactions, in all the studies, 3 studies are not mentioned in the whole article [10, 12, 14],and the other 3 studies report that 37 PSD patients (26 in the control group and 11 in the test group) have adverse reactions[11,13,15], but no serious events.See Table 1 for details.
According to the literature retrieval strategy, 49 articles were obtained, and 48 articles were obtained after deduplication. The titles and abstracts were read to remove articles that did not meet the standards of intervention methods. Articles in which research diseases were not PSD and trials were not clinical also were removed, and then 17 articles were obtained. Next, through browsing the whole paper, there were 11 articles whose outcome indicators did not meet the inclusion criteria. After exclusion, the number of literature included was 6[10,11,12,13,14,15], all of which were Chinese articles. The specific process is shown in Figure 1.
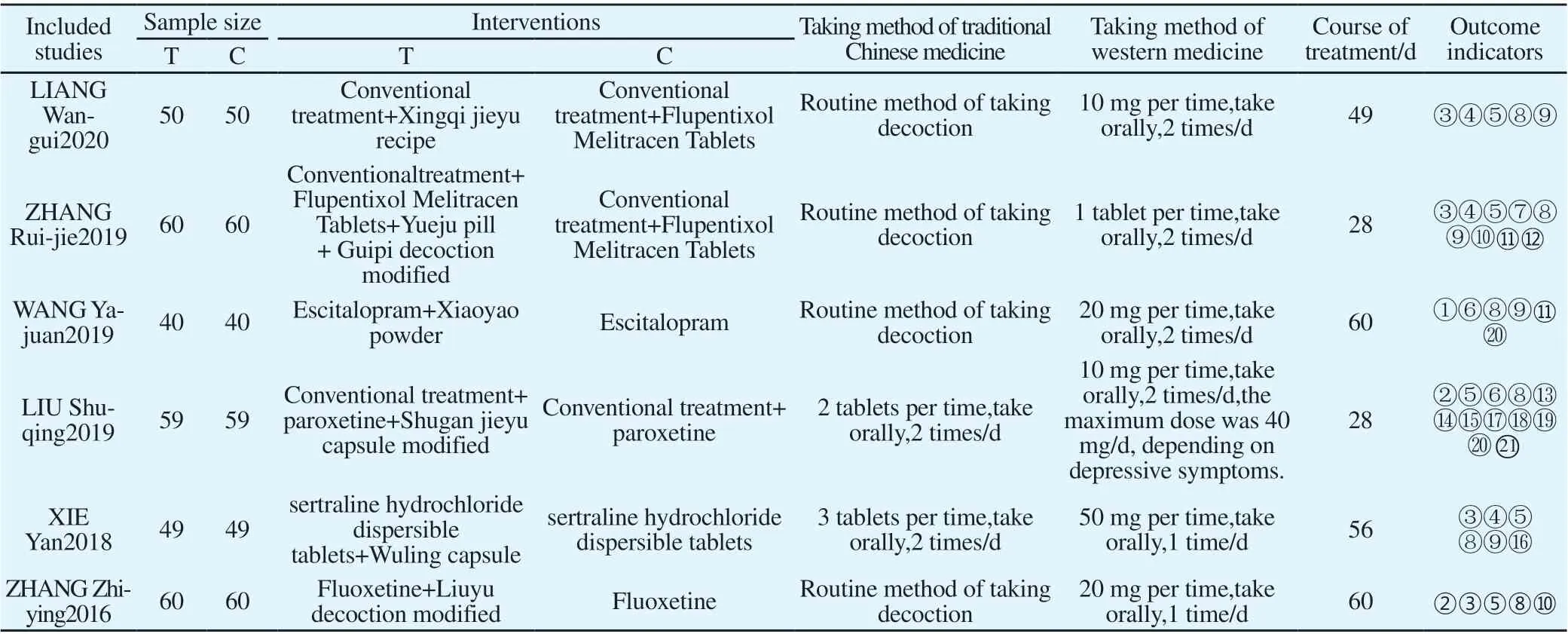
Tab1 Basic information included in the study
3.3 Quality assessment of included literature
The 6 included studies mention randomness at the time of grouping.One study is randomized according to the order of treatment[11] and is assessed as high risk. 3 studies are grouped by random number table [13,14,15]. The remaining studies [10,12] only mention"random"in the text. All studies[10,11,12,13,14,15] do not report the method of random allocation and concealing. In all studies[10,11,12,13,14,15]subjects do not fall off, and none of the research results are selectively reported, as shown in Figure 2.
3.4 Meta analysis
3.4.1 Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) 5 studies report venous blood TNF-α levels [10, 11, 13-15], with a total of 556 patients.
3.4.1.1 Traditional Chinese medicine vs western medicine
The intervention in one study[10] is the use of traditional Chinese medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group. There are 100 patients in total. Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that TCM therapy is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of TNF-in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-4.13, 95%CI (-4.75, -3.51), P<0.000 01], as shown in Figure 3.
3.4.1.2 Traditional Chinese medicine + western medicine vs western medicine
The intervention measures of the 4 studies [11,13-15] are the combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group. Two studies [11,13] use Chinese patent medicine in the experimental group,and the other 2 studies [14, 15] use traditional Chinese medicine decoctions in the experimental group. Because different dosage forms of traditional Chinese medicine have different manufacturing processes and additives, so they were divided into groups and analyzed.
There are a total of 216 patients in the Chinese patent medicine group, with large heterogeneity(P=0.01, I2=84%), which may be caused by the difference in the composition of the two drugs. Using random effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of Chinese patent medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of TNF-α in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-14.6, 95%CI (-18.44, -10.76), P<0.000 01].There are 240 patients in the traditional Chinese medicine decoction group, with large heterogeneity(P=0.000 4, I2=92%).Read the full text and find that one study uses the method of soothing liver-Qi stagnation and relieving depression[15], and the other study uses the method of soothing liver-Qi stagnation and nourishing the heart [14].There are certain differences in the composition of the drugs,where the heterogeneity may come from.Using randoms effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine decoction and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of TNF-α in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-6.65, 95%CI (-10.95, -2.36), P=0.002], as shown in Figure 4.
3.4.2 Interleukin-1 (IL-1)
3.4.3 Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
In the included studies, 4 studies report venous blood IL-6 levels[10,13,14,15], a total of 438 patients.
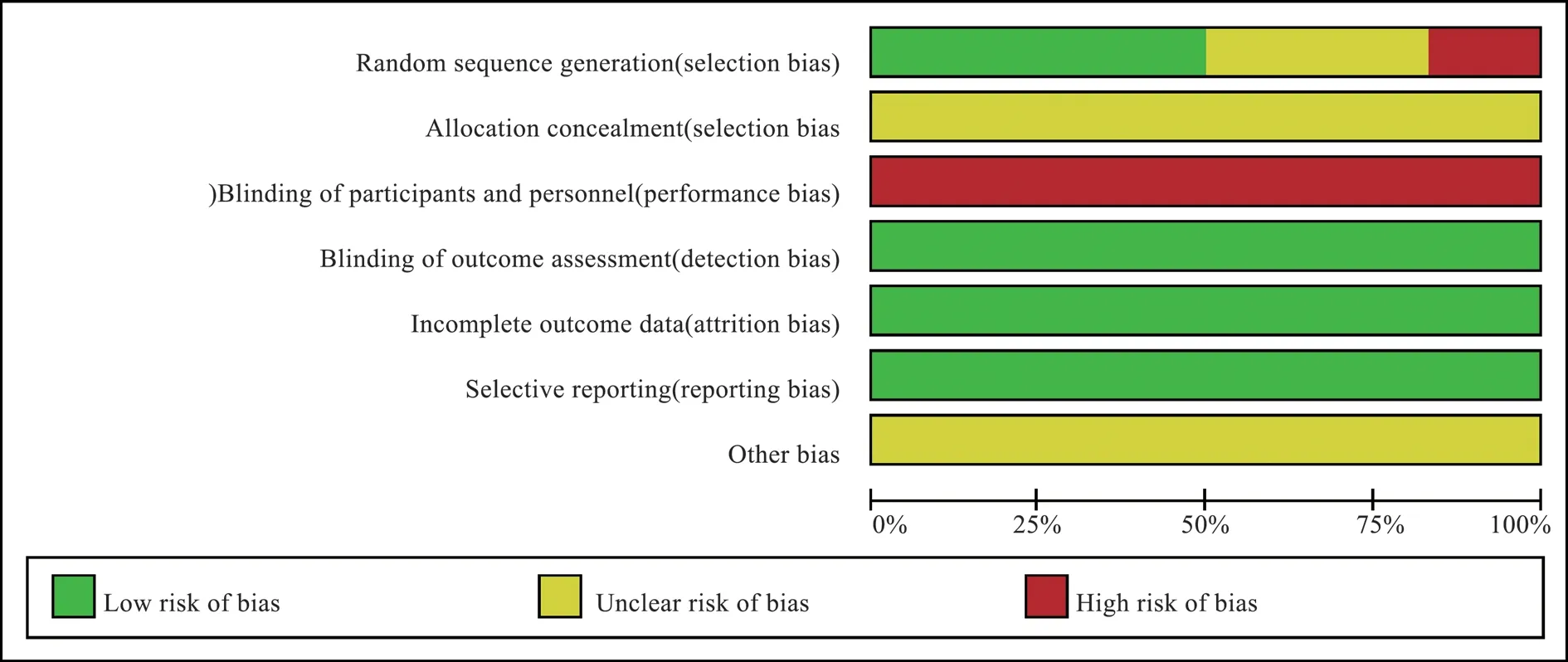
Fig2 Percentage of projects included in the study that produced a risk of bias
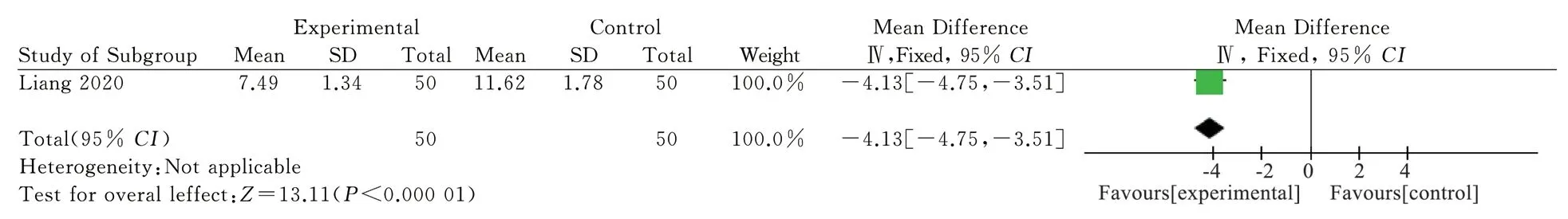
Fig3 Meta-analysis of TNF-α

Fig4 Meta-analysis of TNF-α

Fig5 Meta-analysis of IL-1
3.4.3.1 Traditional Chinese medicine vs western medicine
The intervention measures of 1 study[10] use traditional Chinese medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group, with a total of 100 patients. Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that TCM therapy is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of IL-6 in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-3.39, 95%CI (-3.90, -2.88), P<0.000 01], as shown in the figure 6.

Fig6 Meta analysis of IL 6
3.4.3.2 Traditional Chinese medicine + western medicine vs western medicine
The intervention measures of the 3 studies[13,14,15] are the combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group.There are 338 patients in total. The heterogeneity is large,P<0.000 1,I2=91%. Reading the full text, it is found that there is 1 study [13]using Chinese patent medicine, and the other 2 studies[14,15] using traditional Chinese medicine decoctions. Due to the differences in production process and added ingredients, analyzed after grouping.
There are a total of 98 patients in the Chinese patent medicine group. Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of Chinese patent medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of IL-6 in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-7.6, 95%CI (-9.37, -5.83) ),P<0.000 01]; There are a total of 240 patients in the traditional Chinese medicine decoction group with small heterogeneity(P=0.23,I2=30%).Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine decoction and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of IL-6 in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-3.2, 95%CI (-3.92,-2.48), P<0.000 01] , as shown in Figure 7.
53.Miss Charlotte:The stepsisters are rarely named in any Cinderella tale. Perrault s use of a name comes from his literary embellishment of the tale and was a personal choice. The name he uses in the original French is Javotte.Return to place in story.
3.4.4 Interleukin-8 (IL-8)Among the included studies, 3 studies report venous blood IL-8 levels [10,13,14], with a total of 318 patients.
3.4.4.1 Traditional
Chinese medicine vs western medicine One study[10] uses traditional Chinese medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group, with 100 patients in total. Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that TCM therapy is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of IL-8 in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-2.12, 95%CI (-2.49, -1.75), P<0.000 01],as shown in Figure 8.

Fig7 Meta analysis of IL 6

Fig8 Meta-analysis of IL-8
3.4.4.2 Traditional
Chinese medicine + western medicine vs western medicine Two studies[13,14] use a combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group. There are 218 patients in total, with high heterogeneity(P<0.000 01, I2=96%). Read the full text and find that 1 study[13] uses Chinese patent medicine and another study[14] uses traditional Chinese medicine decoction. The great heterogeneity may come from the differences in the manufacturing process and added ingredients of different dosage forms.Using random effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of IL-8 in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-9.41, 95%CI [-14.89, -3.92], P<0.000 01], as shown in the figure 9.

Fig9 Meta-analysis of IL-8
3.4.5 Homocysteine (Hcy)Two studies report the venous blood Hcy level[11,12]. There are a total of 198 patients with high heterogeneity(P=0.0004, I2=92%).Reading the full text, it is found that the research reported by Liu Shuqing[11] and others uses Chinese patent medicine in intervention, while the research reported by Wang Yajuan[12] and others uses traditional Chinese medicine decoction in intervention.Therefore, the large heterogeneity may come from the differences in manufacturing process and added ingredients. Using random effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the level of Hcy in venous blood of PSD patients[MD=-3.81, 95%CI (-4.62, -2.99), P<0. 000 01],as shown in the figure10.

Fig10 Meta-analysis of Hcy
3.4.6 Hamilto Depression Scale (HAMD)The 6 included studies all report the HAMD scores[10,11,12,13,14,15],with a total of 636 patients.
3.4.6.1 Traditional Chinese medicine vs western medicine
The intervention of one study[10] is the use of traditional Chinese medicine in the experimental group and the use of western medicine in the control group, with a total of 100 patients. Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that TCM therapy is superior to western medicine in reducing the HAMD scores of PSD patients[MD=-4.22, 95%CI (-5.37, -3.07), P<0.000 01], as shown in Figure 11.

Fig11 Meta-analysis of HAMD scores
3.4.6.2 Traditional Chinese medicine + western medicine vs western medicine
The intervention measures of 5 studies[11,12,13,14,15] are combined use of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group, with a total of 536 patients. The heterogeneity is small(P=0.14, I2=42%).Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the HAMD scores of PSD patients[MD=-3.06, 95%CI (-3.39) , -2.73), P<0.000 01],as shown in Figure 12.
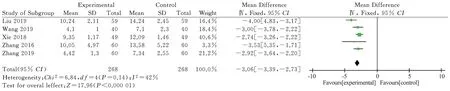
Fig12 Meta-analysis of HAMD scores
3.4.7 NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS)
Four studies report the NIHSS score[10, 12, 13, 14], with a total of 398 patients.
3.4.7.1 Traditional Chinese medicine vs western medicineOne study[10] uses traditional Chinese medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group, with a total of 100 patients. Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that TCM therapy is superior to western medicine in reducing the NIHSS scores of PSD patients[MD=-2.33, 95%CI (-3.43, -1.23), P<0.000 1],as shown in Figure 13.
3.4.7.2 Traditional Chinese medicine + western medicine vs western medicine
The intervention of the three studies[12, 13, 14] is the combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the experimental group and western medicine in the control group with 298 patients in total. And the heterogeneity is large( P<0.000 01, I2=98%).First excluded each study in order, and then used meta-analysis to analyze the sensitivity,but failed to find the source of heterogeneity.Reading the full text one by one, it is found that the heterogeneity is probably caused by differences in dosage forms and prescriptions.Using random effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the NIHSS scores of PSD patients[MD=-4.47, 95%CI (-7.55, -1.39), P=0.004], as shown in the figure. 14.
3.4.8 Barthel Index (BI)
Two studies report the Barthel Index[14, 15], 240 patients in total,with high heterogeneity(P<0.000 01, I2=95%), which may come from differences in composition of the medicines.Using random effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in improving BI index of PSD patients [MD=-12.3,95%CI (-22.66, -1.93), P=0.02], as shown in the figure. 15.

Fig13 Meta-analysis of NIHSS scores

Fig14 Meta-analysis of NIHSS scores
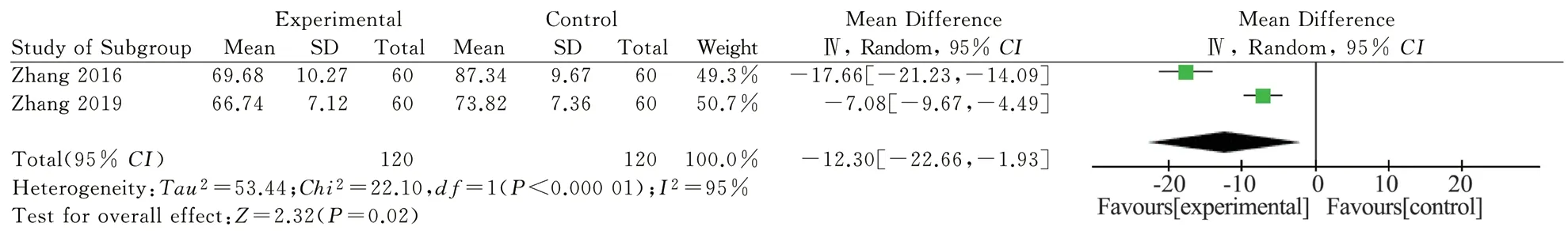
Fig15 Meta-analysis of Barthel scores
3.4.9 Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) scores
Two studies report HAMA scores[12, 14], a total of 200 patients,with good homogeneity(P=0.64, I2=0%).Using fixed effects model analysis, the results show that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine is superior to western medicine in reducing the HAMA scores of PSD patients[MD=-2.83, 95%CI(-3.47, -2.19), P<0.000 01], as shown in Figure 16.

Fig16 Meta-analysis of HAMA scores
3.5 Adverse Reactions
3 studies [10,12,14] do not mention adverse reactions; The other 3 studies [11,13,15] report adverse reactions with a total of 336 patients,of which 37 patients have adverse reactions(26 cases in the control group and 11 cases in the experimental group) including rash, tremor, dizziness, drowsiness, gastrointestinal reactions, loss of appetite, dry stool and drug dependence, with no serious adverse reactions.
3.6 GRADE evaluation of outcome evidence quality
Used GRADEprofiler to assess the quality of the outcome evidence. Due to the inconsistency, imprecision and bias of the data in the study, the evidence levels of HAMA and HAMD scores are moderate. The evidence levels of TNF-α, NIHSS, IL-6 and IL-1 are low.The evidence levels of Hcy, BI and IL-8 are very low, as shown in Table 2.
3.7 Publication bias analysis
This study was not analyzed because the number of studies was less than 10.
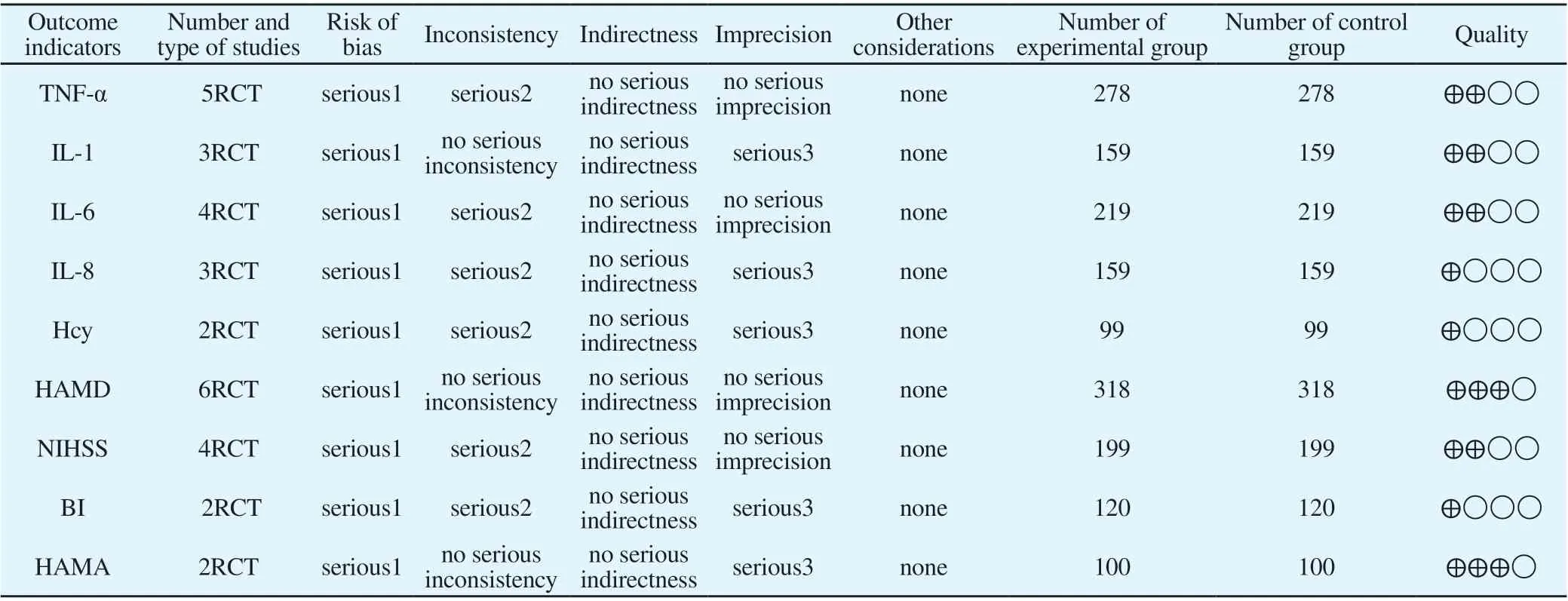
Tab2 GRADE rating of outcomes evidence quality
4. Discussion
4.1 TCM research on post-stroke depression
According to traditional medical theory, post-stroke depression means that the patient has a stroke first and then suffers from depression syndrome. It is a combination of stroke and depression syndrome, and there is no specific disease name. If the priority is discussed, it is based on stroke and depression syndrome is the target[16]. Studies have found that most of the patients suffering from a stroke due to internal injury and loss of emotions will suffer from liver dysfunction and stagnation of qi, which is the initial cause of the stagnation syndrome. Moreover, most stroke patients are deficient in both liver and kidney, and the lingering course of the disease causes the accumulation of pathological products, which further promotes the occurrence of depression[17].Some researchers believe that the TCM pathogenesis of post-stroke depression can be summarized as blood stasis and blockage and insufficient nutrition of the brain[16]. It emphasizes the treatment based on syndrome differentiation, and the treatment methods are mostly regulating the liver and strengthening the spleen, clearing phlegm and relieving depression, replenishing qi and promoting blood circulation. Practice has proved that traditional Chinese medicine is better than western medicine in the treatment of post-stroke depression[18].
4.2 Post-stroke depression and inflammatory factors
Depression and stroke are closely related. On the one hand,depression is an independent risk factor for stroke, on the other hand, depression is a concurrent disease of stroke. The pathogenesis of PSD is roughly divided into two types: biological hypothesis and stress disorder hypothesis.Biological hypothesis suggests that stroke is closely related to depression in biology and neuroendocrine factors such as inflammatory factors in the damaged brain of stroke patients contribute to the occurrence of PSD; The stress disorder hypothesis believes that the stroke population will have stress disorder,which leads to depression[19]. It has been reported that post-stroke patients have significantly higher levels of inflammatory factors such as IFNγ, IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1 than healthy individuals[20].Studies have shown that the elevation of IL-6, CRP and IL-1 in the body contributes to depression[21]. On the one hand, cytokines are closely related to the inflammatory response of stroke, and on the other hand, they contribute to depression, so they participate in the occurrence of PSD[22]. Studies have shown that the serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 in PSD patients are higher than those in non-PSD patients, and as the degree of depression in patients increases,the above factors increase[23]. It has also been reported in foreign literature that the concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-increases significantly in PSD patients compared with non-PSD populations, suggesting that serum IL-6 and TNF-α levels may be potential biomarkers for the development of depression in the acute stage of stroke[24].
4.3 Research results
A total of 6 RCTs are included in this study.The results show that compared with the western medicine alone, the addition of traditional Chinese medicine or traditional Chinese medicine alone in the treatment of PSD patients significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and Hcy.In addition, patients who use traditional Chinese medicine alone or a combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine perform better in the evaluation of HAMD, NIHSS, BI, and HAMA after treatment, and have fewer adverse reactions.Compared with previous systematic reviews and Meta-analysis on the treatment of PSD with traditional Chinese medicine, this study limited the outcome indicators and included studies containing indicators related to inflammatory factors, to provide data support for the effectiveness and mechanism exploration of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of PSD.Although the study suggests that traditional Chinese medicine can reduce the levels of some inflammatory factors in patients with post-stroke depression to a certain extent, and that traditional Chinese medicine alone or a combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine is superior to western medicine in terms of efficacy, the number of studies included in this study is small, and the level of evidence obtained by using the GRADE system is not high.So the results of the study still need to be updated continuously and more high-quality RCT studies need to be included for in-depth discussion.
4.4 Research limitations
There are some limitations in this study: ①The number of included studies is small, which may have publication bias; ②The overall sample size is small, which may affect the accuracy of the results;③The quality of the included studies is not high, and most of the studies do not mention allocation concealment and blinding methods;④There are differences in the dosage forms and components of traditional Chinese medicines used in the included studies, and there are also differences in western medicines used in the control group.These factors may lead to large heterogeneity among studies.
4.5 Hints for future research
More high-quality clinical randomized controlled trials should be carried out.Double blindness should be strictly implemented in RCT, and random concealing schemes should be developed and recorded. In the study of TCM treatment of PSD, the influence of traditional Chinese medicine therapy on inflammatory factors and other mechanism-related indicators should be further explored, so as to provide more in-depth evidence for the effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of PSD.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on depression models of different strains of rats and mice
- Study on TCM intervention of NF-κB signal pathway in the treatment of bronchial asthma
- Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of Liqi Huoxue drop pill in the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary artery disease
- Mechanism of Gan Dou Ling in improving liver fibrosis in Wilson disease based on network pharmacology and experimental verification
- Screening and comprehensive analysis of key genes in liver hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatics
- Design and characterization of a bi-functional bybrid antibacterial peptide LLM against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
